参与本项目,贡献其他语言版本的代码,拥抱开源,让更多学习算法的小伙伴们收益!
给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid ,其中 0 表示一个海洋单元格、1 表示一个陆地单元格。
一次 移动 是指从一个陆地单元格走到另一个相邻(上、下、左、右)的陆地单元格或跨过 grid 的边界。
返回网格中 无法 在任意次数的移动中离开网格边界的陆地单元格的数量。
- 输入:grid = [[0,0,0,0],[1,0,1,0],[0,1,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
- 输出:3
- 解释:有三个 1 被 0 包围。一个 1 没有被包围,因为它在边界上。
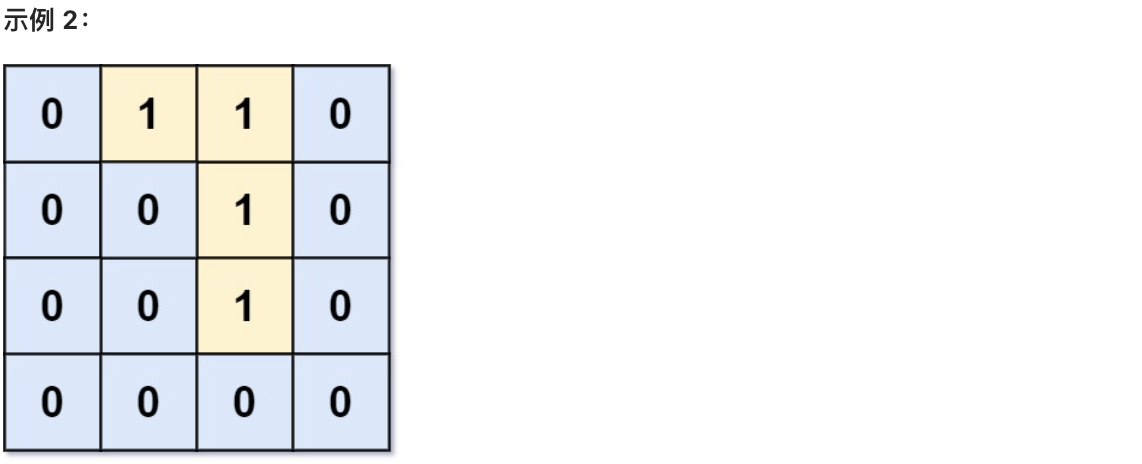
- 输入:grid = [[0,1,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,0]]
- 输出:0
- 解释:所有 1 都在边界上或可以到达边界。
本题使用dfs,bfs,并查集都是可以的。
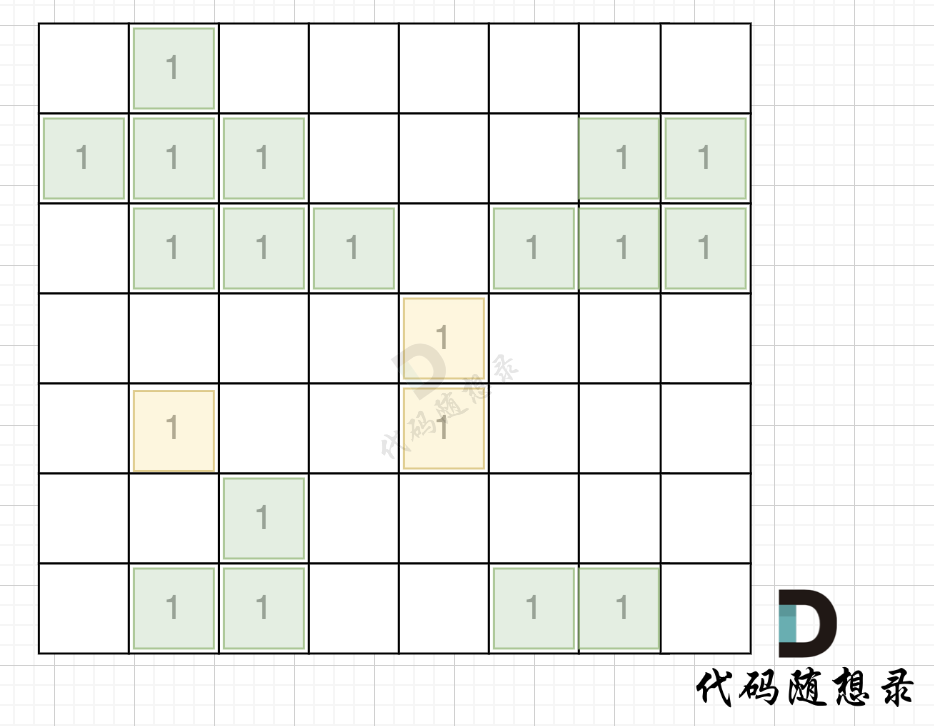
本题要求找到不靠边的陆地面积,那么我们只要从周边找到陆地然后 通过 dfs或者bfs 将周边靠陆地且相邻的陆地都变成海洋,然后再去重新遍历地图的时候,统计此时还剩下的陆地就可以了。
如图,在遍历地图周围四个边,靠地图四边的陆地,都为绿色,
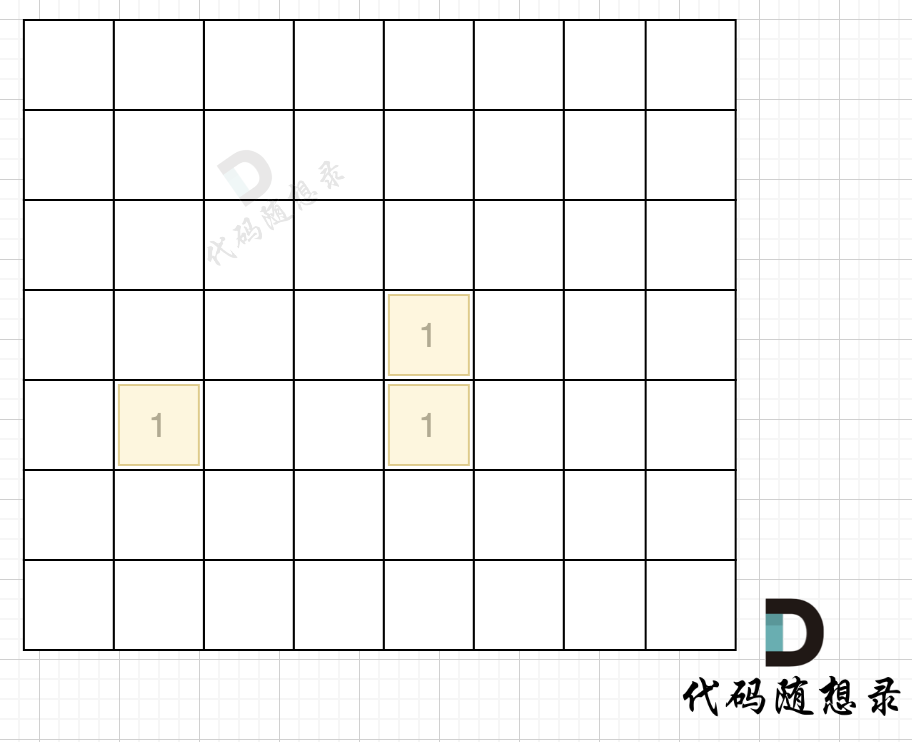
在遇到地图周边陆地的时候,将1都变为0,此时地图为这样:
然后我们再去遍历这个地图,遇到有陆地的地方,去采用深搜或者广搜,边统计所有陆地。
如果对深搜或者广搜不够了解,建议先看这里:深度优先搜索精讲,广度优先搜索精讲
采用深度优先搜索的代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int dir[4][2] = {-1, 0, 0, -1, 1, 0, 0, 1}; // 保存四个方向
int count; // 统计符合题目要求的陆地空格数量
void dfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {
grid[x][y] = 0;
count++;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 向四个方向遍历
int nextx = x + dir[i][0];
int nexty = y + dir[i][1];
// 超过边界
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue;
// 不符合条件,不继续遍历
if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 0) continue;
dfs (grid, nextx, nexty);
}
return;
}
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) dfs(grid, i, 0);
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) dfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) dfs(grid, 0, j);
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) dfs(grid, n - 1, j);
}
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) dfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
return count;
}
};采用广度优先搜索的代码如下:
class Solution {
private:
int count = 0;
int dir[4][2] = {0, 1, 1, 0, -1, 0, 0, -1}; // 四个方向
void bfs(vector<vector<int>>& grid, int x, int y) {
queue<pair<int, int>> que;
que.push({x, y});
grid[x][y] = 0; // 只要加入队列,立刻标记
count++;
while(!que.empty()) {
pair<int ,int> cur = que.front(); que.pop();
int curx = cur.first;
int cury = cur.second;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = curx + dir[i][0];
int nexty = cury + dir[i][1];
if (nextx < 0 || nextx >= grid.size() || nexty < 0 || nexty >= grid[0].size()) continue; // 越界了,直接跳过
