This directory and its sub-directories contain source code for LLVM, a toolkit for the construction of highly optimized compilers, optimizers, and run-time environments. A clang tidy check has been added called MapReduce. The source code for this new check is in the grppi module.
This README briefly describes the added check in this forked clang-tidy project.
This project is meant for educational purposes.
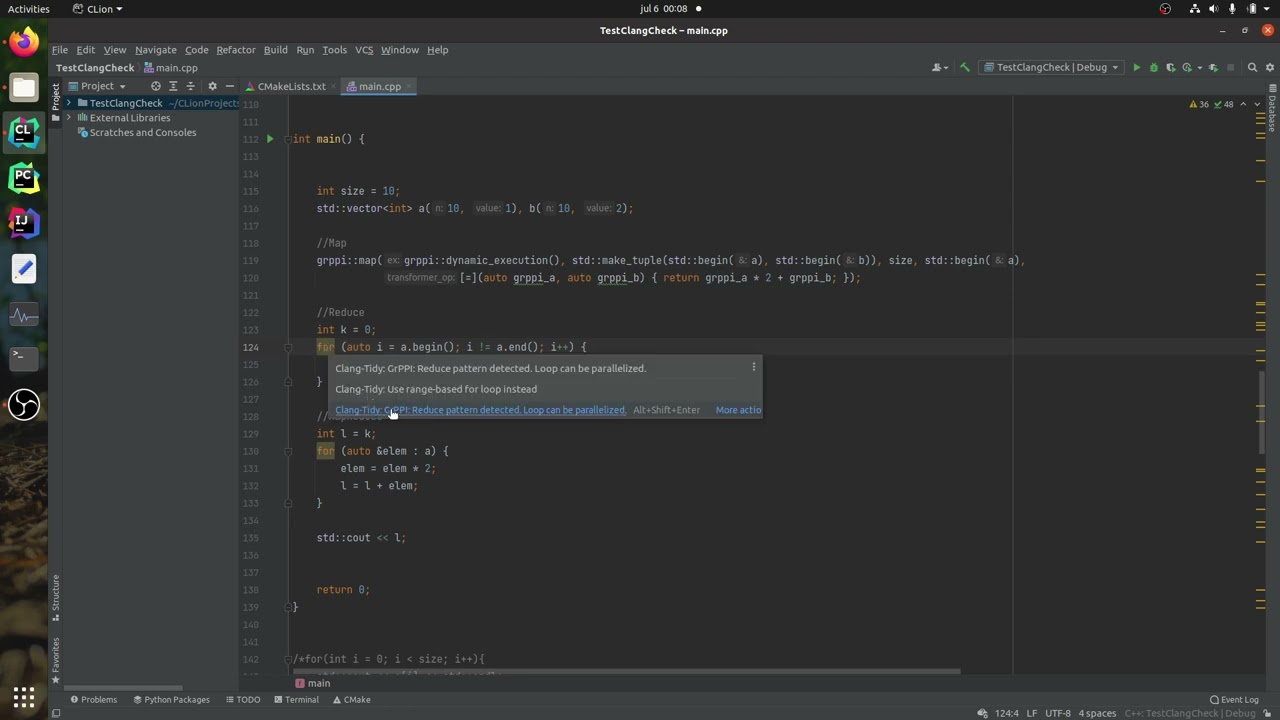
The new MapReduce clang-tidy check looks for loops that can be parallelized. Once found, the check will suggest its parallel equivalent implemented GrPPI(Generic Reusable Parallel Pattern Interface).
More information on GrPPI can be found here:
For code analysis, a combination of Clang matchers and the RecursiveAST Visitor pattern is used. Matchers find candidate loops while the Visitor allows for in-depth exploration.
The files of interest are located in the directories clang-tools-extra/clang-tidy/grppi and clang-tools-extra/unittests/clang-tidy.
Three types of loops will be explored for possible parallelism:
Integer counter is used as index for accessing elements in a vector:
for(int i = 0; i < a.size(); i++){
a[i] = a[i] * 2;
}Iterators are used for accessing elements in a vector:
for(auto i = a.begin(); i != a.end(); i++){
*i = *i * 2;
}Range for loop is used for accessing elements in a vector:
for(auto &elem : a){
elem = elem * 2;
}The same operation is independently applied to all elements in a vector:
int array[10];
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
array[i] = 0;
}And following grppi code will be suggested by the MapReduce check:
grppi::map(grppi::dynamic_execution(), array, 10, array,
[=](auto grppi_array){ return 0;});An associative operator is applied to collect the elements in a vector:
#include <vector>
int main() {
int k = 0;
std::vector<int> a(10);
for(auto i = a.begin(); i != a.end(); i++){
k += *i;
}
}Suggested:
k += grppi::reduce (
grppi::dynamic_execution(), std::begin(a), std::end(a), 0L,
[=](auto grppi_x, auto grppi_y){ return grppi_x + grppi_y ;});A Map and a Reduce are performed consecutively.
#include <vector>
int main () {
int k = 0;
std::vector<int> a(10);
for (auto &e :a) {
e = e * 2;
k += e;
}
}Suggested:
k += grppi::map_reduce(grppi::dynamic_execution(), a, 0L,
[=](auto grppi_a){ return grppi_a * 2;}, [=](auto grppi_x , auto grppi_y)
{ return grppi_x + grppi_y ;});Below is a short video demo of the custom clang-tidy binary integrated into the CLion IDE:
The LLVM Getting Started documentation may be out of date. The Clang Getting Started page might have more accurate information.
This is an example work-flow and configuration to get and build the LLVM source:
-
Get the modified LLVM source code:
git clone https://github.com/danielmartinezdavies/llvm-project-clang-tidy-check.git
-
Configure and build LLVM and Clang-tidy:
-
cd llvm-project-clang-tidy-check -
mkdir build -
cd build -
cmake -G "Unix Makefiles" -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release -DLLVM_ENABLE_PROJECTS="clang;clang-tools-extra;" ../llvm -
make clang-tidy -j8
-
Alternatively:
make install-clang-tidy -j8
Tests for the Map, Reduce and Map Reduce patterns where added to the ClangTidyTests Google Test target. Three suites were added: MapCheckTest, ReduceCheckTest and MapReduceCheckTest.