diff --git a/.github/workflows/main.yml b/.github/workflows/main.yml
index 7d1c7d01c..6cecc9fea 100644
--- a/.github/workflows/main.yml
+++ b/.github/workflows/main.yml
@@ -46,11 +46,11 @@ jobs:
- name: pylint check
run: |
- python -m pylint src/gstools/
+ python -m pylint src/gstools_cython/
- name: cython-lint check
run: |
- cython-lint src/gstools/
+ cython-lint src/gstools_cython/
build_wheels:
name: wheels for ${{ matrix.os }}
@@ -76,7 +76,7 @@ jobs:
path: ./dist/*.whl
build_sdist:
- name: sdist on ${{ matrix.os }} with py ${{ matrix.ver.py }} numpy${{ matrix.ver.np }} scipy${{ matrix.ver.sp }}
+ name: sdist on ${{ matrix.os }} with py ${{ matrix.ver.py }} numpy${{ matrix.ver.np }}
runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
strategy:
fail-fast: false
@@ -84,19 +84,19 @@ jobs:
os: [ubuntu-latest, windows-latest, macos-13, macos-14]
# https://github.com/scipy/oldest-supported-numpy/blob/main/setup.cfg
ver:
- - {py: '3.8', np: '==1.20.0', sp: '==1.5.4'}
- - {py: '3.9', np: '==1.20.0', sp: '==1.5.4'}
- - {py: '3.10', np: '==1.21.6', sp: '==1.7.2'}
- - {py: '3.11', np: '==1.23.2', sp: '==1.9.2'}
- - {py: '3.12', np: '==1.26.2', sp: '==1.11.2'}
- - {py: '3.12', np: '>=2.0.0rc1', sp: '>=1.13.0'}
+ - {py: '3.8', np: '==1.20.0'}
+ - {py: '3.9', np: '==1.20.0'}
+ - {py: '3.10', np: '==1.21.6'}
+ - {py: '3.11', np: '==1.23.2'}
+ - {py: '3.12', np: '==1.26.2'}
+ - {py: '3.12', np: '>=2.0.0rc1'}
exclude:
- os: macos-14
- ver: {py: '3.8', np: '==1.20.0', sp: '==1.5.4'}
+ ver: {py: '3.8', np: '==1.20.0'}
- os: macos-14
- ver: {py: '3.9', np: '==1.20.0', sp: '==1.5.4'}
+ ver: {py: '3.9', np: '==1.20.0'}
- os: macos-14
- ver: {py: '3.10', np: '==1.21.6', sp: '==1.7.2'}
+ ver: {py: '3.10', np: '==1.21.6'}
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
with:
@@ -110,21 +110,18 @@ jobs:
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
- pip install build "coveralls>=3.0.0"
+ pip install build
- - name: Install GSTools
+ - name: Install GSTools-Cython
env:
GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL: 1
run: |
pip install -v --editable .[test]
- name: Run tests
- env:
- GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
run: |
- pip install "numpy${{ matrix.ver.np }}" "scipy${{ matrix.ver.sp }}"
- python -m pytest --cov gstools --cov-report term-missing -v tests/
- python -m coveralls --service=github
+ pip install "numpy${{ matrix.ver.np }}"
+ python -m pytest -v tests/
- name: Build sdist
run: |
@@ -136,6 +133,39 @@ jobs:
with:
path: dist/*.tar.gz
+ coverage:
+ name: coverage
+ runs-on: ubuntu-latest
+
+ steps:
+ - uses: actions/checkout@v4
+ with:
+ fetch-depth: '0'
+
+ - name: Set up Python 3.9
+ uses: actions/setup-python@v5
+ with:
+ python-version: 3.9
+
+ - name: Install dependencies
+ run: |
+ python -m pip install --upgrade pip
+ pip install "coveralls>=3.0.0"
+
+ - name: Install GSTools-Cython
+ env:
+ GSTOOLS_CY_COV: 1
+ run: |
+ pip install -v --editable .[test]
+
+ - name: Run tests
+ env:
+ GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
+ run: |
+ pip install "numpy${{ matrix.ver.np }}"
+ python -m pytest --cov gstools_cython --cov-report term-missing -v tests/
+ python -m coveralls --service=github
+
upload_to_pypi:
needs: [build_wheels, build_sdist]
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
diff --git a/.gitignore b/.gitignore
index bcdc980be..5334b8efb 100644
--- a/.gitignore
+++ b/.gitignore
@@ -112,7 +112,7 @@ info/
*.cpp
# generated version file
-src/gstools/_version.py
+src/gstools_cython/_version.py
# generated docs
docs/source/examples/
diff --git a/.zenodo.json b/.zenodo.json
index ad72d74be..bb6c631c0 100755
--- a/.zenodo.json
+++ b/.zenodo.json
@@ -1,10 +1,6 @@
{
- "license": "LGPL-3.0+",
+ "license": "LGPL-3.0-or-later",
"contributors": [
- {
- "type": "Other",
- "name": "Bane Sullivan"
- },
{
"orcid": "0000-0002-2547-8102",
"affiliation": "Helmholtz Centre for Environmental Research - UFZ",
diff --git a/CHANGELOG.md b/CHANGELOG.md
index 20fb771b2..b1c868b82 100755
--- a/CHANGELOG.md
+++ b/CHANGELOG.md
@@ -1,462 +1,14 @@
# Changelog
-All notable changes to **GSTools** will be documented in this file.
+All notable changes to **GSTools-Cython** will be documented in this file.
-## [1.5.2] - Nifty Neon - 2024-05
+## [1.0.0] - 2024-07
-### Enhancements
-
-- added global variable `config.NUM_THREADS` to select number of threads for parallel computation ([#336](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/336))
-- speed up sampling with emcee by setting `vectorize=True` in `EnsembleSampler` ([#346](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/346))
-- prepare numpy 2 support ([#340](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/340))
- - at least numpy 2.0.0rc1 for building extensions (for Python 3.9 and above)
- - check multiple numpy and scipy versions in CI
- - fixed minimal versions for numpy
- - use `np.asarray` everywhere with `np.atleast_(n)d`
- - fix long/longlong integer issue in cython on windows by always using 64bit integers
-
-### Bugfixes
-- build docs with latest sphinx version ([#340](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/340))
-- fixed zero division error in spectral density of Integral model ([#347](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/347))
-- minor pylint fixes for used-before-assignment issues ([#350](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/350))
-
-### Changes
-- require pyvista 0.40 at least ([#340](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/340))
-- require matplotlib 3.7 at least ([#350](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/350))
-- remove universal2 wheels for macos (we already provide separate intel and arm64 wheels) ([#350](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/350))
-
-
-## [1.5.1] - Nifty Neon - 2023-11
-
-### Enhancements
-
-see [#317](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/317)
-
-- added wheels for Python 3.12
-- dropped support for Python 3.7 (EOL)
-- linted Cython files with cython-lint
-- use Cython 3 to build extensions
-
-
-## [1.5.0] - Nifty Neon - 2023-06
-
-### Enhancements
-- added `temporal` flag to `CovModel` to explicitly specify spatio-temporal models [#308](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/308)
- - rotation between spatial and temporal dimension will be ignored
- - added `spatial_dim` to `CovModel` to explicitly set spatial dimension for spatio-temporal models
- - if not using `spatial_dim`, the provided `dim` needs to include the possible temporal dimension
- - `spatial_dim` is always one less than `field_dim` for spatio-temporal models
- - also works with `latlon=True` to have a spatio-temporal model with geographic coordinates
- - all plotting routines respect this
- - the `Field` class now has a `temporal` attribute which forwards the model attribute
- - automatic variogram fitting in kriging classes for `temporal=True` and `latlon=True` will raise an error
-- added `geo_scale` to `CovModel` to have a more consistent way to set the units of the model length scale for geographic coordinates [#308](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/308)
- - no need to use `rescale` for this anymore (was rather a hack)
- - added `gs.KM_SCALE` which is the same as `gs.EARTH_RADIUS` for kilometer scaling
- - added `gs.DEGREE_SCALE` for great circle distance in degrees
- - added `gs.RADIAN_SCALE` for great circle distance in radians (default and previous behavior)
- - yadrenko variogram respects this and assumes the great circle distances is given in the respective unit
- - `vario_estimate` also has `geo_scale` now to control the units of the bins
-- `vario_estimate` now forwards additional kwargs to `standard_bins` (`bin_no`, `max_dist`) [#308](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/308)
-- added `low` and `high` arguments to `uniform` transformation [#310](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/310)
-
-### Changes
-- `CovModel`s expect special arguments by keyword now [#308](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/308)
-- always use f-strings internally [#283](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/283)
-- removed `verbose` attribute from `RandMeth` classes [#309](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/309)
-- all arguments for `RandMeth` classes key-word-only now except `model` [#309](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/309)
-- rename "package" to "api" in doc structure [#290](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/290)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- latex equations were not rendered correctly in docs [#290](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/290)
-
-
-## [1.4.1] - Sassy Sapphire - 2022-11
-
-### Enhancements
-- new (Exponential-) Integral model added [#243](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/243)
-- added wheels for Python 3.11 [#272](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/272)
-
-### Changes
-- API documentation is polished and fully auto-generated now [#271](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/271)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- fixed approximation of `Matern.spectrum` for big `nu` [#243](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/243)
-- GSTools had wrong version when installed from git archive [#272](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/272)
-- Field.plot: solve long-standing mpl slider bug [#273](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/273)
-
-
-## [1.4.0] - Sassy Sapphire - 2022-08
-
-### Enhancements
-- added Youtube tutorial to documentation [#239](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/239)
-- better support for custom generators [#250](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/250) [#259](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/259)
-- add `valid_value_types` class variable to all field classes [#250](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/250)
-- PyKrige: fix passed variogram in case of latlon models [#254](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/254)
-- add bounds checks for optional arguments of `CovModel` when resetting by class attribute [#255](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/255)
-- minor coverage improvements [#255](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/255)
-- documentation: readability improvements [#257](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/257)
-
-### Changes
-- drop Python 3.6 support (setuptools>60 needs py>3.7) [#241](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/241)
-- move `setup.cfg` content to `pyproject.toml` ([PEP 621](https://peps.python.org/pep-0621/)) [#241](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/241)
-- move to `src/` based package structure (better testing, building and structure) [#241](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/241)
-- use [extension-helpers](https://pypi.org/project/extension-helpers/) for openmp support in `setup.py` [#241](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/241)
-- increase minimal version of meshio to v5.1 [#241](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/241)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- Pyvista v0.32 deprecation warning: use point_data instead of point_arrays [#237](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/237)
-- remove deprecated scipy (v1.9) method pinv2 [#247](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/247)
-- change float comparison in tests [#248](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/248)
-- Cython: solve `-Wsometimes-uninitialized` warning [#255](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/255)
-
-
-## [1.3.5] - Pure Pink - 2022-01
-
-### Changes
-- remove caps for dependencies [#229](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/229)
-- build linux wheels with manylinux2014 for all versions ([CIBW v2.3.1](https://github.com/pypa/cibuildwheel/releases/tag/v2.3.1)) [#227](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/227)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- `Field.mesh` was not compatible with [meshio](https://github.com/nschloe/meshio) v5.1+ [#227](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/227)
-
-
-## [1.3.4] - Pure Pink - 2021-11
-
-### Enhancements
-- add GStools-Core as optional dependency [#215](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/215)
-- provide wheels for Python 3.10 [#211](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/211)
-- provide macOS wheels for Apple Silicon [#211](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/211)
-
-### Changes
-- remove unnecessary `dim` argument in Cython code [#216](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/216)
-
-
-## [1.3.3] - Pure Pink - 2021-08
-
-### Enhancements
-See: [#197](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/197)
-- `gstools.transform`:
- - add keywords `field`, `store`, `process` and `keep_mean` to all transformations to control storage and respect `normalizer`
- - added `apply_function` transformation
- - added `apply` as wrapper for all transformations
- - added `transform` method to all `Field` (sub)classes as interface to `transform.apply`
- - added checks for normal fields to work smoothly with recently added `normalizer` submodule
-- `Field`:
- - allow naming fields when generating and control storage with `store` keyword
- - all subclasses now have the `post_process` keyword (apply mean, normalizer, trend)
- - added subscription to access fields by name (`Field["field"]`)
- - added `set_pos` method to set position tuple
- - allow reusing present `pos` tuple
- - added `pos`, `mesh_type`, `field_names`, `field_shape`, `all_fields` properties
-- `CondSRF`:
- - memory optimization by forwarding `pos` from underlying `krige` instance
- - only recalculate kriging field if `pos` tuple changed (optimized ensemble generation)
-- performance improvement by using `np.asarray` instead of `np.array` where possible
-- updated examples to use new features
-- added incomplete lower gamma function `inc_gamma_low` (for TPLGaussian spectral density)
-- filter `nan` values from `cond_val` array in all kriging routines [#201](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/201)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- `inc_gamma` was defined wrong for integer `s < 0`
-
-
-## [1.3.2] - Pure Pink - 2021-07
-
-### Bugfixes
-- `vario_estimate` was altering the input field under certain circumstances [#180](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/180)
-- `emcee` v3.1 now requires `nsteps` in `run_mcmc()` to be integer (called in `RNG.sample_ln_pdf`) [#184](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/184)
-
-
-## [1.3.1] - Pure Pink - 2021-06
-
-### Enhancements
-- Standalone use of Field class [#166](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/166)
-- add social badges in README [#169](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/169), [#170](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/170)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- use `oldest-supported-numpy` to build cython extensions [#165](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/165)
-
-
-## [1.3.0] - Pure Pink - 2021-04
-
-### Topics
-
-#### Geographical Coordinates Support ([#113](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/113))
-- added boolean init parameter `latlon` to indicate a geographic model. When given, spatial dimension is fixed to `dim=3`, `anis` and `angles` will be ignored, since anisotropy is not well-defined on a sphere.
-- add property `field_dim` to indicate the dimension of the resulting field. Will be 2 if `latlon=True`
-- added yadrenko variogram, covariance and correlation method, since the geographic models are derived from standard models in 3D by plugging in the chordal distance of two points on a sphere derived from there great-circle distance `zeta`:
- - `vario_yadrenko`: given by `variogram(2 * np.sin(zeta / 2))`
- - `cov_yadrenko`: given by `covariance(2 * np.sin(zeta / 2))`
- - `cor_yadrenko`: given by `correlation(2 * np.sin(zeta / 2))`
-- added plotting routines for yadrenko methods described above
-- the `isometrize` and `anisometrize` methods will convert `latlon` tuples (given in degree) to points on the unit-sphere in 3D and vice versa
-- representation of geographical models don't display the `dim`, `anis` and `angles` parameters, but `latlon=True`
-- `fit_variogram` will expect an estimated variogram with great-circle distances given in radians
-- **Variogram estimation**
- - `latlon` switch implemented in `estimate_vario` routine
- - will return a variogram estimated by the great-circle distance (haversine formula) given in radians
-- **Field**
- - added plotting routines for latlon fields
- - no vector fields possible on latlon fields
- - corretly handle pos tuple for latlon fields
-
-#### Krige Unification ([#97](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/97))
-- Swiss Army Knife for kriging: The `Krige` class now provides everything in one place
-- "Kriging the mean" is now possible with the switch `only_mean` in the call routine
-- `Simple`/`Ordinary`/`Universal`/`ExtDrift`/`Detrended` are only shortcuts to `Krige` with limited input parameter list
-- We now use the `covariance` function to build up the kriging matrix (instead of variogram)
-- An `unbiased` switch was added to enable simple kriging (where the unbiased condition is not given)
-- An `exact` switch was added to allow smother results, if a `nugget` is present in the model
-- An `cond_err` parameter was added, where measurement error variances can be given for each conditional point
-- pseudo-inverse matrix is now used to solve the kriging system (can be disabled by the new switch `pseudo_inv`), this is equal to solving the system with least-squares and prevents numerical errors
-- added options `fit_normalizer` and `fit_variogram` to automatically fit normalizer and variogram to given data
-
-#### Directional Variograms and Auto-binning ([#87](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/87), [#106](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/106), [#131](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/131))
-- new routine name `vario_estimate` instead of `vario_estimate_unstructured` (old kept for legacy code) for simplicity
-- new routine name `vario_estimate_axis` instead of `vario_estimate_structured` (old kept for legacy code) for simplicity
-- **vario_estimate**
- - added simple automatic binning routine to determine bins from given data (one third of box diameter as max bin distance, sturges rule for number of bins)
- - allow to pass multiple fields for joint variogram estimation (e.g. for daily precipitation) on same mesh
- - `no_data` option added to allow missing values
- - **masked fields**
- - user can now pass a masked array (or a list of masked arrays) to deselect data points.
- - in addition, a `mask` keyword was added to provide an external mask
- - **directional variograms**
- - diretional variograms can now be estimated
- - either provide a list of direction vectors or angles for directions (spherical coordinates)
- - can be controlled by given angle tolerance and (optional) bandwidth
- - prepared for nD
- - structured fields (pos tuple describes axes) can now be passed to estimate an isotropic or directional variogram
- - distance calculation in cython routines in now independent of dimension
-- **vario_estimate_axis**
- - estimation along array axis now possible in arbitrary dimensions
- - `no_data` option added to allow missing values (sovles [#83](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/83))
- - axis can be given by name (`"x"`, `"y"`, `"z"`) or axis number (`0`, `1`, `2`, `3`, ...)
-
-#### Better Variogram fitting ([#78](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/78), [#145](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/145))
-- fixing sill possible now
-- `loss` is now selectable for smoother handling of outliers
-- r2 score can now be returned to get an impression of the goodness of fitting
-- weights can be passed
-- instead of deselecting parameters, one can also give fix values for each parameter
-- default init guess for `len_scale` is now mean of given bin-centers
-- default init guess for `var` and `nugget` is now mean of given variogram values
-
-#### CovModel update ([#109](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/109), [#122](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/122), [#157](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/157))
-- add new `rescale` argument and attribute to the `CovModel` class to be able to rescale the `len_scale` (usefull for unit conversion or rescaling `len_scale` to coincide with the `integral_scale` like it's the case with the Gaussian model)
- See: [#90](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/90), [GeoStat-Framework/PyKrige#119](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/PyKrige/issues/119)
-- added new `len_rescaled` attribute to the `CovModel` class, which is the rescaled `len_scale`: `len_rescaled = len_scale / rescale`
-- new method `default_rescale` to provide default rescale factor (can be overridden)
-- remove `doctest` calls
-- docstring updates in `CovModel` and derived models
-- updated all models to use the `cor` routine and make use of the `rescale` argument (See: [#90](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/90))
-- TPL models got a separate base class to not repeat code
-- added **new models** (See: [#88](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/88)):
- - `HyperSpherical`: (Replaces the old `Intersection` model) Derived from the intersection of hyper-spheres in arbitrary dimensions. Coincides with the linear model in 1D, the circular model in 2D and the classical spherical model in 3D
- - `SuperSpherical`: like the HyperSpherical, but the shape parameter derived from dimension can be set by the user. Coincides with the HyperSpherical model by default
- - `JBessel`: a hole model valid in all dimensions. The shape parameter controls the dimension it was derived from. For `nu=0.5` this model coincides with the well known `wave` hole model.
- - `TPLSimple`: a simple truncated power law controlled by a shape parameter `nu`. Coincides with the truncated linear model for `nu=1`
- - `Cubic`: to be compatible with scikit-gstat in the future
-- all arguments are now stored as float internally ([#157](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/157))
-- string representation of the `CovModel` class is now using a float precision (`CovModel._prec=3`) to truncate longish output
-- string representation of the `CovModel` class now only shows `anis` and `angles` if model is anisotropic resp. rotated
-- dimension validity check: raise a warning, if given model is not valid in the desired dimension (See: [#86](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/86))
-
-#### Normalizer, Trend and Mean ([#124](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/124))
-
-- new `normalize` submodule containing power-transforms for data to gain normality
-- Base-Class: `Normalizer` providing basic functionality including maximum likelihood fitting
-- added: `LogNormal`, `BoxCox`, `BoxCoxShift`, `YeoJohnson`, `Modulus` and `Manly`
-- normalizer, trend and mean can be passed to SRF, Krige and variogram estimation routines
- - A trend can be a callable function, that represents a trend in input data. For example a linear decrease of temperature with height.
- - The normalizer will be applied after the data was detrended, i.e. the trend was substracted from the data, in order to gain normality.
- - The mean is now interpreted as the mean of the normalized data. The user could also provide a callable mean, but it is mostly meant to be constant.
-
-#### Arbitrary dimensions ([#112](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/112))
-- allow arbitrary dimensions in all routines (CovModel, Krige, SRF, variogram)
-- anisotropy and rotation following a generalization of tait-bryan angles
-- `CovModel` provides `isometrize` and `anisometrize` routines to convert points
-
-#### New Class for Conditioned Random Fields ([#130](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/130))
-- **THIS BREAKS BACKWARD COMPATIBILITY**
-- `CondSRF` replaces the conditioning feature of the SRF class, which was cumbersome and limited to Ordinary and Simple kriging
-- `CondSRF` behaves similar to the `SRF` class, but instead of a covariance model, it takes a kriging class as input. With this kriging class, all conditioning related settings are defined.
-
-### Enhancements
-- Python 3.9 Support [#107](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/107)
-- add routines to format struct. pos tuple by given `dim` or `shape`
-- add routine to format struct. pos tuple by given `shape` (variogram helper)
-- remove `field.tools` subpackage
-- support `meshio>=4.0` and add as dependency
-- PyVista mesh support [#59](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/59)
-- added `EARTH_RADIUS` as constant providing earths radius in km (can be used to rescale models)
-- add routines `latlon2pos` and `pos2latlon` to convert lat-lon coordinates to points on unit-sphere and vice versa
-- a lot of new examples and tutorials
-- `RandMeth` class got a switch to select the sampling strategy
-- plotter for n-D fields added [#141](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/141)
-- antialias for contour plots of 2D fields [#141](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/141)
-- building from source is now configured with `pyproject.toml` to care about build dependencies, see [#154](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/154)
+First release of GSTools-Cython
### Changes
-- drop support for Python 3.5 [#146](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/146)
-- added a finit limit for shape-parameters in some `CovModel`s [#147](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/147)
-- drop usage of `pos2xyz` and `xyz2pos`
-- remove structured option from generators (structured pos need to be converted first)
-- explicitly assert dim=2,3 when generating vector fields
-- simplify `pre_pos` routine to save pos tuple and reformat it an unstructured tuple
-- simplify field shaping
-- simplify plotting routines
-- only the `"unstructured"` keyword is recognized everywhere, everything else is interpreted as `"structured"` (e.g. `"rectilinear"`)
-- use GitHub-Actions instead of TravisCI
-- parallel build now controlled by env-var `GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL=1`, see [#154](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/154)
-- install extra target for `[dev]` dropped, can be reproduced by `pip install gstools[test, doc]`, see [#154](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/154)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- typo in keyword argument for vario_estimate_structured [#80](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/80)
-- isotropic rotation of SRF was not possible [#100](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/100)
-- `CovModel.opt_arg` now sorted [#103](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/103)
-- `CovModel.fit`: check if weights are given as a string (numpy comparison error) [#111](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/111)
-- several pylint fixes ([#159](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/pull/159))
-
-
-## [1.2.1] - Volatile Violet - 2020-04-14
-
-### Bugfixes
-- `ModuleNotFoundError` is not present in py35
-- Fixing Cressie-Bug #76
-- Adding analytical formula for integral scales of rational and stable model
-- remove prange from IncomprRandMeth summators to prevent errors on Win and macOS
-
-
-## [1.2.0] - Volatile Violet - 2020-03-20
-
-### Enhancements
-- different variogram estimator functions can now be used #51
-- the TPLGaussian and TPLExponential now have analytical spectra #67
-- added property `is_isotropic` to `CovModel` #67
-- reworked the whole krige sub-module to provide multiple kriging methods #67
- - Simple
- - Ordinary
- - Universal
- - External Drift Kriging
- - Detrended Kriging
-- a new transformation function for discrete fields has been added #70
-- reworked tutorial section in the documentation #63
-- pyvista interface #29
-
-### Changes
-- Python versions 2.7 and 3.4 are no longer supported #40 #43
-- `CovModel`: in 3D the input of anisotropy is now treated slightly different: #67
- - single given anisotropy value [e] is converted to [1, e] (it was [e, e] before)
- - two given length-scales [l_1, l_2] are converted to [l_1, l_2, l_2] (it was [l_1, l_2, l_1] before)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- a race condition in the structured variogram estimation has been fixed #51
-
-
-## [1.1.1] - Reverberating Red - 2019-11-08
-
-### Enhancements
-- added a changelog. See: [commit fbea883](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/fbea88300d0862393e52f4b7c3d2b15c2039498b)
-
-### Changes
-- deprecation warnings are now printed if Python versions 2.7 or 3.4 are used #40 #41
-
-### Bugfixes
-- define spectral_density instead of spectrum in covariance models since Cov-base derives spectrum. See: [commit 00f2747](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/00f2747fd0503ff8806f2eebfba36acff813416b)
-- better boundaries for `CovModel` parameters. See: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues/37
-
-
-## [1.1.0] - Reverberating Red - 2019-10-01
-
-### Enhancements
-- by using Cython for all the heavy computations, we could achieve quite some speed ups and reduce the memory consumption significantly #16
-- parallel computation in Cython is now supported with the help of OpenMP and the performance increase is nearly linear with increasing cores #16
-- new submodule `krige` providing simple (known mean) and ordinary (estimated mean) kriging working analogous to the srf class
-- interface to pykrige to use the gstools `CovModel` with the pykrige routines (https://github.com/bsmurphy/PyKrige/issues/124)
-- the srf class now provides a `plot` and a `vtk_export` routine
-- incompressible flow fields can now be generated #14
-- new submodule providing several field transformations like: Zinn&Harvey, log-normal, bimodal, ... #13
-- Python 3.4 and 3.7 wheel support #19
-- field can now be generated directly on meshes from [meshio](https://github.com/nschloe/meshio) and [ogs5py](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/ogs5py), see: [commit f4a3439](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/f4a3439400b81d8d9db81a5f7fbf6435f603cf05)
-- the srf and kriging classes now store the last `pos`, `mesh_type` and `field` values to keep them accessible, see: [commit 29f7f1b](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/29f7f1b029866379ce881f44765f72534d757fae)
-- tutorials on all important features of GSTools have been written for you guys #20
-- a new interface to pyvista is provided to export fields to python vtk representation, which can be used for plotting, exploring and exporting fields #29
-
-### Changes
-- the license was changed from GPL to LGPL in order to promote the use of this library #25
-- the rotation angles are now interpreted in positive direction (counter clock wise)
-- the `force_moments` keyword was removed from the SRF call method, it is now in provided as a field transformation #13
-- drop support of python implementations of the variogram estimators #18
-- the `variogram_normed` method was removed from the `CovModel` class due to redundance [commit 25b1647](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/25b164722ac6744ebc7e03f3c0bf1c30be1eba89)
-- the position vector of 1D fields does not have to be provided in a list-like object with length 1 [commit a6f5be8](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/commit/a6f5be8bfd2db1f002e7889ecb8e9a037ea08886)
-
-### Bugfixes
-- several minor bugfixes
-
-
-## [1.0.1] - Bouncy Blue - 2019-01-18
-
-### Bugfixes
-- fixed Numpy and Cython version during build process
-
-
-## [1.0.0] - Bouncy Blue - 2019-01-16
-
-### Enhancements
-- added a new covariance class, which allows the easy usage of arbitrary covariance models
-- added many predefined covariance models, including truncated power law models
-- added [tutorials](https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/latest/tutorials.html) and examples, showing and explaining the main features of GSTools
-- variogram models can be fitted to data
-- prebuilt binaries for many Linux distributions, Mac OS and Windows, making the installation, especially of the Cython code, much easier
-- the generated fields can now easily be exported to vtk files
-- variance scaling is supported for coarser grids
-- added pure Python versions of the variogram estimators, in case somebody has problems compiling Cython code
-- the [documentation](https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/latest/) is now a lot cleaner and easier to use
-- the code is a lot cleaner and more consistent now
-- unit tests are now automatically tested when new code is pushed
-- test coverage of code is shown
-- GeoStat Framework now has a website, visit us: https://geostat-framework.github.io/
-
-### Changes
-- release is not downwards compatible with release v0.4.0
-- SRF creation has been adapted for the `CovModel`
-- a tuple `pos` is now used instead of `x`, `y`, and `z` for the axes
-- renamed `estimate_unstructured` and `estimate_structured` to `vario_estimate_unstructured` and `vario_estimate_structured` for less ambiguity
-
-### Bugfixes
-- several minor bugfixes
-
-
-## [0.4.0] - Glorious Green - 2018-07-17
-
-### Bugfixes
-- import of cython functions put into a try-block
-
-
-## [0.3.6] - Original Orange - 2018-07-17
-
-First release of GSTools.
+- moved Cython files into this separate package
-[Unreleased]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.5.2...HEAD
-[1.5.2]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.5.1...v1.5.2
-[1.5.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.5.0...v1.5.1
-[1.5.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.4.1...v1.5.0
-[1.4.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.4.0...v1.4.1
-[1.4.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.5...v1.4.0
-[1.3.5]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.4...v1.3.5
-[1.3.4]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.3...v1.3.4
-[1.3.3]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.2...v1.3.3
-[1.3.2]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.1...v1.3.2
-[1.3.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.3.0...v1.3.1
-[1.3.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.2.1...v1.3.0
-[1.2.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.2.0...v1.2.1
-[1.2.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.1.1...v1.2.0
-[1.1.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.1.0...v1.1.1
-[1.1.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.0.1...v1.1.0
-[1.0.1]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/v1.0.0...v1.0.1
-[1.0.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/0.4.0...v1.0.0
-[0.4.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/compare/0.3.6...0.4.0
-[0.3.6]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools/releases/tag/0.3.6
+[Unreleased]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools-cython/compare/v1.0.0...HEAD
+[1.0.0]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/gstools-cython/releases/tag/v1.0.0
diff --git a/MANIFEST.in b/MANIFEST.in
index 24184482a..5778d3fa3 100644
--- a/MANIFEST.in
+++ b/MANIFEST.in
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
prune **
recursive-include tests *.py
-recursive-include src/gstools *.py *.pyx
+recursive-include src/gstools_cython *.py *.pyx
include AUTHORS.md LICENSE README.md pyproject.toml setup.py
diff --git a/README.md b/README.md
index 6cb699019..fcc9ed143 100644
--- a/README.md
+++ b/README.md
@@ -1,11 +1,8 @@
-# Welcome to GSTools
+# Welcome to GSTools-Cython
[](https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-3161-2022)
-[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628)
-[](https://badge.fury.io/py/gstools)
-[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/gstools)
-[](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/actions)
-[](https://coveralls.io/github/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools?branch=main)
-[](https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/?badge=stable)
+[](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython/actions)
+[](https://coveralls.io/github/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython?branch=main)
+[](https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools-cython/en/stable/?badge=stable)
[](https://github.com/ambv/black)
@@ -15,36 +12,10 @@
Get in Touch!
 -
- -
-


-Youtube Tutorial on GSTools
-
-
-
- -
-
-
-
-
-## Purpose
-
- -
-GeoStatTools provides geostatistical tools for various purposes:
-- random field generation
-- simple, ordinary, universal and external drift kriging
-- conditioned field generation
-- incompressible random vector field generation
-- (automated) variogram estimation and fitting
-- directional variogram estimation and modelling
-- data normalization and transformation
-- many readily provided and even user-defined covariance models
-- metric spatio-temporal modelling
-- plotting and exporting routines
-
## Installation
@@ -88,275 +59,19 @@ You can cite the Zenodo code publication of GSTools by:
If you want to cite a specific version, have a look at the [Zenodo site](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628).
-## Documentation for GSTools
-
-You can find the documentation under [geostat-framework.readthedocs.io][doc_link].
-
-
-### Tutorials and Examples
-
-The documentation also includes some [tutorials][tut_link], showing the most important use cases of GSTools, which are
-
-- [Random Field Generation][tut1_link]
-- [The Covariance Model][tut2_link]
-- [Variogram Estimation][tut3_link]
-- [Random Vector Field Generation][tut4_link]
-- [Kriging][tut5_link]
-- [Conditioned random field generation][tut6_link]
-- [Field transformations][tut7_link]
-- [Geographic Coordinates][tut8_link]
-- [Spatio-Temporal Modelling][tut9_link]
-- [Normalizing Data][tut10_link]
-- [Miscellaneous examples][tut0_link]
-
-The associated python scripts are provided in the `examples` folder.
-
-
-## Spatial Random Field Generation
-
-The core of this library is the generation of spatial random fields. These fields are generated using the randomisation method, described by [Heße et al. 2014][rand_link].
-
-[rand_link]: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.01.013
-
-
-### Examples
-
-#### Gaussian Covariance Model
-
-This is an example of how to generate a 2 dimensional spatial random field with a gaussian covariance model.
+## Documentation
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-# structured field with a size 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.plot()
-```
-
-
-GeoStatTools provides geostatistical tools for various purposes:
-- random field generation
-- simple, ordinary, universal and external drift kriging
-- conditioned field generation
-- incompressible random vector field generation
-- (automated) variogram estimation and fitting
-- directional variogram estimation and modelling
-- data normalization and transformation
-- many readily provided and even user-defined covariance models
-- metric spatio-temporal modelling
-- plotting and exporting routines
-
## Installation
@@ -88,275 +59,19 @@ You can cite the Zenodo code publication of GSTools by:
If you want to cite a specific version, have a look at the [Zenodo site](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628).
-## Documentation for GSTools
-
-You can find the documentation under [geostat-framework.readthedocs.io][doc_link].
-
-
-### Tutorials and Examples
-
-The documentation also includes some [tutorials][tut_link], showing the most important use cases of GSTools, which are
-
-- [Random Field Generation][tut1_link]
-- [The Covariance Model][tut2_link]
-- [Variogram Estimation][tut3_link]
-- [Random Vector Field Generation][tut4_link]
-- [Kriging][tut5_link]
-- [Conditioned random field generation][tut6_link]
-- [Field transformations][tut7_link]
-- [Geographic Coordinates][tut8_link]
-- [Spatio-Temporal Modelling][tut9_link]
-- [Normalizing Data][tut10_link]
-- [Miscellaneous examples][tut0_link]
-
-The associated python scripts are provided in the `examples` folder.
-
-
-## Spatial Random Field Generation
-
-The core of this library is the generation of spatial random fields. These fields are generated using the randomisation method, described by [Heße et al. 2014][rand_link].
-
-[rand_link]: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.01.013
-
-
-### Examples
-
-#### Gaussian Covariance Model
-
-This is an example of how to generate a 2 dimensional spatial random field with a gaussian covariance model.
+## Documentation
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-# structured field with a size 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.plot()
-```
-
- -
-
-
-GSTools also provides support for [geographic coordinates](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geographic_coordinate_system).
-This works perfectly well with [cartopy](https://scitools.org.uk/cartopy/docs/latest/index.html).
-
-```python
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import cartopy.crs as ccrs
-import gstools as gs
-# define a structured field by latitude and longitude
-lat = lon = range(-80, 81)
-model = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, len_scale=777, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=12345)
-field = srf.structured((lat, lon))
-# Orthographic plotting with cartopy
-ax = plt.subplot(projection=ccrs.Orthographic(-45, 45))
-cont = ax.contourf(lon, lat, field, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
-ax.coastlines()
-ax.set_global()
-plt.colorbar(cont)
-```
-
-
- -
-
+- GSTools: https://https://gstools.readthedocs.io/
+- GSTools-Cython: https://https://gstools-cython.readthedocs.io/
-A similar example but for a three dimensional field is exported to a [VTK](https://vtk.org/) file, which can be visualized with [ParaView](https://www.paraview.org/) or [PyVista](https://docs.pyvista.org) in Python:
-
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-# structured field with a size 100x100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1x1
-x = y = z = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, len_scale=[16, 8, 4], angles=(0.8, 0.4, 0.2))
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y, z), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.vtk_export('3d_field') # Save to a VTK file for ParaView
-
-mesh = srf.to_pyvista() # Create a PyVista mesh for plotting in Python
-mesh.contour(isosurfaces=8).plot()
-```
-
-
- -
-
+## Cython backend
+This package is the cython backend implementation for GSTools.
-## Estimating and Fitting Variograms
-
-The spatial structure of a field can be analyzed with the variogram, which contains the same information as the covariance function.
-
-All covariance models can be used to fit given variogram data by a simple interface.
-
-### Example
-
-This is an example of how to estimate the variogram of a 2 dimensional unstructured field and estimate the parameters of the covariance
-model again.
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-import gstools as gs
-# generate a synthetic field with an exponential model
-x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.
-y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0, seed=19970221)
-field = srf((x, y))
-# estimate the variogram of the field
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field)
-# fit the variogram with a stable model. (no nugget fitted)
-fit_model = gs.Stable(dim=2)
-fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, nugget=False)
-# output
-ax = fit_model.plot(x_max=max(bin_center))
-ax.scatter(bin_center, gamma)
-print(fit_model)
-```
-
-Which gives:
-
-```python
-Stable(dim=2, var=1.85, len_scale=7.42, nugget=0.0, anis=[1.0], angles=[0.0], alpha=1.09)
-```
-
-
- -
-
-
-## Kriging and Conditioned Random Fields
-
-An important part of geostatistics is Kriging and conditioning spatial random
-fields to measurements. With conditioned random fields, an ensemble of field realizations with their variability depending on the proximity of the measurements can be generated.
-
-### Example
-For better visualization, we will condition a 1d field to a few "measurements", generate 100 realizations and plot them:
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import gstools as gs
-
-# conditions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-
-# conditioned spatial random field class
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos, cond_val)
-cond_srf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
-# same output positions for all ensemble members
-grid_pos = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-cond_srf.set_pos(grid_pos)
-
-# seeded ensemble generation
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(20170519)
-for i in range(100):
- field = cond_srf(seed=seed(), store=f"field_{i}")
- plt.plot(grid_pos, field, color="k", alpha=0.1)
-plt.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k")
-plt.show()
-```
-
-
- -
-
-
-## User Defined Covariance Models
-
-One of the core-features of GSTools is the powerful
-[CovModel][cov_link]
-class, which allows to easy define covariance models by the user.
-
-### Example
-
-Here we re-implement the Gaussian covariance model by defining just a
-[correlation][cor_link] function, which takes a non-dimensional distance ``h = r/l``:
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-import gstools as gs
-# use CovModel as the base-class
-class Gau(gs.CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-h**2)
-```
-
-And that's it! With ``Gau`` you now have a fully working covariance model,
-which you could use for field generation or variogram fitting as shown above.
-
-Have a look at the [documentation ][doc_link] for further information on incorporating
-optional parameters and optimizations.
-
-
-## Incompressible Vector Field Generation
-
-Using the original [Kraichnan method][kraichnan_link], incompressible random
-spatial vector fields can be generated.
-
-
-### Example
-
-```python
-import numpy as np
-import gstools as gs
-x = np.arange(100)
-y = np.arange(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, generator='VectorField', seed=19841203)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.plot()
-```
-
-yielding
-
-
-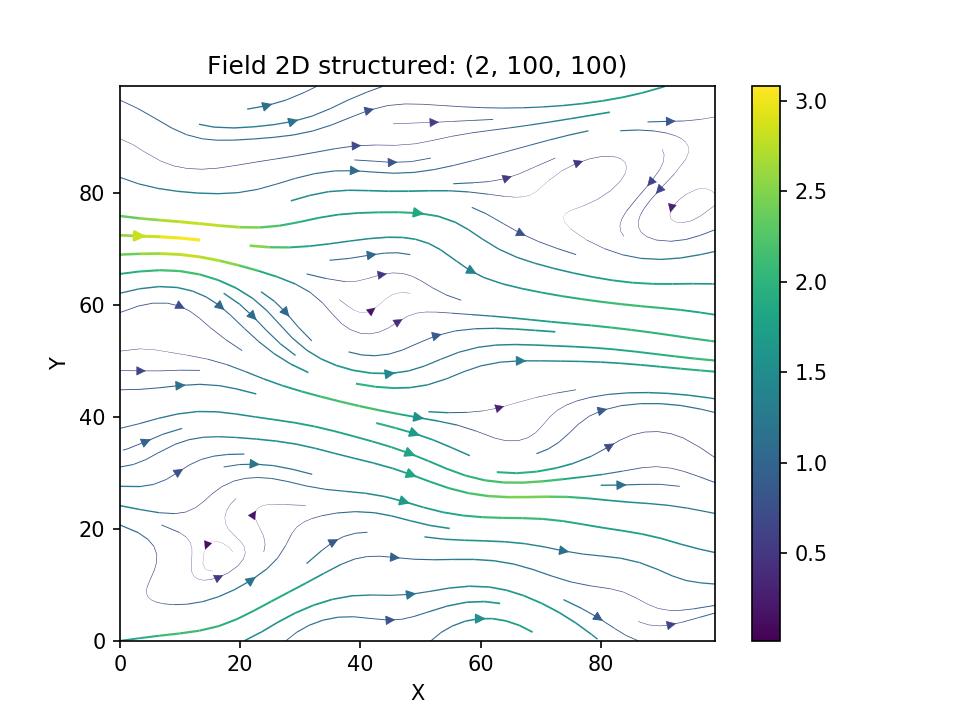 -
-
-
-
-[kraichnan_link]: https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1692799
-
-
-## VTK/PyVista Export
-
-After you have created a field, you may want to save it to file, so we provide
-a handy [VTK][vtk_link] export routine using the `.vtk_export()` or you could
-create a VTK/PyVista dataset for use in Python with to `.to_pyvista()` method:
-
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.vtk_export("field") # Saves to a VTK file
-mesh = srf.to_pyvista() # Create a VTK/PyVista dataset in memory
-mesh.plot()
-```
-
-Which gives a RectilinearGrid VTK file ``field.vtr`` or creates a PyVista mesh
-in memory for immediate 3D plotting in Python.
-
-
-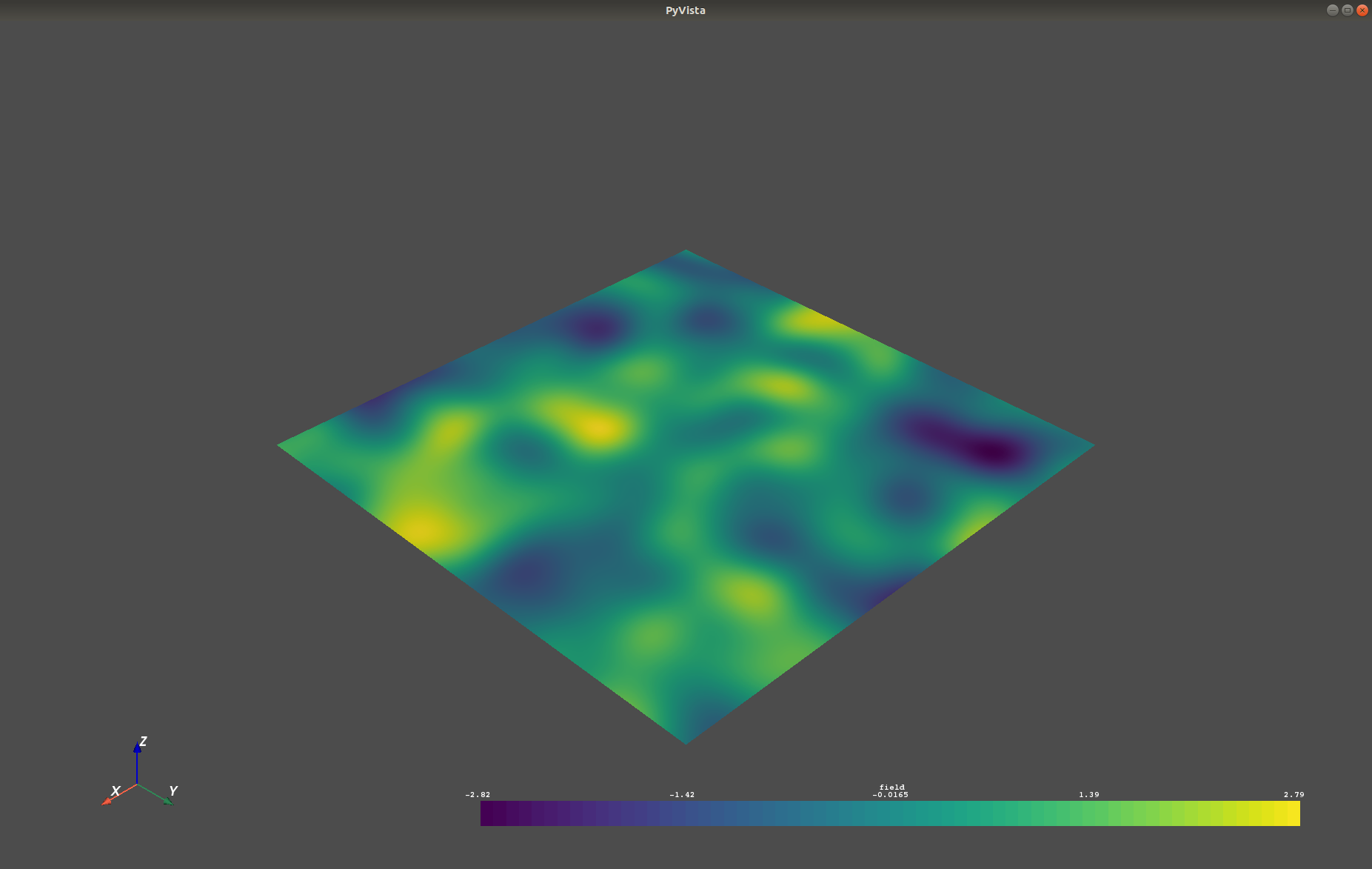 -
-
-
-
-## Requirements:
+## Requirements
- [NumPy >= 1.20.0](https://www.numpy.org)
-- [SciPy >= 1.1.0](https://www.scipy.org/scipylib)
-- [hankel >= 1.0.0](https://github.com/steven-murray/hankel)
-- [emcee >= 3.0.0](https://github.com/dfm/emcee)
-- [pyevtk >= 1.1.1](https://github.com/pyscience-projects/pyevtk)
-- [meshio >= 5.1.0](https://github.com/nschloe/meshio)
-
-### Optional
-
-- [GSTools-Core >= 0.2.0](https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Core)
-- [matplotlib](https://matplotlib.org)
-- [pyvista](https://docs.pyvista.org/)
## Contact
@@ -368,28 +83,4 @@ You can contact us via .
[LGPLv3][license_link] © 2018-2024
-[pip_link]: https://pypi.org/project/gstools
-[conda_link]: https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html
-[conda_forge_link]: https://github.com/conda-forge/gstools-feedstock#installing-gstools
-[conda_pip]: https://docs.conda.io/projects/conda/en/latest/user-guide/tasks/manage-pkgs.html#installing-non-conda-packages
-[pipiflag]: https://pip-python3.readthedocs.io/en/latest/reference/pip_install.html?highlight=i#cmdoption-i
-[winpy_link]: https://winpython.github.io/
-[license_link]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/blob/main/LICENSE
-[cov_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/generated/gstools.covmodel.CovModel.html#gstools.covmodel.CovModel
-[stable_link]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stable_distribution
-[doc_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/
-[doc_install_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/#pip
-[tut_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/tutorials.html
-[tut1_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/01_random_field/index.html
-[tut2_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/02_cov_model/index.html
-[tut3_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/03_variogram/index.html
-[tut4_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/04_vector_field/index.html
-[tut5_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/05_kriging/index.html
-[tut6_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/06_conditioned_fields/index.html
-[tut7_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/07_transformations/index.html
-[tut8_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/08_geo_coordinates/index.html
-[tut9_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/09_spatio_temporal/index.html
-[tut10_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/10_normalizer/index.html
-[tut0_link]: https://geostat-framework.readthedocs.io/projects/gstools/en/stable/examples/00_misc/index.html
-[cor_link]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autocovariance#Normalization
-[vtk_link]: https://www.vtk.org/
+[license_link]: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython/blob/main/LICENSE
diff --git a/docs/source/api.rst b/docs/source/api.rst
index fe12233b0..8364cf371 100644
--- a/docs/source/api.rst
+++ b/docs/source/api.rst
@@ -1,8 +1,8 @@
-===========
-GSTools API
-===========
+==================
+GSTools-Cython API
+==================
-.. automodule:: gstools
+.. automodule:: gstools_cython
.. raw:: latex
diff --git a/docs/source/conf.py b/docs/source/conf.py
index e89928fc9..7d98e0c30 100644
--- a/docs/source/conf.py
+++ b/docs/source/conf.py
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@
# local module should not be added to sys path if it's installed on RTFD
# see: https://stackoverflow.com/a/31882049/6696397
# sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath("../../"))
-from gstools import __version__ as ver
+from gstools_cython import __version__ as ver
def skip(app, what, name, obj, skip, options):
@@ -66,9 +66,7 @@ def setup(app):
"sphinx.ext.autosummary",
"sphinx.ext.napoleon", # parameters look better than with numpydoc only
"numpydoc",
- "sphinx_gallery.gen_gallery",
"m2r2",
- "sphinxcontrib.youtube",
]
# autosummaries from source-files
@@ -109,7 +107,7 @@ def setup(app):
# General information about the project.
curr_year = datetime.datetime.now().year
-project = "GSTools"
+project = "GSTools-Cython"
copyright = f"2018 - {curr_year}, Sebastian Müller, Lennart Schüler"
author = "Sebastian Müller, Lennart Schüler"
@@ -217,8 +215,8 @@ def setup(app):
latex_documents = [
(
master_doc,
- "GeoStatTools.tex",
- "GeoStatTools Documentation",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython.tex",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython Documentation",
"Sebastian Müller, Lennart Schüler",
"manual",
)
@@ -230,7 +228,13 @@ def setup(app):
# One entry per manual page. List of tuples
# (source start file, name, description, authors, manual section).
man_pages = [
- (master_doc, "geostattools", "GeoStatTools Documentation", [author], 1)
+ (
+ master_doc,
+ "geostattools-cython",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython Documentation",
+ [author],
+ 1,
+ )
]
@@ -242,11 +246,11 @@ def setup(app):
texinfo_documents = [
(
master_doc,
- "GeoStatTools",
- "GeoStatTools Documentation",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython Documentation",
author,
- "GeoStatTools",
- "Geo-statistical toolbox.",
+ "GeoStatTools-Cython",
+ "Cython backend for GSTools.",
"Miscellaneous",
)
]
@@ -260,73 +264,4 @@ def setup(app):
intersphinx_mapping = {
"Python": ("https://docs.python.org/", None),
"NumPy": ("https://numpy.org/doc/stable/", None),
- "SciPy": ("https://docs.scipy.org/doc/scipy/", None),
- "matplotlib": ("https://matplotlib.org/stable/", None),
- "hankel": ("https://hankel.readthedocs.io/en/latest/", None),
- "emcee": ("https://emcee.readthedocs.io/en/latest/", None),
-}
-
-# -- Sphinx Gallery Options
-from sphinx_gallery.sorting import FileNameSortKey
-
-# Use pyvista's image scraper for example gallery
-# import pyvista
-# https://github.com/tkoyama010/pyvista-doc-translations/blob/85c835a3ada3a2adefac06ba70e15a101ffa9162/conf.py#L21
-# https://github.com/simpeg/discretize/blob/f414dd7ee7c5ba9a141cb2c37d4b71fdc531eae8/docs/conf.py#L334
-# Make sure off screen is set to true when building locally
-# pyvista.OFF_SCREEN = True
-# # necessary when building the sphinx gallery
-# pyvista.BUILDING_GALLERY = True
-# # Optional - set parameters like theme or window size
-# pyvista.set_plot_theme("document")
-
-sphinx_gallery_conf = {
- # "image_scrapers": ("pyvista", "matplotlib"),
- "remove_config_comments": True,
- # only show "print" output as output
- "capture_repr": (),
- # path to your examples scripts
- "examples_dirs": [
- "../../examples/00_misc/",
- "../../examples/01_random_field/",
- "../../examples/02_cov_model/",
- "../../examples/03_variogram/",
- "../../examples/04_vector_field/",
- "../../examples/05_kriging/",
- "../../examples/06_conditioned_fields/",
- "../../examples/07_transformations/",
- "../../examples/08_geo_coordinates/",
- "../../examples/09_spatio_temporal/",
- "../../examples/10_normalizer/",
- ],
- # path where to save gallery generated examples
- "gallery_dirs": [
- "examples/00_misc/",
- "examples/01_random_field/",
- "examples/02_cov_model/",
- "examples/03_variogram/",
- "examples/04_vector_field/",
- "examples/05_kriging/",
- "examples/06_conditioned_fields/",
- "examples/07_transformations/",
- "examples/08_geo_coordinates/",
- "examples/09_spatio_temporal/",
- "examples/10_normalizer/",
- ],
- # Pattern to search for example files
- "filename_pattern": r"\.py",
- # Remove the "Download all examples" button from the top level gallery
- "download_all_examples": False,
- # Sort gallery example by file name instead of number of lines (default)
- "within_subsection_order": FileNameSortKey,
- # directory where function granular galleries are stored
- "backreferences_dir": None,
- # Modules for which function level galleries are created. In
- "doc_module": "gstools",
- # "first_notebook_cell": (
- # "%matplotlib inline\n"
- # "from pyvista import set_plot_theme\n"
- # "set_plot_theme('document')"
- # ),
- "matplotlib_animations": True,
}
diff --git a/docs/source/contents.rst b/docs/source/contents.rst
index 3224356ee..402d48908 100644
--- a/docs/source/contents.rst
+++ b/docs/source/contents.rst
@@ -7,6 +7,5 @@ Contents
:maxdepth: 3
index
- tutorials
api
changelog
diff --git a/docs/source/index.rst b/docs/source/index.rst
index ecad05830..3bd447c43 100644
--- a/docs/source/index.rst
+++ b/docs/source/index.rst
@@ -1,459 +1 @@
-==================
-GSTools Quickstart
-==================
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/main/docs/source/pics/gstools.png
- :width: 150px
- :align: center
-
-.. only:: html
-
- **Get in Touch!**
-
- |GH-Discussions| |Slack-Swung| |Gitter-GSTools| |Email| |Twitter|
-
- **Youtube Tutorial on GSTools**
-
- .. youtube:: qZBJ-AZXq6Q
- :width: 100%
-
- |
-
-Purpose
-=======
-
-GeoStatTools provides geostatistical tools for various purposes:
-
-- random field generation
-- simple, ordinary, universal and external drift kriging
-- conditioned field generation
-- incompressible random vector field generation
-- (automated) variogram estimation and fitting
-- directional variogram estimation and modelling
-- data normalization and transformation
-- many readily provided and even user-defined covariance models
-- metric spatio-temporal modelling
-- plotting and exporting routines
-
-
-Installation
-============
-
-conda
------
-
-GSTools can be installed via
-`conda `_ on Linux, Mac, and
-Windows.
-Install the package by typing the following command in a command terminal:
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- conda install gstools
-
-In case conda forge is not set up for your system yet, see the easy to follow
-instructions on `conda forge `_.
-Using conda, the parallelized version of GSTools should be installed.
-
-
-pip
----
-
-GSTools can be installed via `pip `_
-on Linux, Mac, and Windows.
-On Windows you can install `WinPython `_ to get
-Python and pip running.
-Install the package by typing the following into command in a command terminal:
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- pip install gstools
-
-To get the latest development version you can install it directly from GitHub:
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- pip install git+git://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools.git@main
-
-If something went wrong during installation, try the :code:`-I` `flag from pip `_.
-
-**Speeding up GSTools by parallelization**
-
-To enable the OpenMP support, you have to provide a C compiler and OpenMP.
-Parallel support is controlled by an environment variable ``GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL``,
-that can be ``0`` or ``1`` (interpreted as ``0`` if not present).
-GSTools then needs to be installed from source:
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- export GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL=1
- pip install --no-binary=gstools gstools
-
-Note, that the ``--no-binary=gstools`` option forces pip to not use a wheel for GSTools.
-
-For the development version, you can do almost the same:
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- export GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL=1
- pip install git+git://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools.git@main
-
-The number of parallel threads can be set with the global variable `config.NUM_THREADS`.
-
-**Using experimental GSTools-Core for even more speed**
-
-You can install the optional dependency `GSTools-Core `_,
-which is a re-implementation of the main algorithms used in GSTools. The new
-package uses the language Rust and it should be faster (in some cases by orders
-of magnitude), safer, and it will potentially completely replace the current
-standard implementation in Cython. Once the package GSTools-Core is available
-on your machine, it will be used by default. In case you want to switch back to
-the Cython implementation, you can set :code:`gstools.config.USE_RUST=False` in
-your code. This also works at runtime. You can install the optional dependency
-e.g. by
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- pip install gstools[rust]
-
-or by manually installing the package
-
-.. code-block:: none
-
- pip install gstools-core
-
-GSTools-Core will automatically use all your cores in parallel, without having
-to use OpenMP or a local C compiler.
-In case you want to restrict the number of threads used, you can use the
-global variable `config.NUM_THREADS` to the desired number.
-
-
-Citation
-========
-
-If you are using GSTools in your publication please cite our paper:
-
- Müller, S., Schüler, L., Zech, A., and Heße, F.: GSTools v1.3: a toolbox for geostatistical modelling in Python, Geosci. Model Dev., 15, 3161–3182, https://doi.org/10.5194/gmd-15-3161-2022, 2022.
-
-You can cite the Zenodo code publication of GSTools by:
-
- Sebastian Müller & Lennart Schüler. GeoStat-Framework/GSTools. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628
-
-If you want to cite a specific version, have a look at the `Zenodo site `__.
-
-
-Tutorials and Examples
-======================
-
-The documentation also includes some `tutorials `__,
-showing the most important use cases of GSTools, which are
-
-- `Random Field Generation `__
-- `The Covariance Model `__
-- `Variogram Estimation `__
-- `Random Vector Field Generation `__
-- `Kriging `__
-- `Conditioned random field generation `__
-- `Field transformations `__
-- `Geographic Coordinates `__
-- `Spatio-Temporal Modelling `__
-- `Normalizing Data `__
-- `Miscellaneous examples `__
-
-
-Spatial Random Field Generation
-===============================
-
-The core of this library is the generation of spatial random fields.
-These fields are generated using the randomisation method, described by
-`Heße et al. 2014 `_.
-
-
-Examples
---------
-
-Gaussian Covariance Model
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-This is an example of how to generate a 2 dimensional spatial random field (:any:`SRF`)
-with a :any:`Gaussian` covariance model.
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- # structured field with a size 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
- x = y = range(100)
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
- srf.plot()
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/main/docs/source/pics/gau_field.png
- :width: 400px
- :align: center
-
-GSTools also provides support for `geographic coordinates `_.
-This works perfectly well with `cartopy `_.
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import cartopy.crs as ccrs
- import gstools as gs
- # define a structured field by latitude and longitude
- lat = lon = range(-80, 81)
- model = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, len_scale=777, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
- srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=12345)
- field = srf.structured((lat, lon))
- # Orthographic plotting with cartopy
- ax = plt.subplot(projection=ccrs.Orthographic(-45, 45))
- cont = ax.contourf(lon, lat, field, transform=ccrs.PlateCarree())
- ax.coastlines()
- ax.set_global()
- plt.colorbar(cont)
-
-.. image:: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/raw/master/img/GS_globe.png
- :width: 400px
- :align: center
-
-A similar example but for a three dimensional field is exported to a
-`VTK `__ file, which can be visualized with
-`ParaView `_ or
-`PyVista `__ in Python:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- # structured field with a size 100x100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1x1
- x = y = z = range(100)
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, len_scale=[16, 8, 4], angles=(0.8, 0.4, 0.2))
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf((x, y, z), mesh_type='structured')
- srf.vtk_export('3d_field') # Save to a VTK file for ParaView
-
- mesh = srf.to_pyvista() # Create a PyVista mesh for plotting in Python
- mesh.contour(isosurfaces=8).plot()
-
-.. image:: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/raw/master/img/GS_pyvista.png
- :width: 400px
- :align: center
-
-
-Estimating and fitting variograms
-=================================
-
-The spatial structure of a field can be analyzed with the variogram, which contains the same information as the covariance function.
-
-All covariance models can be used to fit given variogram data by a simple interface.
-
-
-Examples
---------
-
-This is an example of how to estimate the variogram of a 2 dimensional unstructured field and estimate the parameters of the covariance
-model again.
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import numpy as np
- import gstools as gs
- # generate a synthetic field with an exponential model
- x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.
- y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.
- model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
- srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0, seed=19970221)
- field = srf((x, y))
- # estimate the variogram of the field
- bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field)
- # fit the variogram with a stable model. (no nugget fitted)
- fit_model = gs.Stable(dim=2)
- fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, nugget=False)
- # output
- ax = fit_model.plot(x_max=max(bin_center))
- ax.scatter(bin_center, gamma)
- print(fit_model)
-
-Which gives:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- Stable(dim=2, var=1.85, len_scale=7.42, nugget=0.0, anis=[1.0], angles=[0.0], alpha=1.09)
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/master/img/GS_vario_est.png
- :width: 400px
- :align: center
-
-
-Kriging and Conditioned Random Fields
-=====================================
-
-An important part of geostatistics is Kriging and conditioning spatial random
-fields to measurements. With conditioned random fields, an ensemble of field realizations
-with their variability depending on the proximity of the measurements can be generated.
-
-
-Example
--------
-
-For better visualization, we will condition a 1d field to a few "measurements",
-generate 100 realizations and plot them:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import numpy as np
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- import gstools as gs
-
- # conditions
- cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
- cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-
- # conditioned spatial random field class
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos, cond_val)
- cond_srf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
- # same output positions for all ensemble members
- grid_pos = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
- cond_srf.set_pos(grid_pos)
-
- # seeded ensemble generation
- seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(20170519)
- for i in range(100):
- field = cond_srf(seed=seed(), store=f"field_{i}")
- plt.plot(grid_pos, field, color="k", alpha=0.1)
- plt.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k")
- plt.show()
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/main/docs/source/pics/cond_ens.png
- :width: 600px
- :align: center
-
-
-User defined covariance models
-==============================
-
-One of the core-features of GSTools is the powerful
-:any:`CovModel`
-class, which allows to easy define covariance models by the user.
-
-
-Example
--------
-
-Here we re-implement the Gaussian covariance model by defining just the
-`correlation `_ function,
-which takes a non-dimensional distance :class:`h = r/l`
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import numpy as np
- import gstools as gs
- # use CovModel as the base-class
- class Gau(gs.CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-h**2)
-
-And that's it! With :class:`Gau` you now have a fully working covariance model,
-which you could use for field generation or variogram fitting as shown above.
-
-
-Incompressible Vector Field Generation
-======================================
-
-Using the original `Kraichnan method `_, incompressible random
-spatial vector fields can be generated.
-
-
-Example
--------
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import numpy as np
- import gstools as gs
- x = np.arange(100)
- y = np.arange(100)
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
- srf = gs.SRF(model, generator='VectorField', seed=19841203)
- srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
- srf.plot()
-
-yielding
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/main/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_gau.png
- :width: 600px
- :align: center
-
-
-VTK/PyVista Export
-==================
-
-After you have created a field, you may want to save it to file, so we provide
-a handy `VTK `_ export routine using the :class:`.vtk_export()` or you could
-create a VTK/PyVista dataset for use in Python with to :class:`.to_pyvista()` method:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- x = y = range(100)
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
- srf.vtk_export("field") # Saves to a VTK file
- mesh = srf.to_pyvista() # Create a VTK/PyVista dataset in memory
- mesh.plot()
-
-Which gives a RectilinearGrid VTK file :file:`field.vtr` or creates a PyVista mesh
-in memory for immediate 3D plotting in Python.
-
-.. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/main/docs/source/pics/pyvista_export.png
- :width: 600px
- :align: center
-
-
-Requirements
-============
-
-- `NumPy >= 1.20.0 `_
-- `SciPy >= 1.1.0 `_
-- `hankel >= 1.0.0 `_
-- `emcee >= 3.0.0 `_
-- `pyevtk >= 1.1.1 `_
-- `meshio >= 5.1.0 `_
-
-
-Optional
---------
-
-- `GSTools-Core >= 0.2.0 `_
-- `matplotlib `_
-- `pyvista `_
-
-
-Contact
--------
-
-You can contact us via `info@geostat-framework.org `_.
-
-
-License
-=======
-
-`LGPLv3 `_
-
-
-.. |GH-Discussions| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/GitHub-Discussions-f6f8fa?logo=github&style=flat
- :alt: GH-Discussions
- :target: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/discussions
-.. |Slack-Swung| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/Swung-Slack-4A154B?style=flat&logo=data%3Aimage%2Fpng%3Bbase64%2CiVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABoAAAAaCAYAAACpSkzOAAAABmJLR0QA%2FwD%2FAP%2BgvaeTAAAACXBIWXMAAA7DAAAOwwHHb6hkAAAAB3RJTUUH5AYaFSENGSa5qgAABmZJREFUSMeFlltsVNcVhr%2B1z5m7Zzy%2BxaBwcQrGQOpgCAkKtSBQIqJepKhPBULpQ6sKBVWVKqXtSy%2BR0qYXqa2qRmlDCzjBEZGKUCK1TWqlNiGIEKDQBtf4Fki4OIxnxrex53LOXn2YwbjEtOvlHG3tvX%2Btf%2B21%2Fl%2BYJ1QVEbn1vwLYBWwCVgG1lW0ZoA%2FoAQ6LSP%2BdZ%2BeGzAMiIqK%2Bem0GpxNYVeBj3j2b4NCfM2QnfAAaa11al4fZuCZK24owQJ9v%2BbLryIVbd9wVSNUaEWNVtQPYfXHmAD0T32ZJeBM1Q8d0zzMDUpMwAFgLJU%2BxClURw9NfqedLWxMAHSKyR1WNiNhPAM0B6c%2FbdPORTLuOeUMSNkmMBHgyeo32bwwRDMh8bDM%2BZVl0j6uvPrdYknFnSESWzwUzt%2BkyVlUHx7zh5j%2BmPkXBjosjLkWdominiMQ%2BoiEZxuq8OFRXGXJ5K5%2Fde5nha8VlqjooIlZVBcBUiqeqemjGppd1ptfhSpS8pmmN7GVf4whPNY4Di9m%2BMcR03nK3sBbCQeFbv7gBsExVOyp3l6nz1VtjcM4fTK3Uok5IXtPsrHuPevcBXk8d4dWPX6I%2BsIB9wf1s%2B2Y%2FVbFynUIBIeDeplIECiXl5Iv3kbLogogRgbWukfNumT%2FnlYszBxj3hwXg0cQvqXcfYNu5tVyYPE%2B1G8dXn%2BfW72fH49U8sSlOPGr4SccoF4cKs3WzFrY%2BFCMUNmz%2Ba0aeWR1l15JwJ7DaVPpk1YnJ7xIxtQRNjDXRvTx%2F9ef0Tl0g6SYQhAlvmkH%2Fgv74qUaiTSG8ewJ0%2FGgRK5aG8Cts5ouWDa1RxoDRovK9i9MAq1S12QA7b5ROUdBxBIeQ1ACG49m%2FEXPis7Qk3ChHbx6Qw1dgXVeWB7uyDOctP%2Fx6w2zdrIVIyFCyiq8wXlJOZzyAXQbY%2FGGhC8EAilJ%2BVg7ufxU6IAHeSvewfQEadiDuCr%2B6NE1LU4hwUFAF1xFGRkvEjVDlgiPwVqoEsNkAq0ZKp3EIYrFM2xGm7Uc8u%2FzXjHkTmHIHoCiDM73E3IIsDCtRV3gn7QHQ0hTCt0ooKLw%2FWCAM1AcNISOcHSsBrDRAbc7eQMQBFFciHM18kaZIMz3r%2F0HO5mazytsiw%2FmTtCYiGGCkQlltwkEVjMDVmyUA6oIGR%2BDGjAWoM3f2giHAhH%2BFI5nPsDrWxqWNE9S4tUz5k1S7cQ5df4k9S6qY9JRipXtr4w5WQYH0eHkWrqxy8FTn3AvpmFmIqj%2B76EiQjNfHH1JNWFKc3vABj9V9npw%2FRXfmBNsaoTRnRAQDAgqqMJr1KBWUtUmHaR8WRgzAqAH6FgYexqd4R2Yuns5wcLSFK4U36bj%2FdbbUbGdoZoCi3uS%2Bqtt73TlNWygpqXGfZTGXnKesrwkA9BmgZ0noMZT5R0tQ4hzLfo4rhS46W%2F%2BCAn3T7%2BhDySiWMl2RkHArP8dAesKjPixYVbbUBwB6DHB4QWADIamuHPtkhE0t3ZP7ANhe9zgvXP2dfK0pymRJmQLiEYNW6mEVljYGuDzlkwwaHq51AQ4bERkAetvjP2XCT6H480AJeZsB4N7QYt7OnuSROtRXJV2wNNS4qIJvlbUtERJxhxcv5%2FlNWwygV0QGyzKBv%2FP%2ByFfZXf%2ButoR3UuXcS95mKNgxSjpN3qZZFHwUgFPjx5n2c9wo9ktrtcOZtMeWB2NEw4b2thivPLuIS1M%2BAzmrTy4O4ys7Zv1B5fsnVdWCr7PxYf7vej73ex2YeU1VVY9nu7ShG63vRo%2Fe%2FK1%2B518FbXkjo3OjO1XU2LFRzRZ9VdWDczFQ1VsCOHgpd1G%2FcG6jHrj2vPbn%2BjVdHNfr%2BRH92eXva2MPuvxEQpe%2BHdEnzm%2FQf4%2BrRo%2BldMUbGd393oS2dWU0cDSlw1OequrALVG9Q8rLsquqg2OlzLL2Myu1N5eShgB4CjEnSMSJYrX8Oj0t8UH7NMnX0iSDwmhBWRl3tKs9IcmgGRSRZqtqzFwpL4uWWKvWiMjyZKC24%2F1HbsrLn95Pwk3gCpS0yIw%2Fg6clPC2RLc3QmzvJupoARQsvrItxZmtSkkFz6E6Q%2F2m3PFta44jbCaw%2BO3GK7uybnJs8xfXC1fLYCdTz9NIfsCS0mYVhAHp9ZYdr5J%2F%2F127dxUA2AzuBzRUDWVfZlq4YyG6gs9ImdzWQ%2FwFNRlgCFdG5bAAAAABJRU5ErkJggg%3D%3D
- :alt: Slack-Swung
- :target: https://swung.slack.com/messages/gstools
-.. |Gitter-GSTools| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/Gitter-GeoStat--Framework-ed1965?logo=gitter&style=flat
- :alt: Gitter-GSTools
- :target: https://gitter.im/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools
-.. |Email| image:: https://img.shields.io/badge/Email-GeoStat--Framework-468a88?style=flat&logo=data:image/svg+xml;base64,PHN2ZyB4bWxucz0iaHR0cDovL3d3dy53My5vcmcvMjAwMC9zdmciIHhtbDpzcGFjZT0icHJlc2VydmUiIHdpZHRoPSI1MDAiIGhlaWdodD0iNTAwIj48cGF0aCBkPSJNNDQ4IDg4SDUyYy0yNyAwLTQ5IDIyLTQ5IDQ5djIyNmMwIDI3IDIyIDQ5IDQ5IDQ5aDM5NmMyNyAwIDQ5LTIyIDQ5LTQ5VjEzN2MwLTI3LTIyLTQ5LTQ5LTQ5em0xNiA0OXYyMjZsLTIgNy0xMTUtMTE2IDExNy0xMTd6TTM2IDM2M1YxMzdsMTE3IDExN0wzOCAzNzBsLTItN3ptMjE5LTYzYy0zIDMtNyAzLTEwIDBMNjYgMTIxaDM2OHptLTc5LTIzIDQ2IDQ2YTM5IDM5IDAgMCAwIDU2IDBsNDYtNDYgMTAxIDEwMkg3NXoiIHN0eWxlPSJmaWxsOiNmNWY1ZjU7ZmlsbC1vcGFjaXR5OjEiLz48L3N2Zz4=
- :alt: Email
- :target: mailto:info@geostat-framework.org
-.. |Twitter| image:: https://img.shields.io/twitter/follow/GSFramework?style=social
- :alt: Twitter Follow
- :target: https://twitter.com/GSFramework
+.. mdinclude:: ../../README.md
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/05_ordinary.png b/docs/source/pics/05_ordinary.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8a529968b..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/05_ordinary.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/05_simple.png b/docs/source/pics/05_simple.png
deleted file mode 100644
index fad8c8beb..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/05_simple.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/06_ensemble.png b/docs/source/pics/06_ensemble.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d63139678..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/06_ensemble.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_00_std.png b/docs/source/pics/07_00_std.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 3128e018e..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_00_std.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_01_lognormal.png b/docs/source/pics/07_01_lognormal.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 430327ace..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_01_lognormal.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_02_binary.png b/docs/source/pics/07_02_binary.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7d720f175..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_02_binary.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_03_zinnharvey.png b/docs/source/pics/07_03_zinnharvey.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 949994de1..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_03_zinnharvey.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_04_arcsin.png b/docs/source/pics/07_04_arcsin.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 772ae3f84..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_04_arcsin.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/07_05_combine.png b/docs/source/pics/07_05_combine.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bcd9222e6..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/07_05_combine.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/09_cond_ens.png b/docs/source/pics/09_cond_ens.png
deleted file mode 100644
index ed9a5d5a9..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/09_cond_ens.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/20_gstools.png b/docs/source/pics/20_gstools.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6f2091027..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/20_gstools.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/20_pykrige.png b/docs/source/pics/20_pykrige.png
deleted file mode 100644
index fa5451463..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/20_pykrige.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/3d_gau_field.png b/docs/source/pics/3d_gau_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 862f8cf85..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/3d_gau_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/GS_3d_vector_field.png b/docs/source/pics/GS_3d_vector_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index f1cf0883d..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/GS_3d_vector_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/GS_pyvista_cut.png b/docs/source/pics/GS_pyvista_cut.png
deleted file mode 100644
index bad73abc6..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/GS_pyvista_cut.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/cond_ens.png b/docs/source/pics/cond_ens.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 6c0d5211c..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/cond_ens.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/cov_model_vario.png b/docs/source/pics/cov_model_vario.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7dbbe9ec1..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/cov_model_vario.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/demonstrator.png b/docs/source/pics/demonstrator.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 395a317e2..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/demonstrator.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/exp_vario_fit.png b/docs/source/pics/exp_vario_fit.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 24ec17996..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/exp_vario_fit.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/gau_field.png b/docs/source/pics/gau_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 602d095c7..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/gau_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/gstools.png b/docs/source/pics/gstools.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 5f4be62ce..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/gstools.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/paraview.png b/docs/source/pics/paraview.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7c2a94947..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/paraview.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/pyvista_export.png b/docs/source/pics/pyvista_export.png
deleted file mode 100644
index dc5d0a256..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/pyvista_export.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_exp_ani_rot.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_exp_ani_rot.png
deleted file mode 100644
index d5e348d14..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_exp_ani_rot.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8153a45a9..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field_ens.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field_ens.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7a8ab35e3..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_gau_field_ens.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_merge.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_merge.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 57474e514..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_merge.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_unstr.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_unstr.png
deleted file mode 100644
index c095e3719..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_tut_unstr.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/srf_vector_field.png b/docs/source/pics/srf_vector_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 59d1bad21..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/srf_vector_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/stab_vario_fit.png b/docs/source/pics/stab_vario_fit.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 2b3c6e3c5..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/stab_vario_fit.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/tplstable_field.png b/docs/source/pics/tplstable_field.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 9d1790832..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/tplstable_field.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_aniso_fit_exp.png b/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_aniso_fit_exp.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 8344e93bc..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_aniso_fit_exp.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_fit_exp.png b/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_fit_exp.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 06fc66dbe..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_fit_exp.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_herten.png b/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_herten.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 84303b8fa..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_herten.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_new_herten.png b/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_new_herten.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 7080a2520..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vario_tut_new_herten.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_exp.png b/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_exp.png
deleted file mode 100644
index 492036465..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_exp.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_gau.png b/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_gau.png
deleted file mode 100644
index beafa4128..000000000
Binary files a/docs/source/pics/vec_srf_tut_gau.png and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/docs/source/tutorials.rst b/docs/source/tutorials.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 3c25f597a..000000000
--- a/docs/source/tutorials.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-.. _tutorials:
-
-=================
-GSTools Tutorials
-=================
-
-In the following you will find several Tutorials on how to use GSTools to
-explore its whole beauty and power.
-
-
-.. toctree::
- :includehidden:
- :maxdepth: 1
-
- examples/01_random_field/index
- examples/02_cov_model/index
- examples/03_variogram/index
- examples/04_vector_field/index
- examples/05_kriging/index
- examples/06_conditioned_fields/index
- examples/07_transformations/index
- examples/08_geo_coordinates/index
- examples/09_spatio_temporal/index
- examples/10_normalizer/index
- examples/00_misc/index
-
-.. only:: html
-
- **Youtube Tutorial on GSTools**
-
- .. youtube:: qZBJ-AZXq6Q
- :width: 100%
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/00_tpl_stable.py b/examples/00_misc/00_tpl_stable.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 474b0f558..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/00_tpl_stable.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,62 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Truncated Power Law Variograms
-------------------------------
-
-GSTools also implements truncated power law variograms,
-which can be represented as a superposition of scale dependant modes
-in form of standard variograms, which are truncated by
-a lower- :math:`\ell_{\mathrm{low}}` and
-an upper length-scale :math:`\ell_{\mathrm{up}}`.
-
-This example shows the truncated power law (:any:`TPLStable`) based on the
-:any:`Stable` covariance model and is given by
-
-.. math::
- \gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) =
- \intop_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}}}^{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}
- \gamma(r,\lambda) \frac{\rm d \lambda}{\lambda}
-
-with `Stable` modes on each scale:
-
-.. math::
- \gamma(r,\lambda) &=
- \sigma^2(\lambda)\cdot\left(1-
- \exp\left[- \left(\frac{r}{\lambda}\right)^{\alpha}\right]
- \right)\\
- \sigma^2(\lambda) &= C\cdot\lambda^{2H}
-
-which gives Gaussian modes for ``alpha=2``
-or Exponential modes for ``alpha=1``.
-
-For :math:`\ell_{\mathrm{low}}=0` this results in:
-
-.. math::
- \gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) &=
- \sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\cdot\left(1-
- \frac{2H}{\alpha} \cdot
- E_{1+\frac{2H}{\alpha}}
- \left[\left(\frac{r}{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\right)^{\alpha}\right]
- \right) \\
- \sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}} &=
- C\cdot\frac{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}^{2H}}{2H}
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = y = np.linspace(0, 100, 100)
-model = gs.TPLStable(
- dim=2, # spatial dimension
- var=1, # variance (C is calculated internally, so variance is actually 1)
- len_low=0, # lower truncation of the power law
- len_scale=10, # length scale (a.k.a. range), len_up = len_low + len_scale
- nugget=0.1, # nugget
- anis=0.5, # anisotropy between main direction and transversal ones
- angles=np.pi / 4, # rotation angles
- alpha=1.5, # shape parameter from the stable model
- hurst=0.7, # hurst coefficient from the power law
-)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=1.0, seed=19970221)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/01_export.py b/examples/00_misc/01_export.py
deleted file mode 100644
index e38294fe6..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/01_export.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,25 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Exporting Fields
-----------------
-
-GSTools provides simple exporting routines to convert generated fields to
-`VTK `__ files.
-
-These can be viewed for example with `Paraview `__.
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_path = 'pics/paraview.png'
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-field = srf((x, y), mesh_type="structured")
-srf.vtk_export(filename="field")
-
-###############################################################################
-# The result displayed with Paraview:
-#
-# .. image:: https://raw.githubusercontent.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/master/img/paraview.png
-# :width: 400px
-# :align: center
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/02_check_rand_meth_sampling.py b/examples/00_misc/02_check_rand_meth_sampling.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 58d998b4d..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/02_check_rand_meth_sampling.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Check Random Sampling
----------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
-from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def norm_rad(vec):
- """Direction on the unit sphere."""
- vec = np.array(vec, ndmin=2)
- norm = np.zeros(vec.shape[1])
- for i in range(vec.shape[0]):
- norm += vec[i] ** 2
- norm = np.sqrt(norm)
- return np.einsum("j,ij->ij", 1 / norm, vec), norm
-
-
-def plot_rand_meth_samples(generator):
- """Plot the samples of the rand meth class."""
- norm, rad = norm_rad(generator._cov_sample)
-
- fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 4))
-
- if generator.model.dim == 3:
- ax = fig.add_subplot(121, projection=Axes3D.name)
- u = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
- v = np.linspace(0, np.pi, 100)
- x = np.outer(np.cos(u), np.sin(v))
- y = np.outer(np.sin(u), np.sin(v))
- z = np.outer(np.ones(np.size(u)), np.cos(v))
- ax.plot_surface(x, y, z, rstride=4, cstride=4, color="b", alpha=0.1)
- ax.scatter(norm[0], norm[1], norm[2])
- elif generator.model.dim == 2:
- ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
- u = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
- x = np.cos(u)
- y = np.sin(u)
- ax.plot(x, y, color="b", alpha=0.1)
- ax.scatter(norm[0], norm[1])
- ax.set_aspect("equal")
- else:
- ax = fig.add_subplot(121)
- ax.bar(-1, np.sum(np.isclose(norm, -1)), color="C0")
- ax.bar(1, np.sum(np.isclose(norm, 1)), color="C0")
- ax.set_xticks([-1, 1])
- ax.set_xticklabels(("-1", "1"))
- ax.set_title("Direction sampling")
-
- ax = fig.add_subplot(122)
- x = np.linspace(0, 10 / generator.model.integral_scale)
- y = generator.model.spectral_rad_pdf(x)
- ax.plot(x, y, label="radial spectral density")
- sample_in = np.sum(rad <= np.max(x))
- ax.hist(rad[rad <= np.max(x)], bins=sample_in // 50, density=True)
- ax.set_xlim([0, np.max(x)])
- ax.set_title(f"Radius samples shown {sample_in}/{len(rad)}")
- ax.legend()
- plt.show()
-
-
-model = gs.Stable(dim=3, alpha=1.5)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=2020)
-plot_rand_meth_samples(srf.generator)
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/04_herten.py b/examples/00_misc/04_herten.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 1e1b8a23f..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/04_herten.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,290 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Analyzing the Herten Aquifer with GSTools
------------------------------------------
-
-This example is going to be a bit more extensive and we are going to do some
-basic data preprocessing for the actual variogram estimation. But this example
-will be self-contained and all data gathering and processing will be done in
-this example script.
-
-
-The Data
-^^^^^^^^
-
-We are going to analyse the Herten aquifer, which is situated in Southern
-Germany. Multiple outcrop faces where surveyed and interpolated to a 3D
-dataset. In these publications, you can find more information about the data:
-
-| Bayer, Peter; Comunian, Alessandro; Höyng, Dominik; Mariethoz, Gregoire (2015): Physicochemical properties and 3D geostatistical simulations of the Herten and the Descalvado aquifer analogs. PANGAEA, https://doi.org/10.1594/PANGAEA.844167,
-| Supplement to: Bayer, P et al. (2015): Three-dimensional multi-facies realizations of sedimentary reservoir and aquifer analogs. Scientific Data, 2, 150033, https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2015.33
-|
-
-Retrieving the Data
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-To begin with, we need to download and extract the data. Therefore, we are
-going to use some built-in Python libraries. For simplicity, many values and
-strings will be hardcoded.
-
-You don't have to execute the ``download_herten`` and ``generate_transmissivity``
-functions, since the only produce the ``herten_transmissivity.gz``
-and ``grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt``, which are already present.
-"""
-
-import os
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-VTK_PATH = os.path.join("Herten-analog", "sim-big_1000x1000x140", "sim.vtk")
-
-###############################################################################
-
-
-def download_herten():
- """Download the data, warning: its about 250MB."""
- import urllib.request
- import zipfile
-
- print("Downloading Herten data")
- data_filename = "data.zip"
- data_url = (
- "http://store.pangaea.de/Publications/"
- "Bayer_et_al_2015/Herten-analog.zip"
- )
- urllib.request.urlretrieve(data_url, "data.zip")
- # extract the "big" simulation
- with zipfile.ZipFile(data_filename, "r") as zf:
- zf.extract(VTK_PATH)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-
-
-def generate_transmissivity():
- """Generate a file with a transmissivity field from the HERTEN data."""
- import shutil
-
- import pyvista as pv
-
- print("Loading Herten data with pyvista")
- mesh = pv.read(VTK_PATH)
- herten = mesh.point_data["facies"].reshape(mesh.dimensions, order="F")
- # conductivity values per fazies from the supplementary data
- cond = 1e-4 * np.array(
- [2.5, 2.3, 0.61, 260, 1300, 950, 0.43, 0.006, 23, 1.4]
- )
- # asign the conductivities to the facies
- herten_cond = cond[herten]
- # Next, we are going to calculate the transmissivity,
- # by integrating over the vertical axis
- herten_trans = np.sum(herten_cond, axis=2) * mesh.spacing[2]
- # saving some grid informations
- grid = [mesh.dimensions[:2], mesh.origin[:2], mesh.spacing[:2]]
- print("Saving the transmissivity field and grid information")
- np.savetxt("herten_transmissivity.gz", herten_trans)
- np.savetxt("grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt", grid)
- # Some cleanup. You can comment out these lines to keep the downloaded data
- os.remove("data.zip")
- shutil.rmtree("Herten-analog")
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Downloading and Preprocessing
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# You can uncomment the following two calls, so the data is downloaded
-# and processed again.
-
-# download_herten()
-# generate_transmissivity()
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Analyzing the data
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# The Herten data provides information about the grid, which was already used in
-# the previous code block. From this information, we can create our own grid on
-# which we can estimate the variogram. As a first step, we are going to estimate
-# an isotropic variogram, meaning that we will take point pairs from all
-# directions into account. An unstructured grid is a natural choice for this.
-# Therefore, we are going to create an unstructured grid from the given,
-# structured one. For this, we are going to write another small function
-
-herten_log_trans = np.log(np.loadtxt("herten_transmissivity.gz"))
-dim, origin, spacing = np.loadtxt("grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt")
-
-# create a structured grid on which the data is defined
-x_s = np.arange(origin[0], origin[0] + dim[0] * spacing[0], spacing[0])
-y_s = np.arange(origin[1], origin[1] + dim[1] * spacing[1], spacing[1])
-# create the corresponding unstructured grid for the variogram estimation
-x_u, y_u = np.meshgrid(x_s, y_s)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Let's have a look at the transmissivity field of the Herten aquifer
-
-plt.imshow(herten_log_trans.T, origin="lower", aspect="equal")
-plt.show()
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Estimating the Variogram
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# Finally, everything is ready for the variogram estimation. For the unstructured
-# method, we have to define the bins on which the variogram will be estimated.
-# Through expert knowledge (i.e. fiddling around), we assume that the main
-# features of the variogram will be below 10 metres distance. And because the
-# data has a high spatial resolution, the resolution of the bins can also be
-# high. The transmissivity data is still defined on a structured grid, but we can
-# simply flatten it with :any:`numpy.ndarray.flatten`, in order to bring it into
-# the right shape. It might be more memory efficient to use
-# ``herten_log_trans.reshape(-1)``, but for better readability, we will stick to
-# :any:`numpy.ndarray.flatten`. Taking all data points into account would take a
-# very long time (expert knowledge \*wink\*), thus we will only take 2000 datapoints into account, which are sampled randomly. In order to make the exact
-# results reproducible, we can also set a seed.
-
-
-bins = gs.standard_bins(pos=(x_u, y_u), max_dist=10)
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate(
- (x_u, y_u),
- herten_log_trans.reshape(-1),
- bins,
- sampling_size=2000,
- sampling_seed=19920516,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# The estimated variogram is calculated on the centre of the given bins,
-# therefore, the ``bin_center`` array is also returned.
-
-###############################################################################
-# Fitting the Variogram
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# Now, we can see, if the estimated variogram can be modelled by a common
-# variogram model. Let's try the :any:`Exponential` model.
-
-# fit an exponential model
-fit_model = gs.Exponential(dim=2)
-fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, nugget=False)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Finally, we can visualise some results. For quickly plotting a covariance
-# model, GSTools provides some helper functions.
-
-ax = fit_model.plot(x_max=max(bin_center))
-ax.plot(bin_center, gamma)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# That looks like a pretty good fit! By printing the model, we can directly see
-# the fitted parameters
-
-print(fit_model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# With this data, we could start generating new ensembles of the Herten aquifer
-# with the :any:`SRF` class.
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Estimating the Variogram in Specific Directions
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# Estimating a variogram on a structured grid gives us the possibility to only
-# consider values in a specific direction. This could be a first test, to see if
-# the data is anisotropic.
-# In order to speed up the calculations, we are going to only use every 10th datapoint and for a comparison with the isotropic variogram calculated earlier, we
-# only need the first 21 array items.
-
-
-# estimate the variogram on a structured grid
-# use only every 10th value, otherwise calculations would take very long
-x_s_skip = np.ravel(x_s)[::10]
-y_s_skip = np.ravel(y_s)[::10]
-herten_trans_skip = herten_log_trans[::10, ::10]
-
-###############################################################################
-# With this much smaller data set, we can immediately estimate the variogram in
-# the x- and y-axis
-
-gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(herten_trans_skip, direction="x")
-gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(herten_trans_skip, direction="y")
-
-###############################################################################
-# With these two estimated variograms, we can start fitting :any:`Exponential`
-# covariance models
-
-x_plot = x_s_skip[:21]
-y_plot = y_s_skip[:21]
-# fit an exponential model
-fit_model_x = gs.Exponential(dim=2)
-fit_model_x.fit_variogram(x_plot, gamma_x[:21], nugget=False)
-fit_model_y = gs.Exponential(dim=2)
-fit_model_y.fit_variogram(y_plot, gamma_y[:21], nugget=False)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now, the isotropic variogram and the two variograms in x- and y-direction can
-# be plotted together with their respective models, which will be plotted with
-# dashed lines.
-
-plt.figure() # new figure
-(line,) = plt.plot(bin_center, gamma, label="estimated variogram (isotropic)")
-plt.plot(
- bin_center,
- fit_model.variogram(bin_center),
- color=line.get_color(),
- linestyle="--",
- label="exp. variogram (isotropic)",
-)
-
-(line,) = plt.plot(x_plot, gamma_x[:21], label="estimated variogram in x-dir")
-plt.plot(
- x_plot,
- fit_model_x.variogram(x_plot),
- color=line.get_color(),
- linestyle="--",
- label="exp. variogram in x-dir",
-)
-
-(line,) = plt.plot(y_plot, gamma_y[:21], label="estimated variogram in y-dir")
-plt.plot(
- y_plot,
- fit_model_y.variogram(y_plot),
- color=line.get_color(),
- linestyle="--",
- label="exp. variogram in y-dir",
-)
-
-plt.legend()
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# The plot might be a bit cluttered, but at least it is pretty obvious that the
-# Herten aquifer has no apparent anisotropies in its spatial structure.
-
-print("semivariogram model (isotropic):\n", fit_model)
-print("semivariogram model (in x-dir.):\n", fit_model_x)
-print("semivariogram model (in y-dir.):\n", fit_model_y)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Creating a Spatial Random Field from the Herten Parameters
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# With all the hard work done, it's straight forward now, to generate new
-# *Herten-like realisations*
-
-# create a spatial random field on the low-resolution grid
-srf = gs.SRF(fit_model, seed=19770928)
-srf.structured([x_s_skip, y_s_skip])
-ax = srf.plot()
-ax.set_aspect("equal")
-
-###############################################################################
-# That's pretty neat!
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/05_standalone_field.py b/examples/00_misc/05_standalone_field.py
deleted file mode 100644
index e467f0431..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/05_standalone_field.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,30 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Standalone Field class
-----------------------
-
-The :any:`Field` class of GSTools can be used to plot arbitrary data in nD.
-
-In the following example we will produce 10000 random points in 4D with
-random values and plot them.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-rng = np.random.RandomState(19970221)
-x0 = rng.rand(10000) * 100.0
-x1 = rng.rand(10000) * 100.0
-x2 = rng.rand(10000) * 100.0
-x3 = rng.rand(10000) * 100.0
-values = rng.rand(10000) * 100.0
-
-###############################################################################
-# Only thing needed to instantiate the Field is the dimension.
-#
-# Afterwards we can call the instance like all other Fields
-# (:any:`SRF`, :any:`Krige` or :any:`CondSRF`), but with an additional field.
-
-plotter = gs.field.Field(dim=4)
-plotter(pos=(x0, x1, x2, x3), field=values)
-plotter.plot()
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/README.rst b/examples/00_misc/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index bef7ae572..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,9 +0,0 @@
-Miscellaneous Tutorials
-=======================
-
-More examples which do not really fit into other categories. Some are not more
-than a code snippet, while others are more complex and more than one part of
-GSTools is involved.
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt b/examples/00_misc/grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index 024928d3e..000000000
--- a/examples/00_misc/grid_dim_origin_spacing.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,3 +0,0 @@
-1.000000000000000000e+03 1.000000000000000000e+03
-0.000000000000000000e+00 0.000000000000000000e+00
-5.000000000000000278e-02 5.000000000000000278e-02
diff --git a/examples/00_misc/herten_transmissivity.gz b/examples/00_misc/herten_transmissivity.gz
deleted file mode 100644
index fa1d00e3a..000000000
Binary files a/examples/00_misc/herten_transmissivity.gz and /dev/null differ
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/00_gaussian.py b/examples/01_random_field/00_gaussian.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b7bde5f9c..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/00_gaussian.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-A Very Simple Example
----------------------
-
-We are going to start with a very simple example of a spatial random field
-with an isotropic Gaussian covariance model and following parameters:
-
-- variance :math:`\sigma^2=1`
-- correlation length :math:`\lambda=10`
-
-First, we set things up and create the axes for the field. We are going to
-need the :any:`SRF` class for the actual generation of the spatial random field.
-But :any:`SRF` also needs a covariance model and we will simply take the
-:any:`Gaussian` model.
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = y = range(100)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we create the covariance model with the parameters :math:`\sigma^2` and
-# :math:`\lambda` and hand it over to :any:`SRF`. By specifying a seed,
-# we make sure to create reproducible results:
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-
-###############################################################################
-# With these simple steps, everything is ready to create our first random field.
-# We will create the field on a structured grid (as you might have guessed from
-# the `x` and `y`), which makes it easier to plot.
-
-field = srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Wow, that was pretty easy!
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/01_srf_ensemble.py b/examples/01_random_field/01_srf_ensemble.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 68cc2c0fa..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/01_srf_ensemble.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,54 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Creating an Ensemble of Fields
-------------------------------
-
-Creating an ensemble of random fields would also be
-a great idea. Let's reuse most of the previous code.
-
-We will set the position tuple `pos` before generation to reuse it afterwards.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as pt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = y = np.arange(100)
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf.set_pos([x, y], "structured")
-
-###############################################################################
-# This time, we did not provide a seed to :any:`SRF`, as the seeds will used
-# during the actual computation of the fields. We will create four ensemble
-# members, for better visualisation, save them in to srf class and in a first
-# step, we will be using the loop counter as the seeds.
-
-ens_no = 4
-for i in range(ens_no):
- srf(seed=i, store=f"field{i}")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now let's have a look at the results. We can access the fields by name or
-# index:
-
-fig, ax = pt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
-ax = ax.flatten()
-for i in range(ens_no):
- ax[i].imshow(srf[i].T, origin="lower")
-pt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Using better Seeds
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# It is not always a good idea to use incrementing seeds. Therefore GSTools
-# provides a seed generator :any:`MasterRNG`. The loop, in which the fields are
-# generated would then look like
-
-from gstools.random import MasterRNG
-
-seed = MasterRNG(20170519)
-for i in range(ens_no):
- srf(seed=seed(), store=f"better_field{i}")
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/02_fancier.py b/examples/01_random_field/02_fancier.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 1922cec72..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/02_fancier.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,31 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Creating Fancier Fields
------------------------
-
-Only using Gaussian covariance fields gets boring. Now we are going to create
-much rougher random fields by using an exponential covariance model and we are going to make them anisotropic.
-
-The code is very similar to the previous examples, but with a different
-covariance model class :any:`Exponential`. As model parameters we a using
-following
-
-- variance :math:`\sigma^2=1`
-- correlation length :math:`\lambda=(12, 3)^T`
-- rotation angle :math:`\theta=\pi/8`
-
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = y = np.arange(100)
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=[12.0, 3.0], angles=np.pi / 8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# The anisotropy ratio could also have been set with
-
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=12, anis=0.25, angles=np.pi / 8)
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/03_unstr_srf_export.py b/examples/01_random_field/03_unstr_srf_export.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 94d009525..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/03_unstr_srf_export.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,34 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Using an Unstructured Grid
---------------------------
-
-For many applications, the random fields are needed on an unstructured grid.
-Normally, such a grid would be read in, but we can simply generate one and
-then create a random field at those coordinates.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Creating our own unstructured grid
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(19970221)
-rng = np.random.RandomState(seed())
-x = rng.randint(0, 100, size=10000)
-y = rng.randint(0, 100, size=10000)
-
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=[12, 3], angles=np.pi / 8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-field = srf((x, y))
-srf.vtk_export("field")
-# Or create a PyVista dataset
-# mesh = srf.to_pyvista()
-
-###############################################################################
-ax = srf.plot()
-ax.set_aspect("equal")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Comparing this image to the previous one, you can see that be using the same
-# seed, the same field can be computed on different grids.
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/04_srf_merge.py b/examples/01_random_field/04_srf_merge.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 241ed0793..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/04_srf_merge.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,49 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Merging two Fields
-------------------
-
-We can even generate the same field realisation on different grids. Let's try
-to merge two unstructured rectangular fields.
-
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# creating our own unstructured grid
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(19970221)
-rng = np.random.RandomState(seed())
-x = rng.randint(0, 100, size=10000)
-y = rng.randint(0, 100, size=10000)
-
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=[12, 3], angles=np.pi / 8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-field1 = srf((x, y))
-srf.plot()
-###############################################################################
-# But now we extend the field on the right hand side by creating a new
-# unstructured grid and calculating a field with the same parameters and the
-# same seed on it:
-
-# new grid
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(20011012)
-rng = np.random.RandomState(seed())
-x2 = rng.randint(99, 150, size=10000)
-y2 = rng.randint(20, 80, size=10000)
-
-field2 = srf((x2, y2))
-ax = srf.plot()
-ax.tricontourf(x, y, field1.T, levels=256)
-ax.set_aspect("equal")
-
-###############################################################################
-# The slight mismatch where the two fields were merged is merely due to
-# interpolation problems of the plotting routine. You can convince yourself
-# be increasing the resolution of the grids by a factor of 10.
-#
-# Of course, this merging could also have been done by appending the grid
-# point ``(x2, y2)`` to the original grid ``(x, y)`` before generating the field.
-# But one application scenario would be to generate hugh fields, which would not
-# fit into memory anymore.
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/05_mesh_ensemble.py b/examples/01_random_field/05_mesh_ensemble.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 1e2f0da86..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/05_mesh_ensemble.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,94 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Generating Fields on Meshes
----------------------------
-
-GSTools provides an interface for meshes, to support
-`meshio `_ and
-`ogs5py `_ meshes.
-
-When using `meshio`, the generated fields will be stored immediately in the
-mesh container.
-
-There are two options to generate a field on a given mesh:
-
-- `points="points"` will generate a field on the mesh points
-- `points="centroids"` will generate a field on the cell centroids
-
-In this example, we will generate a simple mesh with the aid of
-`meshzoo `_.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import matplotlib.tri as tri
-import meshio
-import meshzoo
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# generate a triangulated hexagon with meshzoo
-points, cells = meshzoo.ngon(6, 4)
-mesh = meshio.Mesh(points, {"triangle": cells})
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we prepare the SRF class as always. We will generate an ensemble of
-# fields on the generated mesh.
-
-# number of fields
-fields_no = 12
-# model setup
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, len_scale=0.5)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=1)
-
-###############################################################################
-# To generate fields on a mesh, we provide a separate method: :any:`SRF.mesh`.
-# First we generate fields on the mesh-centroids controlled by a seed.
-# You can specify the field name by the keyword `name`.
-
-for i in range(fields_no):
- srf.mesh(mesh, points="centroids", name=f"c-field-{i}", seed=i)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we generate fields on the mesh-points again controlled by a seed.
-
-for i in range(fields_no):
- srf.mesh(mesh, points="points", name=f"p-field-{i}", seed=i)
-
-###############################################################################
-# To get an impression we now want to plot the generated fields.
-# Luckily, matplotlib supports triangular meshes.
-
-triangulation = tri.Triangulation(points[:, 0], points[:, 1], cells)
-# figure setup
-cols = 4
-rows = int(np.ceil(fields_no / cols))
-
-###############################################################################
-# Cell data can be easily visualized with matplotlibs `tripcolor`.
-# To highlight the cell structure, we use `triplot`.
-
-fig = plt.figure(figsize=[2 * cols, 2 * rows])
-for i, field in enumerate(mesh.cell_data, 1):
- ax = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
- ax.tripcolor(triangulation, mesh.cell_data[field][0])
- ax.triplot(triangulation, linewidth=0.5, color="k")
- ax.set_aspect("equal")
-fig.tight_layout()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Point data is plotted via `tricontourf`.
-
-fig = plt.figure(figsize=[2 * cols, 2 * rows])
-for i, field in enumerate(mesh.point_data, 1):
- ax = fig.add_subplot(rows, cols, i)
- ax.tricontourf(triangulation, mesh.point_data[field])
- ax.triplot(triangulation, linewidth=0.5, color="k")
- ax.set_aspect("equal")
-fig.tight_layout()
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Last but not least, `meshio` can be used for what is does best: Exporting.
-# Tada!
-
-mesh.write("mesh_ensemble.vtk")
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/06_pyvista_support.py b/examples/01_random_field/06_pyvista_support.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 29de8dd7a..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/06_pyvista_support.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,58 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Using PyVista meshes
---------------------
-
-`PyVista `__ is a helper module for the
-Visualization Toolkit (VTK) that takes a different approach on interfacing with
-VTK through NumPy and direct array access.
-
-It provides mesh data structures and filtering methods for spatial datasets,
-makes 3D plotting simple and is built for large/complex data geometries.
-
-The :any:`Field.mesh` method enables easy field creation on PyVista meshes
-used by the :any:`SRF` or :any:`Krige` class.
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_path = 'pics/GS_pyvista_cut.png'
-import pyvista as pv
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# We create a structured grid with PyVista containing 50 segments on all three
-# axes each with a length of 2 (whatever unit).
-
-dims, spacing = (50, 50, 50), (2, 2, 2)
-grid = pv.ImageData(dimensions=dims, spacing=spacing)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we set up the SRF class as always. We'll use an anisotropic model.
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, len_scale=[16, 8, 4], angles=(0.8, 0.4, 0.2))
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=19970221)
-
-###############################################################################
-# The PyVista mesh can now be directly passed to the :any:`SRF.mesh` method.
-# When dealing with meshes, one can choose if the field should be generated
-# on the mesh-points (`"points"`) or the cell-centroids (`"centroids"`).
-#
-# In addition we can set a name, under which the resulting field is stored
-# in the mesh.
-
-srf.mesh(grid, points="points", name="random-field")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we have access to PyVista's abundancy of methods to explore the field.
-#
-# .. note::
-# PyVista is not working on readthedocs, but you can try it out yourself by
-# uncommenting the following line of code.
-
-# grid.contour(isosurfaces=8).plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# The result should look like this:
-#
-# .. image:: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/raw/master/img/GS_pyvista_cut.png
-# :width: 400px
-# :align: center
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/07_higher_dimensions.py b/examples/01_random_field/07_higher_dimensions.py
deleted file mode 100755
index b65ab3ead..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/07_higher_dimensions.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,82 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Higher Dimensions
------------------
-
-GSTools provides experimental support for higher dimensions.
-
-Anisotropy is the same as in lower dimensions:
-
-- in `n` dimensions we need `(n-1)` anisotropy ratios
-
-Rotation on the other hand is a bit more complex.
-With increasing dimensions more and more rotation angles are added in order
-to properply describe the rotated axes of anisotropy.
-
-By design the first rotation angles coincide with the lower ones:
-
-- 2D (rotation in x-y plane) -> 3D: first angle describes xy-plane rotation
-- 3D (Tait-Bryan angles) -> 4D: first 3 angles coincide with Tait-Bryan angles
-
-By increasing the dimension from `n` to `(n+1)`, `n` angles are added:
-
-- 2D (1 angle) -> 3D: 3 angles (2 added)
-- 3D (3 angles) -> 4D: 6 angles (3 added)
-
-the following list of rotation-planes are described by the list of
-angles in the model:
-
-1. x-y plane
-2. x-z plane
-3. y-z plane
-4. x-v plane
-5. y-v plane
-6. z-v plane
-7. ...
-
-The rotation direction in these planes have alternating signs
-in order to match Tait-Bryan in 3D.
-
-Let's have a look at a 4D example, where we naively add a 4th dimension.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-dim = 4
-size = 20
-pos = [range(size)] * dim
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=dim, len_scale=5)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-field = srf.structured(pos)
-
-###############################################################################
-# In order to "prove" correctness, we can calculate an empirical variogram
-# of the generated field and fit our model to it.
-
-bin_center, vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- pos, field, sampling_size=2000, mesh_type="structured"
-)
-model.fit_variogram(bin_center, vario)
-print(model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# As you can see, the estimated variance and length scale match our input
-# quite well.
-#
-# Let's have a look at the fit and a x-y cross-section of the 4D field:
-
-f, a = plt.subplots(1, 2, gridspec_kw={"width_ratios": [2, 1]}, figsize=[9, 3])
-model.plot(x_max=max(bin_center), ax=a[0])
-a[0].scatter(bin_center, vario)
-a[1].imshow(field[:, :, 0, 0].T, origin="lower")
-a[0].set_title("isotropic empirical variogram with fitted model")
-a[1].set_title("x-y cross-section")
-f.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# GSTools also provides plotting routines for higher dimensions.
-# Fields are shown by 2D cross-sections, where other dimensions can be
-# controlled via sliders.
-
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/01_random_field/README.rst b/examples/01_random_field/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 6b226b2f9..000000000
--- a/examples/01_random_field/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,17 +0,0 @@
-Random Field Generation
-=======================
-
-The main feature of GSTools is the spatial random field generator :any:`SRF`,
-which can generate random fields following a given covariance model.
-The generator provides a lot of nice features, which will be explained in
-the following
-
-GSTools generates spatial random fields with a given covariance model or
-semi-variogram. This is done by using the so-called randomization method.
-The spatial random field is represented by a stochastic Fourier integral
-and its discretised modes are evaluated at random frequencies.
-
-GSTools supports arbitrary and non-isotropic covariance models.
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/00_intro.py b/examples/02_cov_model/00_intro.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 6b73fd2a1..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/00_intro.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Introductory example
-====================
-
-Let us start with a short example of a self defined model (Of course, we
-provide a lot of predefined models [See: :any:`gstools.covmodel`],
-but they all work the same way).
-Therefore we reimplement the Gaussian covariance model
-by defining just the "normalized"
-`correlation `_
-function:
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-# use CovModel as the base-class
-class Gau(gs.CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Here the parameter ``h`` stands for the normalized range ``r / len_scale``.
-# Now we can instantiate this model:
-
-model = Gau(dim=2, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-
-###############################################################################
-# To have a look at the variogram, let's plot it:
-
-model.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# This is almost identical to the already provided :any:`Gaussian` model.
-# There, a scaling factor is implemented so the len_scale coincides with the
-# integral scale:
-
-gau_model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-gau_model.plot()
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Parameters
-# ----------
-#
-# We already used some parameters, which every covariance models has.
-# The basic ones are:
-#
-# - **dim** : dimension of the model
-# - **var** : variance of the model (on top of the subscale variance)
-# - **len_scale** : length scale of the model
-# - **nugget** : nugget (subscale variance) of the model
-#
-# These are the common parameters used to characterize
-# a covariance model and are therefore used by every model in GSTools.
-# You can also access and reset them:
-
-print("old model:", model)
-model.dim = 3
-model.var = 1
-model.len_scale = 15
-model.nugget = 0.1
-print("new model:", model)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# .. note::
-#
-# - The sill of the variogram is calculated by ``sill = variance + nugget``
-# So we treat the variance as everything **above** the nugget,
-# which is sometimes called **partial sill**.
-# - A covariance model can also have additional parameters.
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/01_basic_methods.py b/examples/02_cov_model/01_basic_methods.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 4c97fba85..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/01_basic_methods.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Basic Methods
-=============
-
-The covariance model class :any:`CovModel` of GSTools provides a set of handy
-methods.
-
-One of the following functions defines the main characterization of the
-variogram:
-
-- ``CovModel.variogram`` : The variogram of the model given by
-
- .. math::
- \gamma\left(r\right)=
- \sigma^2\cdot\left(1-\rho\left(r\right)\right)+n
-
-- ``CovModel.covariance`` : The (auto-)covariance of the model given by
-
- .. math::
- C\left(r\right)= \sigma^2\cdot\rho\left(r\right)
-
-- ``CovModel.correlation`` : The (auto-)correlation
- (or normalized covariance) of the model given by
-
- .. math::
- \rho\left(r\right)
-
-- ``CovModel.cor`` : The normalized correlation taking a
- normalized range given by:
-
- .. math::
- \mathrm{cor}\left(\frac{r}{\ell}\right) = \rho\left(r\right)
-
-
-As you can see, it is the easiest way to define a covariance model by giving a
-correlation function as demonstrated in the introductory example.
-If one of the above functions is given, the others will be determined:
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=10, nugget=0.5)
-ax = model.plot("variogram")
-model.plot("covariance", ax=ax)
-model.plot("correlation", ax=ax)
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/02_aniso_rotation.py b/examples/02_cov_model/02_aniso_rotation.py
deleted file mode 100755
index b7459e396..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/02_aniso_rotation.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Anisotropy and Rotation
-=======================
-
-The internally used (semi-) variogram
-represents the isotropic case for the model.
-Nevertheless, you can provide anisotropy ratios by:
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=10, anis=0.5)
-print(model.anis)
-print(model.len_scale_vec)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# As you can see, we defined just one anisotropy-ratio
-# and the second transversal direction was filled up with ``1.``.
-# You can get the length-scales in each direction by
-# the attribute :any:`CovModel.len_scale_vec`. For full control you can set
-# a list of anistropy ratios: ``anis=[0.5, 0.4]``.
-#
-# Alternatively you can provide a list of length-scales:
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=[10, 5, 4])
-model.plot("vario_spatial")
-print("Anisotropy representations:")
-print("Anis. ratios:", model.anis)
-print("Main length scale", model.len_scale)
-print("All length scales", model.len_scale_vec)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Rotation Angles
-# ---------------
-#
-# The main directions of the field don't have to coincide with the spatial
-# directions :math:`x`, :math:`y` and :math:`z`. Therefore you can provide
-# rotation angles for the model:
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=[10, 2], angles=2.5)
-model.plot("vario_spatial")
-print("Rotation angles", model.angles)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Again, the angles were filled up with ``0.`` to match the dimension and you
-# could also provide a list of angles. The number of angles depends on the
-# given dimension:
-#
-# - in 1D: no rotation performable
-# - in 2D: given as rotation around z-axis
-# - in 3D: given by yaw, pitch, and roll (known as
-# `Tait–Bryan `_
-# angles)
-# - in nD: See the random field example about higher dimensions
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/03_spectral_methods.py b/examples/02_cov_model/03_spectral_methods.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 61c7e49b0..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/03_spectral_methods.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Spectral methods
-================
-
-The spectrum of a covariance model is given by:
-
-.. math:: S(\mathbf{k}) = \left(\frac{1}{2\pi}\right)^n
- \int C(\Vert\mathbf{r}\Vert) e^{i b\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} d^n\mathbf{r}
-
-Since the covariance function :math:`C(r)` is radially symmetric, we can
-calculate this by the
-`hankel-transformation `_:
-
-.. math:: S(k) = \left(\frac{1}{2\pi}\right)^n \cdot
- \frac{(2\pi)^{n/2}}{(bk)^{n/2-1}}
- \int_0^\infty r^{n/2-1} C(r) J_{n/2-1}(bkr) r dr
-
-Where :math:`k=\left\Vert\mathbf{k}\right\Vert`.
-
-Depending on the spectrum, the spectral-density is defined by:
-
-.. math:: \tilde{S}(k) = \frac{S(k)}{\sigma^2}
-
-You can access these methods by:
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-ax = model.plot("spectrum")
-model.plot("spectral_density", ax=ax)
-
-###############################################################################
-# .. note::
-# The spectral-density is given by the radius of the input phase. But it is
-# **not** a probability density function for the radius of the phase.
-# To obtain the pdf for the phase-radius, you can use the methods
-# :any:`CovModel.spectral_rad_pdf`
-# or :any:`CovModel.ln_spectral_rad_pdf` for the logarithm.
-#
-# The user can also provide a cdf (cumulative distribution function) by
-# defining a method called ``spectral_rad_cdf``
-# and/or a ppf (percent-point function)
-# by ``spectral_rad_ppf``.
-#
-# The attributes :any:`CovModel.has_cdf`
-# and :any:`CovModel.has_ppf` will check for that.
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/04_different_scales.py b/examples/02_cov_model/04_different_scales.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 0e2e1991b..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/04_different_scales.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,69 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Different scales
-================
-
-Besides the length-scale, there are many other ways of characterizing a certain
-scale of a covariance model. We provide two common scales with the covariance
-model.
-
-Integral scale
---------------
-
-The `integral scale `_
-of a covariance model is calculated by:
-
-.. math:: I = \int_0^\infty \rho(r) dr
-
-You can access it by:
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Stable(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-print("Main integral scale:", model.integral_scale)
-print("All integral scales:", model.integral_scale_vec)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# You can also specify integral length scales like the ordinary length scale,
-# and len_scale/anis will be recalculated:
-
-model = gs.Stable(dim=3, var=2.0, integral_scale=[10, 4, 2])
-print("Anisotropy ratios:", model.anis)
-print("Main length scale:", model.len_scale)
-print("All length scales:", model.len_scale_vec)
-print("Main integral scale:", model.integral_scale)
-print("All integral scales:", model.integral_scale_vec)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Percentile scale
-# ----------------
-#
-# Another scale characterizing the covariance model, is the percentile scale.
-# It is the distance, where the normalized
-# variogram reaches a certain percentage of its sill.
-
-model = gs.Stable(dim=3, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-per_scale = model.percentile_scale(0.9)
-int_scale = model.integral_scale
-len_scale = model.len_scale
-print("90% Percentile scale:", per_scale)
-print("Integral scale:", int_scale)
-print("Length scale:", len_scale)
-
-###############################################################################
-# .. note::
-#
-# The nugget is neglected by the percentile scale.
-#
-#
-# Comparison
-# ----------
-
-ax = model.plot()
-ax.axhline(1.8, color="k", label=r"90% percentile")
-ax.axvline(per_scale, color="k", linestyle="--", label=r"90% percentile scale")
-ax.axvline(int_scale, color="k", linestyle="-.", label=r"integral scale")
-ax.axvline(len_scale, color="k", linestyle=":", label=r"length scale")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/05_additional_para.py b/examples/02_cov_model/05_additional_para.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 3264cec47..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/05_additional_para.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Additional Parameters
-=====================
-
-Let's pimp our self-defined model ``Gau`` from the introductory example
-by setting the exponent as an additional parameter:
-
-.. math::
- \rho(r) := \exp\left(-\left(\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{\alpha}\right)
-
-This leads to the so called **stable** covariance model and we can define it by
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class Stab(gs.CovModel):
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- return {"alpha": 1.5}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**self.alpha))
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# As you can see, we override the method :any:`CovModel.default_opt_arg`
-# to provide a standard value for the optional argument ``alpha``.
-# We can access it in the correlation function by ``self.alpha``
-#
-# Now we can instantiate this model by either setting alpha implicitly with
-# the default value or explicitly:
-
-model1 = Stab(dim=2, var=2.0, len_scale=10)
-model2 = Stab(dim=2, var=2.0, len_scale=10, alpha=0.5)
-ax = model1.plot()
-model2.plot(ax=ax)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Apparently, the parameter alpha controls the slope of the variogram
-# and consequently the roughness of a generated random field.
-#
-# .. note::
-#
-# You don't have to override the :any:`CovModel.default_opt_arg`,
-# but you will get a ValueError if you don't set it on creation.
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/06_fitting_para_ranges.py b/examples/02_cov_model/06_fitting_para_ranges.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 7c8f083ed..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/06_fitting_para_ranges.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Fitting variogram data
-======================
-
-The model class comes with a routine to fit the model-parameters to given
-variogram data. In the following we will use the self defined stable model
-from a previous example.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class Stab(gs.CovModel):
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- return {"alpha": 1.5}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**self.alpha))
-
-
-# Exemplary variogram data (e.g. estimated from field observations)
-bins = [1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0]
-est_vario = [0.2, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 0.8, 0.9]
-# fitting model
-model = Stab(dim=2)
-# we have to provide boundaries for the parameters
-model.set_arg_bounds(alpha=[0, 3])
-results, pcov = model.fit_variogram(bins, est_vario, nugget=False)
-print("Results:", results)
-
-###############################################################################
-
-ax = model.plot()
-ax.scatter(bins, est_vario, color="k", label="sample variogram")
-ax.legend()
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# As you can see, we have to provide boundaries for the parameters.
-# As a default, the following bounds are set:
-#
-# - additional parameters: ``[-np.inf, np.inf]``
-# - variance: ``[0.0, np.inf]``
-# - len_scale: ``[0.0, np.inf]``
-# - nugget: ``[0.0, np.inf]``
-#
-# Also, you can deselect parameters from fitting, so their predefined values
-# will be kept. In our case, we fixed a ``nugget`` of ``0.0``, which was set
-# by default. You can deselect any standard or
-# optional argument of the covariance model.
-# The second return value ``pcov`` is the estimated covariance of ``popt`` from
-# the used scipy routine :any:`scipy.optimize.curve_fit`.
-#
-# You can use the following methods to manipulate the used bounds:
-#
-# .. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel
-#
-# .. autosummary::
-# CovModel.default_opt_arg_bounds
-# CovModel.default_arg_bounds
-# CovModel.set_arg_bounds
-# CovModel.check_arg_bounds
-#
-# You can override the :any:`CovModel.default_opt_arg_bounds`
-# to provide standard bounds for your additional parameters.
-#
-# To access the bounds you can use:
-#
-# .. autosummary::
-# CovModel.var_bounds
-# CovModel.len_scale_bounds
-# CovModel.nugget_bounds
-# CovModel.opt_arg_bounds
-# CovModel.arg_bounds
diff --git a/examples/02_cov_model/README.rst b/examples/02_cov_model/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 73704183c..000000000
--- a/examples/02_cov_model/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,88 +0,0 @@
-.. _tutorial_02_cov:
-
-The Covariance Model
-====================
-
-One of the core-features of GSTools is the powerful :any:`CovModel`
-class, which allows you to easily define arbitrary covariance models by
-yourself. The resulting models provide a bunch of nice features to explore the
-covariance models.
-
-A covariance model is used to characterize the
-`semi-variogram `_,
-denoted by :math:`\gamma`, of a spatial random field.
-In GSTools, we use the following form for an isotropic and stationary field:
-
-.. math::
- \gamma\left(r\right)=
- \sigma^2\cdot\left(1-\mathrm{cor}\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)\right)+n
-
-Where:
-
- - :math:`r` is the lag distance
- - :math:`\ell` is the main correlation length
- - :math:`s` is a scaling factor for unit conversion or normalization
- - :math:`\sigma^2` is the variance
- - :math:`n` is the nugget (subscale variance)
- - :math:`\mathrm{cor}(h)` is the normalized correlation function depending on
- the non-dimensional distance :math:`h=s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}`
-
-Depending on the normalized correlation function, all covariance models in
-GSTools are providing the following functions:
-
- - :math:`\rho(r)=\mathrm{cor}\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)`
- is the so called
- `correlation `_
- function
- - :math:`C(r)=\sigma^2\cdot\rho(r)` is the so called
- `covariance `_
- function, which gives the name for our GSTools class
-
-.. note::
-
- We are not limited to isotropic models. GSTools supports anisotropy ratios
- for length scales in orthogonal transversal directions like:
-
- - :math:`x_0` (main direction)
- - :math:`x_1` (1. transversal direction)
- - :math:`x_2` (2. transversal direction)
- - ...
-
- These main directions can also be rotated.
- Just have a look at the corresponding examples.
-
-Provided Covariance Models
---------------------------
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel
-
-The following standard covariance models are provided by GSTools
-
-.. autosummary::
- Gaussian
- Exponential
- Matern
- Integral
- Stable
- Rational
- Cubic
- Linear
- Circular
- Spherical
- HyperSpherical
- SuperSpherical
- JBessel
- TPLSimple
-
-As a special feature, we also provide truncated power law (TPL) covariance models
-
-.. autosummary::
- TPLGaussian
- TPLExponential
- TPLStable
-
-These models provide a lower and upper length scale truncation
-for superpositioned models.
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/00_fit_variogram.py b/examples/03_variogram/00_fit_variogram.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 7334ed2c8..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/00_fit_variogram.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Fit Variogram
--------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generate a synthetic field with an exponential model.
-
-x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.0
-y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.0
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0, seed=19970221)
-field = srf((x, y))
-
-###############################################################################
-# Estimate the variogram of the field with 40 bins.
-
-bins = np.arange(40)
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field, bins)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Fit the variogram with a stable model (no nugget fitted).
-
-fit_model = gs.Stable(dim=2)
-fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, nugget=False)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Plot the fitting result.
-
-ax = fit_model.plot(x_max=40)
-ax.scatter(bin_center, gamma)
-print(fit_model)
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/01_find_best_model.py b/examples/03_variogram/01_find_best_model.py
deleted file mode 100755
index eab031cf6..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/01_find_best_model.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Finding the best fitting variogram model
-----------------------------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generate a synthetic field with an exponential model.
-
-x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.0
-y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.0
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0, seed=19970221)
-field = srf((x, y))
-
-###############################################################################
-# Estimate the variogram of the field with 40 bins and plot the result.
-
-bins = np.arange(40)
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field, bins)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Define a set of models to test.
-
-models = {
- "Gaussian": gs.Gaussian,
- "Exponential": gs.Exponential,
- "Matern": gs.Matern,
- "Stable": gs.Stable,
- "Rational": gs.Rational,
- "Circular": gs.Circular,
- "Spherical": gs.Spherical,
- "SuperSpherical": gs.SuperSpherical,
- "JBessel": gs.JBessel,
-}
-scores = {}
-
-###############################################################################
-# Iterate over all models, fit their variogram and calculate the r2 score.
-
-# plot the estimated variogram
-plt.scatter(bin_center, gamma, color="k", label="data")
-ax = plt.gca()
-
-# fit all models to the estimated variogram
-for model in models:
- fit_model = models[model](dim=2)
- para, pcov, r2 = fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, return_r2=True)
- fit_model.plot(x_max=40, ax=ax)
- scores[model] = r2
-
-###############################################################################
-# Create a ranking based on the score and determine the best models
-
-ranking = sorted(scores.items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True)
-print("RANKING by Pseudo-r2 score")
-for i, (model, score) in enumerate(ranking, 1):
- print(f"{i:>6}. {model:>15}: {score:.5}")
-
-plt.show()
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/02_multi_vario.py b/examples/03_variogram/02_multi_vario.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 71048849d..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/02_multi_vario.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,44 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Multi-field variogram estimation
---------------------------------
-
-In this example, we demonstrate how to estimate a variogram from multiple
-fields on the same point-set that should have the same statistical properties.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.0
-y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.0
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generate two synthetic fields with an exponential model.
-
-field1 = srf((x, y), seed=19970221)
-field2 = srf((x, y), seed=20011012)
-fields = [field1, field2]
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we estimate the variograms for both fields individually and then again
-# simultaneously with only one call.
-
-bins = np.arange(40)
-bin_center, gamma1 = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field1, bins)
-bin_center, gamma2 = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field2, bins)
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), fields, bins)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we demonstrate that the mean variogram from both fields coincides
-# with the joined estimated one.
-
-plt.plot(bin_center, gamma1, label="field 1")
-plt.plot(bin_center, gamma2, label="field 2")
-plt.plot(bin_center, gamma, label="joined fields")
-plt.plot(bin_center, 0.5 * (gamma1 + gamma2), ":", label="field 1+2 mean")
-plt.legend()
-plt.show()
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/03_directional_2d.py b/examples/03_variogram/03_directional_2d.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 460c75131..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/03_directional_2d.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,66 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Directional variogram estimation and fitting in 2D
---------------------------------------------------
-
-In this example, we demonstrate how to estimate a directional variogram by
-setting the direction angles in 2D.
-
-Afterwards we will fit a model to this estimated variogram and show the result.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generating synthetic field with anisotropy and a rotation of 22.5 degree.
-
-angle = np.pi / 8
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, len_scale=[10, 5], angles=angle)
-x = y = range(101)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=123456)
-field = srf((x, y), mesh_type="structured")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we are going to estimate a directional variogram with an angular
-# tolerance of 11.25 degree and a bandwith of 8.
-
-bins = range(0, 40, 2)
-bin_center, dir_vario, counts = gs.vario_estimate(
- *((x, y), field, bins),
- direction=gs.rotated_main_axes(dim=2, angles=angle),
- angles_tol=np.pi / 16,
- bandwidth=8,
- mesh_type="structured",
- return_counts=True,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Afterwards we can use the estimated variogram to fit a model to it:
-
-print("Original:")
-print(model)
-model.fit_variogram(bin_center, dir_vario)
-print("Fitted:")
-print(model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Plotting.
-
-fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=[10, 5])
-
-ax1.scatter(bin_center, dir_vario[0], label="emp. vario: pi/8")
-ax1.scatter(bin_center, dir_vario[1], label="emp. vario: pi*5/8")
-ax1.legend(loc="lower right")
-
-model.plot("vario_axis", axis=0, ax=ax1, x_max=40, label="fit on axis 0")
-model.plot("vario_axis", axis=1, ax=ax1, x_max=40, label="fit on axis 1")
-ax1.set_title("Fitting an anisotropic model")
-
-srf.plot(ax=ax2)
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Without fitting a model, we see that the correlation length in the main
-# direction is greater than the transversal one.
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/04_directional_3d.py b/examples/03_variogram/04_directional_3d.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 6a8b6ddfa..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/04_directional_3d.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Directional variogram estimation and fitting in 3D
---------------------------------------------------
-
-In this example, we demonstrate how to estimate a directional variogram by
-setting the estimation directions in 3D.
-
-Afterwards we will fit a model to this estimated variogram and show the result.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generating synthetic field with anisotropy and rotation by Tait-Bryan angles.
-
-dim = 3
-# rotation around z, y, x
-angles = [np.deg2rad(90), np.deg2rad(45), np.deg2rad(22.5)]
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, len_scale=[16, 8, 4], angles=angles)
-x = y = z = range(50)
-pos = (x, y, z)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=1001)
-field = srf.structured(pos)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Here we generate the axes of the rotated coordinate system
-# to get an impression what the rotation angles do.
-
-# All 3 axes of the rotated coordinate-system
-main_axes = gs.rotated_main_axes(dim, angles)
-axis1, axis2, axis3 = main_axes
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we estimate the variogram along the main axes. When the main axes are
-# unknown, one would need to sample multiple directions and look for the one
-# with the longest correlation length (flattest gradient).
-# Then check the transversal directions and so on.
-
-bin_center, dir_vario, counts = gs.vario_estimate(
- pos,
- field,
- direction=main_axes,
- bandwidth=10,
- sampling_size=2000,
- sampling_seed=1001,
- mesh_type="structured",
- return_counts=True,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Afterwards we can use the estimated variogram to fit a model to it.
-# Note, that the rotation angles need to be set beforehand.
-
-print("Original:")
-print(model)
-model.fit_variogram(bin_center, dir_vario)
-print("Fitted:")
-print(model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Plotting main axes and the fitted directional variogram.
-
-fig = plt.figure(figsize=[10, 5])
-ax1 = fig.add_subplot(121, projection=Axes3D.name)
-ax2 = fig.add_subplot(122)
-
-ax1.plot([0, axis1[0]], [0, axis1[1]], [0, axis1[2]], label="0.")
-ax1.plot([0, axis2[0]], [0, axis2[1]], [0, axis2[2]], label="1.")
-ax1.plot([0, axis3[0]], [0, axis3[1]], [0, axis3[2]], label="2.")
-ax1.set_xlim(-1, 1)
-ax1.set_ylim(-1, 1)
-ax1.set_zlim(-1, 1)
-ax1.set_xlabel("X")
-ax1.set_ylabel("Y")
-ax1.set_zlabel("Z")
-ax1.set_title("Tait-Bryan main axis")
-ax1.legend(loc="lower left")
-
-x_max = max(bin_center)
-ax2.scatter(bin_center, dir_vario[0], label="0. axis")
-ax2.scatter(bin_center, dir_vario[1], label="1. axis")
-ax2.scatter(bin_center, dir_vario[2], label="2. axis")
-model.plot("vario_axis", axis=0, ax=ax2, x_max=x_max, label="fit on axis 0")
-model.plot("vario_axis", axis=1, ax=ax2, x_max=x_max, label="fit on axis 1")
-model.plot("vario_axis", axis=2, ax=ax2, x_max=x_max, label="fit on axis 2")
-ax2.set_title("Fitting an anisotropic model")
-ax2.legend()
-
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Also, let's have a look at the field.
-
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/05_auto_fit_variogram.py b/examples/03_variogram/05_auto_fit_variogram.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 2fcc7fbd6..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/05_auto_fit_variogram.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Fit Variogram with automatic binning
-------------------------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-###############################################################################
-# Generate a synthetic field with an exponential model.
-
-x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(1000) * 100.0
-y = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(1000) * 100.0
-model = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=2, len_scale=8)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=0, seed=19970221)
-field = srf((x, y))
-print(field.var())
-###############################################################################
-# Estimate the variogram of the field with automatic binning.
-
-bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field)
-print("estimated bin number:", len(bin_center))
-print("maximal bin distance:", max(bin_center))
-
-###############################################################################
-# Fit the variogram with a stable model (no nugget fitted).
-
-fit_model = gs.Stable(dim=2)
-fit_model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma, nugget=False)
-print(fit_model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Plot the fitting result.
-
-ax = fit_model.plot(x_max=max(bin_center))
-ax.scatter(bin_center, gamma)
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/06_auto_bin_latlon.py b/examples/03_variogram/06_auto_bin_latlon.py
deleted file mode 100644
index cc248ea16..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/06_auto_bin_latlon.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,90 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Automatic binning with lat-lon data
------------------------------------
-
-In this example we demonstrate automatic binning for a tiny data set
-containing temperature records from Germany
-(See the detailed DWD example for more information on the data).
-
-We use a data set from 20 meteo-stations choosen randomly.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# lat, lon, temperature
-data = np.array(
- [
- [52.9336, 8.237, 15.7],
- [48.6159, 13.0506, 13.9],
- [52.4853, 7.9126, 15.1],
- [50.7446, 9.345, 17.0],
- [52.9437, 12.8518, 21.9],
- [53.8633, 8.1275, 11.9],
- [47.8342, 10.8667, 11.4],
- [51.0881, 12.9326, 17.2],
- [48.406, 11.3117, 12.9],
- [49.7273, 8.1164, 17.2],
- [49.4691, 11.8546, 13.4],
- [48.0197, 12.2925, 13.9],
- [50.4237, 7.4202, 18.1],
- [53.0316, 13.9908, 21.3],
- [53.8412, 13.6846, 21.3],
- [54.6792, 13.4343, 17.4],
- [49.9694, 9.9114, 18.6],
- [51.3745, 11.292, 20.2],
- [47.8774, 11.3643, 12.7],
- [50.5908, 12.7139, 15.8],
- ]
-)
-pos = data.T[:2] # lat, lon
-field = data.T[2] # temperature
-
-###############################################################################
-# Since the overall range of these meteo-stations is too low, we can use the
-# data-variance as additional information during the fit of the variogram.
-
-emp_v = gs.vario_estimate(pos, field, latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-sph = gs.Spherical(latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-sph.fit_variogram(*emp_v, sill=np.var(field))
-ax = sph.plot("vario_yadrenko", x_max=2 * np.max(emp_v[0]))
-ax.scatter(*emp_v, label="Empirical variogram")
-ax.legend()
-print(sph)
-
-###############################################################################
-# As we can see, the variogram fitting was successful and providing the data
-# variance helped finding the right length-scale.
-#
-# Now, we'll use this covariance model to interpolate the given data with
-# ordinary kriging.
-
-# enclosing box for data points
-grid_lat = np.linspace(np.min(pos[0]), np.max(pos[0]))
-grid_lon = np.linspace(np.min(pos[1]), np.max(pos[1]))
-# ordinary kriging
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(sph, pos, field)
-krige((grid_lat, grid_lon), mesh_type="structured")
-ax = krige.plot()
-# plotting lat on y-axis and lon on x-axis
-ax.scatter(pos[1], pos[0], 50, c=field, edgecolors="k", label="input")
-ax.legend()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Looks good, doesn't it?
-#
-# This workflow is also implemented in the :any:`Krige` class, by setting
-# ``fit_variogram=True``. Then the whole procedure shortens:
-
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(sph, pos, field, fit_variogram=True)
-krige.structured((grid_lat, grid_lon))
-
-# plot the result
-krige.plot()
-# show the fitting results
-print(krige.model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# This example shows, that setting up variogram estimation and kriging routines
-# is straight forward with GSTools!
diff --git a/examples/03_variogram/README.rst b/examples/03_variogram/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 8eb42a8a8..000000000
--- a/examples/03_variogram/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,14 +0,0 @@
-Variogram Estimation
-====================
-
-Estimating the spatial correlations is an important part of geostatistics.
-These spatial correlations can be expressed by the variogram, which can be
-estimated with the subpackage :any:`gstools.variogram`. The variograms can be
-estimated on structured and unstructured grids.
-
-The same `(semi-)variogram `_ as
-:ref:`tutorial_02_cov` is being used
-by this subpackage.
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/04_vector_field/00_2d_vector_field.py b/examples/04_vector_field/00_2d_vector_field.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 2e7227642..000000000
--- a/examples/04_vector_field/00_2d_vector_field.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,47 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Generating a Random 2D Vector Field
------------------------------------
-
-As a first example we are going to generate a 2d vector field with a Gaussian
-covariance model on a structured grid:
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# the grid
-x = np.arange(100)
-y = np.arange(100)
-
-# a smooth Gaussian covariance model
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, generator="VectorField", seed=19841203)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type="structured")
-srf.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Let us have a look at the influence of the covariance model. Choosing the
-# exponential model and keeping all other parameters the same
-
-# a rougher exponential covariance model
-model2 = gs.Exponential(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf.model = model2
-srf((x, y), mesh_type="structured", seed=19841203)
-srf.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# and we see, that the wiggles are much "rougher" than the smooth Gaussian ones.
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# Applications
-# ~~~~~~~~~~~~
-#
-# One great advantage of the Kraichnan method is, that after some initializations,
-# one can compute the velocity field at arbitrary points, online, with hardly any
-# overhead.
-# This means, that for a Lagrangian transport simulation for example, the velocity
-# can be evaluated at each particle position very efficiently and without any
-# interpolation. These field interpolations are a common problem for Lagrangian
-# methods.
diff --git a/examples/04_vector_field/01_3d_vector_field.py b/examples/04_vector_field/01_3d_vector_field.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 5b1872bd4..000000000
--- a/examples/04_vector_field/01_3d_vector_field.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Generating a Random 3D Vector Field
------------------------------------
-
-In this example we are going to generate a random 3D vector field with a
-Gaussian covariance model. The mesh on which we generate the field will be
-externally defined and it will be generated by PyVista.
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_path = 'pics/GS_3d_vector_field.png'
-import pyvista as pv
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# mainly for setting a white background
-pv.set_plot_theme("document")
-
-###############################################################################
-# create a uniform grid with PyVista
-dims, spacing, origin = (40, 30, 10), (1, 1, 1), (-10, 0, 0)
-mesh = pv.ImageData(dimensions=dims, spacing=spacing, origin=origin)
-
-###############################################################################
-# create an incompressible random 3d velocity field on the given mesh
-# with added mean velocity in x-direction
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, var=3, len_scale=1.5)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=(0.5, 0, 0), generator="VectorField", seed=198412031)
-srf.mesh(mesh, points="points", name="Velocity")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now, we can do the plotting
-streamlines = mesh.streamlines(
- "Velocity",
- terminal_speed=0.0,
- n_points=800,
- source_radius=2.5,
-)
-
-# set a fancy camera position
-cpos = [(25, 23, 17), (0, 10, 0), (0, 0, 1)]
-
-p = pv.Plotter()
-# adding an outline might help navigating in 3D space
-# p.add_mesh(mesh.outline(), color="k")
-p.add_mesh(
- streamlines.tube(radius=0.005),
- show_scalar_bar=False,
- diffuse=0.5,
- ambient=0.5,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# .. note::
-# PyVista is not working on readthedocs, but you can try it out yourself by
-# uncommenting the following line of code.
-
-# p.show(cpos=cpos)
-
-###############################################################################
-# The result should look like this:
-#
-# .. image:: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GeoStat-Framework.github.io/raw/master/img/GS_3d_vector_field.png
-# :width: 400px
-# :align: center
diff --git a/examples/04_vector_field/README.rst b/examples/04_vector_field/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index cbe397125..000000000
--- a/examples/04_vector_field/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,37 +0,0 @@
-Random Vector Field Generation
-==============================
-
-In 1970, Kraichnan was the first to suggest a randomization method.
-For studying the diffusion of single particles in a random incompressible
-velocity field, he came up with a randomization method which includes a
-projector which ensures the incompressibility of the vector field.
-
-
-Without loss of generality we assume that the mean velocity :math:`\bar{U}` is oriented
-towards the direction of the first basis vector :math:`\mathbf{e}_1`. Our goal is now to
-generate random fluctuations with a given covariance model around this mean velocity.
-And at the same time, making sure that the velocity field remains incompressible or
-in other words, ensure :math:`\nabla \cdot \mathbf U = 0`.
-This can be done by using the randomization method we already know, but adding a
-projector to every mode being summed:
-
-
-.. math::
-
- \mathbf{U}(\mathbf{x}) = \bar{U} \mathbf{e}_1 - \sqrt{\frac{\sigma^{2}}{N}}
- \sum_{i=1}^{N} \mathbf{p}(\mathbf{k}_i) \left[ Z_{1,i}
- \cos\left( \langle \mathbf{k}_{i}, \mathbf{x} \rangle \right)
- + \sin\left( \langle \mathbf{k}_{i}, \mathbf{x} \rangle \right) \right]
-
-with the projector
-
-.. math::
-
- \mathbf{p}(\mathbf{k}_i) = \mathbf{e}_1 - \frac{\mathbf{k}_i k_1}{k^2} \; .
-
-By calculating :math:`\nabla \cdot \mathbf U = 0`, it can be verified, that
-the resulting field is indeed incompressible.
-
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/00_simple_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/00_simple_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 1a245b6c3..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/00_simple_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Simple Kriging
---------------
-
-Simple kriging assumes a known mean of the data.
-For simplicity we assume a mean of 0,
-which can be achieved by subtracting the mean from the observed values and
-subsequently adding it to the resulting data.
-
-The resulting equation system for :math:`W` is given by:
-
-.. math::
-
- W = \begin{pmatrix}c(x_1,x_1) & \cdots & c(x_1,x_n) \\
- \vdots & \ddots & \vdots \\
- c(x_n,x_1) & \cdots & c(x_n,x_n)
- \end{pmatrix}^{-1}
- \begin{pmatrix}c(x_1,x_0) \\ \vdots \\ c(x_n,x_0) \end{pmatrix}
-
-Thereby :math:`c(x_i,x_j)` is the covariance of the given observations.
-
-
-Example
-^^^^^^^
-
-Here we use simple kriging in 1D (for plotting reasons) with 5 given observations/conditions.
-The mean of the field has to be given beforehand.
-
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import Gaussian, krige
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-# spatial random field class
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
-
-###############################################################################
-krig = krige.Simple(model, mean=1, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-krig(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/01_ordinary_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/01_ordinary_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d26254ef2..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/01_ordinary_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Ordinary Kriging
-----------------
-
-Ordinary kriging will estimate an appropriate mean of the field,
-based on the given observations/conditions and the covariance model used.
-
-The resulting system of equations for :math:`W` is given by:
-
-.. math::
-
- \begin{pmatrix}W\\\mu\end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}
- c(x_1,x_1) & \cdots & c(x_1,x_n) &1 \\
- \vdots & \ddots & \vdots & \vdots \\
- c(x_n,x_1) & \cdots & c(x_n,x_n) & 1 \\
- 1 &\cdots& 1 & 0
- \end{pmatrix}^{-1}
- \begin{pmatrix}c(x_1,x_0) \\ \vdots \\ c(x_n,x_0) \\ 1\end{pmatrix}
-
-Thereby :math:`c(x_i,x_j)` is the covariance of the given observations
-and :math:`\mu` is a Lagrange multiplier to minimize the kriging error and estimate the mean.
-
-
-Example
-^^^^^^^
-
-Here we use ordinary kriging in 1D (for plotting reasons) with 5 given observations/conditions.
