| comments | difficulty | edit_url | rating | source | tags | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
true |
困难 |
2300 |
第 220 场周赛 Q4 |
|
给你一个 n 个点组成的无向图边集 edgeList ,其中 edgeList[i] = [ui, vi, disi] 表示点 ui 和点 vi 之间有一条长度为 disi 的边。请注意,两个点之间可能有 超过一条边 。
给你一个查询数组queries ,其中 queries[j] = [pj, qj, limitj] ,你的任务是对于每个查询 queries[j] ,判断是否存在从 pj 到 qj 的路径,且这条路径上的每一条边都 严格小于 limitj 。
请你返回一个 布尔数组 answer ,其中 answer.length == queries.length ,当 queries[j] 的查询结果为 true 时, answer 第 j 个值为 true ,否则为 false 。
示例 1:
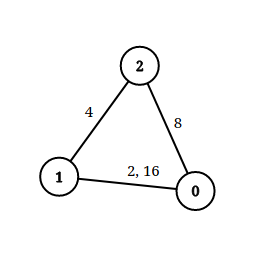
输入:n = 3, edgeList = [[0,1,2],[1,2,4],[2,0,8],[1,0,16]], queries = [[0,1,2],[0,2,5]] 输出:[false,true] 解释:上图为给定的输入数据。注意到 0 和 1 之间有两条重边,分别为 2 和 16 。 对于第一个查询,0 和 1 之间没有小于 2 的边,所以我们返回 false 。 对于第二个查询,有一条路径(0 -> 1 -> 2)两条边都小于 5 ,所以这个查询我们返回 true 。
示例 2:
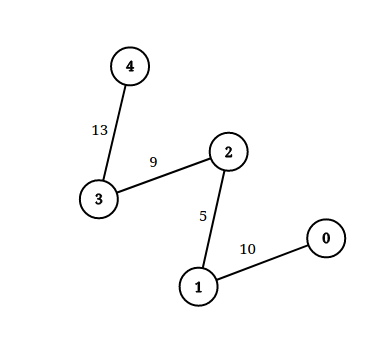
输入:n = 5, edgeList = [[0,1,10],[1,2,5],[2,3,9],[3,4,13]], queries = [[0,4,14],[1,4,13]] 输出:[true,false] 解释:上图为给定数据。
提示:
2 <= n <= 1051 <= edgeList.length, queries.length <= 105edgeList[i].length == 3queries[j].length == 30 <= ui, vi, pj, qj <= n - 1ui != vipj != qj1 <= disi, limitj <= 109- 两个点之间可能有 多条 边。
根据题目要求,我们需要对每个查询
判断两点是否连通可以通过并查集来实现。另外,由于查询的顺序对结果没有影响,因此我们可以先将所有查询按照
然后对于每个查询,我们从边权最小的边开始,将边权严格小于
时间复杂度
class Solution:
def distanceLimitedPathsExist(
self, n: int, edgeList: List[List[int]], queries: List[List[int]]
) -> List[bool]:
def find(x):
if p[x] != x:
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
p = list(range(n))
edgeList.sort(key=lambda x: x[2])
j = 0
ans = [False] * len(queries)
for i, (a, b, limit) in sorted(enumerate(queries), key=lambda x: x[1][2]):
while j < len(edgeList) and edgeList[j][2] < limit:
u, v, _ = edgeList[j]
p[find(u)] = find(v)
j += 1
ans[i] = find(a) == find(b)
return ansclass Solution {
private int[] p;
public boolean[] distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, int[][] edgeList, int[][] queries) {
p = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(edgeList, (a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]);
int m = queries.length;
boolean[] ans = new boolean[m];
Integer[] qid = new Integer[m];
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i) {
qid[i] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(qid, (i, j) -> queries[i][2] - queries[j][2]);
int j = 0;
for (int i : qid) {
int a = queries[i][0], b = queries[i][1], limit = queries[i][2];
while (j < edgeList.length && edgeList[j][2] < limit) {
int u = edgeList[j][0], v = edgeList[j][1];
p[find(u)] = find(v);
++j;
}
ans[i] = find(a) == find(b);
}
return ans;
}
private int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
}class Solution {
public:
vector<bool> distanceLimitedPathsExist(int n, vector<vector<int>>& edgeList, vector<vector<int>>& queries) {
vector<int> p(n);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
sort(edgeList.begin(), edgeList.end(), [](auto& a, auto& b) { return a[2] < b[2]; });
function<int(int)> find = [&](int x) -> int {
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
};
int m = queries.size();
vector<bool> ans(m);
vector<int> qid(m);
iota(qid.begin(), qid.end(), 0);
sort(qid.begin(), qid.end(), [&](int i, int j) { return queries[i][2] < queries[j][2]; });
int j = 0;
for (int i : qid) {
int a = queries[i][0], b = queries[i][1], limit = queries[i][2];
while (j < edgeList.size() && edgeList[j][2] < limit) {
int u = edgeList[j][0], v = edgeList[j][1];
p[find(u)] = find(v);
++j;
}
ans[i] = find(a) == find(b);
}
return ans;
}
};func distanceLimitedPathsExist(n int, edgeList [][]int, queries [][]int) []bool {
p := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
}
sort.Slice(edgeList, func(i, j int) bool { return edgeList[i][2] < edgeList[j][2] })
var find func(int) int
find = func(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
m := len(queries)
