This program comes with absolutely no warranty. No liability is accepted for any loss and risk to public health resulting from use of this software.
| Version | Cover | Build | Docs |
|---|---|---|---|
  |
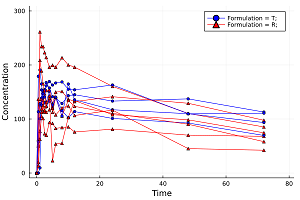
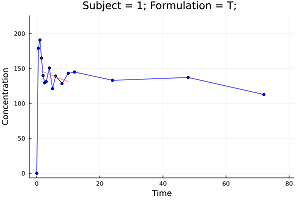
Non-compartment PK analysis (NCA).
Pharmacokinetics, sometimes abbreviated as PK, is a branch of pharmacology dedicated to determine the fate of substances administered to a living organism.
When analyzing pharmacokinetic data, one generally employs either model fitting using nonlinear regression analysis or non-compartmental analysis techniques (NCA). The method one actually employs depends on what is required from the analysis. If the primary requirement is to determine the degree of exposure following administration of a drug (such as AUC), and perhaps the drug's associated pharmacokinetic parameters, such as clearance, elimination half-life, T (max), C (max), etc., then NCA is generally the preferred methodology to use in that it requires fewer assumptions than model-based approaches.[*]
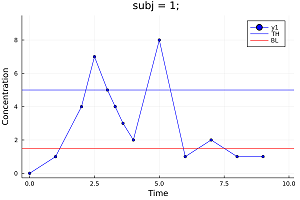
PK urine parameters and PD parameters such as Time Above/Below Baseline/Threshold can be also calculated.
Also this package include recipes for plotting PK/PD data.
- Gabrielsson J, Weiner D. Non-compartmental analysis. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;929:377-89. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-050-2_16. PMID: 23007438.
import Pkg; Pkg.add("MetidaNCA")Pkg.test("MetidaNCA")using DataFrames, CSV, MetidaNCA
pkdata2 = CSV.File(joinpath(dirname(pathof(MetidaNCA)), "..", "test", "csv", "pkdata2.csv")) |> DataFrame
ds = MetidaNCA.pkimport(pkdata2, :Time, :Concentration, [:Subject, :Formulation]; dosetime = MetidaNCA.DoseTime(dose = 100, time = 0))
sort!(ds, :Subject)
dsnca = MetidaNCA.nca!(ds, adm = :ev, calcm = :lint, verbose = 2)