-The estimated mean can be accessed by ``krig.mean``.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import Gaussian, krige
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-# spatial random field class
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
-
-###############################################################################
-krig = krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-krig(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/02_pykrige_interface.py b/examples/05_kriging/02_pykrige_interface.py
deleted file mode 100755
index a6fbf03e1..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/02_pykrige_interface.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Interface to PyKrige
---------------------
-
-To use fancier methods like
-`regression kriging `__,
-we provide an interface to
-`PyKrige `__ (>v1.5), which means
-you can pass a GSTools covariance model to the kriging routines of PyKrige.
-
-To demonstrate the general workflow, we compare ordinary kriging of PyKrige
-with the corresponding GSTools routine in 2D:
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
-from pykrige.ok import OrdinaryKriging
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# conditioning data
-cond_x = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_y = [1.2, 0.6, 3.2, 4.4, 3.8]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-
-# grid definition for output field
-gridx = np.arange(0.0, 5.5, 0.1)
-gridy = np.arange(0.0, 6.5, 0.1)
-
-###############################################################################
-# A GSTools based :any:`Gaussian` covariance model:
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(
- dim=2, len_scale=1, anis=0.2, angles=-0.5, var=0.5, nugget=0.1
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Ordinary Kriging with PyKrige
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# One can pass the defined GSTools model as
-# variogram model, which will `not` be fitted to the given data.
-# By providing the GSTools model, rotation and anisotropy are also
-# automatically defined:
-
-OK1 = OrdinaryKriging(cond_x, cond_y, cond_val, variogram_model=model)
-z1, ss1 = OK1.execute("grid", gridx, gridy)
-plt.imshow(z1, origin="lower")
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Ordinary Kriging with GSTools
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# The :any:`Ordinary` kriging class is provided by GSTools as a shortcut to
-# define ordinary kriging with the general :any:`Krige` class.
-#
-# PyKrige's routines are using exact kriging by default (when given a nugget).
-# To reproduce this behavior in GSTools, we have to set ``exact=True``.
-
-OK2 = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, [cond_x, cond_y], cond_val, exact=True)
-OK2.structured([gridx, gridy])
-ax = OK2.plot()
-ax.set_aspect("equal")
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/03_compare_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/03_compare_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 463faa0a6..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/03_compare_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Compare Kriging
----------------
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import Gaussian, krige
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-
-###############################################################################
-# A gaussian variogram model.
-
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Two kriged fields. One with simple and one with ordinary kriging.
-
-kr1 = krige.Simple(model=model, mean=1, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-kr2 = krige.Ordinary(model=model, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-kr1(gridx)
-kr2(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-
-plt.plot(gridx, kr1.field, label="simple kriged field")
-plt.plot(gridx, kr2.field, label="ordinary kriged field")
-plt.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-plt.legend()
-plt.show()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/04_extdrift_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/04_extdrift_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 2e6a168a5..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/04_extdrift_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-"""
-External Drift Kriging
-----------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import SRF, Gaussian, krige
-
-# synthetic condtions with a drift
-drift_model = Gaussian(dim=1, len_scale=4)
-drift = SRF(drift_model, seed=1010)
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-ext_drift = drift(cond_pos)
-cond_val = ext_drift * 2 + 1
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-grid_drift = drift(gridx)
-# kriging
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=2, len_scale=4)
-krig = krige.ExtDrift(model, cond_pos, cond_val, ext_drift)
-krig(gridx, ext_drift=grid_drift)
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.plot(gridx, grid_drift, label="drift")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/05_universal_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/05_universal_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 5501694ad..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/05_universal_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Universal Kriging
------------------
-
-You can give a polynomial order or a list of self defined
-functions representing the internal drift of the given values.
-This drift will be fitted internally during the kriging interpolation.
-
-In the following we are creating artificial data, where a linear drift
-was added. The resulting samples are then used as input for Universal kriging.
-
-The "linear" drift is then estimated during the interpolation.
-To access only the estimated mean/drift, we provide a switch `only_mean`
-in the call routine.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import SRF, Gaussian, krige
-
-# synthetic condtions with a drift
-drift_model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-drift = SRF(drift_model, seed=101)
-cond_pos = np.linspace(0.1, 8, 10)
-cond_val = drift(cond_pos) + cond_pos * 0.1 + 1
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-drift_field = drift(gridx) + gridx * 0.1 + 1
-# kriging
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-krig = krige.Universal(model, cond_pos, cond_val, "linear")
-krig(gridx)
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.plot(gridx, gridx * 0.1 + 1, ":", label="linear drift")
-ax.plot(gridx, drift_field, "--", label="original field")
-
-mean = krig(gridx, only_mean=True)
-ax.plot(gridx, mean, label="estimated drift")
-
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/06_detrended_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/06_detrended_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 6d20cf1db..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/06_detrended_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Detrended Kriging
------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import SRF, Gaussian, krige
-
-
-def trend(x):
- """Example for a simple linear trend."""
- return x * 0.1 + 1
-
-
-# synthetic condtions with trend/drift
-drift_model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-drift = SRF(drift_model, seed=101)
-cond_pos = np.linspace(0.1, 8, 10)
-cond_val = drift(cond_pos) + trend(cond_pos)
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-drift_field = drift(gridx) + trend(gridx)
-# kriging
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-krig_trend = krige.Detrended(model, cond_pos, cond_val, trend)
-krig_trend(gridx)
-ax = krig_trend.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.plot(gridx, trend(gridx), ":", label="linear trend")
-ax.plot(gridx, drift_field, "--", label="original field")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/07_detrended_ordinary_kriging.py b/examples/05_kriging/07_detrended_ordinary_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 81d017447..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/07_detrended_ordinary_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,32 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Detrended Ordinary Kriging
---------------------------
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import SRF, Gaussian, krige
-
-
-def trend(x):
- """Example for a simple linear trend."""
- return x * 0.1 + 1
-
-
-# synthetic condtions with trend/drift
-drift_model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-drift = SRF(drift_model, seed=101)
-cond_pos = np.linspace(0.1, 8, 10)
-cond_val = drift(cond_pos) + trend(cond_pos)
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-drift_field = drift(gridx) + trend(gridx)
-# kriging
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.1, len_scale=2)
-krig_trend = krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos, cond_val, trend=trend)
-krig_trend(gridx)
-ax = krig_trend.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.plot(gridx, trend(gridx), ":", label="linear trend")
-ax.plot(gridx, drift_field, "--", label="original field")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/08_measurement_errors.py b/examples/05_kriging/08_measurement_errors.py
deleted file mode 100755
index c2965ca0c..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/08_measurement_errors.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,56 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Incorporating measurement errors
---------------------------------
-
-To incorporate the nugget effect and/or given measurement errors,
-one can set `exact` to `False` and provide either individual measurement errors
-for each point or set the nugget as a constant measurement error everywhere.
-
-In the following we will show the influence of the nugget and
-measurement errors.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.1, 1.9, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.74, 0.56, 1.47, 1.74]
-cond_err = [0.01, 0.0, 0.1, 0.05, 0]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-# spatial random field class
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.9, len_scale=1, nugget=0.1)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Here we will use Simple kriging (`unbiased=False`) to interpolate the given
-# conditions.
-
-krig = gs.Krige(
- model=model,
- cond_pos=cond_pos,
- cond_val=cond_val,
- mean=1,
- unbiased=False,
- exact=False,
- cond_err=cond_err,
-)
-krig(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Let's plot the data. You can see, that the estimated values differ more from
-# the input, when the given measurement errors get bigger.
-# In addition we plot the standard deviation.
-
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.fill_between(
- gridx,
- # plus/minus standard deviation (70 percent confidence interval)
- krig.field - np.sqrt(krig.krige_var),
- krig.field + np.sqrt(krig.krige_var),
- alpha=0.3,
- label="Standard deviation",
-)
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/09_pseudo_inverse.py b/examples/05_kriging/09_pseudo_inverse.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 7615d8886..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/09_pseudo_inverse.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Redundant data and pseudo-inverse
----------------------------------
-
-It can happen, that the kriging system gets numerically unstable.
-One reason could be, that the input data contains redundant conditioning points
-that hold different values.
-
-To smoothly deal with such situations, you can use the pseudo
-inverse for the kriging matrix, which is enabled by default.
-
-This will result in the average value for the redundant data.
-
-Example
-^^^^^^^
-
-In the following we have two different values at the same location.
-The resulting kriging field will hold the average at this point.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import Gaussian, krige
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 1.1]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.14]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 8.0, 81)
-# spatial random field class
-model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=1)
-
-###############################################################################
-krig = krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-krig(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-ax = krig.plot()
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/05_kriging/README.rst b/examples/05_kriging/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index ef92e425f..000000000
--- a/examples/05_kriging/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,100 +0,0 @@
-.. _tutorial_05_kriging:
-
-Kriging
-=======
-
-The subpackage :py:mod:`gstools.krige` provides routines for Gaussian process regression,
-also known as kriging.
-Kriging is a method of data interpolation based on predefined covariance models.
-
-The aim of kriging is to derive the value of a field at some point :math:`x_0`,
-when there are fixed observed values :math:`z(x_1)\ldots z(x_n)` at given points :math:`x_i`.
-
-The resluting value :math:`z_0` at :math:`x_0` is calculated as a weighted mean:
-
-.. math::
-
- z_0 = \sum_{i=1}^n w_i \cdot z_i
-
-The weights :math:`W = (w_1,\ldots,w_n)` depent on the given covariance model and the location of the target point.
-
-The different kriging approaches provide different ways of calculating :math:`W`.
-
-The :any:`Krige` class provides everything in one place and you can switch on/off
-the features you want:
-
-* `unbiased`: the weights have to sum up to `1`. If true, this results in
- :any:`Ordinary` kriging, where the mean is estimated, otherwise it will result in
- :any:`Simple` kriging, where the mean has to be given.
-* `drift_functions`: you can give a polynomial order or a list of self defined
- functions representing the internal drift of the given values. This drift will
- be fitted internally during the kriging interpolation. This results in :any:`Universal` kriging.
-* `ext_drift`: You can also give an external drift per point to the routine.
- In contrast to the internal drift, that is evaluated at the desired points with
- the given functions, the external drift has to given for each point form an "external"
- source. This results in :any:`ExtDrift` kriging.
-* `trend`, `mean`, `normalizer`: These are used to pre- and post-process data.
- If you already have fitted a trend model that is provided as a callable function,
- you can give it to the kriging routine. Normalizer are power-transformations
- to gain normality.
- `mean` behaves similar to `trend` but is applied at another position:
-
- 1. conditioning data is de-trended (substracting trend)
- 2. detrended conditioning data is then normalized (in order to follow a normal distribution)
- 3. normalized conditioning data is set to zero mean (subtracting mean)
-
- Cosequently, when there is no normalizer given, trend and mean are the same thing
- and only one should be used.
- :any:`Detrended` kriging is a shortcut to provide only a trend and simple kriging
- with normal data.
-* `exact` and `cond_err`: To incorporate the nugget effect and/or measurement errors,
- one can set `exact` to `False` and provide either individual measurement errors
- for each point or set the nugget as a constant measurement error everywhere.
-* `pseudo_inv`: Sometimes the inversion of the kriging matrix can be numerically unstable.
- This occurs for examples in cases of redundant input values. In this case we provide a switch to
- use the pseudo-inverse of the matrix. Then redundant conditional values will automatically
- be averaged.
-
-.. note::
-
- All mentioned features can be combined within the :any:`Krige` class.
- All other kriging classes are just shortcuts to this class with a limited list
- of input parameters.
-
-The routines for kriging are almost identical to the routines for spatial random fields,
-with regard to their handling.
-First you define a covariance model, as described in :ref:`tutorial_02_cov`,
-then you initialize the kriging class with this model:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- # condtions
- cond_pos = [...]
- cond_val = [...]
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
- krig = gs.krige.Simple(model, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val, mean=1)
-
-The resulting field instance ``krig`` has the same methods as the
-:any:`SRF` class.
-You can call it to evaluate the kriged field at different points,
-you can plot the latest field or you can export the field and so on.
-
-Provided Kriging Methods
-------------------------
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige
-
-The following kriging methods are provided within the
-submodule :any:`gstools.krige`.
-
-.. autosummary::
- Krige
- Simple
- Ordinary
- Universal
- ExtDrift
- Detrended
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/00_condition_ensemble.py b/examples/06_conditioned_fields/00_condition_ensemble.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 5cc07eedf..000000000
--- a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/00_condition_ensemble.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Conditioning with Ordinary Kriging
-----------------------------------
-
-Here we use ordinary kriging in 1D (for plotting reasons)
-with 5 given observations/conditions,
-to generate an ensemble of conditioned random fields.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-
-###############################################################################
-# The conditioned spatial random field class depends on a Krige class in order
-# to handle the conditions.
-# This is created as described in the kriging tutorial.
-#
-# Here we use a Gaussian covariance model and ordinary kriging for conditioning
-# the spatial random field.
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=1.5)
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos, cond_val)
-cond_srf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
-cond_srf.set_pos(gridx)
-
-###############################################################################
-# To generate the ensemble we will use a seed-generator.
-# We can specify individual names for each field by the keyword `store`:
-
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(20170519)
-for i in range(100):
- cond_srf(seed=seed(), store=f"f{i}")
- label = "Conditioned ensemble" if i == 0 else None
- plt.plot(gridx, cond_srf[f"f{i}"], color="k", alpha=0.1, label=label)
-
-fields = [cond_srf[f"f{i}"] for i in range(100)]
-plt.plot(gridx, cond_srf.krige(only_mean=True), label="estimated mean")
-plt.plot(gridx, np.mean(fields, axis=0), linestyle=":", label="Ensemble mean")
-plt.plot(gridx, cond_srf.krige.field, linestyle="dashed", label="kriged field")
-plt.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-# 99 percent confidence interval
-conf = gs.tools.confidence_scaling(0.99)
-plt.fill_between(
- gridx,
- cond_srf.krige.field - conf * np.sqrt(cond_srf.krige.krige_var),
- cond_srf.krige.field + conf * np.sqrt(cond_srf.krige.krige_var),
- alpha=0.3,
- label="99% confidence interval",
-)
-plt.legend()
-plt.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# As you can see, the kriging field coincides with the ensemble mean of the
-# conditioned random fields and the estimated mean
-# is the mean of the far-field.
diff --git a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/01_2D_condition_ensemble.py b/examples/06_conditioned_fields/01_2D_condition_ensemble.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 81f514647..000000000
--- a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/01_2D_condition_ensemble.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,71 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Creating an Ensemble of conditioned 2D Fields
----------------------------------------------
-
-Let's create an ensemble of conditioned random fields in 2D.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# conditioning data (x, y, value)
-cond_pos = [[0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7], [1.2, 0.6, 3.2, 4.4, 3.8]]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-
-# grid definition for output field
-x = np.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
-y = np.arange(0, 5, 0.1)
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=0.5, len_scale=5, anis=0.5, angles=-0.5)
-krige = gs.Krige(model, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
-cond_srf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
-cond_srf.set_pos([x, y], "structured")
-
-###############################################################################
-# To generate the ensemble we will use a seed-generator.
-# By specifying ``store=[f"fld{i}", False, False]``, only the conditioned field
-# is stored with the specified name. The raw random field and the raw kriging
-# field is not stored. This way, we can access each conditioned field by index
-# ``cond_srf[i]``:
-
-seed = gs.random.MasterRNG(20170519)
-ens_no = 4
-for i in range(ens_no):
- cond_srf(seed=seed(), store=[f"fld{i}", False, False])
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now let's have a look at the pairwise differences between the generated
-# fields. We will see, that they coincide at the given conditions.
-
-fig, ax = plt.subplots(ens_no + 1, ens_no + 1, figsize=(8, 8))
-# plotting kwargs for scatter and image
-vmax = np.max(cond_srf.all_fields)
-sc_kw = dict(c=cond_val, edgecolors="k", vmin=0, vmax=vmax)
-im_kw = dict(extent=2 * [0, 5], origin="lower", vmin=0, vmax=vmax)
-for i in range(ens_no):
- # conditioned fields and conditions
- ax[i + 1, 0].imshow(cond_srf[i].T, **im_kw)
- ax[i + 1, 0].scatter(*cond_pos, **sc_kw)
- ax[i + 1, 0].set_ylabel(f"Field {i}", fontsize=10)
- ax[0, i + 1].imshow(cond_srf[i].T, **im_kw)
- ax[0, i + 1].scatter(*cond_pos, **sc_kw)
- ax[0, i + 1].set_title(f"Field {i}", fontsize=10)
- # absolute differences
- for j in range(ens_no):
- ax[i + 1, j + 1].imshow(np.abs(cond_srf[i] - cond_srf[j]).T, **im_kw)
-
-# beautify plots
-ax[0, 0].axis("off")
-for a in ax.flatten():
- a.set_xticklabels([]), a.set_yticklabels([])
- a.set_xticks([]), a.set_yticks([])
-fig.subplots_adjust(wspace=0, hspace=0)
-fig.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# To check if the generated fields are correct, we can have a look at their
-# names:
-
-print(cond_srf.field_names)
diff --git a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/README.rst b/examples/06_conditioned_fields/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 4d7e67981..000000000
--- a/examples/06_conditioned_fields/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,26 +0,0 @@
-Conditioned Fields
-==================
-
-Kriged fields tend to approach the field mean outside the area of observations.
-To generate random fields, that coincide with given observations, but are still
-random according to a given covariance model away from the observations proximity,
-we provide the generation of conditioned random fields.
-
-The idea behind conditioned random fields builds up on kriging.
-First we generate a field with a kriging method, then we generate a random field,
-with 0 as mean and 1 as variance that will be multiplied with the kriging
-standard deviation.
-
-To do so, you can instantiate a :any:`CondSRF` class with a configured
-:any:`Krige` class.
-
-The setup of the a conditioned random field should be as follows:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- krige = gs.Krige(model, cond_pos, cond_val)
- cond_srf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
- field = cond_srf(grid)
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/00_log_normal.py b/examples/07_transformations/00_log_normal.py
deleted file mode 100755
index d44c16270..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/00_log_normal.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,18 +0,0 @@
-"""
-log-normal fields
------------------
-
-Here we transform a field to a log-normal distribution:
-
-See :any:`transform.normal_to_lognormal`
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.transform("normal_to_lognormal") # also "lognormal" works
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/01_binary.py b/examples/07_transformations/01_binary.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 125e29d06..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/01_binary.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,20 +0,0 @@
-"""
-binary fields
--------------
-
-Here we transform a field to a binary field with only two values.
-The dividing value is the mean by default and the upper and lower values
-are derived to preserve the variance.
-
-See :any:`transform.binary`
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.transform("binary")
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/02_discrete.py b/examples/07_transformations/02_discrete.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 48f67a2d7..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/02_discrete.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,45 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Discrete fields
----------------
-
-Here we transform a field to a discrete field with values.
-If we do not give thresholds, the pairwise means of the given
-values are taken as thresholds.
-If thresholds are given, arbitrary values can be applied to the field.
-
-See :any:`transform.discrete`
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# Structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 0.5x0.5
-x = y = np.arange(200) * 0.5
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=5)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-
-###############################################################################
-# Create 5 equidistanly spaced values, thresholds are the arithmetic means
-
-values1 = np.linspace(np.min(srf.field), np.max(srf.field), 5)
-srf.transform("discrete", store="f1", values=values1)
-srf.plot("f1")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Calculate thresholds for equal shares
-# but apply different values to the separated classes
-
-values2 = [0, -1, 2, -3, 4]
-srf.transform("discrete", store="f2", values=values2, thresholds="equal")
-srf.plot("f2")
-
-###############################################################################
-# Create user defined thresholds
-# and apply different values to the separated classes
-
-values3 = [0, 1, 10]
-thresholds = [-1, 1]
-srf.transform("discrete", store="f3", values=values3, thresholds=thresholds)
-srf.plot("f3")
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/03_zinn_harvey.py b/examples/07_transformations/03_zinn_harvey.py
deleted file mode 100755
index fad1fb64e..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/03_zinn_harvey.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,21 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Zinn & Harvey transformation
-----------------------------
-
-Here, we transform a field with the so called "Zinn & Harvey" transformation presented in
-`Zinn & Harvey (2003) `__.
-With this transformation, one could overcome the restriction that in ordinary
-Gaussian random fields the mean values are the ones being the most connected.
-
-See :any:`transform.zinnharvey`
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.transform("zinnharvey", conn="high")
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/04_bimodal.py b/examples/07_transformations/04_bimodal.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 4dd6fb298..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/04_bimodal.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,23 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Bimodal fields
---------------
-
-We provide two transformations to obtain bimodal distributions:
-
-* `arcsin `__.
-* `uquad `__.
-
-Both transformations will preserve the mean and variance of the given field by default.
-
-See: :any:`transform.normal_to_arcsin` and :any:`transform.normal_to_uquad`
-"""
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519)
-field = srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.transform("normal_to_arcsin") # also "arcsin" works
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/05_combinations.py b/examples/07_transformations/05_combinations.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 1fbe367e4..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/05_combinations.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,41 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Combinations
-------------
-
-You can combine different transformations simply by successively applying them.
-
-Here, we first force the single field realization to hold the given moments,
-namely mean and variance.
-Then we apply the Zinn & Harvey transformation to connect the low values.
-Afterwards the field is transformed to a binary field and last but not least,
-we transform it to log-values.
-
-We can select the desired field by its name and we can define an output name
-to store the field.
-
-If you don't specify `field` and `store` everything happens inplace.
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 1
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with a size of 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, mean=-9, seed=20170519)
-srf.structured([x, y])
-srf.transform("force_moments", field="field", store="f_forced")
-srf.transform("zinnharvey", field="f_forced", store="f_zinnharvey", conn="low")
-srf.transform("binary", field="f_zinnharvey", store="f_binary")
-srf.transform("lognormal", field="f_binary", store="f_result")
-srf.plot(field="f_result")
-
-###############################################################################
-# The resulting field could be interpreted as a transmissivity field, where
-# the values of low permeability are the ones being the most connected
-# and only two kinds of soil exist.
-#
-# All stored fields can be accessed and plotted by name:
-
-print("Max binary value:", srf.f_binary.max())
-srf.plot(field="f_zinnharvey")
diff --git a/examples/07_transformations/README.rst b/examples/07_transformations/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index d93c99307..000000000
--- a/examples/07_transformations/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,50 +0,0 @@
-Field transformations
-=====================
-
-The generated fields of gstools are ordinary Gaussian random fields.
-In application there are several transformations to describe real world
-problems in an appropriate manner.
-
-GStools provides a submodule :py:mod:`gstools.transform` with a range of
-common transformations:
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.transform
-
-.. autosummary::
- binary
- discrete
- boxcox
- zinnharvey
- normal_force_moments
- normal_to_lognormal
- normal_to_uniform
- normal_to_arcsin
- normal_to_uquad
- apply_function
-
-
-All the transformations take a field class, that holds a generated field,
-as input and will manipulate this field inplace or store it with a given name.
-
-Simply apply a transformation to a field class:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- ...
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf(...)
- gs.transform.normal_to_lognormal(srf)
-
-Or use the provided wrapper:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- ...
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf(...)
- srf.transform("lognormal")
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/00_field_generation.py b/examples/08_geo_coordinates/00_field_generation.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 5b1a6fca9..000000000
--- a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/00_field_generation.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Working with lat-lon random fields
-----------------------------------
-
-In this example, we demonstrate how to generate a random field on
-geographical coordinates.
-
-First we setup a model, with ``latlon=True``, to get the associated
-Yadrenko model.
-
-In addition, we will use a kilometer scale provided by :any:`KM_SCALE`
-as ``geo_scale`` to have a meaningful length scale in km.
-By default the length scale would be given in radians (:any:`RADIAN_SCALE`).
-A third option is a length scale in degrees (:any:`DEGREE_SCALE`).
-
-To generate the field, we simply pass ``(lat, lon)`` as the position tuple
-to the :any:`SRF` class.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, len_scale=777, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-
-lat = lon = range(-80, 81)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=1234)
-field = srf.structured((lat, lon))
-srf.plot()
-
-###############################################################################
-# This was easy as always! Now we can use this field to estimate the empirical
-# variogram in order to prove, that the generated field has the correct
-# geo-statistical properties.
-# The :any:`vario_estimate` routine also provides a ``latlon`` switch to
-# indicate, that the given field is defined on geographical variables.
-#
-# As we will see, everthing went well... phew!
-
-bin_edges = np.linspace(0, 777 * 3, 30)
-bin_center, emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- (lat, lon),
- field,
- bin_edges,
- latlon=True,
- mesh_type="structured",
- sampling_size=2000,
- sampling_seed=12345,
- geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE,
-)
-
-ax = model.plot("vario_yadrenko", x_max=max(bin_center))
-model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, nugget=False)
-model.plot("vario_yadrenko", ax=ax, label="fitted", x_max=max(bin_center))
-ax.scatter(bin_center, emp_vario, color="k")
-print(model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# .. note::
-#
-# Note, that the estimated variogram coincides with the yadrenko variogram,
-# which means it depends on the great-circle distance given in radians.
-#
-# Keep that in mind when defining bins: The range is at most
-# :math:`\pi\approx 3.14`, which corresponds to the half globe.
diff --git a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/01_dwd_krige.py b/examples/08_geo_coordinates/01_dwd_krige.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 3c17fb7e0..000000000
--- a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/01_dwd_krige.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,174 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Kriging geographical data
--------------------------
-
-In this example we are going to interpolate actual temperature data from
-the German weather service `DWD `_.
-
-Data is retrieved utilizing the beautiful package
-`wetterdienst `_,
-which serves as an API for the DWD data.
-
-For better visualization, we also download a simple shapefile of the German
-borderline with `cartopy `_.
-
-In order to keep the number of dependecies low, the calls of both functions
-shown beneath are commented out.
-"""
-
-# sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 2
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def get_borders_germany():
- """Download simple german shape file with cartopy."""
- import geopandas as gp # 0.8.1
- from cartopy.io import shapereader as shp_read # version 0.18.0
-
- shpfile = shp_read.natural_earth("50m", "cultural", "admin_0_countries")
- df = gp.read_file(shpfile) # only use the simplest polygon
- poly = df.loc[df["ADMIN"] == "Germany"]["geometry"].values[0][0]
- np.savetxt("de_borders.txt", list(poly.exterior.coords))
-
-
-def get_dwd_temperature(date="2020-06-09 12:00:00"):
- """Get air temperature from german weather stations from 9.6.20 12:00."""
- from wetterdienst.dwd import observations as obs # version 0.13.0
-
- settings = dict(
- resolution=obs.DWDObservationResolution.HOURLY,
- start_date=date,
- end_date=date,
- )
- sites = obs.DWDObservationStations(
- parameter_set=obs.DWDObservationParameterSet.TEMPERATURE_AIR,
- period=obs.DWDObservationPeriod.RECENT,
- **settings,
- )
- ids, lat, lon = sites.all().loc[:, ["STATION_ID", "LAT", "LON"]].values.T
- observations = obs.DWDObservationData(
- station_ids=ids,
- parameters=obs.DWDObservationParameter.HOURLY.TEMPERATURE_AIR_200,
- periods=obs.DWDObservationPeriod.RECENT,
- **settings,
- )
- temp = observations.all().VALUE.values
- sel = np.isfinite(temp)
- # select only valid temperature data
- ids, lat, lon, temp = ids.astype(float)[sel], lat[sel], lon[sel], temp[sel]
- head = "id, lat, lon, temp" # add a header to the file
- np.savetxt("temp_obs.txt", np.array([ids, lat, lon, temp]).T, header=head)
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# If you want to download the data again,
-# uncomment the two following lines. We will simply load the resulting
-# files to gain the border polygon and the observed temperature along with
-# the station locations given by lat-lon values.
-
-# get_borders_germany()
-# get_dwd_temperature(date="2020-06-09 12:00:00")
-
-border = np.loadtxt("de_borders.txt")
-ids, lat, lon, temp = np.loadtxt("temp_obs.txt").T
-
-###############################################################################
-# First we will estimate the variogram of our temperature data.
-# As the maximal bin distance we choose 900 km.
-
-bin_center, vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- (lat, lon), temp, latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE, max_dist=900
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we can use this estimated variogram to fit a model to it.
-# Here we will use a :any:`Spherical` model. We select the ``latlon`` option
-# to use the `Yadrenko` variant of the model to gain a valid model for lat-lon
-# coordinates and we set the ``geo_scale`` to the earth-radius. Otherwise the length
-# scale would be given in radians representing the great-circle distance.
-#
-# We deselect the nugget from fitting and plot the result afterwards.
-#
-# .. note::
-#
-# You need to plot the Yadrenko variogram, since the standard variogram
-# still holds the ordinary routine that is not respecting the great-circle
-# distance.
-
-model = gs.Spherical(latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-model.fit_variogram(bin_center, vario, nugget=False)
-ax = model.plot("vario_yadrenko", x_max=max(bin_center))
-ax.scatter(bin_center, vario)
-print(model)
-
-###############################################################################
-# As we see, we have a rather large correlation length of 600 km.
-#
-# Now we want to interpolate the data using :any:`Universal` kriging.
-# In order to tinker around with the data, we will use a north-south drift
-# by assuming a linear correlation with the latitude.
-# This can be done as follows:
-
-
-def north_south_drift(lat, lon):
- return lat
-
-
-uk = gs.krige.Universal(
- model=model,
- cond_pos=(lat, lon),
- cond_val=temp,
- drift_functions=north_south_drift,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we generate the kriging field, by defining a lat-lon grid that covers
-# the whole of Germany. The :any:`Krige` class provides the option to only
-# krige the mean field, so one can have a glimpse at the estimated drift.
-
-g_lat = np.arange(47, 56.1, 0.1)
-g_lon = np.arange(5, 16.1, 0.1)
-
-uk.set_pos((g_lat, g_lon), mesh_type="structured")
-uk(return_var=False, store="temp_field")
-uk(only_mean=True, store="mean_field")
-
-###############################################################################
-# And that's it. Now let's have a look at the generated field and the input
-# data along with the estimated mean:
-
-levels = np.linspace(5, 23, 64)
-fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=[10, 5], sharey=True)
-sca = ax[0].scatter(lon, lat, c=temp, vmin=5, vmax=23, cmap="coolwarm")
-co1 = ax[1].contourf(g_lon, g_lat, uk["temp_field"], levels, cmap="coolwarm")
-co2 = ax[2].contourf(g_lon, g_lat, uk["mean_field"], levels, cmap="coolwarm")
-
-[ax[i].plot(border[:, 0], border[:, 1], color="k") for i in range(3)]
-[ax[i].set_xlim([5, 16]) for i in range(3)]
-[ax[i].set_xlabel("Lon in deg") for i in range(3)]
-ax[0].set_ylabel("Lat in deg")
-
-ax[0].set_title("Temperature observations at 2m\nfrom DWD (2020-06-09 12:00)")
-ax[1].set_title("Interpolated temperature\nwith North-South drift")
-ax[2].set_title("Estimated mean drift\nfrom Universal Kriging")
-
-fmt = dict(orientation="horizontal", shrink=0.5, fraction=0.1, pad=0.2)
-fig.colorbar(co2, ax=ax, **fmt).set_label("T in [°C]")
-
-###############################################################################
-# To get a better impression of the estimated north-south drift, we'll take
-# a look at a cross-section at a longitude of 10 degree:
-
-fig, ax = plt.subplots()
-ax.plot(g_lat, uk["temp_field"][:, 50], label="Interpolated temperature")
-ax.plot(g_lat, uk["mean_field"][:, 50], label="North-South mean drift")
-ax.set_xlabel("Lat in deg")
-ax.set_ylabel("T in [°C]")
-ax.set_title("North-South cross-section at 10°")
-ax.legend()
-
-###############################################################################
-# Interpretion of the results is now up to you! ;-)
diff --git a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/README.rst b/examples/08_geo_coordinates/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index b0cf79d13..000000000
--- a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,68 +0,0 @@
-Geographic Coordinates
-======================
-
-GSTools provides support for
-`geographic coordinates `_
-given by:
-
-- latitude ``lat``: specifies the north–south position of a point on the Earth's surface
-- longitude ``lon``: specifies the east–west position of a point on the Earth's surface
-
-If you want to use this feature for field generation or Kriging, you
-have to set up a geographical covariance Model by setting ``latlon=True``
-in your desired model (see :any:`CovModel`):
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import numpy as np
- import gstools as gs
-
- model = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, var=2, len_scale=np.pi / 16)
-
-By doing so, the model will use the associated `Yadrenko` model on a sphere
-(see `here `_).
-The `len_scale` is given in radians to scale the arc-length.
-In order to have a more meaningful length scale, one can use the ``geo_scale``
-argument:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
-
- model = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, var=2, len_scale=500, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
-
-Then ``len_scale`` can be interpreted as given in km.
-
-A `Yadrenko` model :math:`C` is derived from a valid
-isotropic covariance model in 3D :math:`C_{3D}` by the following relation:
-
-.. math::
- C(\zeta)=C_{3D}\left(2r \cdot \sin\left(\frac{\zeta}{2r}\right)\right)
-
-Where :math:`\zeta` is the
-`great-circle distance `_
-and :math:`r` is the ``geo_scale``.
-
-.. note::
-
- ``lat`` and ``lon`` are given in degree, whereas the great-circle distance
- :math:`zeta` is given in units of the ``geo_scale``.
-
-Note, that :math:`2r \cdot \sin(\frac{\zeta}{2r})` is the
-`chordal distance `_
-of two points on a sphere with radius :math:`r`, which means we simply think of the
-earth surface as a sphere, that is cut out of the surrounding three dimensional space,
-when using the `Yadrenko` model.
-
-.. note::
-
- Anisotropy is not available with the geographical models, since their
- geometry is not euclidean. When passing values for :any:`CovModel.anis`
- or :any:`CovModel.angles`, they will be ignored.
-
- Since the Yadrenko model comes from a 3D model, the model dimension will
- be 3 (see :any:`CovModel.dim`) but the `field_dim` will be 2 in this case
- (see :any:`CovModel.field_dim`).