qid := make([]int, m)
ans := make([]bool, m)
for i := range qid {
qid[i] = i
}
sort.Slice(qid, func(i, j int) bool { return queries[qid[i]][2] < queries[qid[j]][2] })
j := 0
for _, i := range qid {
a, b, limit := queries[i][0], queries[i][1], queries[i][2]
for j < len(edgeList) && edgeList[j][2] < limit {
u, v := edgeList[j][0], edgeList[j][1]
p[find(u)] = find(v)
j++
}
ans[i] = find(a) == find(b)
}
return ans
}impl Solution {
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn distance_limited_paths_exist(
n: i32,
edge_list: Vec<Vec<i32>>,
queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>,
) -> Vec<bool> {
let mut disjoint_set: Vec<usize> = vec![0; n as usize];
let mut ans_vec: Vec<bool> = vec![false; queries.len()];
let mut q_vec: Vec<usize> = vec![0; queries.len()];
// Initialize the set
for i in 0..n {
disjoint_set[i as usize] = i as usize;
}
// Initialize the q_vec
for i in 0..queries.len() {
q_vec[i] = i;
}
// Sort the q_vec based on the query limit, from the lowest to highest
q_vec.sort_by(|i, j| queries[*i][2].cmp(&queries[*j][2]));
// Sort the edge_list based on the edge weight, from the lowest to highest
let mut edge_list = edge_list.clone();
edge_list.sort_by(|i, j| i[2].cmp(&j[2]));
let mut edge_idx: usize = 0;
for q_idx in &q_vec {
let s = queries[*q_idx][0] as usize;
let d = queries[*q_idx][1] as usize;
let limit = queries[*q_idx][2];
// Construct the disjoint set
while edge_idx < edge_list.len() && edge_list[edge_idx][2] < limit {
Solution::union(
edge_list[edge_idx][0] as usize,
edge_list[edge_idx][1] as usize,
&mut disjoint_set,
);
edge_idx += 1;
}
// If the parents of s & d are the same, this query should be `true`
// Otherwise, the current query is `false`
ans_vec[*q_idx] = Solution::check_valid(s, d, &mut disjoint_set);
}
ans_vec
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn find(x: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) -> usize {
if d_set[x] != x {
d_set[x] = Solution::find(d_set[x], d_set);
}
return d_set[x];
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn union(s: usize, d: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) {
let p_s = Solution::find(s, d_set);
let p_d = Solution::find(d, d_set);
d_set[p_s] = p_d;
}
#[allow(dead_code)]
pub fn check_valid(s: usize, d: usize, d_set: &mut Vec<usize>) -> bool {
let p_s = Solution::find(s, d_set);
let p_d = Solution::find(d, d_set);
p_s == p_d
}
}附并查集相关介绍以及常用模板:
并查集是一种树形的数据结构,顾名思义,它用于处理一些不交集的合并及查询问题。 它支持两种操作:
- 查找(Find):确定某个元素处于哪个子集,单次操作时间复杂度
$O(\alpha(n))$ - 合并(Union):将两个子集合并成一个集合,单次操作时间复杂度
$O(\alpha(n))$
其中
以下是并查集的常用模板,需要熟练掌握。其中:
-
n表示节点数 -
p存储每个点的父节点,初始时每个点的父节点都是自己 -
size只有当节点是祖宗节点时才有意义,表示祖宗节点所在集合中,点的数量 -
find(x)函数用于查找$x$ 所在集合的祖宗节点 -
union(a, b)函数用于合并$a$ 和$b$ 所在的集合
p = list(range(n))
size = [1] * n
def find(x):
if p[x] != x:
# 路径压缩
p[x] = find(p[x])
return p[x]
def union(a, b):
pa, pb = find(a), find(b)
if pa == pb:
return
p[pa] = pb
size[pb] += size[pa]int[] p = new int[n];
int[] size = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
p[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
// 路径压缩
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
void union(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) {
return;
}
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}vector<int> p(n);
iota(p.begin(), p.end(), 0);
vector<int> size(n, 1);
int find(int x) {
if (p[x] != x) {
// 路径压缩
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
void unite(int a, int b) {
int pa = find(a), pb = find(b);
if (pa == pb) return;
p[pa] = pb;
size[pb] += size[pa];
}p := make([]int, n)
size := make([]int, n)
for i := range p {
p[i] = i
size[i] = 1
}
func find(x int) int {
if p[x] != x {
// 路径压缩
p[x] = find(p[x])
}
return p[x]
}
func union(a, b int) {
pa, pb := find(a), find(b)
if pa == pb {
return
}
p[pa] = pb
size[pb] += size[pa]
}