FastAPI framework, high performance, easy to learn, fast to code, ready for production
Documentation: https://fastapi.tiangolo.com
Source Code: https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi
FastAPI is a modern, fast (high-performance), web framework for building APIs with Python 3.6+ based on standard Python type hints.
The key features are:
-
Fast: Very high performance, on par with NodeJS and Go (thanks to Starlette and Pydantic). One of the fastest Python frameworks available.
-
Fast to code: Increase the speed to develop features by about 200% to 300% *.
-
Fewer bugs: Reduce about 40% of human (developer) induced errors. *
-
Intuitive: Great editor support. Completion everywhere. Less time debugging.
-
Easy: Designed to be easy to use and learn. Less time reading docs.
-
Short: Minimize code duplication. Multiple features from each parameter declaration. Fewer bugs.
-
Robust: Get production-ready code. With automatic interactive documentation.
-
Standards-based: Based on (and fully compatible with) the open standards for APIs: OpenAPI (previously known as Swagger) and JSON Schema.
* estimation based on tests on an internal development team, building production applications.
Python 3.6+
FastAPI stands on the shoulders of giants:
$ pip install fastapiYou will also need an ASGI server, for production such as uvicorn.
$ pip install uvicorn- Create a file
main.pywith:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}Or use async def...
If your code uses async / await, use async def:
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/")
async def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}Note:
If you don't know, check the "In a hurry?" section about async and await in the docs.
Run the server with:
uvicorn main:app --reloadAbout the command uvicorn main:app --reload...
The command uvicorn main:app refers to:
main: the filemain.py(the Python "module").app: the object created inside ofmain.pywith the lineapp = FastAPI().--reload: make the server restart after code changes. Only do this for development.
Open your browser at http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/5?q=somequery.
You will see the JSON response as:
{"item_id": 5, "q": "somequery"}You already created an API that:
- Receives HTTP requests in the paths
/and/items/{item_id}. - Both paths take
GEToperations (also known as HTTP methods). - The path
/items/{item_id}has a path parameteritem_idthat should be anint. - The path
/items/{item_id}has an optionalstrquery parameterq.
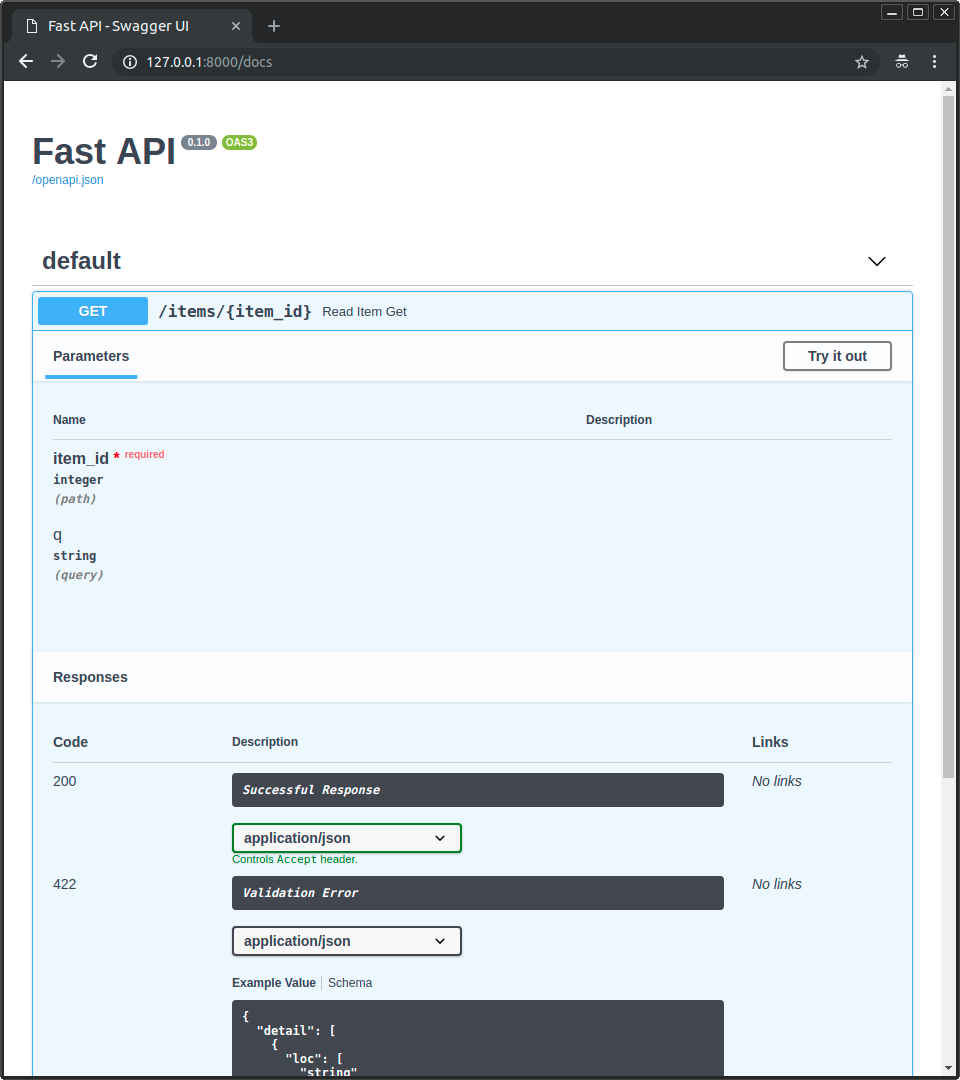
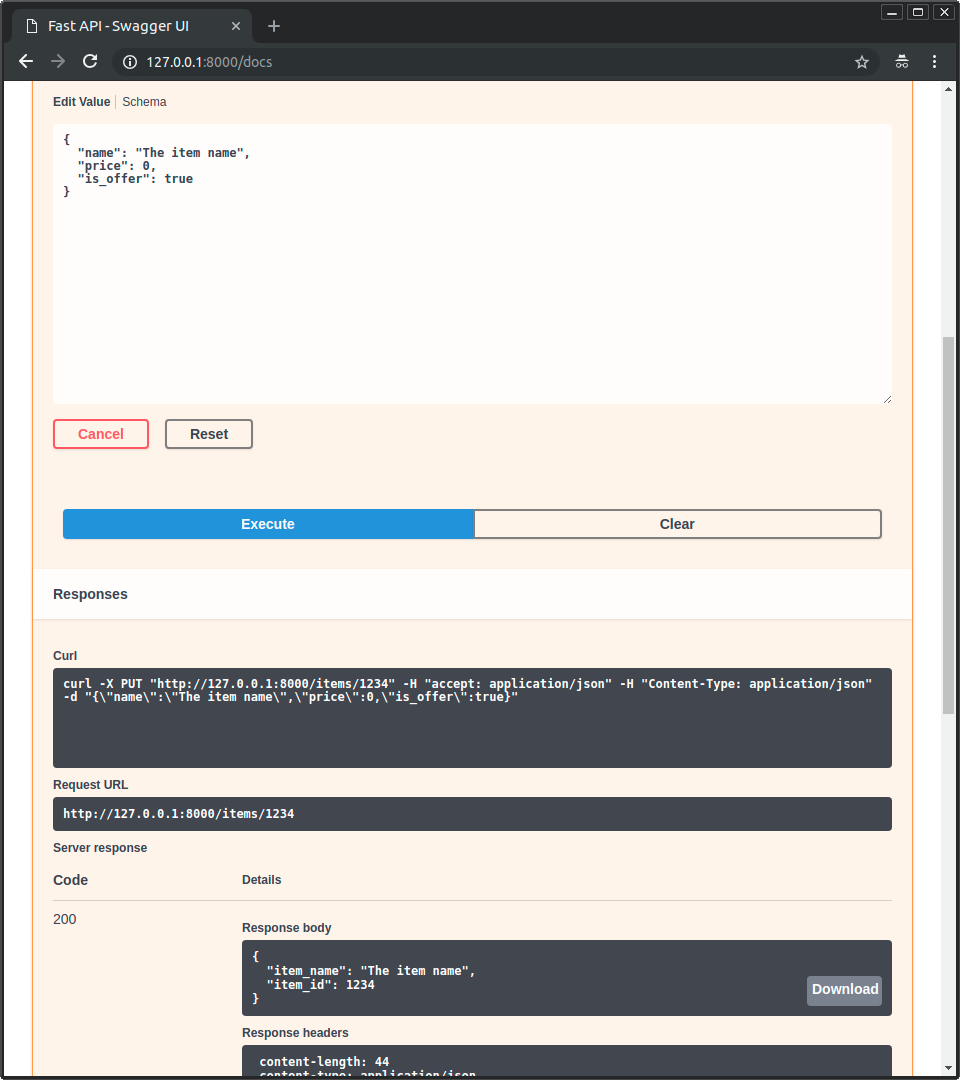
Now go to http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs.
You will see the automatic interactive API documentation (provided by Swagger UI):
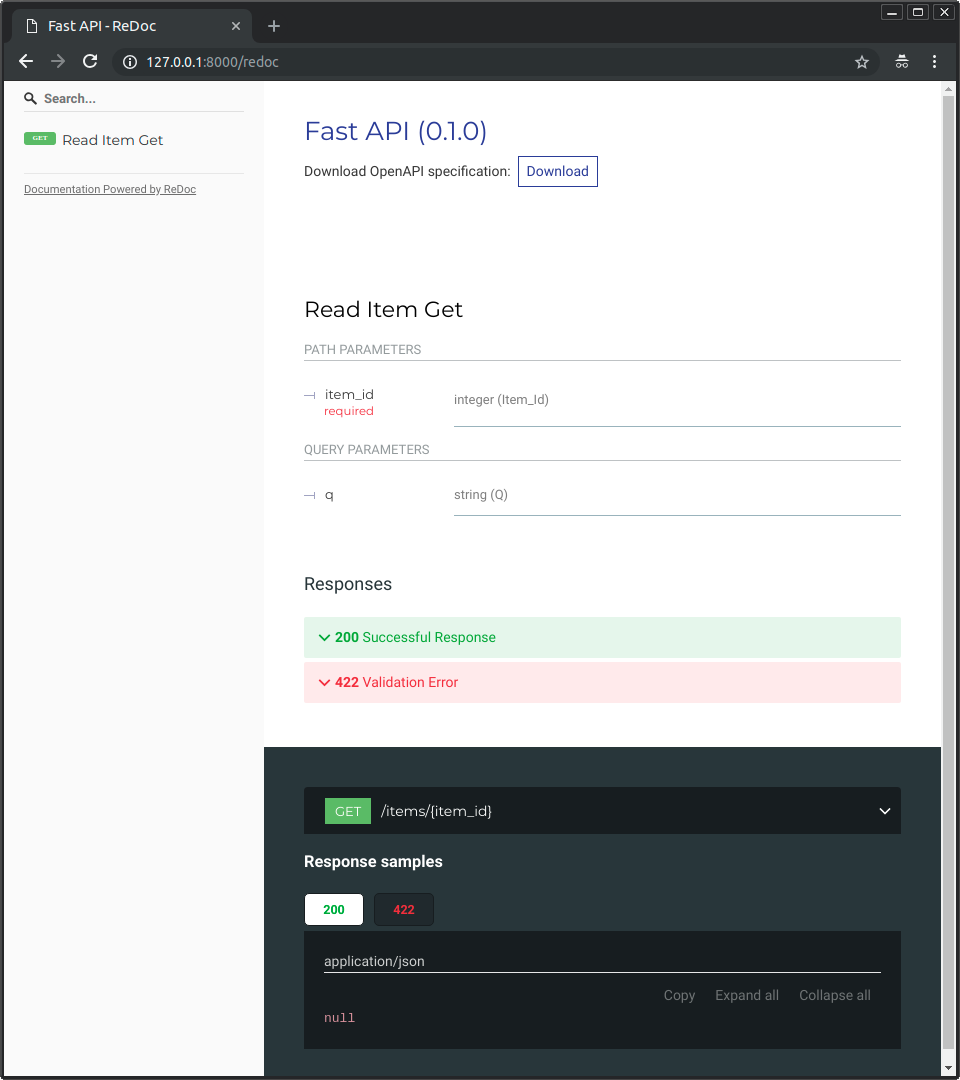
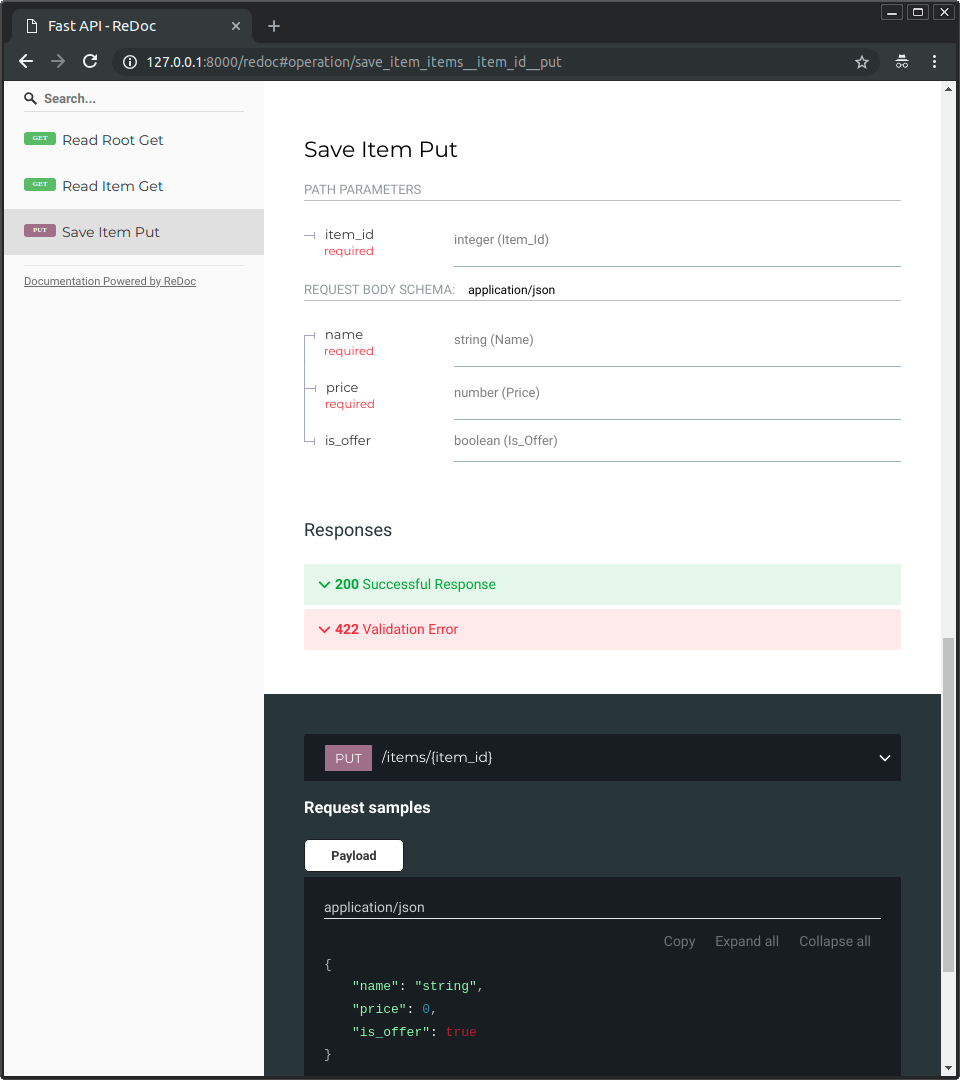
And now, go to http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc.
You will see the alternative automatic documentation (provided by ReDoc):
Now modify the file main.py to receive a body from a PUT request.
Declare the body using standard Python types, thanks to Pydantic.
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
price: float
is_offer: bool = None
@app.get("/")
def read_root():
return {"Hello": "World"}
@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
def read_item(item_id: int, q: str = None):
return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}
@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
def create_item(item_id: int, item: Item):
return {"item_name": item.name, "item_id": item_id}The server should reload automatically (because you added --reload to the uvicorn command above).
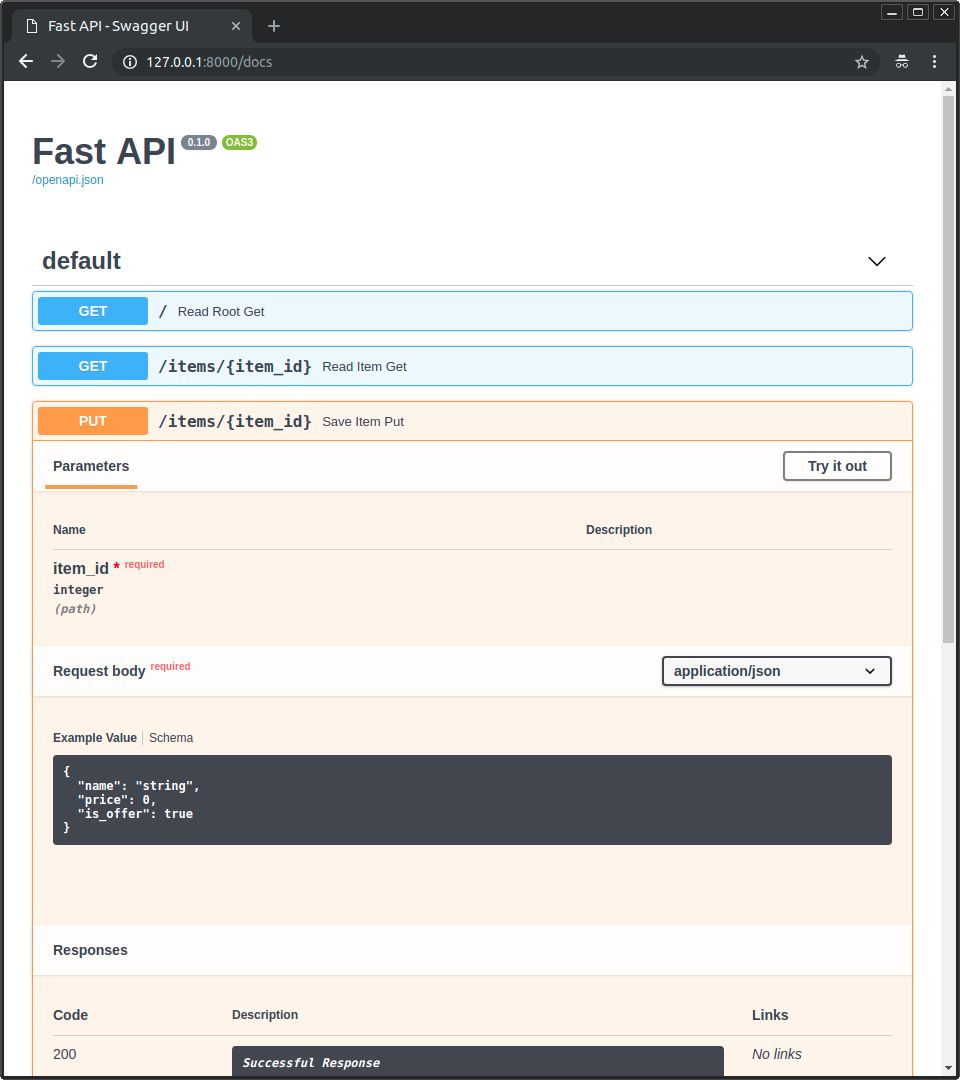
Now go to http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs.
