ArangoDB is a multi-model, open-source database with flexible data models for documents, graphs, and key-values. Build high performance applications using a convenient SQL-like query language or JavaScript extensions. Use ACID transactions if you require them. Scale horizontally with a few mouse clicks.
The supported data models can be mixed in queries and allow ArangoDB to be the aggregation point for your data.
To get started, try one of our 10 minutes tutorials in your favorite programming language or try one of our ArangoDB Cookbook recipes.
For the impatient: download and install
ArangoDB. Start the server arangod and point your browser to http://127.0.0.1:8529/.
- Multi-Model: Documents, graphs and key-value pairs — model your data as you see fit for your application.
- Joins: Conveniently join what belongs together for flexible ad-hoc querying, less data redundancy.
- Transactions: Easy application development keeping your data consistent and safe. No hassle in your client.
Here is an AQL query that makes use of all those features:
Joins and transactions are key features for flexible, secure data designs, widely used in relational databases but lacking in many NoSQL products. However, there is no need to forgo them in ArangoDB. You decide how and when to use joins and strong consistency guarantees, without sacrificing performance and scalability.
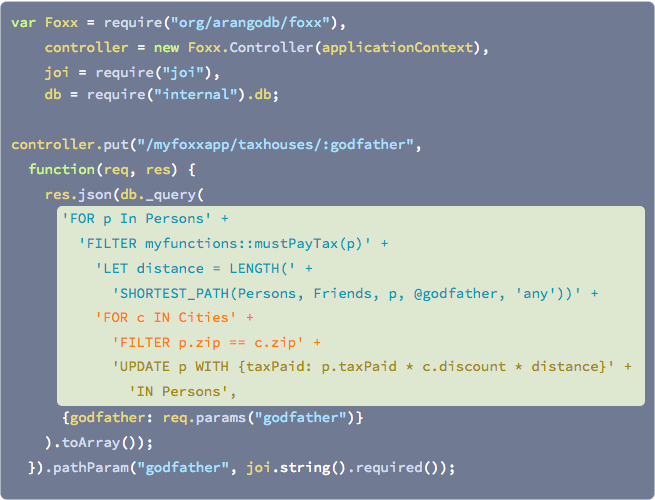
Furthermore, ArangoDB offers a JavaScript framework called Foxx that is executed in the database server with direct access to the data. Build your own data-centric microservices with a few lines of code:
Microservice Example
By extending the HTTP API with user code written in JavaScript, ArangoDB can be turned into a strict schema-enforcing persistence engine.
Next step, bundle your Foxx application as a docker container and get it running in the cloud.
Other features of ArangoDB include:
- Schema-free schemata let you combine the space efficiency of MySQL with the performance power of NoSQL
- Use a data-centric microservices approach with ArangoDB Foxx and fuse your application-logic and database together for maximal throughput
- JavaScript for all: no language zoo, you can use one language from your browser to your back-end
- ArangoDB is multi-threaded - exploit the power of all your cores
- Flexible data modeling: model your data as combination of key-value pairs, documents or graphs - perfect for social relations
- Free index choice: use the correct index for your problem, be it a skip list or a fulltext search
- Configurable durability: let the application decide if it needs more durability or more performance
- Powerful query language (AQL) to retrieve and modify data
- Transactions: run queries on multiple documents or collections with optional transactional consistency and isolation
- Replication and Sharding: set up the database in a master-slave configuration or spread bigger datasets across multiple servers
- It is open source (Apache License 2.0)
For more in-depth information read the design goals of ArangoDB
The What's new in ArangoDB 3.0 can be found in the documentation.
Key features of the 3.0 release are:
- Use of VelocyPack as internal storage format
- AQL improvements
- Much better cluster state management
- Synchronous replication (master/master)
- Unified APIs for CRUD operations
- Persistent indexes
- Upgraded version of V8
- New web admin interface
- Foxx improvements
- Logging improvements
- Improved documentation
Please check the Installation Manual for installation and compilation instructions.
The User Manual has an introductory chapter showing the basic operations of ArangoDB.
We really appreciate feature requests and bug reports. Please use our Github issue tracker for reporting them:
https://github.com/arangodb/arangodb/issues
You can use the Google group for improvements, feature requests, comments:
https://www.arangodb.com/community
StackOverflow is great for questions about AQL, usage scenarios etc.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/arangodb
To chat with the community and the developers we offer a Slack chat: