Note: Cloud Run jobs is a feature in private preview. Only allow-listed projects can currently take advantage of it.
dbt is an open source project to build data transformation pipelines with supported databases such as BigQuery, Postgres, Redshift and more.
In this sample, I want to show you how to setup a scheduled Cloud Run job that uses dbt with BigQuery backend.
I'm assuming that you already have a Google Cloud project setup with BigQuery
enabled, you have gcloud setup to use that project and you have dbt
installed locally.
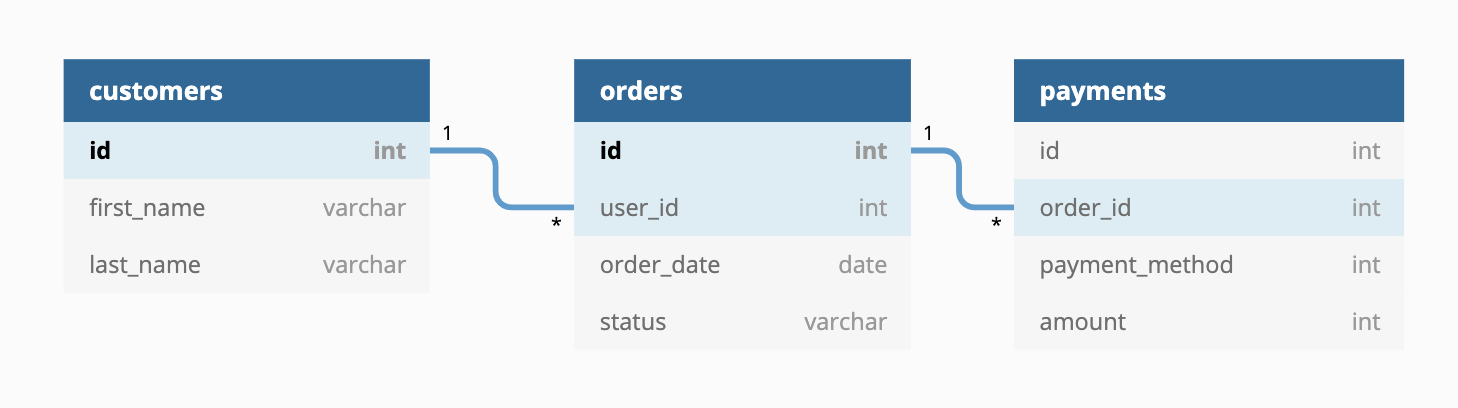
For the sample dbt service, we will use
jaffle-shop. jaffle_shop
is a fictional ecommerce store with the following tables:
There is already a public project dbt-tutorial with a jaffle_shop dataset
in BigQuery:
There is also a tutorial in DBT documentation showing how to transform this dataset with DBT. We will transform this tutorial into a scheduled service.
We already setup the sample project in jaffle-shop folder. Feel free to explore it in detail. We'll highlight a few things.
First, dbt_project.yml file has jaffle_shop name and
profile. It also has a single jaffle_shop model materialized as table.
Second, profiles.yml defines the BigQuery backend for dbt to connect to. This profile uses oauth for authentication to create a BigQuery dataset in your project.
Third, customers.sql defines the
model for dbt. It reads from dbt-tutorial project's jaffle_shop dataset and
creates a new transformed customers table.
Inside the jaffle_shop folder, run dbt with this new profile:
$ dbt run --profiles-dir .
Running with dbt=0.17.2
Found 1 model, 0 tests, 0 snapshots, 0 analyses, 147 macros, 0 operations, 0 seed files, 0 sources
16:16:10 | Concurrency: 1 threads (target='dev')
16:16:10 |
16:16:10 | 1 of 1 START table model dbt_atamel_dataset.customers................ [RUN]
16:16:15 | 1 of 1 OK created table model dbt_atamel_dataset.customers........... [CREATE TABLE (100) in 4.84s]
16:16:15 |
16:16:15 | Finished running 1 table model in 9.96s.
Completed successfully
Done. PASS=1 WARN=0 ERROR=0 SKIP=0 TOTAL=1You should see a new dataset and a customers table created in BigQuery:
Running dbt as a Cloud Run job requires that you run dbt in a container.
dbt has some base images that you can rely on (although the documentation is pretty much non-existent). This is a sample Dockerfile that works:
FROM fishtownanalytics/dbt:0.19.1
USER root
WORKDIR /dbt
COPY script.sh ./
COPY jaffle-shop ./
ENTRYPOINT "./script.sh"In this Dockerfile, we use the dbt base image, copy our dbt project and also the
script to call that project with the profile.
Enable the Cloud Build and Run APIs:
gcloud services enable run.googleapis.com
gcloud services enable cloudbuild.googleapis.comBuild the container:
JOB_NAME=dbt-job
PROJECT_ID=$(gcloud config get-value core/project)
gcloud builds submit --tag gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/$JOB_NAMETo test, first create the job:
REGION=europe-west1
gcloud config set run/region ${REGION}
gcloud alpha run jobs create dbt-job \
--image=gcr.io/$PROJECT_ID/$JOB_NAMERun the job:
gcloud alpha run jobs run dbt-jobYou can see the progress of the execution:
gcloud alpha run executions describe dbt-job-lfwc5
✔ Execution dbt-job-lfwc5 in region europe-west1
1 task completed successfullyAnd, you should see the dataset created with a new customers table in BigQuery:
The final step is to call the Cloud Run job on a schedule. You can do this with Cloud Scheduler.
First, enable the Cloud Scheduler API:
gcloud services enable cloudscheduler.googleapis.comReplace values in messagebody.json with values of your project:
sed -i -e "s/PROJECT_ID/$PROJECT_ID/" ./messagebody.json
sed -i -e "s/JOB_NAME/$JOB_NAME/" ./messagebody.jsonCreate a Cloud Scheduler job to call the service every day at 9:00:
PROJECT_NUMBER="$(gcloud projects describe $(gcloud config get-value project) --format='value(projectNumber)')"
gcloud scheduler jobs create http $JOB_NAME-run --schedule "0 9 * * *" \
--http-method=POST \
--uri=https://$REGION-run.googleapis.com/apis/run.googleapis.com/v1alpha1/namespaces/$PROJECT_ID/jobs \
--oauth-service-account-email=$PROJECT_NUMBER[email protected] \
--message-body-from-file=messagebody.jsonYou can test that the service by manually invoking the job:
gcloud scheduler jobs run $JOB_NAME-runAfter a few seconds, you should see the dataset created with a new customers table in BigQuery: