This project is a software tool developed for a research project and study of the boosting classifier algorithms and representation learning. JTabViz is a Java-based cross-platform software toolkit for machine learning (ML) data analysis, classification, and visualization. It is designed for the visualization and analysis of multidimensional (n-D) tabular ML data to discover and build classification models from logical rules. With supports for feature engineering and data augmentation to analyze how dataset changes impact ML models.
Currently, the JTabViz software supports the following Machine ML classifiers:
- Decision Tree Classifier
- K Nearest Neighbors Classifier
- Linear Discriminant Analysis Classifier
- Principal Component Analysis Classifier
- Random Forest Classifier
- Support (weighted) Sum Classifier (our invention)
We seek to combine these potentially weaker classifiers into a single stronger classifier, as AdaBoost does. Here we visualize classifier mistakes, seek improved representations, and build classification models from first order logic rules which we will later convert into Hyperblocks using our Hyperblock Parser.
Users can load CSV data to view, analyze, and classify with features like normalization, General Line Coordinates (GLCs) visualizations, tabular heatmaps, covariance matrix heatmaps, row manipulation, cell editing, classification rule testing with confusion matrices, automatic pure region discovery, feature engineering using slope and distance calculations, weighted sum features; including trigonometric wrapping, forward/backward differences, and various trigonometric values, optimal coefficient computation for weighted sums, attribute sorting, and data export.
This application has been tested on Windows (10/11), Linux (Pop!_OS), and macOS (M3 Sonoma) and is designed to run on any platform with a Java runtime environment.
To get started, run the build script from the project root directory. The script requires Java Development Kit (JDK) 21, or later, to be installed.
On macOS/Linux:
./build.shOn Windows:
./build.batThis will compile the code, package it with resources into a JAR file, and run the application.
GLCs generalize Cartesian Coordinates to n-D, with a subcategory being n-D to 2-D graph construction algorithms where graphs are commonly polylines, losslessly and reversibly visualizing all attributes and classes of the n-D data in 2-D space, while preserving distance relationships between points. We provide the following GLC visualizations:
| GLC Type | Acronym | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel Coordinates | PC | Drawing all coordinate axes in 2D located parallel to each other. |
| Shifted Paired Coordinates | SPC | Drawing each pair of attributes in 2D as a shifted cartesian plane, connecting cases with polylines. |
| Circular Coordinates | SCC & DCC | Drawing all coordinate axes in 2D as a circle, connecting cases with polylines, circle can be made a polygon or a circle either static or dynamic. |
| Star Coordinates | SC | Drawing all coordinate axes in 2D as a star shape, connecting cases with polylines. |
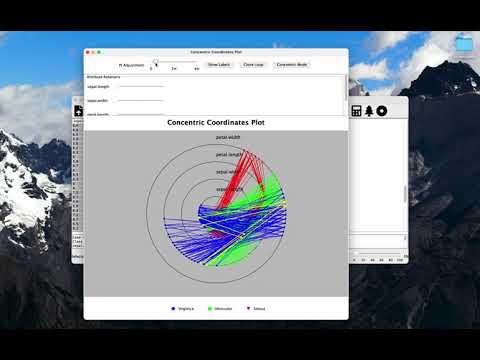
| Concentric Coordinates | CC | Drawing all coordinate axes in 2D as a series of circles nested within each other, connecting cases with polylines, circles can be made freeform or concentric. |
| Line Coordinates | LC | Drawing all coordinate axes in 2D located one after another on a single straight line. |
| Visualization Method \ Available Feature | Spacebar screenshot file export | Legend class view toggle | Selected case highlight | Axis drag and drop freeform | Attribute Label Toggle | Axis direction toggle | Axis scale | Axis rotate | Greedy auto axis order | Curve height | Case frequency | Case slope coloring |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parallel Coordinates | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Shifted Paired Coordinates | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| Circular/Polygon Coordinates | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Radar Plot | X | X | X | X | ||||||||
| Concentric Coordinates | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| In-Line Coordinates | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
Below are screenshots showcasing the exploration of the Fisher Iris dataset, which serves as a benchmark.
Classifier Accuracy: Achieved 98.67% accuracy. The two remaining misclassified cases (one in the Virginica class and one in the Versicolor class) are highlighted in Shifted Paired Coordinates, with the classification function duplicated for the third plot axes pair.

Outlier Discovery in PC: Highlighted outliers for the Virginica class by rearranging axes, sorting by the desired attribute, and using ctrl-click to select and visualize outliers in Parallel Coordinates.

Outlier Discovery in SPC: Sepal Length Outliers highlighted difficult-to-classify sepal length outliers for the Versicolor class in Shifted Paired Coordinates.

Outlier Discovery is SCC: Demonstrated a petal length outlier in the Virginica class using Static Circular Coordinates.

Combined View: Demonstrated the combined view functionality which is modular with a multi-window paradigm.

Outlier Discovery in Combined View: Setosa Sepal Width Outliers highlighted an outlier in the Setosa sepal width attribute.

Classification Conflication Discovery: Versicolor Petal Length Conflicts highlighted conflicting Versicolor cases in the petal length attribute using Star Coordinates.

Covariance Sorting: Demonstrated sorting attributes by covariance against sepal width, highlighting four outstanding cases in Parallel Coordinates and Shifted Paired Coordinates.

Rules Tester: Demonstrated the Rules Tester feature.

Single-Attribute Classification: Demonstrated classifying Fisher Iris data with a single attribute for 75% of the dataset.

MNIST Letters Train Data: Visualized in Shifted Paired Coordinates.

Wisconsin Breast Cancer Data (30 features): Visualized in Parallel Coordinates and Star Coordinates.

Visualizing in Star Coordinates.

Musk Molecule Data (166 features): Visualized in Parallel Coordinates and Shifted Paired Coordinates, with covariance sorting and pure interval visualization.

Sorting by covariances of attribute v7 against all other features still in Parallel Coordinates.

Hiding the classifiable cases with single attribute pure intervals which cover 5% threshold of class or dataset visualized in Parallel Coordinates.

Visualizing the Musk molecule 166 feature data in Shifted Paired Coordinates.

Sorting by covariances of attribute v7 against all other features still in Shifted Paired Coordinates.

Hiding the classifiable cases with single attribute pure intervals which cover 5% threshold of class or dataset visualized in Shifted Paired Coordinates.