if (grid[nextx][nexty] == 1) {
que.push({nextx, nexty});
count++;
grid[nextx][nexty] = 0; // 只要加入队列立刻标记
}
}
}
}
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int n = grid.size(), m = grid[0].size();
// 从左侧边,和右侧边 向中间遍历
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (grid[i][0] == 1) bfs(grid, i, 0);
if (grid[i][m - 1] == 1) bfs(grid, i, m - 1);
}
// 从上边和下边 向中间遍历
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[0][j] == 1) bfs(grid, 0, j);
if (grid[n - 1][j] == 1) bfs(grid, n - 1, j);
}
count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) bfs(grid, i, j);
}
}
return count;
}
};深度优先遍历版本:
class Solution {
// 四个方向
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
// 深度优先遍历,把可以通向边缘部分的 1 全部标记成 true
public void dfs(int[][] grid, int row, int col, boolean[][] visited) {
for (int[] current: position) {
int newRow = row + current[0], newCol = col + current[1];
// 下标越界直接跳过
if (newRow < 0 || newRow >= grid.length || newCol < 0 || newCol >= grid[0].length) continue;
// 当前位置不是 1 或者已经被访问了就直接跳过
if (grid[newRow][newCol] != 1 || visited[newRow][newCol]) continue;
visited[newRow][newCol] = true;
dfs(grid, newRow, newCol, visited);
}
}
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int rowSize = grid.length, colSize = grid[0].length, ans = 0; // ans 记录答案
// 标记数组记录每个值为 1 的位置是否可以到达边界,可以为 true,反之为 false
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
// 左侧边界和右侧边界查找 1 进行标记并进行深度优先遍历
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
if (grid[row][0] == 1 && !visited[row][0]) {
visited[row][0] = true;
dfs(grid, row, 0, visited);
}
if (grid[row][colSize - 1] == 1 && !visited[row][colSize - 1]) {
visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
dfs(grid, row, colSize - 1, visited);
}
}
// 上边界和下边界遍历,但是四个角不用遍历,因为上面已经遍历到了
for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
if (grid[0][col] == 1 && !visited[0][col]) {
visited[0][col] = true;
dfs(grid, 0, col, visited);
}
if (grid[rowSize - 1][col] == 1 && !visited[rowSize - 1][col]) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
dfs(grid, rowSize - 1, col, visited);
}
}
// 查找没有标记过的 1,记录到 ans 中
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] == 1 && !visited[row][col]) ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}广度优先遍历版本:
class Solution {
// 四个方向
private static final int[][] position = {{-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}};