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/de_borders.txt b/examples/08_geo_coordinates/de_borders.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index c8cdb5a88..000000000
--- a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/de_borders.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,492 +0,0 @@
-9.524023437500005684e+00 4.752421874999999574e+01
-9.350000000000022737e+00 4.759892578124999574e+01
-9.182812500000011369e+00 4.767070312499999574e+01
-9.127539062500005684e+00 4.767070312499999574e+01
-8.881152343750017053e+00 4.765639648437499432e+01
-8.874023437500000000e+00 4.766269531249999858e+01
-8.831152343750005684e+00 4.770361328125000000e+01
-8.793066406250005684e+00 4.771655273437500000e+01
-8.770117187500005684e+00 4.770991210937499716e+01
-8.754785156250022737e+00 4.769804687499999574e+01
-8.728320312500017053e+00 4.770004882812499858e+01
-8.617871093750011369e+00 4.776611328125000000e+01
-8.572656250000022737e+00 4.777563476562500000e+01
-8.509863281250005684e+00 4.776689453124999574e+01
-8.435742187500011369e+00 4.773134765624999432e+01
-8.403417968750005684e+00 4.768779296874999574e+01
-8.413281250000011369e+00 4.766269531249999858e+01
-8.451757812500005684e+00 4.765180664062499716e+01
-8.552343750000005684e+00 4.765913085937499716e+01
-8.567089843750011369e+00 4.765190429687499574e+01
-8.570507812500011369e+00 4.763779296874999858e+01
-8.559472656250022737e+00 4.762402343750000000e+01
-8.477636718750005684e+00 4.761269531249999432e+01
-8.454003906250022737e+00 4.759619140625000000e+01
-8.430078125000022737e+00 4.759213867187499858e+01
-8.414746093750011369e+00 4.758959960937500000e+01
-8.327832031250011369e+00 4.760693359375000000e+01
-8.198242187500000000e+00 4.760693359375000000e+01
-8.093750000000000000e+00 4.757617187500000000e+01
-7.927050781250017053e+00 4.756386718749999432e+01
-7.698046875000017053e+00 4.756987304687499574e+01
-7.615625000000022737e+00 4.759272460937499716e+01
-7.565429687500000000e+00 4.760654296874999858e+01
-7.529394531250005684e+00 4.767387695312499574e+01
-7.538574218750000000e+00 4.777363281249999716e+01
-7.593261718750000000e+00 4.790566406249999432e+01
-7.608496093750005684e+00 4.800258789062499432e+01
-7.584179687500011369e+00 4.806430664062499858e+01
-7.616601562500022737e+00 4.815678710937499574e+01
-7.705664062500005684e+00 4.828002929687500000e+01
-7.765136718750000000e+00 4.841000976562499858e+01
-7.794824218750022737e+00 4.854682617187499716e+01
-7.837988281250005684e+00 4.863603515624999574e+01
-7.922753906250022737e+00 4.869853515624999574e+01
-8.124023437500000000e+00 4.887329101562500000e+01
-8.140332031250011369e+00 4.888642578124999716e+01
-8.134863281250005684e+00 4.897358398437499716e+01
-8.080664062500005684e+00 4.898588867187499574e+01
-8.001269531250017053e+00 4.901093749999999716e+01
-7.799218750000022737e+00 4.904189453124999432e+01
-7.610937500000005684e+00 4.906176757812500000e+01
-7.525488281250005684e+00 4.908637695312499716e+01
-7.450585937500022737e+00 4.915219726562499858e+01
-7.404199218750022737e+00 4.915307617187500000e+01
-7.313378906250022737e+00 4.912954101562499432e+01
-7.199902343750011369e+00 4.911362304687499858e+01
-7.117382812500011369e+00 4.912753906249999858e+01
-7.065722656250017053e+00 4.912485351562499858e+01
-7.036718750000005684e+00 4.911269531249999432e+01
-7.022167968750011369e+00 4.912343749999999432e+01
-7.001464843750000000e+00 4.917988281249999716e+01
-6.958300781250017053e+00 4.919462890624999574e+01
-6.891210937500005684e+00 4.920751953125000000e+01
-6.849511718750022737e+00 4.920195312499999574e+01
-6.820703125000022737e+00 4.917392578124999858e+01
-6.776269531250022737e+00 4.915415039062499858e+01
-6.735449218750005684e+00 4.916059570312499716e+01
-6.607617187500011369e+00 4.929086914062499858e+01
-6.574707031250000000e+00 4.931967773437499858e+01
-6.566308593750022737e+00 4.934619140625000000e+01
-6.534277343750005684e+00 4.939467773437499432e+01
-6.458105468750005684e+00 4.944287109375000000e+01
-6.382226562500022737e+00 4.945815429687499432e+01
-6.344335937500005684e+00 4.945273437499999858e+01
-6.348437500000017053e+00 4.951269531250000000e+01
-6.378320312500022737e+00 4.959960937500000000e+01
-6.406738281250000000e+00 4.964497070312499716e+01
-6.444628906250017053e+00 4.968203124999999432e+01
-6.484765625000022737e+00 4.970781249999999574e+01
-6.493750000000005684e+00 4.975439453125000000e+01
-6.487304687500000000e+00 4.979848632812499432e+01
-6.440917968750000000e+00 4.980532226562499432e+01
-6.324609375000022737e+00 4.983789062500000000e+01
-6.256054687500011369e+00 4.987216796874999858e+01
-6.204882812500017053e+00 4.991513671874999858e+01
-6.138183593750000000e+00 4.997431640624999716e+01
-6.109765625000022737e+00 5.003437499999999716e+01
-6.108300781250022737e+00 5.009423828125000000e+01
-6.116503906250017053e+00 5.012099609374999432e+01
-6.121289062500011369e+00 5.013935546874999716e+01
-6.175097656250017053e+00 5.023266601562500000e+01
-6.364453125000011369e+00 5.031616210937500000e+01
-6.343652343750022737e+00 5.040024414062499858e+01
-6.340917968750005684e+00 5.045175781249999858e+01
-6.294921875000000000e+00 5.048549804687499432e+01
-6.203027343750022737e+00 5.049912109374999858e+01
-6.178710937500000000e+00 5.052250976562499574e+01
-6.168457031250000000e+00 5.054536132812499716e+01
-6.235937500000005684e+00 5.059667968750000000e+01
-6.154492187500011369e+00 5.063725585937499574e+01
-6.119433593750017053e+00 5.067924804687499574e+01
-6.005957031250005684e+00 5.073222656249999574e+01
-5.993945312500017053e+00 5.075043945312499716e+01
-6.048437500000005684e+00 5.090488281249999858e+01
-6.006835937500000000e+00 5.094995117187500000e+01
-5.955078125000000000e+00 5.097294921874999574e+01
-5.894726562500011369e+00 5.098422851562499858e+01
-5.867187500000000000e+00 5.100566406249999574e+01
-5.857519531250005684e+00 5.103012695312499858e+01
-5.868359375000011369e+00 5.104531249999999432e+01
-5.939257812500017053e+00 5.104082031249999574e+01
-5.961035156250005684e+00 5.105668945312499574e+01
-6.129980468750005684e+00 5.114741210937499716e+01
-6.136914062500011369e+00 5.116484374999999574e+01
-6.113378906250005684e+00 5.117470703124999432e+01
-6.082421875000022737e+00 5.117998046874999574e+01
-6.074804687500005684e+00 5.119902343749999574e+01
-6.075878906250011369e+00 5.122412109375000000e+01
-6.166210937500011369e+00 5.135483398437499858e+01
-6.192871093750000000e+00 5.141059570312499716e+01
-6.198828125000005684e+00 5.144999999999999574e+01
-6.193261718750022737e+00 5.148891601562499432e+01
-6.141601562500000000e+00 5.155009765624999574e+01
-6.091113281250017053e+00 5.159892578124999574e+01
-6.089355468750000000e+00 5.163779296874999858e+01
-6.052734375000000000e+00 5.165825195312499574e+01
-5.948535156250017053e+00 5.176240234374999716e+01
-5.948730468750000000e+00 5.180268554687499716e+01
-6.007617187500017053e+00 5.183398437500000000e+01
-6.089843750000000000e+00 5.185395507812499716e+01
-6.117187500000000000e+00 5.187041015624999574e+01
-6.166503906250000000e+00 5.188076171875000142e+01
-6.297070312500011369e+00 5.185073242187500142e+01
-6.355664062500011369e+00 5.182465820312499716e+01
-6.372167968750005684e+00 5.183002929687499716e+01
-6.425000000000011369e+00 5.185839843750000000e+01
-6.517578125000000000e+00 5.185395507812499716e+01
-6.741796875000005684e+00 5.191088867187500000e+01
-6.775195312500017053e+00 5.193828124999999574e+01
-6.800390625000005684e+00 5.196738281249999858e+01
-6.802441406250011369e+00 5.198017578124999716e+01
-6.715625000000017053e+00 5.203618164062499574e+01
-6.712988281250005684e+00 5.205688476562500000e+01
-6.724511718750022737e+00 5.208022460937500142e+01
-6.749023437500000000e+00 5.209868164062499574e+01
-6.800390625000005684e+00 5.211123046875000142e+01
-6.855078125000005684e+00 5.213579101562499574e+01
-6.977246093750011369e+00 5.220551757812499716e+01
-7.019628906250005684e+00 5.226601562500000142e+01
-7.032617187500022737e+00 5.233149414062499716e+01
-7.035156250000000000e+00 5.238022460937499858e+01
-7.001855468750022737e+00 5.241899414062499574e+01
-6.968164062500022737e+00 5.244409179687500000e+01
-6.922070312500011369e+00 5.244028320312499858e+01
-6.832519531250000000e+00 5.244228515625000142e+01
-6.748828125000017053e+00 5.246401367187500142e+01
-6.702929687500017053e+00 5.249921874999999716e+01
-6.691601562500011369e+00 5.253017578125000142e+01
-6.712402343750000000e+00 5.254965820312499858e+01
-6.718750000000000000e+00 5.257358398437499858e+01
-6.705371093750017053e+00 5.259765625000000000e+01
-6.710742187500017053e+00 5.261787109374999716e+01
-6.748437500000022737e+00 5.263408203124999574e+01
-7.013183593750000000e+00 5.263354492187500000e+01
-7.033007812500017053e+00 5.265136718750000000e+01
-7.050878906250005684e+00 5.274477539062500142e+01
-7.117089843750022737e+00 5.288701171874999574e+01
-7.179492187500017053e+00 5.296621093750000142e+01
-7.189941406250000000e+00 5.299951171875000000e+01
-7.188964843750000000e+00 5.318720703124999716e+01
-7.197265625000000000e+00 5.328227539062499574e+01
-7.152050781250011369e+00 5.332695312499999574e+01
-7.053320312500005684e+00 5.337583007812499858e+01
-7.074316406250005684e+00 5.347763671874999858e+01
-7.107128906250011369e+00 5.355698242187499858e+01
-7.206445312500022737e+00 5.365454101562500000e+01
-7.285253906250005684e+00 5.368134765624999716e+01
-7.629199218750017053e+00 5.369726562500000000e+01
-8.009277343750000000e+00 5.369072265624999574e+01
-8.167089843750005684e+00 5.354340820312499716e+01
-8.108496093750005684e+00 5.346767578125000142e+01
-8.200781250000005684e+00 5.343242187499999574e+01
-8.245214843750005684e+00 5.344531250000000000e+01
-8.279003906250011369e+00 5.351118164062499716e+01
-8.301562500000017053e+00 5.358413085937500142e+01
-8.333886718750022737e+00 5.360620117187500000e+01
-8.451367187500011369e+00 5.355170898437499716e+01
-8.492675781250000000e+00 5.351435546874999716e+01
-8.495214843750005684e+00 5.339423828124999716e+01
-8.538476562500022737e+00 5.355688476562500000e+01
-8.506250000000022737e+00 5.367075195312499858e+01
-8.528417968750005684e+00 5.378110351562499858e+01
-8.575585937500022737e+00 5.383847656249999858e+01
-8.618945312500017053e+00 5.387500000000000000e+01
-8.897753906250017053e+00 5.383569335937500000e+01
-9.205566406250000000e+00 5.385595703125000000e+01
-9.321972656250011369e+00 5.381347656250000000e+01
-9.585351562500022737e+00 5.360048828125000142e+01
-9.673144531250017053e+00 5.356562499999999716e+01
-9.783984375000017053e+00 5.355463867187499716e+01
-9.631250000000022737e+00 5.360019531249999858e+01
-9.312011718750000000e+00 5.385913085937500000e+01
-9.216406250000005684e+00 5.389121093749999858e+01
-9.069628906250017053e+00 5.390092773437499574e+01
-8.978125000000005684e+00 5.392622070312499716e+01
-8.920410156250000000e+00 5.396533203125000000e+01
-8.903515625000011369e+00 5.400029296874999574e+01
-8.906640625000022737e+00 5.426079101562499574e+01
-8.851562500000000000e+00 5.429956054687500000e+01
-8.780371093750005684e+00 5.431303710937499574e+01
-8.736035156250011369e+00 5.429521484374999574e+01
-8.644921875000022737e+00 5.429497070312499574e+01
-8.625781250000017053e+00 5.435395507812499716e+01
-8.648046875000005684e+00 5.439765624999999716e+01
-8.831152343750005684e+00 5.442753906249999574e+01
-8.951855468750011369e+00 5.446757812499999574e+01
-8.957226562500011369e+00 5.453833007812500000e+01
-8.880957031250005684e+00 5.459394531249999716e+01
-8.789648437500005684e+00 5.469594726562500142e+01
-8.682324218750011369e+00 5.479184570312499858e+01
-8.670312500000022737e+00 5.490341796874999858e+01
-8.670703125000017053e+00 5.490332031250000000e+01
-8.857226562500017053e+00 5.490112304687500000e+01
-8.902929687500005684e+00 5.489692382812499716e+01
-9.185839843750017053e+00 5.484467773437499716e+01
-9.254980468750005684e+00 5.480800781250000142e+01
-9.341992187500011369e+00 5.480629882812500142e+01
-9.498730468750011369e+00 5.484042968749999858e+01
-9.615820312500005684e+00 5.485541992187499716e+01
-9.661230468750005684e+00 5.483437500000000142e+01
-9.725000000000022737e+00 5.482553710937499858e+01
-9.739746093750000000e+00 5.482553710937499858e+01
-9.745898437500017053e+00 5.480717773437499574e+01
-9.892285156250011369e+00 5.478061523437499858e+01
-9.953808593750011369e+00 5.473828125000000000e+01
-1.002216796875001137e+01 5.467392578124999858e+01
-1.002880859375000000e+01 5.458129882812500000e+01
-9.941308593750022737e+00 5.451464843750000000e+01
-9.868652343750000000e+00 5.447246093749999574e+01
-1.014345703125002274e+01 5.448842773437500142e+01
-1.017080078125002274e+01 5.445019531250000000e+01
-1.021240234375000000e+01 5.440893554687500000e+01
-1.036044921875000568e+01 5.443833007812499858e+01
-1.073154296875000568e+01 5.431625976562499858e+01
-1.095595703125002274e+01 5.437568359374999716e+01
-1.101337890625001137e+01 5.437915039062500000e+01
-1.106435546875002274e+01 5.428051757812500000e+01
-1.100859375000001705e+01 5.418115234375000000e+01
-1.081074218750001137e+01 5.407514648437499716e+01
-1.085458984375000568e+01 5.400981445312499574e+01
-1.091777343750001705e+01 5.399531249999999716e+01
-1.110429687500001705e+01 5.400917968750000142e+01
-1.139960937500001137e+01 5.394462890624999574e+01
-1.146113281250001137e+01 5.396474609375000142e+01
-1.170058593750002274e+01 5.411352539062500000e+01
-1.179628906250002274e+01 5.414545898437499716e+01
-1.211132812500000000e+01 5.416831054687499858e+01
-1.216865234375001137e+01 5.422587890624999574e+01
-1.229628906250002274e+01 5.428378906249999858e+01
-1.237851562500000568e+01 5.434702148437499858e+01
-1.257539062500001137e+01 5.446738281249999858e+01
-1.277910156250001705e+01 5.444570312500000142e+01
-1.289804687500000568e+01 5.442265624999999574e+01
-1.302861328125001705e+01 5.441103515625000142e+01
-1.314746093750000000e+01 5.428271484375000000e+01
-1.344804687500001705e+01 5.414086914062500000e+01
-1.372421875000000568e+01 5.415322265625000142e+01
-1.382226562500000000e+01 5.401904296875000000e+01
-1.386552734375001705e+01 5.385336914062499858e+01
-1.395039062500001137e+01 5.380136718749999858e+01
-1.402500000000000568e+01 5.376743164062499858e+01
-1.425000000000000000e+01 5.373188476562499716e+01
-1.425888671875000568e+01 5.372963867187500142e+01
-1.426611328125000000e+01 5.370712890624999858e+01
-1.427988281250000568e+01 5.362475585937500000e+01
-1.429873046875002274e+01 5.355644531249999574e+01
-1.441455078125000000e+01 5.328349609374999574e+01
-1.441230468750001137e+01 5.321674804687499716e+01
-1.441093750000001705e+01 5.319902343749999574e+01
-1.436855468750002274e+01 5.310556640624999858e+01
-1.429316406250001137e+01 5.302675781250000142e+01
-1.419365234375001705e+01 5.298232421875000142e+01
-1.413886718750001137e+01 5.293286132812500000e+01
-1.412861328125001137e+01 5.287822265624999574e+01
-1.425371093750001705e+01 5.278251953124999574e+01
-1.451406250000002274e+01 5.264560546874999858e+01
-1.461943359375001705e+01 5.252851562499999716e+01
-1.456972656250002274e+01 5.243110351562499716e+01
-1.455458984375002274e+01 5.235966796874999574e+01
-1.457392578125001137e+01 5.231416015624999716e+01
-1.461562500000002274e+01 5.227763671874999574e+01
-1.467988281250001137e+01 5.225000000000000000e+01
-1.470537109375001705e+01 5.220747070312499716e+01
-1.469238281250000000e+01 5.215004882812500142e+01
-1.470458984375000000e+01 5.211020507812499858e+01
-1.475253906250000568e+01 5.208183593749999574e+01
-1.474814453125000568e+01 5.207080078125000000e+01
-1.472480468750001137e+01 5.203085937499999858e+01
-1.469296875000000568e+01 5.195800781250000000e+01
-1.467490234375000568e+01 5.190483398437499574e+01
-1.460166015625000568e+01 5.183237304687499858e+01
-1.462392578125002274e+01 5.177080078124999574e+01
-1.468134765625001137e+01 5.169819335937499716e+01
-1.472490234375001705e+01 5.166171874999999858e+01
-1.473867187500002274e+01 5.162714843749999716e+01
-1.471093750000000000e+01 5.154492187500000000e+01
-1.472470703125000568e+01 5.152387695312499716e+01
-1.490595703125001137e+01 5.146333007812499716e+01
-1.493554687500000000e+01 5.143535156249999574e+01
-1.495312500000000000e+01 5.137714843749999716e+01
-1.501660156250000000e+01 5.125273437499999574e+01
-1.496386718750000000e+01 5.109511718749999432e+01
-1.491748046875000000e+01 5.100874023437499716e+01
-1.481425781250001705e+01 5.087163085937499574e+01
-1.480937500000001705e+01 5.085898437499999858e+01
-1.479746093750000568e+01 5.084233398437499574e+01
-1.476650390625002274e+01 5.081831054687499716e+01
-1.472333984375001137e+01 5.081469726562500000e+01
-1.465820312500000000e+01 5.083261718749999858e+01
-1.461357421875001705e+01 5.085556640624999858e+01
-1.462382812500001705e+01 5.091474609374999716e+01
-1.459521484375000000e+01 5.091860351562499432e+01
-1.455966796875000568e+01 5.095493164062499858e+01
-1.454570312500001705e+01 5.099394531249999574e+01
-1.450732421875000000e+01 5.100986328124999858e+01
-1.436728515625000568e+01 5.102626953124999432e+01
-1.431972656250002274e+01 5.103779296874999716e+01
-1.428320312500000000e+01 5.102949218749999716e+01
-1.425585937500000000e+01 5.100185546874999432e+01
-1.427333984375002274e+01 5.097690429687499858e+01
-1.429941406250000568e+01 5.095258789062499716e+01
-1.437705078125000568e+01 5.091406250000000000e+01
-1.436904296875002274e+01 5.089873046874999574e+01
-1.420175781250000568e+01 5.086123046874999432e+01
-1.409648437500001705e+01 5.082275390625000000e+01
-1.399843750000002274e+01 5.080112304687499858e+01
-1.389853515625000568e+01 5.076127929687499574e+01
-1.370136718750001137e+01 5.071650390624999716e+01
-1.355673828125000568e+01 5.070463867187499574e+01
-1.352656250000001137e+01 5.069282226562499716e+01
-1.347255859375002274e+01 5.061694335937500000e+01
-1.343613281250000568e+01 5.060107421875000000e+01
-1.340117187500001705e+01 5.060932617187499716e+01
-1.337460937500000568e+01 5.062172851562499432e+01
-1.334101562500001137e+01 5.061142578124999858e+01
-1.330605468750002274e+01 5.058632812499999432e+01
-1.326953125000000000e+01 5.057641601562500000e+01
-1.323769531250002274e+01 5.057675781249999858e+01
-1.318115234375000000e+01 5.051049804687500000e+01
-1.301640625000001705e+01 5.049038085937499432e+01
-1.299707031250000000e+01 5.045605468750000000e+01
-1.296679687500000000e+01 5.041621093749999716e+01
-1.294267578125001705e+01 5.040644531249999716e+01
-1.286826171875000568e+01 5.042221679687499858e+01
-1.276542968750001705e+01 5.043095703124999574e+01
-1.270644531250002274e+01 5.040913085937499716e+01
-1.263554687500001705e+01 5.039707031249999858e+01
-1.254902343750001137e+01 5.039340820312499858e+01
-1.245263671875000000e+01 5.034980468749999716e+01
-1.235859375000001137e+01 5.027324218749999574e+01
-1.230566406250000000e+01 5.020571289062499432e+01
-1.227734375000000000e+01 5.018144531249999574e+01
-1.223115234375001137e+01 5.024487304687500000e+01
-1.217480468750000000e+01 5.028837890624999574e+01
-1.213486328125000568e+01 5.031093749999999432e+01
-1.209921875000000568e+01 5.031098632812499716e+01
-1.208984375000000000e+01 5.030175781250000000e+01
-1.208974609375002274e+01 5.026855468750000000e+01
-1.212783203125002274e+01 5.021342773437499574e+01
-1.217500000000001137e+01 5.017583007812499574e+01
-1.218251953125002274e+01 5.014804687499999858e+01
-1.220781250000001705e+01 5.009750976562499858e+01
-1.227646484375000568e+01 5.004233398437499858e+01
-1.238417968750002274e+01 4.999858398437499574e+01
-1.245761718750000568e+01 4.995551757812499716e+01
-1.251201171875001705e+01 4.989580078124999574e+01
-1.251250000000001705e+01 4.987744140625000000e+01
-1.249755859375000000e+01 4.985307617187499574e+01
-1.247187500000001137e+01 4.983007812500000000e+01
-1.245019531250000000e+01 4.980014648437499858e+01
-1.239052734375002274e+01 4.973964843749999432e+01
-1.240820312500000000e+01 4.971318359374999574e+01
-1.245703125000000000e+01 4.967978515624999858e+01
-1.250029296875001705e+01 4.963969726562499574e+01
-1.255576171875000568e+01 4.957485351562499432e+01
-1.263203125000001137e+01 4.946123046874999574e+01
-1.268115234375000000e+01 4.941450195312499716e+01
-1.274785156250001705e+01 4.936621093750000000e+01
-1.281337890625002274e+01 4.932934570312500000e+01
-1.291669921875001137e+01 4.933046874999999432e+01
-1.302373046875001705e+01 4.926010742187499858e+01
-1.314052734375002274e+01 4.915834960937499432e+01
-1.322783203125001705e+01 4.911166992187499858e+01
-1.328876953125001137e+01 4.909746093749999574e+01
-1.333906250000001137e+01 4.906079101562500000e+01
-1.338369140625002274e+01 4.900810546874999574e+01
-1.340117187500001705e+01 4.897758789062499574e+01
-1.344072265625001705e+01 4.895556640625000000e+01
-1.354765625000001705e+01 4.895966796874999716e+01
-1.368496093750002274e+01 4.887670898437500000e+01
-1.376992187500002274e+01 4.881596679687499574e+01
-1.381474609375001705e+01 4.876694335937499858e+01
-1.380292968750001137e+01 4.874750976562499716e+01
-1.379746093750000568e+01 4.868642578124999432e+01
-1.379882812500000000e+01 4.862167968749999858e+01
-1.378535156250001137e+01 4.858745117187499574e+01
-1.372392578125001705e+01 4.854238281249999432e+01
-1.369218750000001705e+01 4.853276367187499574e+01
-1.367519531250002274e+01 4.852304687499999858e+01
-1.348662109375001705e+01 4.858183593749999574e+01
-1.347167968750000000e+01 4.857182617187499574e+01
-1.345986328125002274e+01 4.856455078124999858e+01
-1.340937500000001137e+01 4.839414062499999858e+01
-1.337460937500000568e+01 4.836137695312499574e+01
-1.332285156250000568e+01 4.833124999999999716e+01
-1.321523437500002274e+01 4.830190429687499432e+01
-1.314042968750001705e+01 4.828994140624999432e+01
-1.308212890625000568e+01 4.827509765624999716e+01
-1.289746093750000000e+01 4.820371093749999858e+01
-1.281425781250001705e+01 4.816083984374999716e+01
-1.276035156250000568e+01 4.810698242187499574e+01
-1.276005859375001705e+01 4.807597656249999574e+01
-1.284990234375001705e+01 4.798481445312499716e+01
-1.295351562500002274e+01 4.789062500000000000e+01
-1.295419921875000568e+01 4.780776367187499432e+01
-1.290830078125000568e+01 4.774580078124999716e+01
-1.289765625000001137e+01 4.772187499999999716e+01
-1.292812500000002274e+01 4.771284179687499716e+01
-1.298554687500001137e+01 4.770942382812499716e+01
-1.303359375000002274e+01 4.769873046875000000e+01
-1.305410156250002274e+01 4.765512695312499858e+01
-1.304794921875000568e+01 4.757915039062499574e+01
-1.303154296875001705e+01 4.750800781249999716e+01
-1.301435546875001137e+01 4.747807617187499574e+01
-1.296806640625001705e+01 4.747568359374999858e+01
-1.287890625000000000e+01 4.750644531249999858e+01
-1.280937500000001705e+01 4.754218749999999716e+01
-1.278281250000000568e+01 4.756416015624999716e+01
-1.278115234375002274e+01 4.759042968749999858e+01
-1.279619140625001705e+01 4.760703124999999858e+01
-1.277138671875002274e+01 4.763940429687500000e+01
-1.268583984375001705e+01 4.766933593749999432e+01
-1.259423828125000000e+01 4.765629882812499574e+01
-1.252656250000001137e+01 4.763613281249999432e+01
-1.248291015625000000e+01 4.763730468749999858e+01
-1.243574218750001137e+01 4.766611328124999858e+01
-1.236318359375002274e+01 4.768818359374999716e+01
-1.226835937500001705e+01 4.770273437499999858e+01
-1.220927734375001705e+01 4.771826171875000000e+01
-1.219687500000000568e+01 4.770908203124999858e+01
-1.220380859375001137e+01 4.764672851562500000e+01
-1.218564453125000568e+01 4.761953124999999432e+01
-1.171679687500000000e+01 4.758349609375000000e+01
-1.157392578125001137e+01 4.754975585937499716e+01
-1.146992187500001137e+01 4.750610351562500000e+01
-1.139296875000002274e+01 4.748715820312499858e+01
-1.137412109375000568e+01 4.746025390624999574e+01
-1.129794921875000568e+01 4.742490234374999858e+01
-1.121191406250000000e+01 4.741362304687499574e+01
-1.119121093750001705e+01 4.742519531249999432e+01
-1.113603515625001705e+01 4.740888671874999716e+01
-1.104199218750000000e+01 4.739311523437499574e+01
-1.098085937500002274e+01 4.739814453124999716e+01
-1.095214843750000000e+01 4.742670898437499716e+01
-1.089394531250002274e+01 4.747045898437500000e+01
-1.087060546875000000e+01 4.750078124999999574e+01
-1.087304687500000000e+01 4.752021484374999716e+01
-1.074160156250002274e+01 4.752412109374999716e+01
-1.065869140625000000e+01 4.754721679687499858e+01
-1.048281250000002274e+01 4.754179687499999574e+01
-1.043945312500000000e+01 4.755156249999999574e+01
-1.043037109375001137e+01 4.754106445312499574e+01
-1.040390625000000568e+01 4.741699218750000000e+01
-1.036914062500000000e+01 4.736606445312499858e+01
-1.031279296875001705e+01 4.731342773437499716e+01
-1.024062500000002274e+01 4.728413085937499716e+01
-1.018300781250002274e+01 4.727880859375000000e+01
-1.018574218750001137e+01 4.731718749999999574e+01
-1.020029296875000568e+01 4.736342773437499432e+01
-1.015878906250000568e+01 4.737426757812500000e+01
-1.009648437500001705e+01 4.737958984374999716e+01
-1.006630859375002274e+01 4.739335937499999574e+01
-1.007421875000000000e+01 4.742851562499999574e+01
-1.005986328125001705e+01 4.744907226562499858e+01
-1.003408203125002274e+01 4.747358398437499716e+01
-9.971582031250022737e+00 4.750532226562499716e+01
-9.839160156250017053e+00 4.755229492187499574e+01
-9.748925781250022737e+00 4.757553710937499858e+01
-9.715136718750017053e+00 4.755078125000000000e+01
-9.650585937500011369e+00 4.752587890625000000e+01
-9.548925781250005684e+00 4.753403320312499858e+01
-9.524023437500005684e+00 4.752421874999999574e+01
diff --git a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/temp_obs.txt b/examples/08_geo_coordinates/temp_obs.txt
deleted file mode 100644
index aa8e60fc8..000000000
--- a/examples/08_geo_coordinates/temp_obs.txt
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,494 +0,0 @@
-# id, lat, lon, temp
-4.400000000000000000e+01 5.293359999999999843e+01 8.237000000000000099e+00 1.569999999999999929e+01
-7.300000000000000000e+01 4.861590000000000344e+01 1.305059999999999931e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-7.800000000000000000e+01 5.248530000000000229e+01 7.912600000000000300e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-9.100000000000000000e+01 5.074459999999999837e+01 9.345000000000000639e+00 1.700000000000000000e+01
-9.600000000000000000e+01 5.294369999999999976e+01 1.285180000000000078e+01 2.189999999999999858e+01
-1.020000000000000000e+02 5.386330000000000240e+01 8.127499999999999503e+00 1.190000000000000036e+01
-1.250000000000000000e+02 4.783420000000000272e+01 1.086669999999999980e+01 1.140000000000000036e+01
-1.310000000000000000e+02 5.108809999999999718e+01 1.293260000000000076e+01 1.719999999999999929e+01
-1.420000000000000000e+02 4.840599999999999881e+01 1.131170000000000009e+01 1.290000000000000036e+01
-1.500000000000000000e+02 4.972729999999999961e+01 8.116400000000000503e+00 1.719999999999999929e+01
-1.510000000000000000e+02 4.946909999999999741e+01 1.185459999999999958e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-1.540000000000000000e+02 4.801970000000000027e+01 1.229250000000000043e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-1.610000000000000000e+02 5.042369999999999663e+01 7.420200000000000351e+00 1.810000000000000142e+01
-1.640000000000000000e+02 5.303159999999999741e+01 1.399080000000000013e+01 2.130000000000000071e+01
-1.670000000000000000e+02 5.384120000000000061e+01 1.368459999999999965e+01 2.130000000000000071e+01
-1.830000000000000000e+02 5.467920000000000158e+01 1.343430000000000035e+01 1.739999999999999858e+01
-1.910000000000000000e+02 4.996940000000000026e+01 9.911400000000000432e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-1.980000000000000000e+02 5.137449999999999761e+01 1.129199999999999982e+01 2.019999999999999929e+01
-2.170000000000000000e+02 4.787740000000000151e+01 1.136430000000000007e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-2.220000000000000000e+02 5.059080000000000155e+01 1.271390000000000065e+01 1.580000000000000071e+01
-2.320000000000000000e+02 4.842530000000000001e+01 1.094170000000000087e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-2.570000000000000000e+02 4.872699999999999676e+01 8.245699999999999363e+00 1.359999999999999964e+01
-2.590000000000000000e+02 4.780639999999999645e+01 7.638700000000000045e+00 1.440000000000000036e+01
-2.820000000000000000e+02 4.987429999999999808e+01 1.092060000000000031e+01 1.580000000000000071e+01
-2.940000000000000000e+02 5.231989999999999696e+01 9.429999999999999716e+00 2.150000000000000000e+01
-2.980000000000000000e+02 5.434060000000000201e+01 1.271080000000000076e+01 1.769999999999999929e+01
-3.030000000000000000e+02 5.206139999999999901e+01 1.349959999999999916e+01 2.119999999999999929e+01
-3.140000000000000000e+02 5.116040000000000276e+01 1.450420000000000087e+01 2.039999999999999858e+01
-3.200000000000000000e+02 4.996670000000000300e+01 1.151970000000000027e+01 1.469999999999999929e+01
-3.300000000000000000e+02 4.956170000000000186e+01 8.967299999999999827e+00 1.409999999999999964e+01
-3.420000000000000000e+02 5.231700000000000017e+01 8.169399999999999551e+00 1.639999999999999858e+01
-3.680000000000000000e+02 5.281519999999999726e+01 9.924799999999999400e+00 1.919999999999999929e+01
-3.770000000000000000e+02 4.910699999999999932e+01 7.996699999999999697e+00 1.669999999999999929e+01
-3.790000000000000000e+02 5.090740000000000265e+01 1.126650000000000063e+01 1.810000000000000142e+01
-3.900000000000000000e+02 5.098369999999999891e+01 8.368299999999999628e+00 1.480000000000000071e+01
-4.000000000000000000e+02 5.263089999999999691e+01 1.350220000000000020e+01 2.250000000000000000e+01
-4.030000000000000000e+02 5.245369999999999777e+01 1.330170000000000030e+01 1.919999999999999929e+01
-4.100000000000000000e+02 5.240400000000000347e+01 1.373090000000000011e+01 2.080000000000000071e+01
-4.200000000000000000e+02 5.254469999999999885e+01 1.355979999999999919e+01 2.169999999999999929e+01
-4.270000000000000000e+02 5.238069999999999737e+01 1.353059999999999974e+01 2.250000000000000000e+01
-4.300000000000000000e+02 5.256439999999999912e+01 1.330879999999999974e+01 2.060000000000000142e+01
-4.330000000000000000e+02 5.246750000000000114e+01 1.340210000000000079e+01 2.060000000000000142e+01
-4.450000000000000000e+02 5.182180000000000319e+01 1.171100000000000030e+01 2.200000000000000000e+01
-4.600000000000000000e+02 4.926409999999999911e+01 6.686799999999999855e+00 1.519999999999999929e+01
-5.350000000000000000e+02 5.003719999999999857e+01 7.307900000000000063e+00 1.769999999999999929e+01
-5.910000000000000000e+02 5.339110000000000156e+01 1.068779999999999930e+01 1.889999999999999858e+01
-5.960000000000000000e+02 5.400280000000000058e+01 1.119079999999999941e+01 1.630000000000000071e+01
-6.030000000000000000e+02 5.072930000000000206e+01 7.203999999999999737e+00 1.760000000000000142e+01
-6.170000000000000000e+02 5.187299999999999756e+01 6.886300000000000310e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-6.560000000000000000e+02 5.172339999999999804e+01 1.060210000000000008e+01 1.580000000000000071e+01
-6.620000000000000000e+02 5.229149999999999920e+01 1.044640000000000057e+01 1.939999999999999858e+01
-6.910000000000000000e+02 5.304500000000000171e+01 8.797900000000000276e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-7.010000000000000000e+02 5.353320000000000078e+01 8.576100000000000279e+00 1.380000000000000071e+01
-7.040000000000000000e+02 5.344509999999999650e+01 9.138999999999999346e+00 1.610000000000000142e+01
-7.220000000000000000e+02 5.179860000000000042e+01 1.061829999999999963e+01 1.009999999999999964e+01
-7.550000000000000000e+02 4.951820000000000022e+01 9.321300000000000807e+00 1.600000000000000000e+01
-7.570000000000000000e+02 4.796249999999999858e+01 7.998300000000000409e+00 1.280000000000000071e+01
-7.600000000000000000e+02 5.336290000000000333e+01 9.943500000000000227e+00 1.750000000000000000e+01
-7.660000000000000000e+02 5.017459999999999809e+01 7.059499999999999886e+00 1.680000000000000071e+01
-7.690000000000000000e+02 5.228170000000000073e+01 9.088900000000000645e+00 1.889999999999999858e+01
-8.170000000000000000e+02 5.103059999999999974e+01 8.814600000000000435e+00 1.850000000000000000e+01
-8.400000000000000000e+02 5.043130000000000024e+01 1.261139999999999972e+01 1.080000000000000071e+01
-8.500000000000000000e+02 5.259590000000000032e+01 1.002960000000000029e+01 1.939999999999999858e+01
-8.530000000000000000e+02 5.079129999999999967e+01 1.287199999999999989e+01 1.710000000000000142e+01
-8.560000000000000000e+02 4.788430000000000319e+01 1.254039999999999999e+01 1.330000000000000071e+01
-8.670000000000000000e+02 5.030660000000000309e+01 1.096790000000000020e+01 1.739999999999999858e+01
-8.800000000000000000e+02 5.177600000000000335e+01 1.431680000000000064e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-8.910000000000000000e+02 5.387129999999999797e+01 8.705799999999999983e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-8.960000000000000000e+02 5.107780000000000342e+01 1.086190000000000033e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-9.170000000000000000e+02 4.988089999999999691e+01 8.677899999999999281e+00 1.639999999999999858e+01
-9.530000000000000000e+02 4.976189999999999714e+01 7.054199999999999804e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-9.540000000000000000e+02 5.417960000000000065e+01 7.458700000000000330e+00 1.250000000000000000e+01
-9.630000000000000000e+02 5.258809999999999718e+01 8.342399999999999594e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-9.790000000000000000e+02 5.073640000000000327e+01 8.267200000000000770e+00 2.060000000000000142e+01
-9.830000000000000000e+02 4.855619999999999692e+01 1.055990000000000073e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-9.910000000000000000e+02 5.091159999999999997e+01 1.370870000000000033e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-1.001000000000000000e+03 5.164509999999999934e+01 1.357469999999999999e+01 2.110000000000000142e+01
-1.048000000000000000e+03 5.112800000000000011e+01 1.375430000000000064e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-1.050000000000000000e+03 5.102210000000000178e+01 1.384699999999999953e+01 2.000000000000000000e+01
-1.051000000000000000e+03 5.102479999999999905e+01 1.377500000000000036e+01 1.980000000000000071e+01
-1.052000000000000000e+03 5.221739999999999782e+01 1.216409999999999947e+01 2.150000000000000000e+01
-1.072000000000000000e+03 4.947189999999999799e+01 8.192899999999999849e+00 1.669999999999999929e+01
-1.078000000000000000e+03 5.129599999999999937e+01 6.768600000000000172e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-1.103000000000000000e+03 4.810029999999999717e+01 1.198719999999999963e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-1.107000000000000000e+03 4.985199999999999676e+01 1.049910000000000032e+01 1.559999999999999964e+01
-1.161000000000000000e+03 4.887769999999999726e+01 1.123489999999999966e+01 1.450000000000000000e+01
-1.197000000000000000e+03 4.898949999999999960e+01 1.013119999999999976e+01 1.459999999999999964e+01
-1.200000000000000000e+03 5.406909999999999883e+01 9.010500000000000398e+00 1.519999999999999929e+01
-1.207000000000000000e+03 5.027049999999999841e+01 1.227420000000000044e+01 1.450000000000000000e+01
-1.214000000000000000e+03 4.820120000000000005e+01 8.108800000000000452e+00 1.250000000000000000e+01
-1.224000000000000000e+03 4.813779999999999859e+01 7.835099999999999731e+00 1.400000000000000000e+01
-1.228000000000000000e+03 5.416510000000000247e+01 6.346000000000000085e+00 1.180000000000000071e+01
-1.246000000000000000e+03 5.184179999999999922e+01 8.060700000000000642e+00 1.819999999999999929e+01
-1.262000000000000000e+03 4.834770000000000323e+01 1.181339999999999968e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-1.266000000000000000e+03 5.429919999999999902e+01 9.316200000000000259e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-1.270000000000000000e+03 5.098290000000000077e+01 1.096080000000000076e+01 1.639999999999999858e+01
-1.279000000000000000e+03 4.964970000000000283e+01 1.100740000000000052e+01 1.480000000000000071e+01
-1.297000000000000000e+03 5.120409999999999684e+01 1.001379999999999981e+01 1.639999999999999858e+01
-1.300000000000000000e+03 5.125399999999999778e+01 8.156499999999999417e+00 1.309999999999999964e+01
-1.303000000000000000e+03 5.140409999999999968e+01 6.967699999999999783e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-1.327000000000000000e+03 5.071189999999999998e+01 6.790499999999999758e+00 1.440000000000000036e+01
-1.332000000000000000e+03 4.848319999999999652e+01 1.272409999999999997e+01 1.290000000000000036e+01
-1.339000000000000000e+03 5.291570000000000107e+01 1.018849999999999945e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-1.346000000000000000e+03 4.787489999999999668e+01 8.003800000000000026e+00 4.700000000000000178e+00
-1.357000000000000000e+03 4.998069999999999879e+01 1.183760000000000012e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-1.358000000000000000e+03 5.042830000000000013e+01 1.295350000000000001e+01 9.400000000000000355e+00
-1.411000000000000000e+03 5.053090000000000259e+01 1.004800000000000004e+01 1.300000000000000000e+01
-1.420000000000000000e+03 5.002590000000000003e+01 8.521300000000000097e+00 1.800000000000000000e+01
-1.424000000000000000e+03 5.012689999999999912e+01 8.669399999999999551e+00 1.819999999999999929e+01
-1.443000000000000000e+03 4.802320000000000277e+01 7.834299999999999820e+00 1.380000000000000071e+01
-1.451000000000000000e+03 5.382770000000000010e+01 9.249299999999999855e+00 1.619999999999999929e+01
-1.468000000000000000e+03 4.845380000000000109e+01 8.409000000000000696e+00 9.599999999999999645e+00
-1.503000000000000000e+03 5.306430000000000291e+01 7.902199999999999669e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-1.504000000000000000e+03 5.111899999999999977e+01 9.279899999999999594e+00 1.869999999999999929e+01
-1.526000000000000000e+03 5.056680000000000064e+01 9.653299999999999770e+00 1.819999999999999929e+01
-1.544000000000000000e+03 5.251290000000000191e+01 1.139409999999999989e+01 2.100000000000000000e+01
-1.550000000000000000e+03 4.748299999999999699e+01 1.106209999999999916e+01 1.440000000000000036e+01
-1.580000000000000000e+03 4.998590000000000089e+01 7.954799999999999649e+00 1.989999999999999858e+01
-1.584000000000000000e+03 4.792419999999999902e+01 8.647299999999999542e+00 1.130000000000000071e+01
-1.587000000000000000e+03 4.894809999999999661e+01 1.142890000000000050e+01 1.309999999999999964e+01
-1.590000000000000000e+03 5.149419999999999931e+01 6.246299999999999741e+00 1.680000000000000071e+01
-1.602000000000000000e+03 4.843299999999999983e+01 7.993000000000000327e+00 1.450000000000000000e+01
-1.605000000000000000e+03 5.238750000000000284e+01 1.216009999999999991e+01 2.230000000000000071e+01
-1.612000000000000000e+03 5.088130000000000308e+01 1.212889999999999979e+01 1.830000000000000071e+01
-1.639000000000000000e+03 5.060170000000000101e+01 8.643900000000000361e+00 1.760000000000000142e+01
-1.645000000000000000e+03 5.096560000000000201e+01 9.050000000000000711e+00 1.930000000000000071e+01
-1.666000000000000000e+03 5.482730000000000103e+01 9.505800000000000693e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-1.684000000000000000e+03 5.116219999999999857e+01 1.495059999999999967e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-1.691000000000000000e+03 5.150019999999999953e+01 9.950699999999999434e+00 1.580000000000000071e+01
-1.694000000000000000e+03 5.360600000000000165e+01 1.210330000000000084e+01 1.960000000000000142e+01
-1.721000000000000000e+03 4.966400000000000148e+01 1.122390000000000043e+01 1.259999999999999964e+01
-1.735000000000000000e+03 4.878940000000000055e+01 1.362899999999999956e+01 1.280000000000000071e+01
-1.736000000000000000e+03 5.357309999999999661e+01 1.067970000000000041e+01 1.800000000000000000e+01
-1.757000000000000000e+03 5.409669999999999845e+01 1.340559999999999974e+01 1.919999999999999929e+01
-1.759000000000000000e+03 5.424369999999999692e+01 1.391019999999999968e+01 1.850000000000000000e+01
-1.766000000000000000e+03 5.213439999999999941e+01 7.696900000000000297e+00 1.610000000000000142e+01
-1.832000000000000000e+03 4.911290000000000333e+01 1.313380000000000081e+01 7.000000000000000000e+00
-1.863000000000000000e+03 5.026670000000000016e+01 9.185399999999999565e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-1.869000000000000000e+03 5.331530000000000058e+01 1.393379999999999974e+01 2.019999999999999929e+01
-1.886000000000000000e+03 4.848780000000000001e+01 1.026079999999999970e+01 1.290000000000000036e+01
-1.964000000000000000e+03 4.994449999999999790e+01 6.382100000000000328e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-1.975000000000000000e+03 5.363320000000000221e+01 9.988099999999999312e+00 1.739999999999999858e+01
-1.981000000000000000e+03 5.347769999999999868e+01 9.895699999999999719e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-2.014000000000000000e+03 5.246439999999999770e+01 9.677899999999999281e+00 2.039999999999999858e+01
-2.023000000000000000e+03 4.879180000000000206e+01 1.070620000000000083e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-2.039000000000000000e+03 5.190019999999999811e+01 1.056990000000000052e+01 1.789999999999999858e+01
-2.044000000000000000e+03 5.165200000000000102e+01 1.113669999999999938e+01 1.750000000000000000e+01
-2.074000000000000000e+03 4.837519999999999953e+01 8.980000000000000426e+00 1.130000000000000071e+01
-2.110000000000000000e+03 5.104110000000000014e+01 6.104199999999999626e+00 1.490000000000000036e+01
-2.115000000000000000e+03 5.417499999999999716e+01 7.892000000000000348e+00 1.400000000000000000e+01
-2.171000000000000000e+03 5.085199999999999676e+01 9.737700000000000244e+00 1.869999999999999929e+01
-2.174000000000000000e+03 5.162550000000000239e+01 1.036950000000000038e+01 1.619999999999999929e+01
-2.201000000000000000e+03 5.457500000000000284e+01 1.310440000000000005e+01 1.680000000000000071e+01
-2.211000000000000000e+03 5.073709999999999809e+01 7.652800000000000047e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-2.252000000000000000e+03 5.089900000000000091e+01 1.474569999999999936e+01 1.880000000000000071e+01
-2.261000000000000000e+03 5.031230000000000047e+01 1.187599999999999945e+01 1.590000000000000036e+01
-2.290000000000000000e+03 4.780089999999999861e+01 1.101079999999999970e+01 9.800000000000000711e+00
-2.303000000000000000e+03 5.431459999999999866e+01 9.538999999999999702e+00 1.630000000000000071e+01
-2.306000000000000000e+03 5.431940000000000168e+01 1.067319999999999958e+01 1.480000000000000071e+01
-2.315000000000000000e+03 5.176570000000000249e+01 1.316660000000000075e+01 1.930000000000000071e+01
-2.319000000000000000e+03 4.788230000000000075e+01 1.169609999999999950e+01 1.309999999999999964e+01
-2.323000000000000000e+03 5.185289999999999822e+01 9.495300000000000296e+00 1.960000000000000142e+01
-2.362000000000000000e+03 5.056510000000000105e+01 7.484300000000000175e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-2.385000000000000000e+03 4.969270000000000209e+01 7.326399999999999579e+00 1.630000000000000071e+01
-2.410000000000000000e+03 4.871119999999999806e+01 1.153619999999999912e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-2.429000000000000000e+03 5.398969999999999914e+01 9.569599999999999440e+00 1.689999999999999858e+01
-2.437000000000000000e+03 5.445700000000000074e+01 9.520300000000000651e+00 1.580000000000000071e+01
-2.444000000000000000e+03 5.092510000000000048e+01 1.158300000000000018e+01 2.019999999999999929e+01
-2.480000000000000000e+03 5.006430000000000291e+01 8.993000000000000327e+00 1.810000000000000142e+01
-2.483000000000000000e+03 5.118030000000000257e+01 8.489100000000000534e+00 1.380000000000000071e+01
-2.485000000000000000e+03 4.891700000000000159e+01 9.687099999999999156e+00 1.380000000000000071e+01
-2.486000000000000000e+03 4.942620000000000147e+01 7.755700000000000038e+00 1.669999999999999929e+01
-2.497000000000000000e+03 5.050139999999999674e+01 6.526399999999999757e+00 1.269999999999999929e+01
-2.559000000000000000e+03 4.772330000000000183e+01 1.033479999999999954e+01 1.240000000000000036e+01
-2.564000000000000000e+03 5.437760000000000105e+01 1.014240000000000030e+01 1.530000000000000071e+01
-2.575000000000000000e+03 4.918039999999999878e+01 9.980000000000000426e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-2.578000000000000000e+03 5.399949999999999761e+01 1.143410000000000082e+01 1.639999999999999858e+01
-2.597000000000000000e+03 5.022399999999999665e+01 1.007920000000000016e+01 1.730000000000000071e+01
-2.600000000000000000e+03 4.973629999999999995e+01 1.017810000000000059e+01 1.769999999999999929e+01
-2.601000000000000000e+03 5.022180000000000177e+01 8.446899999999999409e+00 1.259999999999999964e+01
-2.618000000000000000e+03 5.084579999999999700e+01 1.048029999999999973e+01 1.409999999999999964e+01
-2.627000000000000000e+03 5.155539999999999878e+01 1.388449999999999918e+01 2.030000000000000071e+01
-2.629000000000000000e+03 5.176120000000000232e+01 6.095399999999999707e+00 1.580000000000000071e+01
-2.638000000000000000e+03 4.810540000000000305e+01 8.754799999999999471e+00 9.000000000000000000e+00
-2.641000000000000000e+03 5.151850000000000307e+01 1.290649999999999942e+01 2.000000000000000000e+01
-2.667000000000000000e+03 5.086460000000000292e+01 7.157499999999999751e+00 1.830000000000000071e+01
-2.680000000000000000e+03 5.028399999999999892e+01 1.044560000000000066e+01 1.800000000000000000e+01
-2.700000000000000000e+03 4.883019999999999783e+01 1.148719999999999963e+01 1.380000000000000071e+01
-2.704000000000000000e+03 5.175110000000000099e+01 1.200939999999999941e+01 2.069999999999999929e+01
-2.708000000000000000e+03 4.766519999999999868e+01 1.108050000000000068e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-2.712000000000000000e+03 4.769519999999999982e+01 9.130699999999999150e+00 1.450000000000000000e+01
-2.750000000000000000e+03 5.025229999999999819e+01 1.132089999999999996e+01 1.719999999999999929e+01
-2.773000000000000000e+03 4.942830000000000013e+01 1.190160000000000018e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-2.794000000000000000e+03 5.293630000000000280e+01 1.240930000000000000e+01 2.150000000000000000e+01
-2.796000000000000000e+03 5.391559999999999775e+01 1.227899999999999991e+01 1.880000000000000071e+01
-2.812000000000000000e+03 4.836469999999999914e+01 7.828000000000000291e+00 1.450000000000000000e+01
-2.814000000000000000e+03 4.851209999999999667e+01 9.764499999999999957e+00 1.119999999999999929e+01
-2.856000000000000000e+03 5.191729999999999734e+01 1.308779999999999966e+01 1.900000000000000000e+01
-2.878000000000000000e+03 5.139090000000000202e+01 1.187860000000000049e+01 1.900000000000000000e+01
-2.886000000000000000e+03 4.821759999999999735e+01 9.909700000000000841e+00 1.200000000000000000e+01
-2.905000000000000000e+03 4.818489999999999895e+01 1.085069999999999979e+01 1.230000000000000071e+01
-2.907000000000000000e+03 5.479030000000000200e+01 8.951399999999999579e+00 1.340000000000000036e+01
-2.925000000000000000e+03 5.139330000000000354e+01 1.031230000000000047e+01 1.739999999999999858e+01
-2.928000000000000000e+03 5.131510000000000105e+01 1.244619999999999926e+01 2.110000000000000142e+01
-2.932000000000000000e+03 5.143480000000000274e+01 1.223959999999999937e+01 2.030000000000000071e+01
-2.947000000000000000e+03 5.113329999999999842e+01 8.034800000000000608e+00 1.540000000000000036e+01
-2.951000000000000000e+03 5.310070000000000334e+01 1.148639999999999972e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-2.953000000000000000e+03 4.785969999999999658e+01 8.230800000000000338e+00 9.599999999999999645e+00
-2.961000000000000000e+03 5.449960000000000093e+01 1.027369999999999983e+01 1.380000000000000071e+01
-2.968000000000000000e+03 5.098940000000000339e+01 6.977699999999999569e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-2.985000000000000000e+03 5.093829999999999814e+01 1.420930000000000071e+01 1.939999999999999858e+01
-3.015000000000000000e+03 5.220850000000000080e+01 1.411800000000000033e+01 2.010000000000000142e+01
-3.028000000000000000e+03 5.178540000000000276e+01 8.838800000000000878e+00 1.780000000000000071e+01
-3.031000000000000000e+03 5.163360000000000127e+01 8.394500000000000739e+00 1.900000000000000000e+01
-3.032000000000000000e+03 5.501100000000000279e+01 8.412499999999999645e+00 1.340000000000000036e+01
-3.034000000000000000e+03 5.045049999999999812e+01 1.163499999999999979e+01 1.639999999999999858e+01
-3.042000000000000000e+03 5.056170000000000186e+01 8.238599999999999923e+00 1.930000000000000071e+01
-3.083000000000000000e+03 5.192669999999999675e+01 1.387969999999999970e+01 2.119999999999999929e+01
-3.086000000000000000e+03 5.380250000000000199e+01 1.069890000000000008e+01 1.789999999999999858e+01
-3.093000000000000000e+03 5.297240000000000038e+01 1.113739999999999952e+01 1.860000000000000142e+01
-3.098000000000000000e+03 5.124519999999999698e+01 7.642500000000000071e+00 1.530000000000000071e+01
-3.126000000000000000e+03 5.210289999999999822e+01 1.158270000000000088e+01 2.050000000000000000e+01
-3.137000000000000000e+03 4.996560000000000201e+01 8.213900000000000645e+00 1.689999999999999858e+01
-3.147000000000000000e+03 4.877250000000000085e+01 1.221790000000000020e+01 1.330000000000000071e+01
-3.155000000000000000e+03 5.010150000000000148e+01 6.800900000000000389e+00 1.610000000000000142e+01
-3.158000000000000000e+03 5.254679999999999751e+01 1.454519999999999946e+01 2.089999999999999858e+01
-3.164000000000000000e+03 5.084920000000000329e+01 8.774599999999999511e+00 1.960000000000000142e+01
-3.166000000000000000e+03 5.065100000000000335e+01 1.314690000000000047e+01 1.450000000000000000e+01
-3.167000000000000000e+03 5.066210000000000235e+01 7.960300000000000153e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-3.196000000000000000e+03 5.332229999999999848e+01 1.193190000000000062e+01 2.180000000000000071e+01
-3.204000000000000000e+03 5.073349999999999937e+01 1.088150000000000084e+01 1.660000000000000142e+01
-3.226000000000000000e+03 5.172590000000000288e+01 1.151089999999999947e+01 2.050000000000000000e+01
-3.231000000000000000e+03 5.056119999999999948e+01 1.037710000000000043e+01 1.540000000000000036e+01
-3.234000000000000000e+03 5.112939999999999685e+01 1.343280000000000030e+01 1.880000000000000071e+01
-3.244000000000000000e+03 4.798199999999999932e+01 1.013840000000000074e+01 1.200000000000000000e+01
-3.254000000000000000e+03 5.271560000000000201e+01 7.317599999999999660e+00 1.610000000000000142e+01
-3.257000000000000000e+03 4.947729999999999961e+01 9.762199999999999989e+00 1.669999999999999929e+01
-3.268000000000000000e+03 4.816940000000000310e+01 8.943300000000000693e+00 9.500000000000000000e+00
-3.271000000000000000e+03 4.885479999999999734e+01 1.291890000000000072e+01 1.469999999999999929e+01
-3.278000000000000000e+03 4.853770000000000095e+01 9.273400000000000531e+00 1.240000000000000036e+01
-3.284000000000000000e+03 4.966910000000000025e+01 9.008499999999999730e+00 1.630000000000000071e+01
-3.287000000000000000e+03 4.971759999999999735e+01 9.099700000000000344e+00 1.490000000000000036e+01
-3.289000000000000000e+03 5.072809999999999775e+01 1.178379999999999939e+01 1.789999999999999858e+01
-3.307000000000000000e+03 4.747789999999999822e+01 1.126529999999999987e+01 1.250000000000000000e+01
-3.319000000000000000e+03 4.976440000000000197e+01 9.253000000000000114e+00 1.630000000000000071e+01
-3.340000000000000000e+03 5.043829999999999814e+01 7.806099999999999817e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-3.362000000000000000e+03 4.897209999999999752e+01 8.873400000000000176e+00 1.390000000000000036e+01
-3.366000000000000000e+03 4.827900000000000347e+01 1.250239999999999974e+01 1.400000000000000000e+01
-3.376000000000000000e+03 5.251760000000000161e+01 1.412320000000000064e+01 2.069999999999999929e+01
-3.379000000000000000e+03 4.816320000000000334e+01 1.154289999999999949e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-3.402000000000000000e+03 4.838510000000000133e+01 9.483700000000000685e+00 1.059999999999999964e+01
-3.426000000000000000e+03 5.156600000000000250e+01 1.470079999999999920e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-3.442000000000000000e+03 5.035739999999999839e+01 8.750600000000000378e+00 1.610000000000000142e+01
-3.484000000000000000e+03 4.870859999999999701e+01 1.121470000000000056e+01 1.580000000000000071e+01
-3.485000000000000000e+03 4.831150000000000233e+01 1.037729999999999997e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-3.490000000000000000e+03 5.053459999999999752e+01 7.085300000000000153e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-3.509000000000000000e+03 5.310199999999999676e+01 1.304209999999999958e+01 2.069999999999999929e+01
-3.513000000000000000e+03 5.050019999999999953e+01 1.113439999999999941e+01 1.280000000000000071e+01
-3.527000000000000000e+03 5.089229999999999876e+01 9.404999999999999361e+00 1.590000000000000036e+01
-3.540000000000000000e+03 5.084459999999999980e+01 7.371999999999999886e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-3.545000000000000000e+03 4.934400000000000119e+01 7.229700000000000237e+00 1.839999999999999858e+01
-3.571000000000000000e+03 4.981739999999999924e+01 1.186379999999999946e+01 1.369999999999999929e+01
-3.591000000000000000e+03 5.067430000000000234e+01 6.424000000000000377e+00 1.240000000000000036e+01
-3.603000000000000000e+03 4.938949999999999818e+01 9.966699999999999449e+00 1.459999999999999964e+01
-3.612000000000000000e+03 5.267110000000000269e+01 9.222899999999999210e+00 1.919999999999999929e+01
-3.621000000000000000e+03 4.882529999999999859e+01 1.050670000000000037e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-3.623000000000000000e+03 5.082939999999999969e+01 6.660199999999999676e+00 1.459999999999999964e+01
-3.631000000000000000e+03 5.371229999999999905e+01 7.151900000000000368e+00 1.380000000000000071e+01
-3.639000000000000000e+03 5.376469999999999771e+01 8.658300000000000551e+00 1.480000000000000071e+01
-3.660000000000000000e+03 5.036019999999999897e+01 6.869699999999999918e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-3.667000000000000000e+03 4.942580000000000240e+01 1.125380000000000003e+01 1.340000000000000036e+01
-3.668000000000000000e+03 4.950300000000000011e+01 1.105489999999999995e+01 1.419999999999999929e+01
-3.679000000000000000e+03 4.761869999999999692e+01 1.216649999999999920e+01 1.569999999999999929e+01
-3.730000000000000000e+03 4.739840000000000231e+01 1.027590000000000003e+01 1.450000000000000000e+01
-3.734000000000000000e+03 4.912800000000000011e+01 9.352499999999999147e+00 1.700000000000000000e+01
-3.739000000000000000e+03 4.945210000000000150e+01 1.243650000000000055e+01 1.180000000000000071e+01
-3.761000000000000000e+03 4.920700000000000074e+01 9.517599999999999838e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-3.811000000000000000e+03 5.129599999999999937e+01 1.309280000000000044e+01 1.950000000000000000e+01
-3.821000000000000000e+03 5.108729999999999905e+01 1.192919999999999980e+01 1.950000000000000000e+01
-3.836000000000000000e+03 5.045380000000000109e+01 1.022109999999999985e+01 1.700000000000000000e+01
-3.857000000000000000e+03 4.763620000000000232e+01 1.038920000000000066e+01 1.159999999999999964e+01
-3.875000000000000000e+03 4.915100000000000335e+01 1.168960000000000043e+01 1.230000000000000071e+01
-3.897000000000000000e+03 5.408930000000000149e+01 1.087729999999999997e+01 1.669999999999999929e+01
-3.904000000000000000e+03 4.953540000000000276e+01 6.378899999999999793e+00 1.880000000000000071e+01
-3.925000000000000000e+03 4.893289999999999651e+01 8.697300000000000253e+00 1.290000000000000036e+01
-3.927000000000000000e+03 4.793449999999999989e+01 9.286899999999999267e+00 1.130000000000000071e+01
-3.939000000000000000e+03 4.919120000000000203e+01 7.587900000000000311e+00 1.569999999999999929e+01
-3.946000000000000000e+03 5.048190000000000310e+01 1.213000000000000078e+01 1.719999999999999929e+01
-3.975000000000000000e+03 4.947769999999999868e+01 1.153570000000000029e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-3.987000000000000000e+03 5.238130000000000308e+01 1.306220000000000070e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-4.024000000000000000e+03 5.436430000000000007e+01 1.347710000000000008e+01 1.800000000000000000e+01
-4.032000000000000000e+03 5.179529999999999745e+01 1.113199999999999967e+01 1.950000000000000000e+01
-4.036000000000000000e+03 5.138949999999999818e+01 1.154119999999999990e+01 1.930000000000000071e+01
-4.039000000000000000e+03 5.373310000000000031e+01 9.877599999999999270e+00 1.719999999999999929e+01
-4.063000000000000000e+03 5.244610000000000127e+01 8.590600000000000236e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-4.094000000000000000e+03 4.780619999999999692e+01 9.620599999999999596e+00 1.390000000000000036e+01
-4.104000000000000000e+03 4.904249999999999687e+01 1.210190000000000055e+01 1.430000000000000071e+01
-4.127000000000000000e+03 5.099060000000000059e+01 7.695800000000000196e+00 1.639999999999999858e+01
-4.160000000000000000e+03 4.874249999999999972e+01 8.923999999999999488e+00 1.130000000000000071e+01
-4.169000000000000000e+03 4.867029999999999745e+01 7.993900000000000006e+00 1.440000000000000036e+01
-4.175000000000000000e+03 4.755899999999999750e+01 7.772100000000000009e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-4.177000000000000000e+03 4.897259999999999991e+01 8.330099999999999838e+00 1.480000000000000071e+01
-4.189000000000000000e+03 4.814789999999999992e+01 9.459600000000000009e+00 1.209999999999999964e+01
-4.261000000000000000e+03 4.787530000000000285e+01 1.212800000000000011e+01 1.469999999999999929e+01
-4.271000000000000000e+03 5.418030000000000257e+01 1.208079999999999998e+01 1.669999999999999929e+01
-4.275000000000000000e+03 5.312879999999999825e+01 9.339800000000000324e+00 1.719999999999999929e+01
-4.280000000000000000e+03 4.921620000000000061e+01 1.110350000000000037e+01 1.380000000000000071e+01
-4.287000000000000000e+03 4.938479999999999848e+01 1.017319999999999958e+01 1.500000000000000000e+01
-4.300000000000000000e+03 4.818139999999999645e+01 8.635600000000000165e+00 1.140000000000000036e+01
-4.301000000000000000e+03 4.985020000000000095e+01 7.871000000000000441e+00 2.089999999999999858e+01
-4.323000000000000000e+03 4.964679999999999893e+01 7.883700000000000152e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-4.336000000000000000e+03 4.921280000000000143e+01 7.107700000000000351e+00 1.700000000000000000e+01
-4.349000000000000000e+03 4.895689999999999742e+01 9.070999999999999730e+00 1.369999999999999929e+01
-4.354000000000000000e+03 4.878320000000000078e+01 1.331460000000000043e+01 1.400000000000000000e+01
-4.371000000000000000e+03 5.210419999999999874e+01 8.752100000000000435e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-4.377000000000000000e+03 5.035179999999999723e+01 1.000339999999999918e+01 1.550000000000000000e+01
-4.393000000000000000e+03 5.432789999999999964e+01 8.603099999999999525e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-4.411000000000000000e+03 4.991949999999999932e+01 8.967100000000000293e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-4.445000000000000000e+03 5.176579999999999870e+01 1.065329999999999977e+01 1.569999999999999929e+01
-4.464000000000000000e+03 5.056790000000000163e+01 1.180410000000000004e+01 1.580000000000000071e+01
-4.466000000000000000e+03 5.452750000000000341e+01 9.548700000000000188e+00 1.569999999999999929e+01
-4.480000000000000000e+03 5.034470000000000312e+01 9.553399999999999892e+00 1.810000000000000142e+01
-4.501000000000000000e+03 5.065460000000000207e+01 1.076929999999999943e+01 1.180000000000000071e+01
-4.508000000000000000e+03 5.029679999999999751e+01 6.419400000000000439e+00 1.300000000000000000e+01
-4.548000000000000000e+03 5.018469999999999942e+01 1.207910000000000039e+01 1.490000000000000036e+01
-4.559000000000000000e+03 4.916440000000000055e+01 1.261749999999999972e+01 1.359999999999999964e+01
-4.560000000000000000e+03 5.049249999999999972e+01 9.122600000000000264e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-4.592000000000000000e+03 4.932780000000000342e+01 1.208709999999999951e+01 1.330000000000000071e+01
-4.605000000000000000e+03 5.064410000000000167e+01 1.119359999999999999e+01 1.830000000000000071e+01
-4.625000000000000000e+03 5.364249999999999829e+01 1.138719999999999999e+01 1.860000000000000142e+01
-4.642000000000000000e+03 5.289110000000000156e+01 1.172969999999999935e+01 2.050000000000000000e+01
-4.651000000000000000e+03 5.190400000000000347e+01 1.018849999999999945e+01 1.839999999999999858e+01
-4.703000000000000000e+03 4.807189999999999941e+01 9.194300000000000139e+00 1.200000000000000000e+01
-4.706000000000000000e+03 4.827179999999999893e+01 1.302730000000000032e+01 1.400000000000000000e+01
-4.709000000000000000e+03 4.999960000000000093e+01 7.598099999999999632e+00 1.540000000000000036e+01
-4.745000000000000000e+03 5.296039999999999992e+01 9.792999999999999261e+00 1.819999999999999929e+01
-4.763000000000000000e+03 5.106069999999999709e+01 9.926600000000000534e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-4.841000000000000000e+03 5.369460000000000122e+01 8.873499999999999943e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-4.857000000000000000e+03 5.355340000000000344e+01 9.609700000000000131e+00 1.750000000000000000e+01
-4.878000000000000000e+03 5.166460000000000008e+01 1.088109999999999999e+01 1.680000000000000071e+01
-4.887000000000000000e+03 4.866559999999999775e+01 9.864800000000000679e+00 1.140000000000000036e+01
-4.896000000000000000e+03 5.466539999999999822e+01 9.804999999999999716e+00 1.519999999999999929e+01
-4.911000000000000000e+03 4.882750000000000057e+01 1.255969999999999942e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-4.928000000000000000e+03 4.882809999999999917e+01 9.199999999999999289e+00 1.269999999999999929e+01
-4.931000000000000000e+03 4.868829999999999814e+01 9.223499999999999588e+00 1.230000000000000071e+01
-4.978000000000000000e+03 5.063900000000000290e+01 1.002280000000000015e+01 1.610000000000000142e+01
-4.997000000000000000e+03 5.097710000000000008e+01 1.234190000000000076e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-5.009000000000000000e+03 5.376100000000000279e+01 1.255739999999999945e+01 1.810000000000000142e+01
-5.014000000000000000e+03 5.327579999999999671e+01 8.985699999999999577e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-5.017000000000000000e+03 5.040019999999999811e+01 1.138889999999999958e+01 1.440000000000000036e+01
-5.029000000000000000e+03 4.947370000000000090e+01 7.038499999999999979e+00 1.639999999999999858e+01
-5.046000000000000000e+03 4.985759999999999792e+01 1.235420000000000051e+01 1.380000000000000071e+01
-5.064000000000000000e+03 5.128970000000000340e+01 6.443699999999999761e+00 1.680000000000000071e+01
-5.097000000000000000e+03 5.406609999999999872e+01 1.276750000000000007e+01 1.919999999999999929e+01
-5.099000000000000000e+03 4.973259999999999792e+01 6.613100000000000200e+00 1.880000000000000071e+01
-5.100000000000000000e+03 4.974790000000000134e+01 6.658299999999999663e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-5.109000000000000000e+03 5.359969999999999857e+01 1.330390000000000050e+01 2.000000000000000000e+01
-5.111000000000000000e+03 4.803110000000000213e+01 1.253960000000000008e+01 1.359999999999999964e+01
-5.133000000000000000e+03 5.133440000000000225e+01 8.913199999999999790e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-5.142000000000000000e+03 5.374439999999999884e+01 1.406969999999999921e+01 1.950000000000000000e+01
-5.146000000000000000e+03 5.294140000000000157e+01 1.052890000000000015e+01 2.010000000000000142e+01
-5.149000000000000000e+03 4.957410000000000139e+01 1.019149999999999956e+01 1.630000000000000071e+01
-5.158000000000000000e+03 5.216009999999999991e+01 1.117590000000000039e+01 1.919999999999999929e+01
-5.229000000000000000e+03 4.804529999999999745e+01 8.460800000000000765e+00 1.059999999999999964e+01
-5.275000000000000000e+03 4.924450000000000216e+01 8.537399999999999878e+00 1.710000000000000142e+01
-5.279000000000000000e+03 5.161939999999999884e+01 9.574899999999999523e+00 1.500000000000000000e+01
-5.280000000000000000e+03 5.392240000000000322e+01 1.022669999999999924e+01 1.780000000000000071e+01
-5.300000000000000000e+03 5.025959999999999894e+01 8.360699999999999577e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-5.335000000000000000e+03 5.089629999999999654e+01 1.054840000000000089e+01 1.739999999999999858e+01
-5.347000000000000000e+03 5.150390000000000157e+01 9.111800000000000566e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-5.349000000000000000e+03 5.351959999999999695e+01 1.266539999999999999e+01 2.130000000000000071e+01
-5.371000000000000000e+03 5.049730000000000274e+01 9.942700000000000315e+00 1.159999999999999964e+01
-5.397000000000000000e+03 4.966629999999999967e+01 1.218449999999999989e+01 1.369999999999999929e+01
-5.404000000000000000e+03 4.840240000000000009e+01 1.169459999999999944e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-5.424000000000000000e+03 5.101769999999999783e+01 1.135440000000000005e+01 1.980000000000000071e+01
-5.426000000000000000e+03 4.937579999999999814e+01 8.121299999999999741e+00 1.300000000000000000e+01
-5.433000000000000000e+03 4.955340000000000344e+01 6.812000000000000277e+00 1.780000000000000071e+01
-5.440000000000000000e+03 4.901149999999999807e+01 1.093079999999999963e+01 1.400000000000000000e+01
-5.480000000000000000e+03 5.157630000000000337e+01 7.887900000000000134e+00 1.800000000000000000e+01
-5.490000000000000000e+03 5.184539999999999793e+01 1.076859999999999928e+01 1.810000000000000142e+01
-5.516000000000000000e+03 5.452830000000000155e+01 1.106060000000000088e+01 1.500000000000000000e+01
-5.538000000000000000e+03 4.788269999999999982e+01 1.115760000000000041e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-5.541000000000000000e+03 5.013199999999999790e+01 8.317000000000000171e+00 1.689999999999999858e+01
-5.546000000000000000e+03 5.212069999999999936e+01 1.245850000000000080e+01 1.910000000000000142e+01
-5.562000000000000000e+03 4.865160000000000196e+01 8.680099999999999483e+00 1.109999999999999964e+01
-5.629000000000000000e+03 5.188920000000000243e+01 1.264450000000000074e+01 2.060000000000000142e+01
-5.640000000000000000e+03 5.355040000000000333e+01 7.667200000000000237e+00 1.409999999999999964e+01
-5.643000000000000000e+03 5.318639999999999901e+01 1.249489999999999945e+01 2.200000000000000000e+01
-5.664000000000000000e+03 4.829529999999999745e+01 8.239100000000000534e+00 1.340000000000000036e+01
-5.676000000000000000e+03 5.239620000000000033e+01 1.068919999999999959e+01 1.969999999999999929e+01
-5.688000000000000000e+03 4.770029999999999859e+01 8.105700000000000571e+00 1.059999999999999964e+01
-5.692000000000000000e+03 4.960510000000000019e+01 8.365899999999999892e+00 1.689999999999999858e+01
-5.705000000000000000e+03 4.977040000000000219e+01 9.957599999999999341e+00 1.719999999999999929e+01
-5.715000000000000000e+03 5.246050000000000324e+01 9.431100000000000705e+00 2.000000000000000000e+01
-5.717000000000000000e+03 5.122560000000000002e+01 7.105199999999999960e+00 1.639999999999999858e+01
-5.731000000000000000e+03 4.767830000000000013e+01 8.380100000000000549e+00 1.390000000000000036e+01
-5.745000000000000000e+03 5.296640000000000015e+01 1.332680000000000042e+01 2.100000000000000000e+01
-5.750000000000000000e+03 5.103139999999999787e+01 1.214949999999999974e+01 2.019999999999999929e+01
-5.779000000000000000e+03 5.073140000000000072e+01 1.375159999999999982e+01 1.309999999999999964e+01
-5.792000000000000000e+03 4.742099999999999937e+01 1.098479999999999990e+01 2.799999999999999822e+00
-5.797000000000000000e+03 5.068789999999999907e+01 1.243290000000000006e+01 1.750000000000000000e+01
-5.800000000000000000e+03 4.902799999999999869e+01 1.323850000000000016e+01 1.250000000000000000e+01
-5.822000000000000000e+03 5.286299999999999955e+01 8.698800000000000310e+00 1.689999999999999858e+01
-5.825000000000000000e+03 5.261979999999999791e+01 1.278669999999999973e+01 2.089999999999999858e+01
-5.839000000000000000e+03 5.338810000000000144e+01 7.228699999999999903e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-5.856000000000000000e+03 4.854509999999999792e+01 1.335319999999999929e+01 1.319999999999999929e+01
-5.871000000000000000e+03 4.994619999999999749e+01 7.264499999999999957e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-5.906000000000000000e+03 4.950619999999999976e+01 8.558500000000000441e+00 1.630000000000000071e+01
-5.930000000000000000e+03 5.464099999999999824e+01 1.002379999999999960e+01 1.490000000000000036e+01
-5.941000000000000000e+03 4.767540000000000333e+01 1.246979999999999933e+01 1.440000000000000036e+01
-6.093000000000000000e+03 5.321390000000000242e+01 1.047039999999999971e+01 1.839999999999999858e+01
-6.105000000000000000e+03 5.431940000000000168e+01 9.805099999999999483e+00 1.569999999999999929e+01
-6.109000000000000000e+03 5.338369999999999749e+01 1.437279999999999980e+01 2.089999999999999858e+01
-6.129000000000000000e+03 5.105930000000000035e+01 1.442660000000000053e+01 1.939999999999999858e+01
-6.157000000000000000e+03 5.364099999999999824e+01 8.080799999999999983e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-6.158000000000000000e+03 4.922469999999999857e+01 1.060839999999999961e+01 1.369999999999999929e+01
-6.159000000000000000e+03 5.295420000000000016e+01 7.319600000000000328e+00 1.519999999999999929e+01
-6.163000000000000000e+03 5.416539999999999822e+01 1.035190000000000055e+01 1.619999999999999929e+01
-6.170000000000000000e+03 5.201919999999999789e+01 1.472540000000000049e+01 1.960000000000000142e+01
-6.197000000000000000e+03 5.186639999999999873e+01 9.271000000000000796e+00 1.719999999999999929e+01
-6.199000000000000000e+03 5.424839999999999662e+01 1.304180000000000028e+01 1.930000000000000071e+01
-6.217000000000000000e+03 4.924060000000000059e+01 6.935100000000000264e+00 1.860000000000000142e+01
-6.258000000000000000e+03 4.768449999999999989e+01 9.440899999999999181e+00 1.530000000000000071e+01
-6.259000000000000000e+03 4.902100000000000080e+01 9.603300000000000836e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-6.260000000000000000e+03 4.933279999999999887e+01 9.704000000000000625e+00 1.559999999999999964e+01
-6.262000000000000000e+03 4.876950000000000074e+01 9.873699999999999477e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-6.263000000000000000e+03 4.777380000000000138e+01 8.821899999999999409e+00 1.359999999999999964e+01
-6.264000000000000000e+03 5.141400000000000148e+01 8.650000000000000355e+00 1.580000000000000071e+01
-6.265000000000000000e+03 5.236129999999999995e+01 1.238669999999999938e+01 2.219999999999999929e+01
-6.266000000000000000e+03 5.203040000000000020e+01 1.096260000000000012e+01 1.860000000000000142e+01
-6.272000000000000000e+03 5.084259999999999735e+01 1.025179999999999936e+01 1.630000000000000071e+01
-6.273000000000000000e+03 5.250750000000000028e+01 1.185510000000000019e+01 2.050000000000000000e+01
-6.275000000000000000e+03 4.867049999999999699e+01 9.462699999999999889e+00 1.369999999999999929e+01
-6.305000000000000000e+03 5.120609999999999928e+01 1.049779999999999980e+01 1.930000000000000071e+01
-6.310000000000000000e+03 5.410490000000000066e+01 1.382390000000000008e+01 1.869999999999999929e+01
-6.312000000000000000e+03 4.953139999999999787e+01 1.064179999999999993e+01 1.480000000000000071e+01
-6.314000000000000000e+03 5.105069999999999908e+01 1.330030000000000001e+01 1.769999999999999929e+01
-6.336000000000000000e+03 5.001319999999999766e+01 9.653999999999999915e+00 1.590000000000000036e+01
-6.337000000000000000e+03 5.176630000000000109e+01 7.519400000000000084e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-6.344000000000000000e+03 5.039399999999999835e+01 8.142300000000000537e+00 1.950000000000000000e+01
-6.346000000000000000e+03 4.820700000000000074e+01 1.120350000000000001e+01 1.290000000000000036e+01
-6.347000000000000000e+03 5.005789999999999651e+01 1.029720000000000013e+01 1.710000000000000142e+01
-7.075000000000000000e+03 4.870199999999999818e+01 1.184929999999999950e+01 1.309999999999999964e+01
-7.099000000000000000e+03 5.201109999999999900e+01 1.039659999999999940e+01 1.660000000000000142e+01
-7.105000000000000000e+03 4.783500000000000085e+01 1.265479999999999983e+01 1.350000000000000000e+01
-7.106000000000000000e+03 5.207139999999999702e+01 8.456500000000000128e+00 1.789999999999999858e+01
-7.187000000000000000e+03 4.976359999999999673e+01 9.406299999999999883e+00 1.710000000000000142e+01
-7.298000000000000000e+03 5.452680000000000149e+01 9.042500000000000426e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-7.319000000000000000e+03 4.873740000000000094e+01 1.073930000000000007e+01 1.450000000000000000e+01
-7.321000000000000000e+03 5.115070000000000050e+01 1.133210000000000051e+01 1.939999999999999858e+01
-7.329000000000000000e+03 5.054670000000000130e+01 1.228630000000000067e+01 1.600000000000000000e+01
-7.330000000000000000e+03 5.146329999999999671e+01 7.977999999999999758e+00 1.700000000000000000e+01
-7.331000000000000000e+03 4.860990000000000322e+01 1.026740000000000030e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-7.341000000000000000e+03 5.009000000000000341e+01 8.786199999999999122e+00 1.750000000000000000e+01
-7.343000000000000000e+03 5.061990000000000123e+01 1.348160000000000025e+01 1.390000000000000036e+01
-7.350000000000000000e+03 4.910880000000000223e+01 1.282310000000000016e+01 1.190000000000000036e+01
-7.351000000000000000e+03 5.331750000000000256e+01 1.341750000000000043e+01 2.110000000000000142e+01
-7.364000000000000000e+03 5.168200000000000216e+01 1.230419999999999980e+01 2.010000000000000142e+01
-7.367000000000000000e+03 5.196430000000000149e+01 9.807199999999999918e+00 1.889999999999999858e+01
-7.368000000000000000e+03 5.100070000000000192e+01 1.036209999999999987e+01 1.600000000000000000e+01
-7.369000000000000000e+03 4.916230000000000189e+01 1.036609999999999943e+01 1.319999999999999929e+01
-7.370000000000000000e+03 4.939099999999999824e+01 1.268379999999999974e+01 1.219999999999999929e+01
-7.373000000000000000e+03 5.359839999999999804e+01 6.702399999999999913e+00 1.430000000000000071e+01
-7.374000000000000000e+03 5.208129999999999882e+01 6.940900000000000070e+00 1.469999999999999929e+01
-7.389000000000000000e+03 5.274609999999999843e+01 1.384270000000000067e+01 2.139999999999999858e+01
-7.393000000000000000e+03 5.144930000000000092e+01 1.425329999999999941e+01 1.989999999999999858e+01
-7.394000000000000000e+03 5.003150000000000119e+01 1.197450000000000081e+01 1.359999999999999964e+01
-7.395000000000000000e+03 4.865950000000000131e+01 1.253880000000000017e+01 1.380000000000000071e+01
-7.396000000000000000e+03 5.050840000000000174e+01 9.224700000000000344e+00 1.350000000000000000e+01
-7.403000000000000000e+03 4.779549999999999699e+01 1.003240000000000087e+01 1.230000000000000071e+01
-7.410000000000000000e+03 5.075130000000000052e+01 9.022399999999999309e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-7.412000000000000000e+03 5.000829999999999842e+01 9.423799999999999955e+00 1.509999999999999964e+01
-7.419000000000000000e+03 5.066100000000000136e+01 1.207559999999999967e+01 1.810000000000000142e+01
-7.420000000000000000e+03 5.110439999999999827e+01 1.171119999999999983e+01 1.960000000000000142e+01
-7.424000000000000000e+03 4.777239999999999753e+01 1.290729999999999933e+01 1.639999999999999858e+01
-7.427000000000000000e+03 5.401879999999999882e+01 9.925499999999999545e+00 1.660000000000000142e+01
-7.428000000000000000e+03 5.041669999999999874e+01 1.081559999999999988e+01 1.700000000000000000e+01
-7.431000000000000000e+03 4.801299999999999812e+01 1.155240000000000045e+01 1.290000000000000036e+01
-7.432000000000000000e+03 5.264229999999999876e+01 1.066269999999999918e+01 1.919999999999999929e+01
-1.367000000000000000e+04 5.150880000000000081e+01 6.701800000000000423e+00 1.730000000000000071e+01
-1.367400000000000000e+04 4.929429999999999978e+01 8.905300000000000438e+00 1.550000000000000000e+01
-1.367500000000000000e+04 5.208180000000000121e+01 9.407700000000000173e+00 2.039999999999999858e+01
-1.369600000000000000e+04 5.159660000000000224e+01 7.404799999999999827e+00 1.710000000000000142e+01
-1.370000000000000000e+04 5.133290000000000219e+01 7.341099999999999959e+00 1.580000000000000071e+01
-1.371000000000000000e+04 4.857339999999999947e+01 1.225760000000000005e+01 1.269999999999999929e+01
-1.371100000000000000e+04 5.068200000000000216e+01 1.151500000000000057e+01 1.839999999999999858e+01
-1.371300000000000000e+04 5.108990000000000009e+01 7.628899999999999793e+00 1.650000000000000000e+01
-1.377700000000000000e+04 5.224669999999999703e+01 1.095919999999999916e+01 1.980000000000000071e+01
-1.396500000000000000e+04 4.826389999999999958e+01 8.813399999999999679e+00 1.040000000000000036e+01
-1.500000000000000000e+04 5.079829999999999757e+01 6.024399999999999977e+00 1.290000000000000036e+01
-1.520700000000000000e+04 5.128349999999999653e+01 9.358999999999999986e+00 1.710000000000000142e+01
-1.544400000000000000e+04 4.844180000000000064e+01 9.921599999999999753e+00 1.169999999999999929e+01
-1.555500000000000000e+04 4.787610000000000099e+01 1.058489999999999931e+01 1.080000000000000071e+01
diff --git a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/01_precip_1d.py b/examples/09_spatio_temporal/01_precip_1d.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4b4c6b8a1..000000000
--- a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/01_precip_1d.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,130 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Creating a 1D Synthetic Precipitation Field
--------------------------------------------
-
-In this example we will create a time series of a 1D synthetic precipitation
-field.
-
-We'll start off by creating a Gaussian random field with an exponential
-variogram, which seems to reproduce the spatial correlations of precipitation
-fields quite well. We'll create a daily timeseries over a one dimensional cross
-section of 50km. This workflow is suited for sub daily precipitation time
-series.
-"""
-
-import copy
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# fix the seed for reproducibility
-seed = 20170521
-# spatial axis of 50km with a resolution of 1km
-x = np.arange(0, 50, 1.0)
-# half daily timesteps over three months
-t = np.arange(0.0, 90.0, 0.5)
-
-# space-time anisotropy ratio given in units d / km
-st_anis = 0.4
-
-# an exponential variogram with a corr. lengths of 2d and 5km
-model = gs.Exponential(
- temporal=True, spatial_dim=1, var=1, len_scale=5, anis=st_anis
-)
-# create a spatial random field instance
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=seed)
-
-pos, time = [x], [t]
-
-# a Gaussian random field which is also saved internally for the transformations
-srf.structured(pos + time)
-P_gau = copy.deepcopy(srf.field)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Next, we could take care of the dry periods. Therefore we would simply
-# introduce a lower threshold value. But we will combine this step with the
-# next one. Anyway, for demonstration purposes, we will also do it with the
-# threshold value now.
-
-threshold = 0.85
-P_cut = copy.deepcopy(srf.field)
-P_cut[P_cut <= threshold] = 0.0
-
-###############################################################################
-# With the above lines of code we have created a cut off Gaussian spatial
-# random field with an exponential variogram. But precipitation fields are not
-# distributed Gaussian. Thus, we will now transform the field with an inverse
-# box-cox transformation (create a non-Gaussian field) , which is often used to
-# account for the skewness of precipitation fields. Different values have been
-# suggested for the transformation parameter lambda, but we will stick to 1/2.
-# As already mentioned, we will perform the cutoff for the dry periods with
-# this transformation implicitly with the shift. The warning will tell you
-# that values have indeed been cut off and it can be ignored. We call the
-# resulting field Gaussian anamorphosis.
-
-# the lower this value, the more will be cut off, a value of 0.2 cuts off
-# nearly everything in this example.
-cutoff = 0.55
-gs.transform.boxcox(srf, lmbda=0.5, shift=-1.0 / cutoff)
-
-###############################################################################
-# As a last step, the amount of precipitation is set. This should of course be
-# calibrated towards observations (the same goes for the threshold, the
-# variance, correlation length, and so on).
-
-amount = 2.0
-srf.field *= amount
-P_ana = srf.field
-
-###############################################################################
-# Finally we can have a look at the fields resulting from each step. Note, that
-# the cutoff of the cut Gaussian only approximates the cutoff values from the
-# box-cox transformation. For a closer look, we will examine a cross section
-# at an arbitrary location. And afterwards we will create a contour plot for
-# visual candy.
-
-fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
-
-axs[0, 0].set_title("Gaussian")
-axs[0, 0].plot(t, P_gau[20, :])
-axs[0, 0].set_ylabel(r"$P$ / mm")
-
-axs[0, 1].set_title("Cut Gaussian")
-axs[0, 1].plot(t, P_cut[20, :])
-
-axs[1, 0].set_title("Cut Gaussian Anamorphosis")
-axs[1, 0].plot(t, P_ana[20, :])
-axs[1, 0].set_xlabel(r"$t$ / d")
-axs[1, 0].set_ylabel(r"$P$ / mm")
-
-axs[1, 1].set_title("Different Cross Section")
-axs[1, 1].plot(t, P_ana[10, :])
-axs[1, 1].set_xlabel(r"$t$ / d")
-
-plt.tight_layout()
-
-fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2, sharex=True, sharey=True)
-
-axs[0, 0].set_title("Gaussian")
-cont = axs[0, 0].contourf(t, x, P_gau, cmap="PuBu", levels=10)
-cbar = fig.colorbar(cont, ax=axs[0, 0])
-cbar.ax.set_ylabel(r"$P$ / mm")
-axs[0, 0].set_ylabel(r"$x$ / km")
-
-axs[0, 1].set_title("Cut Gaussian")
-cont = axs[0, 1].contourf(t, x, P_cut, cmap="PuBu", levels=10)
-cbar = fig.colorbar(cont, ax=axs[0, 1])
-cbar.ax.set_ylabel(r"$P$ / mm")
-axs[0, 1].set_xlabel(r"$t$ / d")
-
-axs[1, 0].set_title("Cut Gaussian Anamorphosis")
-cont = axs[1, 0].contourf(t, x, P_ana, cmap="PuBu", levels=10)
-cbar = fig.colorbar(cont, ax=axs[1, 0])
-cbar.ax.set_ylabel(r"$P$ / mm")
-axs[1, 0].set_xlabel(r"$t$ / d")
-axs[1, 0].set_ylabel(r"$x$ / km")
-
-fig.delaxes(axs[1, 1])
-plt.tight_layout()
diff --git a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/02_precip_2d.py b/examples/09_spatio_temporal/02_precip_2d.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 81c789649..000000000
--- a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/02_precip_2d.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,76 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Creating a 2D Synthetic Precipitation Field
--------------------------------------------
-
-In this example we'll create a time series of a 2D synthetic precipitation
-field.
-
-Very similar to the previous tutorial, we'll start off by creating a Gaussian
-random field with an exponential variogram, which seems to reproduce the
-spatial correlations of precipitation fields quite well. We'll create a daily
-timeseries over a two dimensional domain of 50km x 40km. This workflow is
-suited for sub daily precipitation time series.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.animation as animation
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# fix the seed for reproducibility
-seed = 20170521
-# 1st spatial axis of 50km with a resolution of 1km
-x = np.arange(0, 50, 1.0)
-# 2nd spatial axis of 40km with a resolution of 1km
-y = np.arange(0, 40, 1.0)
-# half daily timesteps over three months
-t = np.arange(0.0, 90.0, 0.5)
-
-# space-time anisotropy ratio given in units d / km
-st_anis = 0.4
-
-# an exponential variogram with a corr. lengths of 5km, 5km, and 2d
-model = gs.Exponential(
- temporal=True, spatial_dim=2, var=1, len_scale=5, anis=st_anis
-)
-# create a spatial random field instance
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=seed)
-
-pos, time = [x, y], [t]
-
-# the Gaussian random field
-srf.structured(pos + time)
-
-# account for the skewness and the dry periods
-cutoff = 0.55
-gs.transform.boxcox(srf, lmbda=0.5, shift=-1.0 / cutoff)
-
-# adjust the amount of precipitation
-amount = 4.0
-srf.field *= amount
-
-###############################################################################
-# plot the 2d precipitation field over time as an animation.
-
-
-def _update_ani(time_step):
- im.set_array(srf.field[:, :, time_step].T)
- return (im,)
-
-
-fig, ax = plt.subplots()
-im = ax.imshow(
- srf.field[:, :, 0].T,
- cmap="Blues",
- interpolation="bicubic",
- origin="lower",
-)
-cbar = fig.colorbar(im)
-cbar.ax.set_ylabel(r"Precipitation $P$ / mm")
-ax.set_xlabel(r"$x$ / km")
-ax.set_ylabel(r"$y$ / km")
-
-ani = animation.FuncAnimation(
- fig, _update_ani, len(t), interval=100, blit=True
-)
diff --git a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/03_geographic_coordinates.py b/examples/09_spatio_temporal/03_geographic_coordinates.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b1cfbff64..000000000
--- a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/03_geographic_coordinates.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,38 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Working with spatio-temporal lat-lon fields
--------------------------------------------
-
-In this example, we demonstrate how to generate a spatio-temporal
-random field on geographical coordinates.
-
-First we setup a model, with ``latlon=True`` and ``temporal=True``,
-to get the associated spatio-temporal Yadrenko model.
-
-In addition, we will use a kilometer scale provided by :any:`KM_SCALE`
-as ``geo_scale`` to have a meaningful length scale in km.
-By default the length scale would be given in radians (:any:`RADIAN_SCALE`).
-A third option is a length scale in degrees (:any:`DEGREE_SCALE`).
-
-To generate the field, we simply pass ``(lat, lon, time)`` as the position tuple
-to the :any:`SRF` class.
-
-We will set a spatial length-scale of `1000` and a time length-scale of `100` days.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-model = gs.Matern(
- latlon=True,
- temporal=True,
- var=1,
- len_scale=[1000, 100],
- geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE,
-)
-
-lat = lon = np.linspace(-80, 81, 50)
-time = np.linspace(0, 777, 50)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=1234)
-field = srf.structured((lat, lon, time))
-srf.plot()
diff --git a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/README.rst b/examples/09_spatio_temporal/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 3cb06b9e2..000000000
--- a/examples/09_spatio_temporal/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,65 +0,0 @@
-Spatio-Temporal Modeling
-========================
-
-Spatio-Temporal modelling can provide insights into time dependent processes
-like rainfall, air temperature or crop yield.
-
-GSTools provides the metric spatio-temporal model for all covariance models
-by setting ``temporal=True``, which enhances the spatial model dimension with
-a time dimension to result in the spatio-temporal dimension.
-Since the model dimension is then higher than the spatial dimension, you can use
-the ``spatial_dim`` argument to explicitly set the spatial dimension.
-Doing that and setting a spatio-temporal anisotropy ratio looks like this:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- import gstools as gs
- dim = 3 # spatial dimension
- st_anis = 0.4
- st_model = gs.Exponential(temporal=True, spatial_dim=dim, anis=st_anis)
-
-Since it is given in the name "spatio-temporal", time is always treated as last dimension.
-You could also use ``dim`` to specify the dimension but note that it needs to include
-the temporal dimension.
-
-There are now three different dimension attributes giving information about (i) the
-model dimension (``dim``), (ii) the field dimension (``field_dim``, including time) and
-(iii) the spatial dimension (``spatial_dim`` always 1 less than ``field_dim`` for temporal models).
-Model and field dimension can differ in case of geographic coordinates where the model dimension is 3,
-but the field or parametric dimension is 2.
-If the model is spatio-temporal with geographic coordinates, the model dimension is 4,
-the field dimension is 3 and the spatial dimension is 2.
-
-In the case above we get:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- st_model.dim == 4
- st_model.field_dim == 4
- st_model.spatial_dim == 3
-
-This formulation enables us to have spatial anisotropy and rotation defined as in
-non-temporal models, without altering the behavior in the time dimension:
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- anis = [0.4, 0.2] # spatial anisotropy in 3D
- angles = [0.5, 0.4, 0.3] # spatial rotation in 3D
- st_model = gs.Exponential(temporal=True, spatial_dim=dim, anis=anis+[st_anis], angles=angles)
-
-In order to generate spatio-temporal position tuples, GSTools provides a
-convenient function :any:`generate_st_grid`. The output can be used for
-spatio-temporal random field generation (or kriging resp. conditioned fields):
-
-.. code-block:: python
-
- pos = dim * [1, 2, 3] # 3 points in space (1,1,1), (2,2,2) and (3,3,3)
- time = range(10) # 10 time steps
- st_grid = gs.generate_st_grid(pos, time)
- st_rf = gs.SRF(st_model)
- st_field = st_rf(st_grid).reshape(-1, len(time))
-
-Then we can access the different time-steps by the last array index.
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/examples/10_normalizer/00_lognormal_kriging.py b/examples/10_normalizer/00_lognormal_kriging.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 9880bc37a..000000000
--- a/examples/10_normalizer/00_lognormal_kriging.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-r"""
-Log-Normal Kriging
-------------------
-
-Log Normal kriging is a term to describe a special workflow for kriging to
-deal with log-normal data, like conductivity or transmissivity in hydrogeology.
-
-It simply means to first convert the input data to a normal distribution, i.e.
-applying a logarithic function, then interpolating these values with kriging
-and transforming the result back with the exponential function.
-
-The resulting kriging variance describes the error variance of the log-values
-of the target variable.
-
-In this example we will use ordinary kriging.
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# condtions
-cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1, 3.3, 4.7]
-cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74, 1.47, 1.74]
-# resulting grid
-gridx = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 151)
-# stable covariance model
-model = gs.Stable(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2.56, alpha=1.9)
-
-###############################################################################
-# In order to result in log-normal kriging, we will use the :any:`LogNormal`
-# Normalizer. This is a parameter-less normalizer, so we don't have to fit it.
-normalizer = gs.normalizer.LogNormal
-
-###############################################################################
-# Now we generate the interpolated field as well as the mean field.
-# This can be done by setting `only_mean=True` in :any:`Krige.__call__`.
-# The result is then stored as `mean_field`.
-#
-# In terms of log-normal kriging, this mean represents the geometric mean of
-# the field.
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, cond_pos, cond_val, normalizer=normalizer)
-# interpolate the field
-krige(gridx)
-# also generate the mean field
-krige(gridx, only_mean=True)
-
-###############################################################################
-# And that's it. Let's have a look at the results.
-ax = krige.plot()
-# plotting the geometric mean
-krige.plot("mean_field", ax=ax)
-# plotting the conditioning data
-ax.scatter(cond_pos, cond_val, color="k", zorder=10, label="Conditions")
-ax.legend()
diff --git a/examples/10_normalizer/01_auto_fit.py b/examples/10_normalizer/01_auto_fit.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 71ad13851..000000000
--- a/examples/10_normalizer/01_auto_fit.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,107 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Automatic fitting
------------------
-
-In order to demonstrate how to automatically fit normalizer and variograms,
-we generate synthetic log-normal data, that should be interpolated with
-ordinary kriging.
-
-Normalizers are fitted by minimizing the likelihood function and variograms
-are fitted by estimating the empirical variogram with automatic binning and
-fitting the theoretical model to it. Thereby the sill is constrained to match
-the field variance.
-
-Artificial data
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-Here we generate log-normal data following a Gaussian covariance model.
-We will generate the "original" field on a 60x60 mesh, from which we will take
-samples in order to pretend a situation of data-scarcity.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-# structured field with edge length of 50
-x = y = range(51)
-pos = gs.generate_grid([x, y])
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=20170519, normalizer=gs.normalizer.LogNormal())
-# generate the original field
-srf(pos)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Here, we sample 60 points and set the conditioning points and values.
-
-ids = np.arange(srf.field.size)
-samples = np.random.RandomState(20210201).choice(ids, size=60, replace=False)
-
-# sample conditioning points from generated field
-cond_pos = pos[:, samples]
-cond_val = srf.field[samples]
-
-###############################################################################
-# Fitting and Interpolation
-# ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-#
-# Now we want to interpolate the "measured" samples
-# and we want to normalize the given data with the BoxCox transformation.
-#
-# Here we set up the kriging routine and use a :any:`Stable` model, that should
-# be fitted automatically to the given data
-# and we pass the :any:`BoxCox` normalizer in order to gain normality.
-#
-# The normalizer will be fitted automatically to the data,
-# by setting ``fit_normalizer=True``.
-#
-# The covariance/variogram model will be fitted by an automatic workflow
-# by setting ``fit_variogram=True``.
-
-krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model=gs.Stable(dim=2),
- cond_pos=cond_pos,
- cond_val=cond_val,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.BoxCox(),
- fit_normalizer=True,
- fit_variogram=True,
-)
-
-###############################################################################
-# First, let's have a look at the fitting results:
-
-print(krige.model)
-print(krige.normalizer)
-
-###############################################################################
-# As we see, it went quite well. Variance is a bit underestimated, but
-# length scale and nugget are good. The shape parameter of the stable model
-# is correctly estimated to be close to `2`,
-# so we result in a Gaussian like model.
-#
-# The BoxCox parameter `lmbda` was estimated to be almost 0, which means,
-# the log-normal distribution was correctly fitted.
-#
-# Now let's run the kriging interpolation.
-
-krige(pos)
-
-###############################################################################
-# Plotting
-# ^^^^^^^^
-#
-# Finally let's compare the original, sampled and interpolated fields.
-# As we'll see, there is a lot of information in the covariance structure
-# of the measurement samples and the field is reconstructed quite accurately.
-
-fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=[8, 3])
-ax[0].imshow(srf.field.reshape(len(x), len(y)).T, origin="lower")
-ax[1].scatter(*cond_pos, c=cond_val)
-ax[2].imshow(krige.field.reshape(len(x), len(y)).T, origin="lower")
-# titles
-ax[0].set_title("original field")
-ax[1].set_title("sampled field")
-ax[2].set_title("interpolated field")
-# set aspect ratio to equal in all plots
-[ax[i].set_aspect("equal") for i in range(3)]
diff --git a/examples/10_normalizer/02_compare.py b/examples/10_normalizer/02_compare.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 2dd74488c..000000000
--- a/examples/10_normalizer/02_compare.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,67 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Normalizer Comparison
----------------------
-
-Let's compare the transformation behavior of the provided normalizers.
-
-But first, we define a convenience routine and make some imports as always.
-"""
-
-import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def dashes(i=1, max_n=12, width=1):
- """Return line dashes."""
- return i * [width, width] + [max_n * 2 * width - 2 * i * width, width]
-
-
-###############################################################################
-# We select 4 normalizers depending on a single parameter lambda and
-# plot their transformation behavior within the interval [-5, 5].
-#
-# For the shape parameter lambda, we create a list of 8 values ranging from
-# -1 to 2.5.
-
-lmbdas = [i * 0.5 for i in range(-2, 6)]
-normalizers = [
- gs.normalizer.BoxCox,
- gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson,
- gs.normalizer.Modulus,
- gs.normalizer.Manly,
-]
-
-###############################################################################
-# Let's plot them!
-
-fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=[8, 8])
-for i, norm in enumerate(normalizers):
- # correctly setting the data range
- x_rng = norm().normalize_range
- x = np.linspace(max(-5, x_rng[0] + 0.01), min(5, x_rng[1] - 0.01))
- for j, lmbda in enumerate(lmbdas):
- ax.flat[i].plot(
- x,
- norm(lmbda=lmbda).normalize(x),
- label=r"$\lambda=" + str(lmbda) + "$",
- color="k",
- alpha=0.2 + j * 0.1,
- dashes=dashes(j),
- )
- # axis formatting
- ax.flat[i].grid(which="both", color="grey", linestyle="-", alpha=0.2)
- ax.flat[i].set_ylim((-5, 5))
- ax.flat[i].set_xlim((-5, 5))
- ax.flat[i].set_title(norm().name)
-# figure formatting
-handles, labels = ax.flat[-1].get_legend_handles_labels()
-fig.legend(handles, labels, loc="lower center", ncol=4, handlelength=3.0)
-fig.suptitle("Normalizer Comparison", fontsize=20)
-fig.show()
-
-###############################################################################
-# The missing :any:`LogNormal` transformation is covered by the :any:`BoxCox`
-# transformation for lambda=0. The :any:`BoxCoxShift` transformation is
-# simply the :any:`BoxCox` transformation shifted on the X-axis.
diff --git a/examples/10_normalizer/README.rst b/examples/10_normalizer/README.rst
deleted file mode 100644
index 930756be9..000000000
--- a/examples/10_normalizer/README.rst
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,55 +0,0 @@
-Normalizing Data
-================
-
-When dealing with real-world data, one can't assume it to be normal distributed.
-In fact, many properties are modeled by applying different transformations,
-for example conductivity is often assumed to be log-normal or precipitation
-is transformed using the famous box-cox power transformation.
-
-These "normalizers" are often represented as parameteric power transforms and
-one is interested in finding the best parameter to gain normality in the input
-data.
-
-This is of special interest when kriging should be applied, since the target
-variable of the kriging interpolation is assumed to be normal distributed.
-
-GSTools provides a set of Normalizers and routines to automatically fit these
-to input data by minimizing the likelihood function.
-
-Mean, Trend and Normalizers
----------------------------
-
-All Field classes (:any:`SRF`, :any:`Krige` or :any:`CondSRF`) provide the input
-of `mean`, `normalizer` and `trend`:
-
-* A `trend` can be a callable function, that represents a trend in input data.
- For example a linear decrease of temperature with height.
-
-* The `normalizer` will be applied after the data was detrended, i.e. the trend
- was substracted from the data, in order to gain normality.
-
-* The `mean` is now interpreted as the mean of the normalized data. The user
- could also provide a callable mean, but it is mostly meant to be constant.
-
-When no normalizer is given, `trend` and `mean` basically behave the same.
-We just decided that a trend is associated with raw data and a mean is used
-in the context of normally distributed data.
-
-Provided Normalizers
---------------------
-
-The following normalizers can be passed to all Field-classes and variogram
-estimation routines or can be used as standalone tools to analyse data.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.normalizer
-
-.. autosummary::
- LogNormal
- BoxCox
- BoxCoxShift
- YeoJohnson
- Modulus
- Manly
-
-Examples
---------
diff --git a/pyproject.toml b/pyproject.toml
index cd0dc6ede..265bf0976 100644
--- a/pyproject.toml
+++ b/pyproject.toml
@@ -2,7 +2,7 @@
requires = [
"setuptools>=64",
"setuptools_scm>=7",
- "numpy>=2.0.0rc1,<2.3; python_version >= '3.9'",
+ "numpy>=2.0.0rc1; python_version >= '3.9'",
"oldest-supported-numpy; python_version < '3.9'",
"Cython>=3.0.10,<3.1.0",
"extension-helpers>=1",
@@ -11,8 +11,8 @@ build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
[project]
requires-python = ">=3.8"
-name = "gstools"
-description = "GSTools: A geostatistical toolbox."
+name = "gstools_cython"
+description = "Cython backend for GSTools."
authors = [
{name = "Sebastian Müller, Lennart Schüler", email = "info@geostat-framework.org"},
]
@@ -46,33 +46,20 @@ classifiers = [
"Topic :: Utilities",
]
dependencies = [
- "emcee>=3.0.0",
- "hankel>=1.0.0",
- "meshio>=5.1.0",
"numpy>=1.20.0",
- "pyevtk>=1.1.1",
- "scipy>=1.1.0",
]
[project.optional-dependencies]
doc = [
"m2r2>=0.2.8",
- "matplotlib>=3.7",
- "meshzoo>=0.7",
"numpydoc>=1.1",
- "pykrige>=1.5,<2",
- "pyvista>=0.40",
"sphinx>=7",
- "sphinx-gallery>=0.8",
"sphinx-rtd-theme>=2",
- "sphinxcontrib-youtube>=1.1",
]
-plotting = [
- "matplotlib>=3.7",
- "pyvista>=0.40",
+test = [
+ "pytest-cov>=3",
+ "Cython>=3.0.10,<3.1.0",
]
-rust = ["gstools_core>=0.2.0,<1"]
-test = ["pytest-cov>=3"]
lint = [
"black>=24",
"pylint",
@@ -81,18 +68,18 @@ lint = [
]
[project.urls]
-Changelog = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md"
+Changelog = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython/blob/main/CHANGELOG.md"
Conda-Forge = "https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/gstools"
Documentation = "https://gstools.readthedocs.io"
Homepage = "https://geostat-framework.org/#gstools"
-Source = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools"
-Tracker = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools/issues"
+Source = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython"
+Tracker = "https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/GSTools-Cython/issues"
[tool.setuptools]
license-files = ["LICENSE"]
[tool.setuptools_scm]
-write_to = "src/gstools/_version.py"
+write_to = "src/gstools_cython/_version.py"
write_to_template = "__version__ = '{version}'"
local_scheme = "no-local-version"
fallback_version = "0.0.0.dev0"
@@ -100,10 +87,8 @@ fallback_version = "0.0.0.dev0"
[tool.isort]
profile = "black"
multi_line_output = 3
-line_length = 79
[tool.black]
-line-length = 79
target-version = [
"py38",
"py39",
@@ -114,13 +99,12 @@ target-version = [
[tool.coverage]
[tool.coverage.run]
- source = ["gstools"]
+ plugins = ["Cython.Coverage"]
+ source = ["gstools_cython"]
omit = [
"*docs*",
"*examples*",
"*tests*",
- "*/src/gstools/covmodel/plot.py",
- "*/src/gstools/field/plot.py",
]
[tool.coverage.report]
@@ -134,8 +118,6 @@ target-version = [
[tool.pylint.main]
extension-pkg-whitelist = [
"numpy",
- "scipy",
- "gstools_core",
]
ignore = "_version.py"
load-plugins = [
diff --git a/setup.py b/setup.py
index b27548a94..1cf7fd456 100644
--- a/setup.py
+++ b/setup.py
@@ -1,4 +1,4 @@
-"""GSTools: A geostatistical toolbox."""
+"""GSTools-Cython: Cython backend for GSTools."""
import os
@@ -8,27 +8,37 @@
from setuptools import Extension, setup
# cython extensions
-CY_MODULES = [
+CY_MODS = [
Extension(
- name=f"gstools.{ext}",
- sources=[os.path.join("src", "gstools", *ext.split(".")) + ".pyx"],
+ name=f"gstools_cython.{ext}",
+ sources=[os.path.join("src", "gstools_cython", ext) + ".pyx"],
include_dirs=[np.get_include()],
define_macros=[("NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API", "NPY_1_7_API_VERSION")],
)
- for ext in ["field.summator", "variogram.estimator", "krige.krigesum"]
+ for ext in ["field", "krige", "variogram"]
]
# you can set GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL=0 or GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL=1
open_mp = False
if int(os.getenv("GSTOOLS_BUILD_PARALLEL", "0")):
- added = [add_openmp_flags_if_available(mod) for mod in CY_MODULES]
- if any(added):
- open_mp = True
- print(f"## GSTools setup: OpenMP used: {open_mp}")
+ added = [add_openmp_flags_if_available(mod) for mod in CY_MODS]
+ open_mp = any(added)
+ print(f"## GSTools-Cython setup: OpenMP used: {open_mp}")
else:
- print("## GSTools setup: OpenMP not wanted by the user.")
+ print("## GSTools-Cython setup: OpenMP not wanted by the user.")
+compiler_directives = {}
+if int(os.getenv("GSTOOLS_CY_DOCS", "0")):
+ print(f"## GSTools-Cython setup: embed signatures for documentation")
+ compiler_directives["embedsignature"] = True
+if int(os.getenv("GSTOOLS_CY_COV", "0")):
+ print(f"## GSTools-Cython setup: enable line-trace for coverage")
+ compiler_directives["linetrace"] = True
+ for mod in CY_MODS:
+ mod.define_macros.append(("CYTHON_TRACE_NOGIL", "1"))
+
+options = {
+ "compile_time_env": {"OPENMP": open_mp},
+ "compiler_directives": compiler_directives,
+}
# setup - do not include package data to ignore .pyx files in wheels
-setup(
- ext_modules=cythonize(CY_MODULES, compile_time_env={"OPENMP": open_mp}),
- include_package_data=False,
-)
+setup(ext_modules=cythonize(CY_MODS, **options), include_package_data=False)
diff --git a/src/gstools/__init__.py b/src/gstools/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 11e63a2b3..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,245 +0,0 @@
-"""
-Purpose
-=======
-
-GeoStatTools is a library providing geostatistical tools
-for random field generation, conditioned field generation,
-kriging and variogram estimation
-based on a list of provided or even user-defined covariance models.
-
-The following functionalities are directly provided on module-level.
-
-Subpackages
-===========
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree: api
-
- covmodel
- field
- variogram
- krige
- random
- tools
- transform
- normalizer
-
-Classes
-=======
-
-Kriging
-^^^^^^^
-Swiss-Army-Knife for Kriging. For short cut classes see: :any:`gstools.krige`
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige
-
-.. autosummary::
- Krige
-
-Spatial Random Field
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-Classes for (conditioned) random field generation
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field
-
-.. autosummary::
- SRF
- CondSRF
-
-Covariance Base-Class
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-Class to construct user defined covariance models
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel
-
-.. autosummary::
- CovModel
-
-Covariance Models
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-Standard Covariance Models
-~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-
-.. autosummary::
- Gaussian
- Exponential
- Matern
- Integral
- Stable
- Rational
- Cubic
- Linear
- Circular
- Spherical
- HyperSpherical
- SuperSpherical
- JBessel
-
-Truncated Power Law Covariance Models
-~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
-
-.. autosummary::
- TPLGaussian
- TPLExponential
- TPLStable
- TPLSimple
-
-Functions
-=========
-
-VTK-Export
-^^^^^^^^^^
-Routines to export fields to the vtk format
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools
-
-.. autosummary::
- vtk_export
- to_vtk
-
-Geometric
-^^^^^^^^^
-Some convenient functions for geometric operations
-
-.. autosummary::
- rotated_main_axes
- generate_grid
- generate_st_grid
-
-Variogram Estimation
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-Estimate the variogram of a given field with these routines
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.variogram
-
-.. autosummary::
- vario_estimate
- vario_estimate_axis
- standard_bins
-
-Misc
-====
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools
-
-.. autosummary::
- EARTH_RADIUS
- KM_SCALE
- DEGREE_SCALE
- RADIAN_SCALE
-"""
-
-# Hooray!
-from gstools import (
- config,
- covmodel,
- field,
- krige,
- normalizer,
- random,
- tools,
- transform,
- variogram,
-)
-from gstools.covmodel import (
- Circular,
- CovModel,
- Cubic,
- Exponential,
- Gaussian,
- HyperSpherical,
- Integral,
- JBessel,
- Linear,
- Matern,
- Rational,
- Spherical,
- Stable,
- SuperSpherical,
- TPLExponential,
- TPLGaussian,
- TPLSimple,
- TPLStable,
-)
-from gstools.field import SRF, CondSRF
-from gstools.krige import Krige
-from gstools.tools import (
- DEGREE_SCALE,
- EARTH_RADIUS,
- KM_SCALE,
- RADIAN_SCALE,
- generate_grid,
- generate_st_grid,
- rotated_main_axes,
- to_vtk,
- to_vtk_structured,
- to_vtk_unstructured,
- vtk_export,
- vtk_export_structured,
- vtk_export_unstructured,
-)
-from gstools.variogram import (
- standard_bins,
- vario_estimate,
- vario_estimate_axis,
- vario_estimate_structured,
- vario_estimate_unstructured,
-)
-
-try:
- from gstools._version import __version__
-except ModuleNotFoundError: # pragma: no cover
- # package is not installed
- __version__ = "0.0.0.dev0"
-
-__all__ = ["__version__"]
-__all__ += ["covmodel", "field", "variogram", "krige", "random", "tools"]
-__all__ += ["transform", "normalizer", "config"]
-__all__ += [
- "CovModel",
- "Gaussian",
- "Exponential",
- "Matern",
- "Integral",
- "Stable",
- "Rational",
- "Cubic",
- "Linear",
- "Circular",
- "Spherical",
- "HyperSpherical",
- "SuperSpherical",
- "JBessel",
- "TPLGaussian",
- "TPLExponential",
- "TPLStable",
- "TPLSimple",
-]
-
-__all__ += [
- "vario_estimate",
- "vario_estimate_axis",
- "vario_estimate_structured",
- "vario_estimate_unstructured",
- "standard_bins",
-]
-
-__all__ += [
- "Krige",
- "SRF",
- "CondSRF",
- "rotated_main_axes",
- "generate_grid",
- "generate_st_grid",
- "EARTH_RADIUS",
- "KM_SCALE",
- "DEGREE_SCALE",
- "RADIAN_SCALE",
- "vtk_export",
- "vtk_export_structured",
- "vtk_export_unstructured",
- "to_vtk",
- "to_vtk_structured",
- "to_vtk_unstructured",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/config.py b/src/gstools/config.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 24ce20c7e..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/config.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,16 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing global variables.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.config
-
-"""
-
-NUM_THREADS = None
-
-# pylint: disable=W0611
-try: # pragma: no cover
- import gstools_core
-
- USE_RUST = True
-except ImportError:
- USE_RUST = False
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/__init__.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 28ab81f21..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing a set of handy covariance models.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel
-
-Subpackages
-^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- plot
-
-Covariance Base-Class
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-Class to construct user defined covariance models
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- CovModel
-
-Covariance Models
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-Standard Covariance Models
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- Gaussian
- Exponential
- Matern
- Integral
- Stable
- Rational
- Cubic
- Linear
- Circular
- Spherical
- HyperSpherical
- SuperSpherical
- JBessel
-
-Truncated Power Law Covariance Models
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- TPLGaussian
- TPLExponential
- TPLStable
- TPLSimple
-"""
-
-from gstools.covmodel.base import CovModel
-from gstools.covmodel.models import (
- Circular,
- Cubic,
- Exponential,
- Gaussian,
- HyperSpherical,
- Integral,
- JBessel,
- Linear,
- Matern,
- Rational,
- Spherical,
- Stable,
- SuperSpherical,
-)
-from gstools.covmodel.tpl_models import (
- TPLExponential,
- TPLGaussian,
- TPLSimple,
- TPLStable,
-)
-
-__all__ = [
- "CovModel",
- "Gaussian",
- "Exponential",
- "Matern",
- "Integral",
- "Stable",
- "Rational",
- "Cubic",
- "Linear",
- "Circular",
- "Spherical",
- "HyperSpherical",
- "SuperSpherical",
- "JBessel",
- "TPLGaussian",
- "TPLExponential",
- "TPLStable",
- "TPLSimple",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/base.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/base.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 23e198812..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/base.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,1210 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing the base class for covariance models.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.base
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- CovModel
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, R0201, E1101, C0302, W0613
-import copy
-
-import numpy as np
-from hankel import SymmetricFourierTransform as SFT
-from scipy.integrate import quad as integral
-
-from gstools.covmodel import plot
-from gstools.covmodel.fit import fit_variogram
-from gstools.covmodel.tools import (
- _init_subclass,
- check_arg_bounds,
- check_bounds,
- compare,
- default_arg_from_bounds,
- model_repr,
- percentile_scale,
- set_arg_bounds,
- set_dim,
- set_len_anis,
- set_model_angles,
- set_opt_args,
- spectral_rad_pdf,
-)
-from gstools.tools import RADIAN_SCALE
-from gstools.tools.geometric import (
- great_circle_to_chordal,
- latlon2pos,
- matrix_anisometrize,
- matrix_isometrize,
- pos2latlon,
- rotated_main_axes,
-)
-
-__all__ = ["CovModel"]
-
-# default arguments for hankel.SymmetricFourierTransform
-HANKEL_DEFAULT = {"a": -1, "b": 1, "N": 200, "h": 0.001, "alt": True}
-
-
-class CovModel:
- r"""Base class for the GSTools covariance models.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`, optional
- dimension of the model.
- Includes the temporal dimension if temporal is true.
- To specify only the spatial dimension in that case, use `spatial_dim`.
- Default: ``3``
- var : :class:`float`, optional
- variance of the model (the nugget is not included in "this" variance)
- Default: ``1.0``
- len_scale : :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- length scale of the model.
- If a single value is given, the same length-scale will be used for
- every direction. If multiple values (for main and transversal
- directions) are given, `anis` will be
- recalculated accordingly. If only two values are given in 3D,
- the latter one will be used for both transversal directions.
- Default: ``1.0``
- nugget : :class:`float`, optional
- nugget of the model. Default: ``0.0``
- anis : :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- anisotropy ratios in the transversal directions [e_y, e_z].
-
- * e_y = l_y / l_x
- * e_z = l_z / l_x
-
- If only one value is given in 3D, e_y will be set to 1.
- This value will be ignored, if multiple len_scales are given.
- Default: ``1.0``
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- angles of rotation (given in rad):
-
- * in 2D: given as rotation around z-axis
- * in 3D: given by yaw, pitch, and roll (known as Tait–Bryan angles)
-
- Default: ``0.0``
- integral_scale : :class:`float` or :class:`list` or :any:`None`, optional
- If given, ``len_scale`` will be ignored and recalculated,
- so that the integral scale of the model matches the given one.
- Default: :any:`None`
- rescale : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Optional rescaling factor to divide the length scale with.
- This could be used for unit conversion or rescaling the length scale
- to coincide with e.g. the integral scale.
- Will be set by each model individually.
- Default: :any:`None`
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the model is describing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude. When using this, the model will internally
- use the associated 'Yadrenko' model to represent a valid model.
- This means, the spatial distance :math:`r` will be replaced by
- :math:`2\sin(\alpha/2)`, where :math:`\alpha` is the great-circle
- distance, which is equal to the spatial distance of two points in 3D.
- As a consequence, `dim` will be set to `3` and anisotropy will be
- disabled. `geo_scale` can be set to e.g. earth's radius,
- to have a meaningful `len_scale` parameter.
- Default: False
- geo_scale : :class:`float`, optional
- Geographic unit scaling in case of latlon coordinates to get a
- meaningful length scale unit.
- By default, len_scale is assumed to be in radians with latlon=True.
- Can be set to :any:`KM_SCALE` to have len_scale in km or
- :any:`DEGREE_SCALE` to have len_scale in degrees.
- Default: :any:`RADIAN_SCALE`
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Create a metric spatio-temporal covariance model.
- Setting this to true will increase `dim` and `field_dim` by 1.
- `spatial_dim` will be `field_dim - 1`.
- The time-dimension is appended, meaning the pos tuple is (x,y,z,...,t).
- Default: False
- spatial_dim : :class:`int`, optional
- spatial dimension of the model.
- If given, the model dimension will be determined from this spatial dimension
- and the possible temporal dimension if temporal is ture.
- Default: None
- var_raw : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- raw variance of the model which will be multiplied with
- :any:`CovModel.var_factor` to result in the actual variance.
- If given, ``var`` will be ignored.
- (This is just for models that override :any:`CovModel.var_factor`)
- Default: :any:`None`
- hankel_kw: :class:`dict` or :any:`None`, optional
- Modify the init-arguments of
- :any:`hankel.SymmetricFourierTransform`
- used for the spectrum calculation. Use with caution (Better: Don't!).
- ``None`` is equivalent to ``{"a": -1, "b": 1, "N": 1000, "h": 0.001}``.
- Default: :any:`None`
- **opt_arg
- Optional arguments are covered by these keyword arguments.
- If present, they are described in the section `Other Parameters`.
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- dim=3,
- var=1.0,
- len_scale=1.0,
- nugget=0.0,
- anis=1.0,
- angles=0.0,
- *,
- integral_scale=None,
- rescale=None,
- latlon=False,
- geo_scale=RADIAN_SCALE,
- temporal=False,
- spatial_dim=None,
- var_raw=None,
- hankel_kw=None,
- **opt_arg,
- ):
- # assert, that we use a subclass
- # this is the case, if __init_subclass__ is called, which creates
- # the "variogram"... so we check for that
- if not hasattr(self, "variogram"):
- raise TypeError("Don't instantiate 'CovModel' directly!")
-
- # prepare dim setting
- self._dim = None
- self._hankel_kw = None
- self._sft = None
- # prepare parameters (they are checked in dim setting)
- self._rescale = None
- self._len_scale = None
- self._anis = None
- self._angles = None
- # prepare parameters boundaries
- self._var_bounds = None
- self._len_scale_bounds = None
- self._nugget_bounds = None
- self._anis_bounds = None
- self._opt_arg_bounds = {}
- # Set latlon and temporal first
- self._latlon = bool(latlon)
- self._temporal = bool(temporal)
- self._geo_scale = abs(float(geo_scale))
- # SFT class will be created within dim.setter but needs hankel_kw
- self.hankel_kw = hankel_kw
- # using time increases model dimension given by "spatial_dim"
- self.dim = (
- dim if spatial_dim is None else spatial_dim + int(self.temporal)
- )
-
- # optional arguments for the variogram-model
- set_opt_args(self, opt_arg)
-
- # set standard boundaries for variance, len_scale, nugget and opt_arg
- bounds = self.default_arg_bounds()
- bounds.update(self.default_opt_arg_bounds())
- self.set_arg_bounds(check_args=False, **bounds)
-
- # set parameters
- self.rescale = rescale
- self._nugget = float(nugget)
-
- # set anisotropy and len_scale, disable anisotropy for latlon models
- self._len_scale, self._anis = set_len_anis(
- self.dim, len_scale, anis, self.latlon
- )
- self._angles = set_model_angles(
- self.dim, angles, self.latlon, self.temporal
- )
-
- # set var at last, because of the var_factor (to be right initialized)
- if var_raw is None:
- self._var = None
- self.var = var
- else:
- self._var = float(var_raw)
- self._integral_scale = None
- self.integral_scale = integral_scale
- # set var again, if int_scale affects var_factor
- if var_raw is None:
- self._var = None
- self.var = var
- else:
- self._var = float(var_raw)
- # final check for parameter bounds
- self.check_arg_bounds()
- # additional checks for the optional arguments (provided by user)
- self.check_opt_arg()
- # precision for printing
- self._prec = 3
-
- # one of these functions needs to be overridden
- def __init_subclass__(cls):
- """Initialize gstools covariance model."""
- _init_subclass(cls)
-
- # modify the docstrings: class docstring gets attributes added
- if cls.__doc__ is None:
- cls.__doc__ = "User defined GSTools Covariance-Model."
- cls.__doc__ += CovModel.__doc__[45:]
- # overridden functions get standard doc if no new doc was created
- ign = ["__", "variogram", "covariance", "cor"]
- for att, attr_cls in cls.__dict__.items():
- if any(att.startswith(i) for i in ign) or att not in dir(CovModel):
- continue
- attr_doc = getattr(CovModel, att).__doc__
- if attr_cls.__doc__ is None:
- attr_cls.__doc__ = attr_doc
-
- # special variogram functions
-
- def vario_axis(self, r, axis=0):
- r"""Variogram along axis of anisotropy."""
- if axis == 0:
- return self.variogram(r)
- return self.variogram(np.abs(r) / self.anis[axis - 1])
-
- def cov_axis(self, r, axis=0):
- r"""Covariance along axis of anisotropy."""
- if axis == 0:
- return self.covariance(r)
- return self.covariance(np.abs(r) / self.anis[axis - 1])
-
- def cor_axis(self, r, axis=0):
- r"""Correlation along axis of anisotropy."""
- if axis == 0:
- return self.correlation(r)
- return self.correlation(np.abs(r) / self.anis[axis - 1])
-
- def vario_yadrenko(self, zeta):
- r"""Yadrenko variogram for great-circle distance from latlon-pos."""
- return self.variogram(great_circle_to_chordal(zeta, self.geo_scale))
-
- def cov_yadrenko(self, zeta):
- r"""Yadrenko covariance for great-circle distance from latlon-pos."""
- return self.covariance(great_circle_to_chordal(zeta, self.geo_scale))
-
- def cor_yadrenko(self, zeta):
- r"""Yadrenko correlation for great-circle distance from latlon-pos."""
- return self.correlation(great_circle_to_chordal(zeta, self.geo_scale))
-
- def vario_spatial(self, pos):
- r"""Spatial variogram respecting anisotropy and rotation."""
- return self.variogram(self._get_iso_rad(pos))
-
- def cov_spatial(self, pos):
- r"""Spatial covariance respecting anisotropy and rotation."""
- return self.covariance(self._get_iso_rad(pos))
-
- def cor_spatial(self, pos):
- r"""Spatial correlation respecting anisotropy and rotation."""
- return self.correlation(self._get_iso_rad(pos))
-
- def vario_nugget(self, r):
- """Isotropic variogram of the model respecting the nugget at r=0."""
- r = np.asarray(np.abs(r), dtype=np.double)
- r_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(r, 0))
- res = np.empty_like(r, dtype=np.double)
- res[r_gz] = self.variogram(r[r_gz])
- res[np.logical_not(r_gz)] = 0.0
- return res
-
- def cov_nugget(self, r):
- """Isotropic covariance of the model respecting the nugget at r=0."""
- r = np.asarray(np.abs(r), dtype=np.double)
- r_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(r, 0))
- res = np.empty_like(r, dtype=np.double)
- res[r_gz] = self.covariance(r[r_gz])
- res[np.logical_not(r_gz)] = self.sill
- return res
-
- def plot(self, func="variogram", **kwargs): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot a function of a the CovModel.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- func : :class:`str`, optional
- Function to be plotted. Could be one of:
-
- * "variogram"
- * "covariance"
- * "correlation"
- * "vario_spatial"
- * "cov_spatial"
- * "cor_spatial"
- * "vario_yadrenko"
- * "cov_yadrenko"
- * "cor_yadrenko"
- * "vario_axis"
- * "cov_axis"
- * "cor_axis"
- * "spectrum"
- * "spectral_density"
- * "spectral_rad_pdf"
-
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to the plotting function
- `"plot_" + func` in :py:mod:`gstools.covmodel.plot`.
-
- See Also
- --------
- gstools.covmodel.plot
- """
- routine = getattr(plot, "plot_" + func)
- return routine(self, **kwargs)
-
- # pykrige functions
-
- def pykrige_vario(self, args=None, r=0): # pragma: no cover
- """Isotropic variogram of the model for pykrige."""
- if self.latlon:
- return self.vario_yadrenko(np.deg2rad(r))
- return self.variogram(r)
-
- @property
- def pykrige_anis(self):
- """2D anisotropy ratio for pykrige."""
- if self.dim == 2:
- return 1 / self.anis[0]
- return 1.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_anis_y(self):
- """3D anisotropy ratio in y direction for pykrige."""
- if self.dim >= 2:
- return 1 / self.anis[0]
- return 1.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_anis_z(self):
- """3D anisotropy ratio in z direction for pykrige."""
- if self.dim == 3:
- return 1 / self.anis[1]
- return 1.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_angle(self):
- """2D rotation angle for pykrige."""
- if self.dim == 2:
- return self.angles[0] / np.pi * 180
- return 0.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_angle_z(self):
- """3D rotation angle around z for pykrige."""
- if self.dim >= 2:
- return self.angles[0] / np.pi * 180
- return 0.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_angle_y(self):
- """3D rotation angle around y for pykrige."""
- if self.dim == 3:
- return self.angles[1] / np.pi * 180
- return 0.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_angle_x(self):
- """3D rotation angle around x for pykrige."""
- if self.dim == 3:
- return self.angles[2] / np.pi * 180
- return 0.0 # pragma: no cover
-
- @property
- def pykrige_kwargs(self):
- """Keyword arguments for pykrige routines."""
- kwargs = {
- "variogram_model": "custom",
- "variogram_parameters": [],
- "variogram_function": self.pykrige_vario,
- }
- if self.dim == 1:
- add_kwargs = {}
- elif self.dim == 2:
- add_kwargs = {
- "anisotropy_scaling": self.pykrige_anis,
- "anisotropy_angle": self.pykrige_angle,
- }
- else:
- add_kwargs = {
- "anisotropy_scaling_y": self.pykrige_anis_y,
- "anisotropy_scaling_z": self.pykrige_anis_z,
- "anisotropy_angle_x": self.pykrige_angle_x,
- "anisotropy_angle_y": self.pykrige_angle_y,
- "anisotropy_angle_z": self.pykrige_angle_z,
- }
- kwargs.update(add_kwargs)
- return kwargs
-
- # methods for optional/default arguments (can be overridden)
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Provide default optional arguments by the user.
-
- Should be given as a dictionary when overridden.
- """
- return {
- opt: default_arg_from_bounds(bnd)
- for (opt, bnd) in self.default_opt_arg_bounds().items()
- }
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Provide default boundaries for optional arguments."""
- res = {}
- for opt in self.opt_arg:
- res[opt] = [-np.inf, np.inf]
- return res
-
- def check_opt_arg(self):
- """Run checks for the optional arguments.
-
- This is in addition to the bound-checks
-
- Notes
- -----
- * You can use this to raise a ValueError/warning
- * Any return value will be ignored
- * This method will only be run once, when the class is initialized
- """
-
- def check_dim(self, dim):
- """Check the given dimension."""
- return True
-
- def fix_dim(self):
- """Set a fix dimension for the model."""
- return None
-
- def var_factor(self):
- """Factor for the variance."""
- return 1.0
-
- def default_rescale(self):
- """Provide default rescaling factor."""
- return 1.0
-
- # calculation of different scales
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self):
- """Calculate the integral scale of the isotrope model."""
- self._integral_scale = integral(self.correlation, 0, np.inf)[0]
- return self._integral_scale
-
- def percentile_scale(self, per=0.9):
- """Calculate the percentile scale of the isotrope model.
-
- This is the distance, where the given percentile of the variance
- is reached by the variogram
- """
- return percentile_scale(self, per)
-
- # spectrum methods (can be overridden for speedup)
-
- def spectrum(self, k):
- r"""
- Spectrum of the covariance model.
-
- This is given by:
-
- .. math:: S(\mathbf{k}) = \left(\frac{1}{2\pi}\right)^n
- \int C(r) e^{i \mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{r}} d^n\mathbf{r}
-
- Internally, this is calculated by the hankel transformation:
-
- .. math:: S(k) = \left(\frac{1}{2\pi}\right)^n \cdot
- \frac{(2\pi)^{n/2}}{k^{n/2-1}}
- \int_0^\infty r^{n/2} C(r) J_{n/2-1}(kr) dr
-
- Where :math:`C(r)` is the covariance function of the model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- k : :class:`float`
- Radius of the phase: :math:`k=\left\Vert\mathbf{k}\right\Vert`
- """
- return self.spectral_density(k) * self.var
-
- def spectral_density(self, k):
- r"""
- Spectral density of the covariance model.
-
- This is given by:
-
- .. math:: \tilde{S}(k) = \frac{S(k)}{\sigma^2}
-
- Where :math:`S(k)` is the spectrum of the covariance model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- k : :class:`float`
- Radius of the phase: :math:`k=\left\Vert\mathbf{k}\right\Vert`
- """
- k = np.asarray(np.abs(k), dtype=np.double)
- return self._sft.transform(self.correlation, k, ret_err=False)
-
- def spectral_rad_pdf(self, r):
- """Radial spectral density of the model."""
- return spectral_rad_pdf(self, r)
-
- def ln_spectral_rad_pdf(self, r):
- """Log radial spectral density of the model."""
- with np.errstate(divide="ignore"):
- return np.log(self.spectral_rad_pdf(r))
-
- def _has_cdf(self):
- """State if a cdf is defined with 'spectral_rad_cdf'."""
- return hasattr(self, "spectral_rad_cdf")
-
- def _has_ppf(self):
- """State if a ppf is defined with 'spectral_rad_ppf'."""
- return hasattr(self, "spectral_rad_ppf")
-
- # spatial routines
-
- def isometrize(self, pos):
- """Make a position tuple ready for isotropic operations."""
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape((self.field_dim, -1))
- if self.latlon:
- return latlon2pos(
- pos,
- radius=self.geo_scale,
- temporal=self.temporal,
- time_scale=self.anis[-1],
- )
- return np.dot(matrix_isometrize(self.dim, self.angles, self.anis), pos)
-
- def anisometrize(self, pos):
- """Bring a position tuple into the anisotropic coordinate-system."""
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape((self.dim, -1))
- if self.latlon:
- return pos2latlon(
- pos,
- radius=self.geo_scale,
- temporal=self.temporal,
- time_scale=self.anis[-1],
- )
- return np.dot(
- matrix_anisometrize(self.dim, self.angles, self.anis), pos
- )
-
- def main_axes(self):
- """Axes of the rotated coordinate-system."""
- return rotated_main_axes(self.dim, self.angles)
-
- def _get_iso_rad(self, pos):
- """Isometrized radians."""
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape((self.dim, -1))
- iso = np.dot(matrix_isometrize(self.dim, self.angles, self.anis), pos)
- return np.linalg.norm(iso, axis=0)
-
- # fitting routine
-
- def fit_variogram(
- self,
- x_data,
- y_data,
- anis=True,
- sill=None,
- init_guess="default",
- weights=None,
- method="trf",
- loss="soft_l1",
- max_eval=None,
- return_r2=False,
- curve_fit_kwargs=None,
- **para_select,
- ):
- """
- Fitting the variogram-model to an empirical variogram.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- x_data : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The bin-centers of the empirical variogram.
- y_data : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The measured variogram
- If multiple are given, they are interpreted as the directional
- variograms along the main axis of the associated rotated
- coordinate system.
- Anisotropy ratios will be estimated in that case.
- anis : :class:`bool`, optional
- In case of a directional variogram, you can control anisotropy
- by this argument. Deselect the parameter from fitting, by setting
- it "False".
- You could also pass a fixed value to be set in the model.
- Then the anisotropy ratios wont be altered during fitting.
- Default: True
- sill : :class:`float` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Here you can provide a fixed sill for the variogram.
- It needs to be in a fitting range for the var and nugget bounds.
- If variance or nugget are not selected for estimation,
- the nugget will be recalculated to fulfill:
-
- * sill = var + nugget
- * if the variance is bigger than the sill,
- nugget will bet set to its lower bound
- and the variance will be set to the fitting partial sill.
-
- If variance is deselected, it needs to be less than the sill,
- otherwise a ValueError comes up. Same for nugget.
- If sill=False, it will be deselected from estimation
- and set to the current sill of the model.
- Then, the procedure above is applied.
- Default: None
- init_guess : :class:`str` or :class:`dict`, optional
- Initial guess for the estimation. Either:
-
- * "default": using the default values of the covariance model
- ("len_scale" will be mean of given bin centers;
- "var" and "nugget" will be mean of given variogram values
- (if in given bounds))
- * "current": using the current values of the covariance model
- * dict: dictionary with parameter names and given value
- (separate "default" can bet set to "default" or "current" for
- unspecified values to get same behavior as given above
- ("default" by default))
- Example: ``{"len_scale": 10, "default": "current"}``
-
- Default: "default"
- weights : :class:`str`, :class:`numpy.ndarray`, :class:`callable`, optional
- Weights applied to each point in the estimation. Either:
-
- * 'inv': inverse distance ``1 / (x_data + 1)``
- * list: weights given per bin
- * callable: function applied to x_data
-
- If callable, it must take a 1-d ndarray.
- Then ``weights = f(x_data)``.
- Default: None
- method : {'trf', 'dogbox'}, optional
- Algorithm to perform minimization.
-
- * 'trf' : Trust Region Reflective algorithm,
- particularly suitable for large sparse problems with bounds.
- Generally robust method.
- * 'dogbox' : dogleg algorithm with rectangular trust regions,
- typical use case is small problems with bounds.
- Not recommended for problems with rank-deficient Jacobian.
-
- Default: 'trf'
- loss : :class:`str` or :class:`callable`, optional
- Determines the loss function in scipys curve_fit.
- The following keyword values are allowed:
-
- * 'linear' (default) : ``rho(z) = z``. Gives a standard
- least-squares problem.
- * 'soft_l1' : ``rho(z) = 2 * ((1 + z)**0.5 - 1)``. The smooth
- approximation of l1 (absolute value) loss. Usually a good
- choice for robust least squares.
- * 'huber' : ``rho(z) = z if z <= 1 else 2*z**0.5 - 1``. Works
- similarly to 'soft_l1'.
- * 'cauchy' : ``rho(z) = ln(1 + z)``. Severely weakens outliers
- influence, but may cause difficulties in optimization process.
- * 'arctan' : ``rho(z) = arctan(z)``. Limits a maximum loss on
- a single residual, has properties similar to 'cauchy'.
-
- If callable, it must take a 1-d ndarray ``z=f**2`` and return an
- array_like with shape (3, m) where row 0 contains function values,
- row 1 contains first derivatives and row 2 contains second
- derivatives. Default: 'soft_l1'
- max_eval : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- Maximum number of function evaluations before the termination.
- If None (default), the value is chosen automatically: 100 * n.
- return_r2 : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return the r2 score of the estimation.
- Default: False
- curve_fit_kwargs : :class:`dict`, optional
- Other keyword arguments passed to scipys curve_fit. Default: None
- **para_select
- You can deselect parameters from fitting, by setting
- them "False" using their names as keywords.
- You could also pass fixed values for each parameter.
- Then these values will be applied and the involved parameters wont
- be fitted.
- By default, all parameters are fitted.
-
- Returns
- -------
- fit_para : :class:`dict`
- Dictionary with the fitted parameter values
- pcov : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The estimated covariance of `popt` from
- :any:`scipy.optimize.curve_fit`.
- To compute one standard deviation errors
- on the parameters use ``perr = np.sqrt(np.diag(pcov))``.
- r2_score : :class:`float`, optional
- r2 score of the curve fitting results. Only if return_r2 is True.
-
- Notes
- -----
- You can set the bounds for each parameter by accessing
- :any:`CovModel.set_arg_bounds`.
-
- The fitted parameters will be instantly set in the model.
- """
- return fit_variogram(
- model=self,
- x_data=x_data,
- y_data=y_data,
- anis=anis,
- sill=sill,
- init_guess=init_guess,
- weights=weights,
- method=method,
- loss=loss,
- max_eval=max_eval,
- return_r2=return_r2,
- curve_fit_kwargs=curve_fit_kwargs,
- **para_select,
- )
-
- # bounds setting and checks
-
- def default_arg_bounds(self):
- """Provide default boundaries for arguments.
-
- Given as a dictionary.
- """
- res = {
- "var": (0.0, np.inf, "oo"),
- "len_scale": (0.0, np.inf, "oo"),
- "nugget": (0.0, np.inf, "co"),
- "anis": (0.0, np.inf, "oo"),
- }
- return res
-
- def set_arg_bounds(self, check_args=True, **kwargs):
- r"""Set bounds for the parameters of the model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- check_args : bool, optional
- Whether to check if the arguments are in their valid bounds.
- In case not, a proper default value will be determined.
- Default: True
- **kwargs
- Parameter name as keyword ("var", "len_scale", "nugget", )
- and a list of 2 or 3 values: ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return set_arg_bounds(self, check_args, **kwargs)
-
- def check_arg_bounds(self):
- """Check arguments to be within their given bounds."""
- return check_arg_bounds(self)
-
- # bounds properties
-
- @property
- def var_bounds(self):
- """:class:`list`: Bounds for the variance.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Is a list of 2 or 3 values: ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return self._var_bounds
-
- @var_bounds.setter
- def var_bounds(self, bounds):
- if not check_bounds(bounds):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Given bounds for 'var' are not valid, got: {bounds}"
- )
- self._var_bounds = bounds
-
- @property
- def len_scale_bounds(self):
- """:class:`list`: Bounds for the length scale.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Is a list of 2 or 3 values: ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return self._len_scale_bounds
-
- @len_scale_bounds.setter
- def len_scale_bounds(self, bounds):
- if not check_bounds(bounds):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Given bounds for 'len_scale' are not valid, got: {bounds}"
- )
- self._len_scale_bounds = bounds
-
- @property
- def nugget_bounds(self):
- """:class:`list`: Bounds for the nugget.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Is a list of 2 or 3 values: ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return self._nugget_bounds
-
- @nugget_bounds.setter
- def nugget_bounds(self, bounds):
- if not check_bounds(bounds):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Given bounds for 'nugget' are not valid, got: {bounds}"
- )
- self._nugget_bounds = bounds
-
- @property
- def anis_bounds(self):
- """:class:`list`: Bounds for the nugget.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Is a list of 2 or 3 values: ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return self._anis_bounds
-
- @anis_bounds.setter
- def anis_bounds(self, bounds):
- if not check_bounds(bounds):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Given bounds for 'anis' are not valid, got: {bounds}"
- )
- self._anis_bounds = bounds
-
- @property
- def opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """:class:`dict`: Bounds for the optional arguments.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Keys are the opt-arg names and values are lists of 2 or 3 values:
- ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- return self._opt_arg_bounds
-
- @property
- def arg_bounds(self):
- """:class:`dict`: Bounds for all parameters.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Keys are the arg names and values are lists of 2 or 3 values:
- ``[a, b]`` or ``[a, b, ]`` where
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- res = {
- "var": self.var_bounds,
- "len_scale": self.len_scale_bounds,
- "nugget": self.nugget_bounds,
- "anis": self.anis_bounds,
- }
- res.update(self.opt_arg_bounds)
- return res
-
- @property
- def temporal(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the model is a metric spatio-temporal one."""
- return self._temporal
-
- # geographical coordinates related
-
- @property
- def latlon(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the model depends on geographical coords."""
- return self._latlon
-
- @property
- def geo_scale(self):
- """:class:`float`: Geographic scaling for geographical coords."""
- return self._geo_scale
-
- @property
- def field_dim(self):
- """:class:`int`: The (parametric) field dimension of the model (with time)."""
- return 2 + int(self.temporal) if self.latlon else self.dim
-
- @property
- def spatial_dim(self):
- """:class:`int`: The spatial field dimension of the model (without time)."""
- return 2 if self.latlon else self.dim - int(self.temporal)
-
- # standard parameters
-
- @property
- def dim(self):
- """:class:`int`: The dimension of the model."""
- return self._dim
-
- @dim.setter
- def dim(self, dim):
- set_dim(self, dim)
-
- @property
- def var(self):
- """:class:`float`: The variance of the model."""
- return self._var * self.var_factor()
-
- @var.setter
- def var(self, var):
- self._var = float(var) / self.var_factor()
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def var_raw(self):
- """:class:`float`: The raw variance of the model without factor.
-
- (See. CovModel.var_factor)
- """
- return self._var
-
- @var_raw.setter
- def var_raw(self, var_raw):
- self._var = float(var_raw)
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def nugget(self):
- """:class:`float`: The nugget of the model."""
- return self._nugget
-
- @nugget.setter
- def nugget(self, nugget):
- self._nugget = float(nugget)
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def len_scale(self):
- """:class:`float`: The main length scale of the model."""
- return self._len_scale
-
- @len_scale.setter
- def len_scale(self, len_scale):
- self._len_scale, anis = set_len_anis(
- self.dim, len_scale, self.anis, self.latlon
- )
- if self.latlon:
- self._anis = np.array((self.dim - 1) * [1], dtype=np.double)
- else:
- self._anis = anis
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def rescale(self):
- """:class:`float`: Rescale factor for the length scale of the model."""
- return self._rescale
-
- @rescale.setter
- def rescale(self, rescale):
- rescale = self.default_rescale() if rescale is None else rescale
- self._rescale = abs(float(rescale))
-
- @property
- def len_rescaled(self):
- """:class:`float`: The rescaled main length scale of the model."""
- return self._len_scale / self._rescale
-
- @property
- def anis(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: The anisotropy factors of the model."""
- return self._anis
-
- @anis.setter
- def anis(self, anis):
- self._len_scale, self._anis = set_len_anis(
- self.dim, self.len_scale, anis, self.latlon
- )
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def angles(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: Rotation angles (in rad) of the model."""
- return self._angles
-
- @angles.setter
- def angles(self, angles):
- self._angles = set_model_angles(
- self.dim, angles, self.latlon, self.temporal
- )
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- @property
- def integral_scale(self):
- """:class:`float`: The main integral scale of the model.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- If integral scale is not setable.
- """
- self._integral_scale = self.calc_integral_scale()
- return self._integral_scale
-
- @integral_scale.setter
- def integral_scale(self, integral_scale):
- if integral_scale is not None:
- # format int-scale right
- self.len_scale = integral_scale
- integral_scale = self.len_scale
- # reset len_scale
- self.len_scale = 1.0
- int_tmp = self.calc_integral_scale()
- self.len_scale = integral_scale / int_tmp
- if not np.isclose(self.integral_scale, integral_scale, rtol=1e-3):
- raise ValueError(
- f"{self.name}: Integral scale could not be set correctly! "
- "Please just provide a 'len_scale'!"
- )
-
- @property
- def hankel_kw(self):
- """:class:`dict`: :any:`hankel.SymmetricFourierTransform` kwargs."""
- return self._hankel_kw
-
- @hankel_kw.setter
- def hankel_kw(self, hankel_kw):
- if self._hankel_kw is None or hankel_kw is None:
- self._hankel_kw = copy.copy(HANKEL_DEFAULT)
- if hankel_kw is not None:
- self._hankel_kw.update(hankel_kw)
- if self.dim is not None:
- self._sft = SFT(ndim=self.dim, **self.hankel_kw)
-
- @property
- def dist_func(self):
- """:class:`tuple` of :any:`callable`: pdf, cdf and ppf.
-
- Spectral distribution info from the model.
- """
- pdf = self.spectral_rad_pdf
- cdf = None
- ppf = None
- if self.has_cdf:
- cdf = self.spectral_rad_cdf
- if self.has_ppf:
- ppf = self.spectral_rad_ppf
- return pdf, cdf, ppf
-
- @property
- def has_cdf(self):
- """:class:`bool`: State if a cdf is defined by the user."""
- return self._has_cdf()
-
- @property
- def has_ppf(self):
- """:class:`bool`: State if a ppf is defined by the user."""
- return self._has_ppf()
-
- @property
- def sill(self):
- """:class:`float`: The sill of the variogram.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This is calculated by:
- * ``sill = variance + nugget``
- """
- return self.var + self.nugget
-
- @property
- def arg(self):
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: Names of all arguments."""
- return ["var", "len_scale", "nugget", "anis", "angles"] + self._opt_arg
-
- @property
- def arg_list(self):
- """:class:`list` of :class:`float`: Values of all arguments."""
- alist = [self.var, self.len_scale, self.nugget, self.anis, self.angles]
- for opt in self.opt_arg:
- alist.append(getattr(self, opt))
- return alist
-
- @property
- def iso_arg(self):
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: Names of isotropic arguments."""
- return ["var", "len_scale", "nugget"] + self._opt_arg
-
- @property
- def iso_arg_list(self):
- """:class:`list` of :class:`float`: Values of isotropic arguments."""
- alist = [self.var, self.len_scale, self.nugget]
- for opt in self.opt_arg:
- alist.append(getattr(self, opt))
- return alist
-
- @property
- def opt_arg(self):
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: Names of the optional arguments."""
- return self._opt_arg
-
- @property
- def len_scale_vec(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: The length scales in each direction.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This is calculated by:
- * ``len_scale_vec[0] = len_scale``
- * ``len_scale_vec[1] = len_scale*anis[0]``
- * ``len_scale_vec[2] = len_scale*anis[1]``
- """
- res = np.zeros(self.dim, dtype=np.double)
- res[0] = self.len_scale
- for i in range(1, self._dim):
- res[i] = self.len_scale * self.anis[i - 1]
- return res
-
- @property
- def integral_scale_vec(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: The integral scales in each direction.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This is calculated by:
- * ``integral_scale_vec[0] = integral_scale``
- * ``integral_scale_vec[1] = integral_scale*anis[0]``
- * ``integral_scale_vec[2] = integral_scale*anis[1]``
- """
- res = np.zeros(self.dim, dtype=np.double)
- res[0] = self.integral_scale
- for i in range(1, self.dim):
- res[i] = self.integral_scale * self.anis[i - 1]
- return res
-
- @property
- def name(self):
- """:class:`str`: The name of the CovModel class."""
- return self.__class__.__name__
-
- @property
- def do_rotation(self):
- """:any:`bool`: State if a rotation is performed."""
- return not np.all(np.isclose(self.angles, 0.0))
-
- @property
- def is_isotropic(self):
- """:any:`bool`: State if a model is isotropic."""
- return np.all(np.isclose(self.anis, 1.0))
-
- def __eq__(self, other):
- """Compare CovModels."""
- if not isinstance(other, CovModel):
- return False
- return compare(self, other)
-
- def __setattr__(self, name, value):
- """Set an attribute."""
- super().__setattr__(name, value)
- # if an optional variogram argument was given, check bounds
- if hasattr(self, "_opt_arg") and name in self._opt_arg:
- self.check_arg_bounds()
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return model_repr(self)
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/fit.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/fit.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 8b19f4977..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/fit.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,540 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for the covariance-model.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.fit
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- fit_variogram
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0632
-import numpy as np
-from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
-
-from gstools.covmodel.tools import check_arg_in_bounds, default_arg_from_bounds
-from gstools.tools.geometric import great_circle_to_chordal, set_anis
-
-__all__ = ["fit_variogram"]
-
-
-DEFAULT_PARA = ["var", "len_scale", "nugget"]
-
-
-def fit_variogram(
- model,
- x_data,
- y_data,
- anis=True,
- sill=None,
- init_guess="default",
- weights=None,
- method="trf",
- loss="soft_l1",
- max_eval=None,
- return_r2=False,
- curve_fit_kwargs=None,
- **para_select,
-):
- """
- Fitting a variogram-model to an empirical variogram.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model to fit.
- x_data : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The bin-centers of the empirical variogram.
- y_data : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The measured variogram
- If multiple are given, they are interpreted as the directional
- variograms along the main axis of the associated rotated
- coordinate system.
- Anisotropy ratios will be estimated in that case.
- anis : :class:`bool`, optional
- In case of a directional variogram, you can control anisotropy
- by this argument. Deselect the parameter from fitting, by setting
- it "False".
- You could also pass a fixed value to be set in the model.
- Then the anisotropy ratios won't be altered during fitting.
- Default: True
- sill : :class:`float` or :class:`bool` or :any:`None`, optional
- Here you can provide a fixed sill for the variogram.
- It needs to be in a fitting range for the var and nugget bounds.
- If variance or nugget are not selected for estimation,
- the nugget will be recalculated to fulfill:
-
- * sill = var + nugget
- * if the variance is bigger than the sill,
- nugget will bet set to its lower bound
- and the variance will be set to the fitting partial sill.
-
- If variance is deselected, it needs to be less than the sill,
- otherwise a ValueError comes up. Same for nugget.
- If sill=False, it will be deselected from estimation
- and set to the current sill of the model.
- Then, the procedure above is applied.
