-
The first one allows the user to search for a building coordinate by searching for an address
-
The second one allows the user to convert OSM lat and lon degree decimal values to Rhino Points.
 This script downloads an OSM file and saves it to drive from a centre point or a search term
This script downloads an OSM file and saves it to drive from a centre point or a search term
- search - [string] Search query of the location
- midLat - [float] (optional) latitude of the building
- midLon - [float] (optional) longitude of the building
- bbox - [int] Dimension of one side of bounding box for OSM
- path - [string] A folder directory to save the OSM File
- run - [boolean] A boolean toggle to download the OSM file (Run once)
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
import math
import urllib2
import json
KEY = 'YOUR API KEY HERE'
if search:
print 'Search Tag found'
query = search.replace(" ", "%20")
url = 'http://api.positionstack.com/v1/forward?access_key='+KEY+'&query='+query
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
data = json.load(response)
midLon = data['data'][0]['longitude']
midLat = data['data'][0]['latitude']
else:
print 'Search Tag not Found. Enter search term or use midLat and midLon'
R = 6371000
#111110 is the distance of 1 degree in meters for the Y direction (Latitude) #X distance per degree = [cosine(latitude)*Y distance in radians] #bbox here is the dimension of the boundarybox side
dY = (bbox/2) / 111110
dX = dY / math.cos(math.radians(midLat))
a = str(midLon - dX)
b = str(midLat - dY)
c = str(midLon + dX)
d = str(midLat + dY)
bbox = a +','+ b + ',' + c + ',' + d
url = 'https://overpass-api.de/api/map?bbox='+bbox
if run:
response = urllib2.urlopen(url)
filePath = path+'file.osm'
mydata = response.read()
file = open(filePath, "w")
file.write(mydata)
file.close()
else:
filePath = path+'file.osm'
 This example is to demonstrate how decimal degree coordinates can be translated to cartesian points
This example is to demonstrate how decimal degree coordinates can be translated to cartesian points
import rhinoscriptsyntax as rs
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import ghpythonlib.treehelpers as th
import math
R = 6371000
lat = []
lon = []
tree = ET.parse(filePath)
root = tree.getroot()
for element in root.findall('node'):
lat.append(float(element.get('lat')))
lon.append(float(element.get('lon')))
for element in root.findall('bounds'):
minlat = float(element.get('minlat'))
minlon = float(element.get('minlon'))
maxlat = float(element.get('maxlat'))
maxlon = float(element.get('maxlon'))
midlat = (minlat+maxlat)/2
midlon = (minlon+maxlon)/2
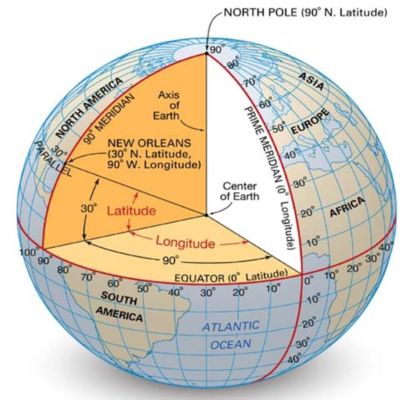
The Longitude distance per degree is along the x-axis remains constant around the circumference of the earth The Latitude distance per degree however, varies. It is largest by the equator and shorter towards the pole since the Latitude lines are parallel to oneanother.
(2 * pi * R) Radian Distance = 360 degrees
Y Distance per degree = (pi * R) / 180 (Where R is the radius of the earth in meters - 6371000m)
X Distance per degree = cosine(Latitude) * Y Distance per degree
ydistperdegree = (math.pi*R)/180
xdistperdegree = ((math.cos(midlat*(math.pi/180))*R)*(math.pi/180))
x_comp = []
y_comp = []
for i in lon:
x_comp.append((i-minlon)*xdistperdegree)
for i in lat:
y_comp.append((i-minlat)*ydistperdegree)
Points = []
for i in range(len(x_comp)):
Points.append(rs.CreatePoint(x_comp[i],y_comp[i],0))
plane = rs.WorldXYPlane()
Boundary = rs.AddRectangle(plane,((maxlon-minlon)*xdistperdegree),((maxlat-minlat)*ydistperdegree))