// 广度优先遍历,把可以通向边缘部分的 1 全部标记成 true
public void bfs(int[][] grid, Queue<int[]> queue, boolean[][] visited) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int[] curPos = queue.poll();
for (int[] current: position) {
int row = curPos[0] + current[0], col = curPos[1] + current[1];
// 下标越界直接跳过
if (row < 0 || row >= grid.length || col < 0 || col >= grid[0].length)
continue;
// 当前位置不是 1 或者已经被访问了就直接跳过
if (visited[row][col] || grid[row][col] == 0) continue;
visited[row][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, col});
}
}
}
public int numEnclaves(int[][] grid) {
int rowSize = grid.length, colSize = grid[0].length, ans = 0; // ans 记录答案
// 标记数组记录每个值为 1 的位置是否可以到达边界,可以为 true,反之为 false
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[rowSize][colSize];
Queue<int[]> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
// 搜索左侧边界和右侧边界查找 1 存入队列
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
if (grid[row][0] == 1) {
visited[row][0] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, 0});
}
if (grid[row][colSize - 1] == 1) {
visited[row][colSize - 1] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{row, colSize - 1});
}
}
// 搜索上边界和下边界遍历,但是四个角不用遍历,因为上面已经遍历到了
for (int col = 1; col < colSize - 1; col++) {
if (grid[0][col] == 1) {
visited[0][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{0, col});
}
if (grid[rowSize - 1][col] == 1 && !visited[rowSize - 1][col]) {
visited[rowSize - 1][col] = true;
queue.add(new int[]{rowSize - 1, col});
}
}
bfs(grid, queue, visited); // 广度优先遍历
// 查找没有标记过的 1,记录到 ans 中
for (int row = 0; row < rowSize; row++) {
for (int col = 0; col < colSize; col++) {
if (grid[row][col] == 1 && !visited[row][col]) ++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
}深度优先遍历
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]] # 四个方向
# 深度优先遍历,把可以通向边缘部分的 1 全部标记成 true
def dfs(self, grid: List[List[int]], row: int, col: int, visited: List[List[bool]]) -> None:
for current in self.position:
newRow, newCol = row + current[0], col + current[1]
# 索引下标越界
if newRow < 0 or newRow >= len(grid) or newCol < 0 or newCol >= len(grid[0]):
continue
# 当前位置值不是 1 或者已经被访问过了
if grid[newRow][newCol] == 0 or visited[newRow][newCol]: continue
visited[newRow][newCol] = True
self.dfs(grid, newRow, newCol, visited)
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rowSize, colSize, ans = len(grid), len(grid[0]), 0
# 标记数组记录每个值为 1 的位置是否可以到达边界,可以为 True,反之为 False
visited = [[False for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
# 搜索左边界和右边界,对值为 1 的位置进行深度优先遍历
for row in range(rowSize):
if grid[row][0] == 1:
visited[row][0] = True
self.dfs(grid, row, 0, visited)
if grid[row][colSize - 1] == 1:
visited[row][colSize - 1] = True
self.dfs(grid, row, colSize - 1, visited)
# 搜索上边界和下边界,对值为 1 的位置进行深度优先遍历,但是四个角不需要,因为上面遍历过了
for col in range(1, colSize - 1):
if grid[0][col] == 1:
visited[0][col] = True
self.dfs(grid, 0, col, visited)
if grid[rowSize - 1][col] == 1:
visited[rowSize - 1][col] = True
self.dfs(grid, rowSize - 1, col, visited)
# 找出矩阵中值为 1 但是没有被标记过的位置,记录答案
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
if grid[row][col] == 1 and not visited[row][col]:
ans += 1
return ans广度优先遍历
class Solution:
def __init__(self):
self.position = [[-1, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1]] # 四个方向
# 广度优先遍历,把可以通向边缘部分的 1 全部标记成 true
def bfs(self, grid: List[List[int]], queue: deque, visited: List[List[bool]]) -> None:
while queue:
curPos = queue.popleft()
for current in self.position:
row, col = curPos[0] + current[0], curPos[1] + current[1]
# 索引下标越界
if row < 0 or row >= len(grid) or col < 0 or col >= len(grid[0]): continue
# 当前位置值不是 1 或者已经被访问过了
if grid[row][col] == 0 or visited[row][col]: continue
visited[row][col] = True
queue.append([row, col])
def numEnclaves(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
rowSize, colSize, ans = len(grid), len(grid[0]), 0
# 标记数组记录每个值为 1 的位置是否可以到达边界,可以为 True,反之为 False
visited = [[False for _ in range(colSize)] for _ in range(rowSize)]
queue = deque() # 队列
# 搜索左侧边界和右侧边界查找 1 存入队列
for row in range(rowSize):
if grid[row][0] == 1:
visited[row][0] = True
queue.append([row, 0])
if grid[row][colSize - 1] == 1:
visited[row][colSize - 1] = True
queue.append([row, colSize - 1])
# 搜索上边界和下边界查找 1 存入队列,但是四个角不用遍历,因为上面已经遍历到了
for col in range(1, colSize - 1):
if grid[0][col] == 1:
visited[0][col] = True
queue.append([0, col])
if grid[rowSize - 1][col] == 1:
visited[rowSize - 1][col] = True
queue.append([rowSize - 1, col])
self.bfs(grid, queue, visited) # 广度优先遍历
# 找出矩阵中值为 1 但是没有被标记过的位置,记录答案
for row in range(rowSize):
for col in range(colSize):
if grid[row][col] == 1 and not visited[row][col]:
ans += 1
return ans-
- 统计封闭岛屿的数目