| comments | difficulty | edit_url | tags | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
Medium |
|
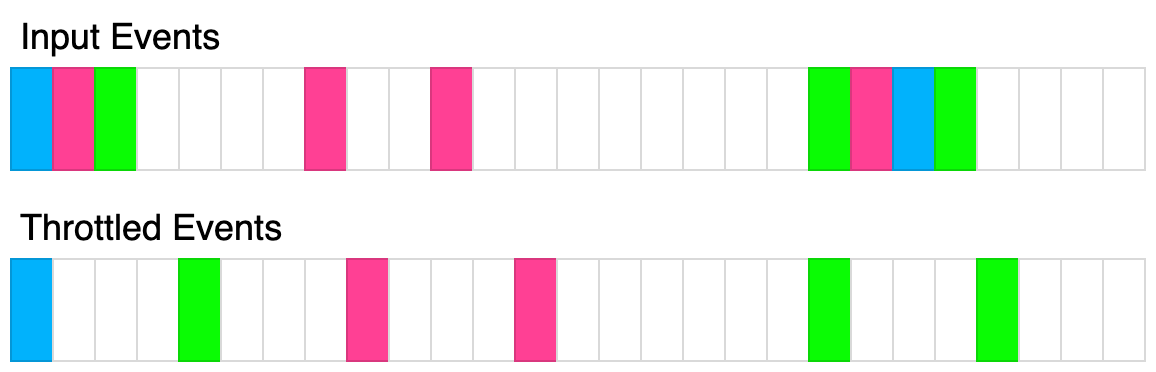
Given a function fn and a time in milliseconds t, return a throttled version of that function.
A throttled function is first called without delay and then, for a time interval of t milliseconds, can't be executed but should store the latest function arguments provided to call fn with them after the end of the delay.
For instance, t = 50ms, and the function was called at 30ms, 40ms, and 60ms.
At 30ms, without delay, the throttled function fn should be called with the arguments, and calling the throttled function fn should be blocked for the following t milliseconds.
At 40ms, the function should just save arguments.
At 60ms, arguments should overwrite currently stored arguments from the second call because the second and third calls are made before 80ms. Once the delay has passed, the throttled function fn should be called with the latest arguments provided during the delay period, and it should also create another delay period of 80ms + t.
Example 1:
Input:
t = 100,
calls = [
{"t":20,"inputs":[1]}
]
Output: [{"t":20,"inputs":[1]}]
Explanation: The 1st call is always called without delay
Example 2:
Input:
t = 50,
calls = [
{"t":50,"inputs":[1]},
{"t":75,"inputs":[2]}
]
Output: [{"t":50,"inputs":[1]},{"t":100,"inputs":[2]}]
Explanation:
The 1st is called a function with arguments (1) without delay.
The 2nd is called at 75ms, within the delay period because 50ms + 50ms = 100ms, so the next call can be reached at 100ms. Therefore, we save arguments from the 2nd call to use them at the callback of the 1st call.
Example 3:
Input:
t = 70,
calls = [
{"t":50,"inputs":[1]},
{"t":75,"inputs":[2]},
{"t":90,"inputs":[8]},
{"t": 140, "inputs":[5,7]},
{"t": 300, "inputs": [9,4]}
]
Output: [{"t":50,"inputs":[1]},{"t":120,"inputs":[8]},{"t":190,"inputs":[5,7]},{"t":300,"inputs":[9,4]}]
Explanation:
The 1st is called a function with arguments (1) without delay.
The 2nd is called at 75ms within the delay period because 50ms + 70ms = 120ms, so it should only save arguments.
The 3rd is also called within the delay period, and because we need just the latest function arguments, we overwrite previous ones. After the delay period, we do a callback at 120ms with saved arguments. That callback makes another delay period of 120ms + 70ms = 190ms so that the next function can be called at 190ms.
The 4th is called at 140ms in the delay period, so it should be called as a callback at 190ms. That will create another delay period of 190ms + 70ms = 260ms.
The 5th is called at 300ms, but it is after 260ms, so it should be called immediately and should create another delay period of 300ms + 70ms = 370ms.
Constraints:
0 <= t <= 10001 <= calls.length <= 100 <= calls[i].t <= 10000 <= calls[i].inputs[j], calls[i].inputs.length <= 10
type F = (...args: any[]) => void;
const throttle = (fn: F, t: number): F => {
let pending = false;
let nextArgs;
const wrapper = (...args) => {
nextArgs = args;
if (!pending) {
fn(...args);
pending = true;
nextArgs = undefined;
setTimeout(() => {
pending = false;
if (nextArgs) wrapper(...nextArgs);
}, t);
}
};
return wrapper;
};
/**
* const throttled = throttle(console.log, 100);
* throttled("log"); // logged immediately.
* throttled("log"); // logged at t=100ms.
*/