- The interactive API documentation will be automatically updated, including the new body:
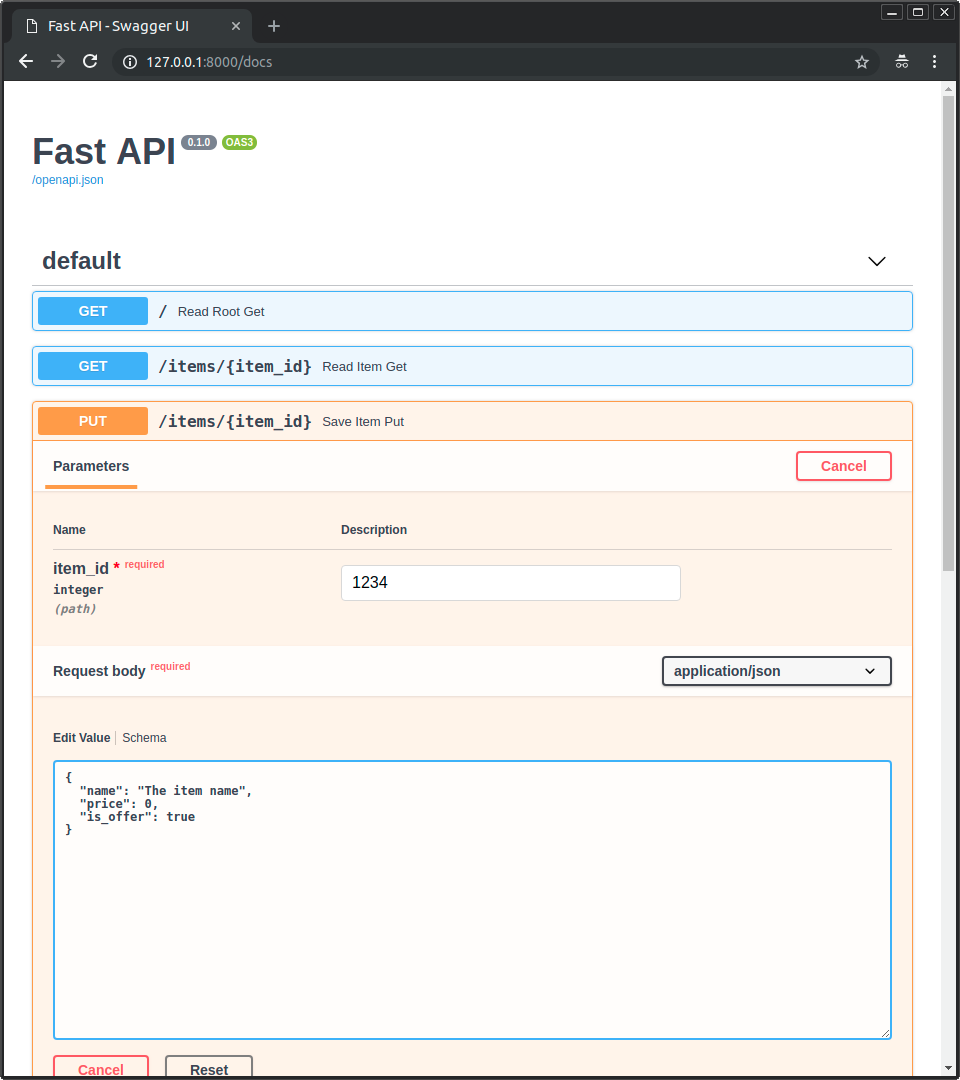
- Click on the button "Try it out", it allows you to fill the parameters and directly interact with the API:
- Then click on the "Execute" button, the user interface will communicate with your API, send the parameters, get the results and show them on the screen:
And now, go to http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc.
- The alternative documentation will also reflect the new query parameter and body:
In summary, you declare once the types of parameters, body, etc. as function parameters.
You do that with standard modern Python types.
You don't have to learn a new syntax, the methods or classes of a specific library, etc.
Just standard Python 3.6+.
For example, for an int:
item_id: intor for a more complex Item model:
item: Item...and with that single declaration you get:
- Editor support, including:
- Completion.
- Type checks.
- Validation of data:
- Automatic and clear errors when the data is invalid.
- Validation even for deeply nested JSON objects.
- Conversion of input data: coming from the network to Python data and types. Reading from:
- JSON.
- Path parameters.
- Query parameters.
- Cookies.
- Headers.
- Forms.
- Files.
- Conversion of output data: converting from Python data and types to network data (as JSON):
- Convert Python types (
str,int,float,bool,list, etc). datetimeobjects.UUIDobjects.- Database models.
- ...and many more.
- Convert Python types (
- Automatic interactive API documentation, including 2 alternative user interfaces:
- Swagger UI.
- ReDoc.
Coming back to the previous code example, FastAPI will:
- Validate that there is an
item_idin the path forGETandPUTrequests. - Validate that the
item_idis of typeintforGETandPUTrequests.- If it is not, the client will see a useful, clear error.
- Check if there is an optional query parameter named
q(as inhttp://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?q=somequery) forGETrequests.- As the
qparameter is declared with= None, it is optional. - Without the
Noneit would be required (as is the body in the case withPUT).
- As the
- For
PUTrequests to/items/{item_id}, Read the body as JSON:- Check that it has a required attribute
namethat should be astr. - Check that is has a required attribute
pricethat has to be afloat. - Check that it has an optional attribute
is_offer, that should be abool, if present. - All this would also work for deeply nested JSON objects.
- Check that it has a required attribute
- Convert from and to JSON automatically.
- Document everything with OpenAPI, that can be used by:
- Interactive documentation systems.
- Automatic client code generation systems, for many languages.
- Provide 2 interactive documentation web interfaces directly.
We just scratched the surface, but you already get the idea of how it all works.
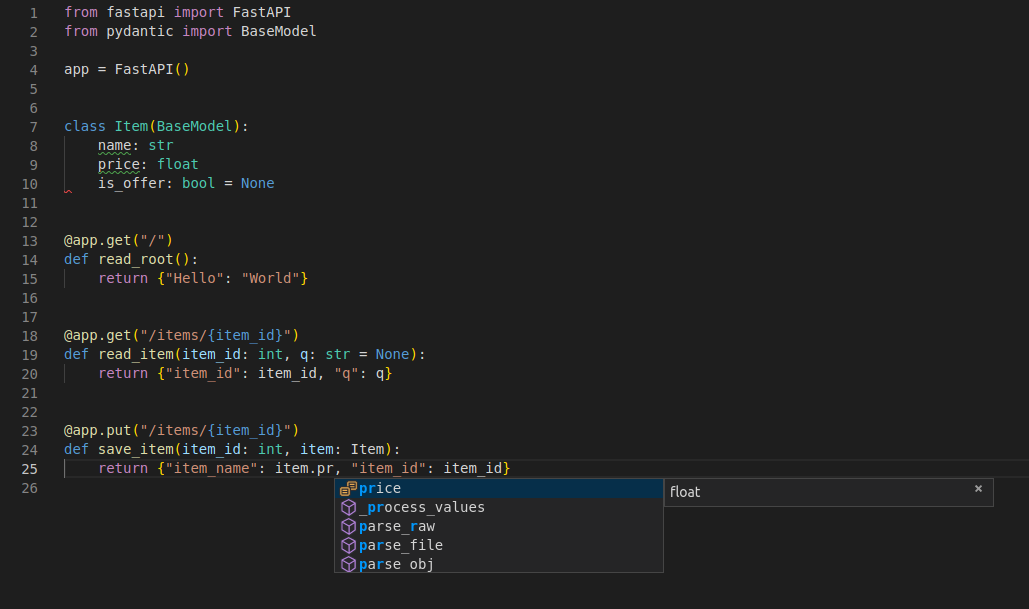
Try changing the line with:
return {"item_name": item.name, "item_id": item_id}...from:
... "item_name": item.name ......to:
... "item_price": item.price ......and see how your editor will auto-complete the attributes and know their types:
For a more complete example including more features, see the Tutorial - User Guide.
Spoiler alert: the tutorial - user guide includes:
- Declaration of parameters from other different places as: headers, cookies, form fields and files.
- How to set validation constraints as
maximum_lengthorregex. - A very powerful and easy to use Dependency Injection system.
- Security and authentication, including support for OAuth2 with JWT tokens and HTTP Basic auth.
- More advanced (but equally easy) techniques for declaring deeply nested JSON models (thanks to Pydantic).
- Many extra features (thanks to Starlette) as:
- WebSockets
- GraphQL
- extremely easy tests based on
requestsandpytest - CORS
- Cookie Sessions
- ...and more.
Independent TechEmpower benchmarks show FastAPI applications running under Uvicorn as one of the fastest Python frameworks available, only below Starlette and Uvicorn themselves (used internally by FastAPI). (*)
To understand more about it, see the section Benchmarks.
Used by Pydantic:
ujson- for faster JSON "parsing".email_validator- for email validation.
Used by Starlette:
requests- Required if you want to use theTestClient.aiofiles- Required if you want to useFileResponseorStaticFiles.jinja2- Required if you want to use the default template configuration.python-multipart- Required if you want to support form "parsing", withrequest.form().itsdangerous- Required forSessionMiddlewaresupport.pyyaml- Required forSchemaGeneratorsupport.graphene- Required forGraphQLAppsupport.ujson- Required if you want to useUJSONResponse.
Used by FastAPI / Starlette:
uvicorn- for the server that loads and serves your application.
You can install all of these with pip3 install fastapi[all].
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.