- Cross-platform support: Runs on any platform with a Java runtime environment.
- CSV Data Handling: Load and display CSV data in a tabular view.
- Plot Screenshots: Capture plot screenshots using the space bar (currently available in Shifted Paired Coordinates, with plans to extend to other plots).
- Normalization: Normalize numerical columns.
- Missing Data Highlighting: Identify and highlight missing data.
- Covariance Matrix: Display a covariance matrix with a heatmap overlay.
- Covariance Sorting: Sort columns by the covariance of all attributes against a selected attribute.
- Multiple Visualizations: Visualize data using heatmaps, Parallel Coordinates, Shifted Paired Coordinates, Static Circular Coordinates, and Star Coordinates.
- Row Manipulation: Insert, delete, clone, copy contents, and edit individual cell values.
- Customization: Customize font color, class color, class point style, and highlight class fields.
- Data Export: Export modified data to CSV.
- Rule Testing: Test classification rules and display results in a Confusion Matrix.
- Rule Serialization: Save (only locally) and reload classification rules.
- Row Highlighting: Highlight selected rows in visualization views.
- Pure Region Discovery: Discover and highlight pure regions where all data points belong to the same class.
- Rule Combination: Combine rules to maintain the largest surrounding pure rule.
- Rule Threshold Slider: Adjust the threshold for rule coverage over a class or dataset.
- Feature Engineering: Insert feature columns with direct trigonometric attribute values, such as arccos(attribute), or calculate forward/backward differences wrapped in trigonometric functions.
- Weighted Sum Feature Engineering: Insert a weighted sum column with custom coefficients, optionally wrapped in a trigonometric function.
- Slope Distance Feature Engineering: Insert slope-distance values for the attributes as paired columns, duplicate last column as needed when missing required attribute count.
- Gradient Descent Optimization: Automatically discover optimal coefficients for weighted sum features, maximizing class separability.
Using a sliding window algorithm, JTabViz automatically identifies pure intervals within individual attributes. Only the most significant regions are used for classification, filtered by a threshold slider to ensure coverage of a class or the dataset.
JTabViz applies trigonometric functions to forward differences, backward differences, and direct attribute values to uncover patterns and interactions in the data:
- sin: Emphasizes periodic or cyclic relationships between attributes, making it easier to detect recurring patterns.
- cos: Highlights rotational or angular relationships between attributes, helping to uncover how attributes might cyclically influence each other.
- tan: Focuses on the rate of change between attributes, useful for identifying steep trends or shifts in the data.
- Forward Differences: The trigonometric functions are applied to the differences between each attribute value and the next one in the sequence. This highlights how changes from one data point to the next evolve cyclically, rotationally, or in terms of their rate of change.
- Backward Differences: Similar to forward differences, but here the trigonometric functions are applied to the differences between each attribute value and the previous one. This can help in understanding how past values influence current trends, especially in a cyclical or rotational context.
- Direct Attribute Values: Trigonometric functions are directly applied to the raw attribute values themselves. This approach reveals inherent periodicity, rotation, or trends in the data, independent of any sequence-based differences.
JTabViz allows for the creation of Weighted Sum Features from existing attributes, enhancing class separability, reducing dimensionality, and improving model representation. A new feature created by combining multiple existing features using a set of coefficients.
New Feature} = c_1(x_1) + c_2(x_2) + ... + c_n(x_n)
where:
c_1, c_2, ..., c_n are the coefficients.
x_1, x_2, ..., x_n are the original features.
JTabViz includes a gradient descent algorithm that optimizes coefficients to maximize between-class variance and minimize within-class variance, ensuring effective class separation.
Apply trigonometric functions (sin, cos, tan, and their inverses) to Weighted Sum features to reveal non-linear relationships and rotational patterns.
Suppose you have a dataset with features x1, x2, and x3:
New Feature = 0.5(x1) + 0.3(x2) - 0.2(x3)
Wrapped with cos function:
Transformed Feature = cos(0.5(x1) + 0.3(x2) - 0.2(x3))
This transformation can provide deeper insights and improve classification.
JTabViz can insert columns of features engineered with slope and distance calculations to explore relationships between pairs of numeric attributes:
Slope: Measures the rate of change between two attributes, calculated as:
slope = (Y2 − Y1) / (X2 − X1)
Distance: Represents the Euclidean distance between two points in 2D space, calculated as:
distance = (X2 − X1)^2 + (Y2 − Y1)^2
Attribute Pairing: Attributes are paired sequentially. If there are an odd number of columns, the last one is duplicated to complete the pair.
These features help identify patterns, clusters, or anomalies, in the data.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/AvaAvarai/jtabviz.git
-
Navigate to the project directory.
-
Compile the project:
javac -d out -cp "libs/*" src/*.java
-
Run the compiled project:
java -cp ".;libs/*" src.MainNote: For macOS and Linux, replace the semicolon (
;) in the classpath (-cp) with a colon (:).
JTabViz accepts datasets in CSV (Comma-Separated Values) file format. Here are the key points about the expected data format:
-
File Extension: The data file should have a .csv extension.
-
Data Types:
- Numerical data is preferred for optimal visualization and analysis.
- Non-numerical (categorical) data and blank fields are also accepted.
-
Class Column:
- A column representing the class or category of each data point is expected.
- This column can appear in any position.
- Should be titled 'class' (case-insensitive, so 'Class' or 'CLASS' are also acceptable).
- The class column is used for color-coding and shape assignment in various visualizations.
-
Header Row:
- The first row of the CSV file should contain column (attribute) names.
-
Delimiter:
- Values should be separated by commas.
dataset structure:
| x1 | x2 | x3 | x4 | x5 | class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3.14 | 2.71 | 1.41 | 0.58 | 1.73 | A |
| 2.22 | 4.44 | 3.33 | 1.11 | 5.55 | B |
| 0.87 | 1.23 | 3.45 | 5.67 | 7.89 | A |
| 9.99 | 8.88 | 7.77 | 6.66 | 5.55 | C |
| 1.23 | 4.56 | 7.89 | 2.34 | 5.67 | B |
example.csv:
x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, class,
3.14, 2.71, 1.41, 0.58, 1.73, A,
2.22, 4.44, 3.33, 1.11, 5.55, B,
0.87, 1.23, 3.45, 5.67, 7.89, A,
9.99, 8.88, 7.77, 6.66, 5.55, C,
1.23, 4.56, 7.89, 2.34, 5.67, B
(The class column can be in any position with no case sensitivity.)
The user interface icons are sourced from Font Awesome, converted using the fa2png tool.
This project is built on the Java Swing graphics library and uses no external libraries. We include a subfolder with UML generation and SVG to PNG conversion using PlantUML, library included in the project, licensed under the GNU GPL .
JTabViz is licensed under the MIT License, allowing free use for both personal and commercial purposes. For full terms, see the LICENSE file.
Font Awesome Free is open-source and GPL friendly, allowing use in commercial, open-source, or almost any type of project. For more information, visit the Font Awesome License page.