- Default: None
- init_guess : :class:`str` or :class:`dict`, optional
- Initial guess for the estimation. Either:
-
- * "default": using the default values of the covariance model
- ("len_scale" will be mean of given bin centers;
- "var" and "nugget" will be mean of given variogram values
- (if in given bounds))
- * "current": using the current values of the covariance model
- * dict: dictionary with parameter names and given value
- (separate "default" can bet set to "default" or "current" for
- unspecified values to get same behavior as given above
- ("default" by default))
- Example: ``{"len_scale": 10, "default": "current"}``
-
- Default: "default"
- weights : :class:`str`, :class:`numpy.ndarray`, :class:`callable`optional
- Weights applied to each point in the estimation. Either:
-
- * 'inv': inverse distance ``1 / (x_data + 1)``
- * list: weights given per bin
- * callable: function applied to x_data
-
- If callable, it must take a 1-d ndarray. Then ``weights = f(x_data)``.
- Default: None
- method : {'trf', 'dogbox'}, optional
- Algorithm to perform minimization.
-
- * 'trf' : Trust Region Reflective algorithm, particularly suitable
- for large sparse problems with bounds. Generally robust method.
- * 'dogbox' : dogleg algorithm with rectangular trust regions,
- typical use case is small problems with bounds. Not recommended
- for problems with rank-deficient Jacobian.
-
- Default: 'trf'
- loss : :class:`str` or :class:`callable`, optional
- Determines the loss function in scipys curve_fit.
- The following keyword values are allowed:
-
- * 'linear' (default) : ``rho(z) = z``. Gives a standard
- least-squares problem.
- * 'soft_l1' : ``rho(z) = 2 * ((1 + z)**0.5 - 1)``. The smooth
- approximation of l1 (absolute value) loss. Usually a good
- choice for robust least squares.
- * 'huber' : ``rho(z) = z if z <= 1 else 2*z**0.5 - 1``. Works
- similarly to 'soft_l1'.
- * 'cauchy' : ``rho(z) = ln(1 + z)``. Severely weakens outliers
- influence, but may cause difficulties in optimization process.
- * 'arctan' : ``rho(z) = arctan(z)``. Limits a maximum loss on
- a single residual, has properties similar to 'cauchy'.
-
- If callable, it must take a 1-d ndarray ``z=f**2`` and return an
- array_like with shape (3, m) where row 0 contains function values,
- row 1 contains first derivatives and row 2 contains second
- derivatives. Default: 'soft_l1'
- max_eval : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- Maximum number of function evaluations before the termination.
- If None (default), the value is chosen automatically: 100 * n.
- return_r2 : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return the r2 score of the estimation.
- Default: False
- curve_fit_kwargs : :class:`dict`, optional
- Other keyword arguments passed to scipys curve_fit. Default: None
- **para_select
- You can deselect parameters from fitting, by setting
- them "False" using their names as keywords.
- You could also pass fixed values for each parameter.
- Then these values will be applied and the involved parameters wont
- be fitted.
- By default, all parameters are fitted.
-
- Returns
- -------
- fit_para : :class:`dict`
- Dictionary with the fitted parameter values
- pcov : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The estimated covariance of `popt` from
- :any:`scipy.optimize.curve_fit`.
- To compute one standard deviation errors
- on the parameters use ``perr = np.sqrt(np.diag(pcov))``.
- r2_score : :class:`float`, optional
- r2 score of the curve fitting results. Only if return_r2 is True.
-
- Notes
- -----
- You can set the bounds for each parameter by accessing
- :any:`CovModel.set_arg_bounds`.
-
- The fitted parameters will be instantly set in the model.
- """
- # preprocess selected parameters
- para, sill, constrain_sill, anis = _pre_para(
- model, para_select, sill, anis
- )
- # check curve_fit kwargs
- curve_fit_kwargs = {} if curve_fit_kwargs is None else curve_fit_kwargs
- # check method
- if method not in ["trf", "dogbox"]:
- raise ValueError("fit: method needs to be either 'trf' or 'dogbox'")
- # prepare variogram data
- # => concatenate directional variograms to have a 1D array for x and y
- x_data, y_data, is_dir_vario = _check_vario(model, x_data, y_data)
- # prepare init guess dictionary
- init_guess = _pre_init_guess(
- model, init_guess, np.mean(x_data), np.mean(y_data)
- )
- # only fit anisotropy if a directional variogram was given
- anis &= is_dir_vario
- # set weights
- _set_weights(model, weights, x_data, curve_fit_kwargs, is_dir_vario)
- # set the lower/upper boundaries for the variogram-parameters
- bounds, init_guess_list = _init_curve_fit_para(
- model, para, init_guess, constrain_sill, sill, anis
- )
- # create the fitting curve
- curve_fit_kwargs["f"] = _get_curve(
- model, para, constrain_sill, sill, anis, is_dir_vario
- )
- # set the remaining kwargs for curve_fit
- curve_fit_kwargs["bounds"] = bounds
- curve_fit_kwargs["p0"] = init_guess_list
- curve_fit_kwargs["xdata"] = x_data
- curve_fit_kwargs["ydata"] = y_data
- curve_fit_kwargs["loss"] = loss
- curve_fit_kwargs["max_nfev"] = max_eval
- curve_fit_kwargs["method"] = method
- # fit the variogram
- popt, pcov = curve_fit(**curve_fit_kwargs)
- # convert the results
- fit_para = _post_fitting(model, para, popt, anis, is_dir_vario)
- # calculate the r2 score if wanted
- if return_r2:
- return fit_para, pcov, _r2_score(model, x_data, y_data, is_dir_vario)
- return fit_para, pcov
-
-
-def _pre_para(model, para_select, sill, anis):
- """Preprocess selected parameters."""
- var_last = False
- var_tmp = 0.0 # init value
- for par in para_select:
- if par not in model.arg_bounds:
- raise ValueError(f"fit: unknown parameter in selection: {par}")
- if not isinstance(para_select[par], bool):
- if par == "var":
- var_last = True
- var_tmp = float(para_select[par])
- else:
- setattr(model, par, float(para_select[par]))
- para_select[par] = False
- # set variance last due to possible recalculations
- if var_last:
- model.var = var_tmp
- # remove those that were set to True
- para_select = {k: v for k, v in para_select.items() if not v}
- # handling the sill
- sill = None if (isinstance(sill, bool) and sill) else sill
- if sill is not None:
- sill = model.sill if isinstance(sill, bool) else float(sill)
- constrain_sill = True
- sill_low = model.arg_bounds["var"][0] + model.arg_bounds["nugget"][0]
- sill_up = model.arg_bounds["var"][1] + model.arg_bounds["nugget"][1]
- if not sill_low <= sill <= sill_up:
- raise ValueError("fit: sill out of bounds.")
- if "var" in para_select and "nugget" in para_select:
- if model.var > sill:
- model.nugget = model.arg_bounds["nugget"][0]
- model.var = sill - model.nugget
- else:
- model.nugget = sill - model.var
- elif "var" in para_select:
- if model.var > sill:
- raise ValueError(
- "fit: if sill is fixed and variance deselected, "
- "the set variance should be less than the given sill."
- )
- para_select["nugget"] = False
- model.nugget = sill - model.var
- elif "nugget" in para_select:
- if model.nugget > sill:
- raise ValueError(
- "fit: if sill is fixed and nugget deselected, "
- "the set nugget should be less than the given sill."
- )
- para_select["var"] = False
- model.var = sill - model.nugget
- else:
- # deselect the nugget, to recalculate it accordingly
- # nugget = sill - var
- para_select["nugget"] = False
- else:
- constrain_sill = False
- # select all parameters to be fitted
- para = {par: True for par in DEFAULT_PARA}
- para.update({opt: True for opt in model.opt_arg})
- # now deselect unwanted parameters
- para.update(para_select)
- # check if anisotropy should be fitted or set
- if not isinstance(anis, bool):
- model.anis = anis
- anis = False
- return para, sill, constrain_sill, anis
-
-
-def _pre_init_guess(model, init_guess, mean_x=1.0, mean_y=1.0):
- # init guess should be a dict
- if not isinstance(init_guess, dict):
- init_guess = {"default": init_guess}
- # "default" init guess is the respective default value
- default_guess = init_guess.pop("default", "default")
- if default_guess not in ["default", "current"]:
- raise ValueError(f"fit_variogram: unknown def. guess: {default_guess}")
- default = default_guess == "default"
- # check invalid names for given init guesses
- invalid_para = set(init_guess) - set(model.iso_arg + ["anis"])
- if invalid_para:
- raise ValueError(f"fit_variogram: unknown init guess: {invalid_para}")
- bnd = model.arg_bounds
- # default length scale is mean of given bin centers (respecting "rescale")
- init_guess.setdefault(
- "len_scale", mean_x * model.rescale if default else model.len_scale
- )
- # init guess for variance and nugget is mean of given variogram
- for par in ["var", "nugget"]:
- init_guess.setdefault(par, mean_y if default else getattr(model, par))
- # anis setting
- init_guess.setdefault(
- "anis", default_arg_from_bounds(bnd["anis"]) if default else model.anis
- )
- # correctly handle given values for anis (need a list of values)
- init_guess["anis"] = list(set_anis(model.dim, init_guess["anis"]))
- # set optional arguments
- for opt in model.opt_arg:
- init_guess.setdefault(
- opt,
- (
- default_arg_from_bounds(bnd[opt])
- if default
- else getattr(model, opt)
- ),
- )
- # convert all init guesses to float (except "anis")
- for arg in model.iso_arg:
- init_guess[arg] = float(init_guess[arg])
- return init_guess
-
-
-def _check_vario(model, x_data, y_data):
- # prepare variogram data
- x_data = np.asarray(x_data).reshape(-1)
- y_data = np.asarray(y_data).reshape(-1)
- # if multiple variograms are given, they will be interpreted
- # as directional variograms along the main rotated axes of the model
- is_dir_vario = False
- if model.dim > 1 and x_data.size * model.dim == y_data.size:
- is_dir_vario = True
- # concatenate multiple variograms
- x_data = np.tile(x_data, model.dim)
- elif x_data.size != y_data.size:
- raise ValueError(
- "CovModel.fit_variogram: Wrong number of empirical variograms! "
- "Either provide only one variogram to fit an isotropic model, "
- "or directional ones for all main axes to fit anisotropy."
- )
- if is_dir_vario and model.latlon:
- raise ValueError(
- "CovModel.fit_variogram: lat-lon models don't support anisotropy."
- )
- if model.latlon:
- # convert to yadrenko model
- x_data = great_circle_to_chordal(x_data, model.geo_scale)
- return x_data, y_data, is_dir_vario
-
-
-def _set_weights(model, weights, x_data, curve_fit_kwargs, is_dir_vario):
- if weights is not None:
- if callable(weights):
- weights = 1.0 / weights(x_data)
- elif isinstance(weights, str) and weights == "inv":
- weights = 1.0 + x_data
- else:
- if is_dir_vario and weights.size * model.dim == x_data.size:
- weights = np.tile(weights, model.dim)
- weights = 1.0 / np.asarray(weights).reshape(-1)
- curve_fit_kwargs["sigma"] = weights
- curve_fit_kwargs["absolute_sigma"] = True
-
-
-def _init_curve_fit_para(model, para, init_guess, constrain_sill, sill, anis):
- """Create initial guess and bounds for fitting."""
- low_bounds = []
- top_bounds = []
- init_guess_list = []
- for par in DEFAULT_PARA:
- if para[par]:
- low_bounds.append(model.arg_bounds[par][0])
- if par == "var" and constrain_sill: # var <= sill in this case
- top_bounds.append(sill)
- else:
- top_bounds.append(model.arg_bounds[par][1])
- init_guess_list.append(
- _init_guess(
- bounds=[low_bounds[-1], top_bounds[-1]],
- default=init_guess[par],
- )
- )
- for opt in model.opt_arg:
- if para[opt]:
- low_bounds.append(model.arg_bounds[opt][0])
- top_bounds.append(model.arg_bounds[opt][1])
- init_guess_list.append(
- _init_guess(
- bounds=[low_bounds[-1], top_bounds[-1]],
- default=init_guess[opt],
- )
- )
- if anis:
- for i in range(model.dim - 1):
- low_bounds.append(model.anis_bounds[0])
- top_bounds.append(model.anis_bounds[1])
- init_guess_list.append(
- _init_guess(
- bounds=[low_bounds[-1], top_bounds[-1]],
- default=init_guess["anis"][i],
- )
- )
- return (low_bounds, top_bounds), init_guess_list
-
-
-def _init_guess(bounds, default):
- """Proper determination of initial guess."""
- if bounds[0] < default < bounds[1]:
- return default
- return default_arg_from_bounds(bounds)
-
-
-def _get_curve(model, para, constrain_sill, sill, anis, is_dir_vario):
- """Create the curve for scipys curve_fit."""
- var_save = model.var
-
- # we need arg1, otherwise curve_fit throws an error (bug?!)
- def curve(x, arg1, *args):
- """Adapted Variogram function."""
- args = (arg1,) + args
- para_skip = 0
- opt_skip = 0
- if para["var"]:
- var_tmp = args[para_skip]
- if constrain_sill:
- nugget_tmp = sill - var_tmp
- # punishment, if resulting nugget out of range for fixed sill
- if check_arg_in_bounds(model, "nugget", nugget_tmp) > 0:
- return np.full_like(x, np.inf)
- # nugget estimation deselected in this case
- model.nugget = nugget_tmp
- para_skip += 1
- if para["len_scale"]:
- model.len_scale = args[para_skip]
- para_skip += 1
- if para["nugget"]:
- model.nugget = args[para_skip]
- para_skip += 1
- for opt in model.opt_arg:
- if para[opt]:
- setattr(model, opt, args[para_skip + opt_skip])
- opt_skip += 1
- # set var at last because of var_factor (other parameter needed)
- if para["var"]:
- model.var = var_tmp
- # needs to be reset for TPL models when len_scale was changed
- else:
- model.var = var_save
- if is_dir_vario:
- if anis:
- model.anis = args[1 - model.dim :]
- xs = x[: x.size // model.dim]
- out = np.array([], dtype=np.double)
- for i in range(model.dim):
- out = np.concatenate((out, model.vario_axis(xs, axis=i)))
- return out
- return model.variogram(x)
-
- return curve
-
-
-def _post_fitting(model, para, popt, anis, is_dir_vario):
- """Postprocess fitting results and application to model."""
- fit_para = {}
- para_skip = 0
- opt_skip = 0
- var_tmp = 0.0 # init value
- for par in DEFAULT_PARA:
- if para[par]:
- if par == "var": # set variance last
- var_tmp = popt[para_skip]
- else:
- setattr(model, par, popt[para_skip])
- fit_para[par] = popt[para_skip]
- para_skip += 1
- else:
- fit_para[par] = getattr(model, par)
- for opt in model.opt_arg:
- if para[opt]:
- setattr(model, opt, popt[para_skip + opt_skip])
- fit_para[opt] = popt[para_skip + opt_skip]
- opt_skip += 1
- else:
- fit_para[opt] = getattr(model, opt)
- if is_dir_vario:
- if anis:
- model.anis = popt[1 - model.dim :]
- fit_para["anis"] = model.anis
- # set var at last because of var_factor (other parameter needed)
- if para["var"]:
- model.var = var_tmp
- return fit_para
-
-
-def _r2_score(model, x_data, y_data, is_dir_vario):
- """Calculate the R2 score."""
- if is_dir_vario:
- xs = x_data[: x_data.size // model.dim]
- vario = np.array([], dtype=np.double)
- for i in range(model.dim):
- vario = np.concatenate((vario, model.vario_axis(xs, axis=i)))
- else:
- vario = model.variogram(x_data)
- residuals = y_data - vario
- ss_res = np.sum(residuals**2)
- ss_tot = np.sum((y_data - np.mean(y_data)) ** 2)
- return 1.0 - (ss_res / ss_tot)
-
-
-def logistic_weights(p=0.1, mean=0.7): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Return a logistic weights function.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- p : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter for the growth rate.
- Within this percentage of the data range, the function will
- be in the upper resp. lower percentile p. The default is 0.1.
- mean : :class:`float`, optional
- Percentage of the data range, where this function has its
- sigmoid's midpoint. The default is 0.7.
-
- Returns
- -------
- callable
- Weighting function.
- """
-
- # define the callable weights function
- def func(x_data):
- """Callable function for the weights."""
- x_range = np.amax(x_data) - np.amin(x_data)
- # logit function for growth rate
- growth = np.log(p / (1 - p)) / (p * x_range)
- x_mean = mean * x_range + np.amin(x_data)
- return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(growth * (x_mean - x_data)))
-
- return func
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/models.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/models.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b1a9d68ec..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/models.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,960 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing different covariance models.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.models
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- Gaussian
- Exponential
- Matern
- Integral
- Stable
- Rational
- Cubic
- Linear
- Circular
- Spherical
- HyperSpherical
- SuperSpherical
- JBessel
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, E1101, R0201
-import warnings
-
-import numpy as np
-from scipy import special as sps
-
-from gstools.covmodel.base import CovModel
-from gstools.covmodel.tools import AttributeWarning
-from gstools.tools.special import exp_int, inc_gamma_low
-
-__all__ = [
- "Gaussian",
- "Exponential",
- "Matern",
- "Integral",
- "Stable",
- "Rational",
- "Cubic",
- "Linear",
- "Circular",
- "Spherical",
- "HyperSpherical",
- "SuperSpherical",
- "JBessel",
-]
-
-
-class Gaussian(CovModel):
- r"""The Gaussian covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following variogram [Webster2007]_:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r)=
- \sigma^{2}
- \left(1-\exp\left(-\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}\right)\right)+n
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=\frac{\sqrt{\pi}}{2}`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Gaussian normalized correlation function."""
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
- def default_rescale(self):
- """Gaussian rescaling factor to result in integral scale."""
- return np.sqrt(np.pi) / 2.0
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- return (self.len_rescaled / 2.0 / np.sqrt(np.pi)) ** self.dim * np.exp(
- -((k * self.len_rescaled / 2.0) ** 2)
- )
-
- def spectral_rad_cdf(self, r):
- """Gaussian radial spectral cdf."""
- r = np.asarray(r, dtype=np.double)
- if self.dim == 1:
- return sps.erf(r * self.len_rescaled / 2.0)
- if self.dim == 2:
- return 1.0 - np.exp(-((r * self.len_rescaled / 2.0) ** 2))
- if self.dim == 3:
- return sps.erf(
- r * self.len_rescaled / 2.0
- ) - r * self.len_rescaled / np.sqrt(np.pi) * np.exp(
- -((r * self.len_rescaled / 2.0) ** 2)
- )
- return None # pragma: no cover
-
- def spectral_rad_ppf(self, u):
- """Gaussian radial spectral ppf.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Not defined for 3D.
- """
- u = np.asarray(u, dtype=np.double)
- if self.dim == 1:
- return 2.0 / self.len_rescaled * sps.erfinv(u)
- if self.dim == 2:
- return 2.0 / self.len_rescaled * np.sqrt(-np.log(1.0 - u))
- return None # pragma: no cover
-
- def _has_cdf(self):
- return self.dim in [1, 2, 3]
-
- def _has_ppf(self):
- return self.dim in [1, 2]
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return self.len_rescaled * np.sqrt(np.pi) / 2.0
-
-
-class Exponential(CovModel):
- r"""The Exponential covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following variogram [Webster2007]_:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r)=
- \sigma^{2}
- \left(1-\exp\left(-s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)\right)+n
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Exponential normalized correlation function."""
- return np.exp(-h)
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- return (
- self.len_rescaled**self.dim
- * sps.gamma((self.dim + 1) / 2.0)
- / (np.pi * (1.0 + (k * self.len_rescaled) ** 2))
- ** ((self.dim + 1) / 2.0)
- )
-
- def spectral_rad_cdf(self, r):
- """Exponential radial spectral cdf."""
- r = np.asarray(r, dtype=np.double)
- if self.dim == 1:
- return np.arctan(r * self.len_rescaled) * 2.0 / np.pi
- if self.dim == 2:
- return 1.0 - 1.0 / np.sqrt(1.0 + (r * self.len_rescaled) ** 2)
- if self.dim == 3:
- return (
- (
- np.arctan(r * self.len_rescaled)
- - r
- * self.len_rescaled
- / (1.0 + (r * self.len_rescaled) ** 2)
- )
- * 2.0
- / np.pi
- )
- return None # pragma: no cover
-
- def spectral_rad_ppf(self, u):
- """Exponential radial spectral ppf.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Not defined for 3D.
- """
- u = np.asarray(u, dtype=np.double)
- if self.dim == 1:
- return np.tan(np.pi / 2 * u) / self.len_rescaled
- if self.dim == 2:
- u_power = np.divide(
- 1,
- u**2,
- out=np.full_like(u, np.inf),
- where=np.logical_not(np.isclose(u, 0)),
- )
- return np.sqrt(u_power - 1.0) / self.len_rescaled
- return None # pragma: no cover
-
- def _has_cdf(self):
- return self.dim in [1, 2, 3]
-
- def _has_ppf(self):
- return self.dim in [1, 2]
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return self.len_rescaled
-
-
-class Stable(CovModel):
- r"""The stable covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function
- [Wackernagel2003]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \exp\left(- \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{\alpha}\right)
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`\alpha` is a shape parameter with :math:`\alpha\in(0,2]`
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Wackernagel2003] Wackernagel, H. "Multivariate geostatistics",
- Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2003)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- alpha : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``(0, 2]``
- Default: ``1.5``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"alpha": 1.5}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"alpha": 1.5}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"alpha": [0, 2, "oc"]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"alpha": [0, 2, "oc"]}
-
- def check_opt_arg(self):
- """Check the optional arguments.
-
- Warns
- -----
- alpha
- If alpha is < 0.3, the model tends to a nugget model and gets
- numerically unstable.
- """
- if self.alpha < 0.3:
- warnings.warn(
- "Stable: parameter 'alpha' is < 0.3, "
- "count with unstable results",
- AttributeWarning,
- )
-
- def cor(self, h):
- r"""Stable normalized correlation function."""
- return np.exp(-np.power(h, self.alpha))
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return self.len_rescaled * sps.gamma(1.0 + 1.0 / self.alpha)
-
-
-class Matern(CovModel):
- r"""The Matérn covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Rasmussen2003]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \frac{2^{1-\nu}}{\Gamma\left(\nu\right)} \cdot
- \left(\sqrt{\nu}\cdot s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{\nu} \cdot
- \mathrm{K}_{\nu}\left(\sqrt{\nu}\cdot s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`\Gamma` is the gamma function and :math:`\mathrm{K}_{\nu}`
- is the modified Bessel function of the second kind.
-
- :math:`\nu` is a shape parameter and should be >= 0.2.
-
- If :math:`\nu > 20`, a gaussian model is used, since it represents
- the limiting case:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \exp\left(-\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{2\ell}\right)^2\right)
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Rasmussen2003] Rasmussen, C. E.,
- "Gaussian processes in machine learning." Summer school on
- machine learning. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, (2003)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- nu : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``[0.2, 30]``
- Default: ``1.0``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": 1.0}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": 1.0}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": [0.2, 30.0, "cc"]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": [0.2, 30.0, "cc"]}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Matérn normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.asarray(np.abs(h), dtype=np.double)
- # for nu > 20 we just use the gaussian model
- if self.nu > 20.0:
- return np.exp(-((h / 2.0) ** 2))
- # calculate by log-transformation to prevent numerical errors
- h_gz = h[h > 0.0]
- res = np.ones_like(h)
- res[h > 0.0] = np.exp(
- (1.0 - self.nu) * np.log(2)
- - sps.loggamma(self.nu)
- + self.nu * np.log(np.sqrt(self.nu) * h_gz)
- ) * sps.kv(self.nu, np.sqrt(self.nu) * h_gz)
- # if nu >> 1 we get errors for the farfield, there 0 is approached
- res[np.logical_not(np.isfinite(res))] = 0.0
- # covariance is positive
- res = np.maximum(res, 0.0)
- return res
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- x = (k * self.len_rescaled) ** 2
- # for nu > 20 we just use an approximation of the gaussian model
- if self.nu > 20.0:
- return (
- (self.len_rescaled / np.sqrt(np.pi)) ** self.dim
- * np.exp(-x)
- * (1 + 0.5 * x**2 / self.nu)
- * np.sqrt(1 + x / self.nu) ** (-self.dim)
- )
- return (self.len_rescaled / np.sqrt(np.pi)) ** self.dim * np.exp(
- -(self.nu + self.dim / 2.0) * np.log(1.0 + x / self.nu)
- + sps.loggamma(self.nu + self.dim / 2.0)
- - sps.loggamma(self.nu)
- - self.dim * np.log(np.sqrt(self.nu))
- )
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return (
- self.len_rescaled
- * np.pi
- / np.sqrt(self.nu)
- / sps.beta(self.nu, 0.5)
- )
-
-
-class Integral(CovModel):
- r"""The Exponential Integral covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Mueller2021]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \frac{\nu}{2}\cdot
- E_{1+\frac{\nu}{2}}\left( \left( s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell} \right)^2 \right)
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`E_s(x)` is the exponential integral.
-
- :math:`\nu` is a shape parameter (1 by default).
-
- For :math:`\nu \to \infty`, a gaussian model is approached, since it represents
- the limiting case:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \exp\left(-\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^2\right)
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Mueller2021] Müller, S., Heße, F., Attinger, S., and Zech, A.,
- "The extended generalized radial flow model and effective
- conductivity for truncated power law variograms",
- Adv. Water Resour., 156, 104027, (2021)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- nu : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``(0.0, 50]``
- Default: ``1.0``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": 1.0}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": 1.0}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": [0.0, 50.0, "oc"]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": [0.0, 50.0, "oc"]}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Exponential Integral normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.asarray(h, dtype=np.double)
- return 0.5 * self.nu * exp_int(1.0 + 0.5 * self.nu, h**2)
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- fac = (0.5 * self.len_rescaled / np.sqrt(np.pi)) ** self.dim
- lim = fac * self.nu / (self.nu + self.dim)
- # for nu > 50 we just use an approximation of the gaussian model
- if self.nu > 50.0:
- x = (k * self.len_rescaled / 2) ** 2
- return lim * np.exp(-x) * (1 + 2 * x / (self.nu + self.dim + 2))
- # separate calculation at origin
- s = (self.nu + self.dim) / 2
- res = np.empty_like(k)
- k_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(k, 0))
- x = (k[k_gz] * self.len_rescaled / 2) ** 2
- # limit at k=0 (inc_gamma_low(s, x) / x**s -> 1/s for x -> 0)
- res[np.logical_not(k_gz)] = lim
- res[k_gz] = 0.5 * self.nu * fac / x**s * inc_gamma_low(s, x)
- return res
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return (
- self.len_rescaled * self.nu * np.sqrt(np.pi) / (2 * self.nu + 2.0)
- )
-
-
-class Rational(CovModel):
- r"""The rational quadratic covariance model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Rasmussen2003]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \left(1 + \frac{1}{\alpha} \cdot
- \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^2\right)^{-\alpha}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`\alpha` is a shape parameter and should be > 0.5.
-
- For :math:`\alpha\to\infty` this model converges to the Gaussian model:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r)=
- \exp\left(-\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}\right)
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Rasmussen2003] Rasmussen, C. E.,
- "Gaussian processes in machine learning." Summer school on
- machine learning. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, (2003)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- alpha : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``[0.5, 50]``
- Default: ``1.0``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"alpha": 1.0}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"alpha": 1.0}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"alpha": [0.5, 50.0]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"alpha": [0.5, 50.0]}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Rational normalized correlation function."""
- return np.power(1 + h**2 / self.alpha, -self.alpha)
-
- def calc_integral_scale(self): # noqa: D102
- return (
- self.len_rescaled
- * np.sqrt(np.pi * self.alpha)
- * sps.gamma(self.alpha - 0.5)
- / sps.gamma(self.alpha)
- / 2.0
- )
-
-
-class Cubic(CovModel):
- r"""The Cubic covariance model.
-
- A model with reverse curvature near the origin and a finite range of
- correlation.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Chiles2009]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- 1- 7 \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}
- + \frac{35}{4} \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{3}
- - \frac{7}{2} \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{5}
- + \frac{3}{4} \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{7}
- & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Chiles2009] Chiles, J. P., & Delfiner, P.,
- "Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty" (Vol. 497),
- John Wiley & Sons. (2009)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Spherical normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.minimum(np.abs(h, dtype=np.double), 1.0)
- return 1.0 - 7 * h**2 + 8.75 * h**3 - 3.5 * h**5 + 0.75 * h**7
-
-
-class Linear(CovModel):
- r"""The bounded linear covariance model.
-
- This model is derived from the relative intersection area of
- two lines in 1D, where the middle points have a distance of :math:`r`
- and the line lengths are :math:`\ell`.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Webster2007]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- 1-s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell} & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Linear normalized correlation function."""
- return np.maximum(1 - np.abs(h, dtype=np.double), 0.0)
-
- def check_dim(self, dim):
- """Linear model is only valid in 1D."""
- return dim < 2
-
-
-class Circular(CovModel):
- r"""The circular covariance model.
-
- This model is derived as the relative intersection area of
- two discs in 2D, where the middle points have a distance of :math:`r`
- and the diameters are given by :math:`\ell`.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Webster2007]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- \frac{2}{\pi}\cdot
- \left(
- \cos^{-1}\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right) -
- s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\cdot\sqrt{1-\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}}
- \right)
- & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Circular normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.asarray(np.abs(h), dtype=np.double)
- res = np.zeros_like(h)
- # arccos is instable around h=1
- h_l1 = h < 1.0
- h_low = h[h_l1]
- res[h_l1] = (
- 2 / np.pi * (np.arccos(h_low) - h_low * np.sqrt(1 - h_low**2))
- )
- return res
-
- def check_dim(self, dim):
- """Circular model is only valid in 1D and 2D."""
- return dim < 3
-
-
-class Spherical(CovModel):
- r"""The Spherical covariance model.
-
- This model is derived from the relative intersection area of
- two spheres in 3D, where the middle points have a distance of :math:`r`
- and the diameters are given by :math:`\ell`.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Webster2007]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- 1-\frac{3}{2}\cdot s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell} +
- \frac{1}{2}\cdot\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{3}
- & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Spherical normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.minimum(np.abs(h, dtype=np.double), 1.0)
- return 1.0 - 1.5 * h + 0.5 * h**3
-
- def check_dim(self, dim):
- """Spherical model is only valid in 1D, 2D and 3D."""
- return dim < 4
-
-
-class HyperSpherical(CovModel):
- r"""The Hyper-Spherical covariance model.
-
- This model is derived from the relative intersection area of
- two d-dimensional hyperspheres,
- where the middle points have a distance of :math:`r`
- and the diameters are given by :math:`\ell`.
-
- In 1D this is the Linear model, in 2D the Circular model
- and in 3D the Spherical model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Matern1960]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- 1-s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\cdot\frac{
- _{2}F_{1}\left(\frac{1}{2},-\frac{d-1}{2},\frac{3}{2},
- \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}\right)}
- {_{2}F_{1}\left(\frac{1}{2},-\frac{d-1}{2},\frac{3}{2},1\right)}
- & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`d` is the dimension.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Matern1960] Matern B., "Spatial Variation",
- Swedish National Institute for Forestry Research, (1960)
- """
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Hyper-Spherical normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.asarray(h, dtype=np.double)
- res = np.zeros_like(h)
- h_l1 = h < 1
- nu = (self.dim - 1.0) / 2.0
- fac = 1.0 / sps.hyp2f1(0.5, -nu, 1.5, 1)
- res[h_l1] = 1 - h[h_l1] * fac * sps.hyp2f1(0.5, -nu, 1.5, h[h_l1] ** 2)
- return res
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- res = np.empty_like(k)
- kl = k * self.len_rescaled
- kl_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(k, 0))
- res[kl_gz] = sps.gamma(self.dim / 2 + 1) / np.sqrt(np.pi) ** self.dim
- res[kl_gz] *= sps.jv(self.dim / 2, kl[kl_gz] / 2) ** 2
- res[kl_gz] /= k[kl_gz] ** self.dim
- res[np.logical_not(kl_gz)] = (
- (self.len_rescaled / 4) ** self.dim
- / sps.gamma(self.dim / 2 + 1)
- / np.sqrt(np.pi) ** self.dim
- )
- return res
-
-
-class SuperSpherical(CovModel):
- r"""The Super-Spherical covariance model.
-
- This model is derived from the relative intersection area of
- two d-dimensional hyperspheres,
- where the middle points have a distance of :math:`r`
- and the diameters are given by :math:`\ell`.
- It is than valid in all lower dimensions.
- By default it coincides with the Hyper-Spherical model.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Matern1960]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \begin{cases}
- 1-s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\cdot\frac{
- _{2}F_{1}\left(\frac{1}{2},-\nu,\frac{3}{2},
- \left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{2}\right)}
- {_{2}F_{1}\left(\frac{1}{2},-\nu,\frac{3}{2},1\right)}
- & r<\frac{\ell}{s}\\
- 0 & r\geq\frac{\ell}{s}
- \end{cases}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`\nu\geq\frac{d-1}{2}` is a shape parameter.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Matern1960] Matern B., "Spatial Variation",
- Swedish National Institute for Forestry Research, (1960)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- nu : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``[(dim-1)/2, 50]``
- Default: ``(dim-1)/2``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": (dim-1)/2}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": (self.dim - 1) / 2}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": [(dim-1)/2, 50.0]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": [(self.dim - 1) / 2, 50.0]}
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """Super-Spherical normalized correlation function."""
- h = np.asarray(h, dtype=np.double)
- res = np.zeros_like(h)
- h_l1 = h < 1
- fac = 1.0 / sps.hyp2f1(0.5, -self.nu, 1.5, 1.0)
- res[h_l1] = 1.0 - h[h_l1] * fac * sps.hyp2f1(
- 0.5, -self.nu, 1.5, h[h_l1] ** 2
- )
- return res
-
-
-class JBessel(CovModel):
- r"""The J-Bessel hole model.
-
- This covariance model is a valid hole model, meaning it has areas
- of negative correlation but a valid spectral density.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This model is given by the following correlation function [Chiles2009]_:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \Gamma(\nu+1) \cdot
- \frac{\mathrm{J}_{\nu}\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)}
- {\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{2\ell}\right)^{\nu}}
-
- Where the standard rescale factor is :math:`s=1`.
- :math:`\Gamma` is the gamma function and :math:`\mathrm{J}_{\nu}`
- is the Bessel functions of the first kind.
- :math:`\nu\geq\frac{d}{2}-1` is a shape parameter,
- which defaults to :math:`\nu=\frac{d}{2}`,
- since the spectrum of the model gets instable for
- :math:`\nu\to\frac{d}{2}-1`.
-
- For :math:`\nu=\frac{1}{2}` (valid in d=1,2,3)
- we get the so-called 'Wave' model:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \frac{\sin\left(s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}\right)}{s\cdot\frac{r}{\ell}}
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Chiles2009] Chiles, J. P., & Delfiner, P.,
- "Geostatistics: modeling spatial uncertainty" (Vol. 497),
- John Wiley & Sons. (2009)
-
- Other Parameters
- ----------------
- nu : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Standard range: ``[dim/2 - 1, 50]``
- Default: ``dim/2``
- """
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- """Defaults for the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": dim/2}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Defaults for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": self.dim / 2}
-
- def default_opt_arg_bounds(self):
- """Defaults for boundaries of the optional arguments.
-
- * ``{"nu": [dim/2 - 1, 50.0]}``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Boundaries for optional arguments
- """
- return {"nu": [self.dim / 2 - 1, 50.0]}
-
- def check_opt_arg(self):
- """Check the optional arguments.
-
- Warns
- -----
- nu
- If nu is close to dim/2 - 1, the model tends to get unstable.
- """
- if abs(self.nu - self.dim / 2 + 1) < 0.01:
- warnings.warn(
- "JBessel: parameter 'nu' is close to d/2-1, "
- "count with unstable results",
- AttributeWarning,
- )
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """J-Bessel correlation."""
- h = np.asarray(h, dtype=np.double)
- h_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(h, 0))
- hh = h[h_gz]
- res = np.ones_like(h)
- nu = self.nu
- res[h_gz] = sps.gamma(nu + 1) * sps.jv(nu, hh) / (hh / 2.0) ** nu
- return res
-
- def spectral_density(self, k): # noqa: D102
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- k_ll = k < 1.0 / self.len_rescaled
- kk = k[k_ll]
- res = np.zeros_like(k)
- # the model is degenerated for nu=d/2-1, so we tweak the spectral pdf
- # and cut of the divisor at nu-(d/2-1)=0.01 (gamma(0.01) about 100)
- res[k_ll] = (
- (self.len_rescaled / np.sqrt(np.pi)) ** self.dim
- * sps.gamma(self.nu + 1.0)
- / np.minimum(sps.gamma(self.nu - self.dim / 2 + 1), 100.0)
- * (1.0 - (kk * self.len_rescaled) ** 2) ** (self.nu - self.dim / 2)
- )
- return res
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/plot.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/plot.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 32148c14a..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/plot.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,288 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing plotting routines for the covariance models.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.plot
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- plot_variogram
- plot_covariance
- plot_correlation
- plot_vario_yadrenko
- plot_cov_yadrenko
- plot_cor_yadrenko
- plot_vario_axis
- plot_cov_axis
- plot_cor_axis
- plot_vario_spatial
- plot_cov_spatial
- plot_cor_spatial
- plot_spectrum
- plot_spectral_density
- plot_spectral_rad_pdf
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, C0415, E1130
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.tools.geometric import generate_grid
-from gstools.tools.misc import get_fig_ax
-
-__all__ = [
- "plot_variogram",
- "plot_covariance",
- "plot_correlation",
- "plot_vario_yadrenko",
- "plot_cov_yadrenko",
- "plot_cor_yadrenko",
- "plot_vario_axis",
- "plot_cov_axis",
- "plot_cor_axis",
- "plot_vario_spatial",
- "plot_cov_spatial",
- "plot_cor_spatial",
- "plot_spectrum",
- "plot_spectral_density",
- "plot_spectral_rad_pdf",
-]
-
-
-# plotting routines #######################################################
-
-
-def _plot_spatial(dim, pos, field, fig, ax, temporal, **kwargs):
- from gstools.field.plot import plot_1d, plot_nd
-
- if dim == 1:
- return plot_1d(pos, field, fig, ax, temporal, **kwargs)
- return plot_nd(
- pos, field, "structured", fig, ax, temporal=temporal, **kwargs
- )
-
-
-def plot_vario_spatial(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot spatial variogram of a given CovModel."""
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(-x_max, x_max) + x_min
- pos = [x_s] * model.dim
- shp = tuple(len(p) for p in pos)
- fld = model.vario_spatial(generate_grid(pos)).reshape(shp)
- return _plot_spatial(
- model.dim, pos, fld, fig, ax, model.temporal, **kwargs
- )
-
-
-def plot_cov_spatial(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot spatial covariance of a given CovModel."""
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(-x_max, x_max) + x_min
- pos = [x_s] * model.dim
- shp = tuple(len(p) for p in pos)
- fld = model.cov_spatial(generate_grid(pos)).reshape(shp)
- return _plot_spatial(
- model.dim, pos, fld, fig, ax, model.temporal, **kwargs
- )
-
-
-def plot_cor_spatial(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot spatial correlation of a given CovModel."""
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(-x_max, x_max) + x_min
- pos = [x_s] * model.dim
- shp = tuple(len(p) for p in pos)
- fld = model.cor_spatial(generate_grid(pos)).reshape(shp)
- return _plot_spatial(
- model.dim, pos, fld, fig, ax, model.temporal, **kwargs
- )
-
-
-def plot_variogram(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot variogram of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} variogram")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.variogram(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_covariance(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot covariance of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} covariance")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.covariance(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_correlation(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot correlation function of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} correlation")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.correlation(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_vario_yadrenko(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot Yadrenko variogram of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = min(3 * model.len_scale, model.geo_scale * np.pi)
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} Yadrenko variogram")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.vario_yadrenko(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_cov_yadrenko(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot Yadrenko covariance of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = min(3 * model.len_scale, model.geo_scale * np.pi)
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} Yadrenko covariance")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.cov_yadrenko(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_cor_yadrenko(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot Yadrenko correlation function of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = min(3 * model.len_scale, model.geo_scale * np.pi)
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} Yadrenko correlation")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.cor_yadrenko(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_vario_axis(
- model, axis=0, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot variogram of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} variogram on axis {axis}")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.vario_axis(x_s, axis), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_cov_axis(
- model, axis=0, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot variogram of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} covariance on axis {axis}")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.cov_axis(x_s, axis), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_cor_axis(
- model, axis=0, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot variogram of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 * model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} correlation on axis {axis}")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.cor_axis(x_s, axis), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_spectrum(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot spectrum of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 / model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} {model.dim}D spectrum")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.spectrum(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_spectral_density(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot spectral density of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 / model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} {model.dim}D spectral-density")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.spectral_density(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_spectral_rad_pdf(
- model, x_min=0.0, x_max=None, fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot radial spectral pdf of a given CovModel."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- if x_max is None:
- x_max = 3 / model.len_scale
- x_s = np.linspace(x_min, x_max)
- kwargs.setdefault("label", f"{model.name} {model.dim}D spectral-rad-pdf")
- ax.plot(x_s, model.spectral_rad_pdf(x_s), **kwargs)
- ax.legend()
- fig.show()
- return ax
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/tools.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/tools.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dddeb4413..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/tools.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,647 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for the covariance-model.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.tools
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- AttributeWarning
- rad_fac
- set_opt_args
- set_len_anis
- check_bounds
- check_arg_in_bounds
- default_arg_from_bounds
- spectral_rad_pdf
- percentile_scale
- set_arg_bounds
- check_arg_bounds
- set_dim
- compare
- model_repr
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0212
-import warnings
-
-import numpy as np
-from hankel import SymmetricFourierTransform as SFT
-from scipy import special as sps
-from scipy.optimize import root
-
-from gstools.tools.geometric import no_of_angles, set_angles, set_anis
-from gstools.tools.misc import list_format
-
-__all__ = [
- "AttributeWarning",
- "rad_fac",
- "set_opt_args",
- "set_len_anis",
- "set_model_angles",
- "check_bounds",
- "check_arg_in_bounds",
- "default_arg_from_bounds",
- "spectral_rad_pdf",
- "percentile_scale",
- "set_arg_bounds",
- "check_arg_bounds",
- "set_dim",
- "compare",
- "model_repr",
-]
-
-
-class AttributeWarning(UserWarning):
- """Attribute warning for CovModel class."""
-
-
-def _init_subclass(cls):
- """Initialize gstools covariance model."""
-
- def variogram(self, r):
- """Isotropic variogram of the model."""
- return self.var - self.covariance(r) + self.nugget
-
- def covariance(self, r):
- """Covariance of the model."""
- return self.var * self.correlation(r)
-
- def correlation(self, r):
- """Correlation function of the model."""
- return 1.0 - (self.variogram(r) - self.nugget) / self.var
-
- def correlation_from_cor(self, r):
- """Correlation function of the model."""
- r = np.asarray(np.abs(r), dtype=np.double)
- return self.cor(r / self.len_rescaled)
-
- def cor_from_correlation(self, h):
- """Correlation taking a non-dimensional range."""
- h = np.asarray(np.abs(h), dtype=np.double)
- return self.correlation(h * self.len_rescaled)
-
- abstract = True
- if hasattr(cls, "cor"):
- if not hasattr(cls, "correlation"):
- cls.correlation = correlation_from_cor
- abstract = False
- else:
- cls.cor = cor_from_correlation
- if not hasattr(cls, "variogram"):
- cls.variogram = variogram
- else:
- abstract = False
- if not hasattr(cls, "covariance"):
- cls.covariance = covariance
- else:
- abstract = False
- if not hasattr(cls, "correlation"):
- cls.correlation = correlation
- else:
- abstract = False
- if abstract:
- raise TypeError(
- f"Can't instantiate class '{cls.__name__}', "
- "without providing at least one of the methods "
- "'cor', 'variogram', 'covariance' or 'correlation'."
- )
-
-
-# Helping functions ###########################################################
-
-
-def rad_fac(dim, r):
- """Volume element of the n-dimensional spherical coordinates.
-
- Given as a factor for integration of a radial-symmetric function.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- r : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Given radii.
- """
- if dim == 1:
- fac = 2.0
- elif dim == 2:
- fac = 2 * np.pi * r
- elif dim == 3:
- fac = 4 * np.pi * r**2
- else: # pragma: no cover
- fac = (
- dim
- * r ** (dim - 1)
- * np.sqrt(np.pi) ** dim
- / sps.gamma(dim / 2 + 1)
- )
- return fac
-
-
-def set_opt_args(model, opt_arg):
- """
- Set optional arguments in the model class.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- opt_arg : :class:`dict`
- Dictionary with optional arguments.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When an optional argument has an already taken name.
- """
- model._opt_arg = []
- # look up the defaults for the optional arguments (defined by the user)
- default = model.default_opt_arg()
- for opt_name in opt_arg:
- if opt_name not in default:
- warnings.warn(
- f"The given optional argument '{opt_name}' "
- "is unknown or has at least no defined standard value. "
- "Or you made a Typo... hehe.",
- AttributeWarning,
- )
- # add the default values if not specified
- for def_arg in default:
- if def_arg not in opt_arg:
- opt_arg[def_arg] = default[def_arg]
- # save names of the optional arguments (sort them by name)
- model._opt_arg = sorted(opt_arg)
- # add the optional arguments as attributes to the class
- for opt_name in opt_arg:
- if opt_name in dir(model): # "dir" also respects properties
- raise ValueError(
- f"parameter '{opt_name}' has a 'bad' name, "
- "since it is already present in "
- "the class. It could not be added to the model."
- )
- # Magic happens here
- setattr(model, opt_name, float(opt_arg[opt_name]))
-
-
-def set_len_anis(dim, len_scale, anis, latlon=False):
- """Set the length scale and anisotropy factors for the given dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- len_scale : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the length scale of the SRF in x direction or in x- (y-, ...) direction
- anis : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal axes
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the model is describing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude. In this case there is no spatial anisotropy.
- Default: False
-
- Returns
- -------
- len_scale : :class:`float`
- the main length scale of the SRF in x direction
- anis : :class:`list`, optional
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal axes
-
- Notes
- -----
- If ``len_scale`` is given by at least two values,
- ``anis`` will be recalculated.
-
- If ``len_scale`` is given as list with to few values, the latter value will
- be used for the remaining dimensions. (e.g. [l_1, l_2] in 3D is equal to
- [l_1, l_2, l_2])
-
- If to few ``anis`` values are given, the first dimensions will be filled
- up with 1. (eg. anis=[e] in 3D is equal to anis=[1, e])
- """
- ls_tmp = np.array(len_scale, dtype=np.double)
- ls_tmp = np.atleast_1d(ls_tmp)[:dim]
- # use just one length scale (x-direction)
- out_len_scale = ls_tmp[0]
- # set the anisotropies in y- and z-direction according to the input
- if len(ls_tmp) == 1:
- out_anis = set_anis(dim, anis)
- else:
- # fill up length-scales with the latter len_scale, such that len()==dim
- if len(ls_tmp) < dim:
- ls_tmp = np.pad(ls_tmp, (0, dim - len(ls_tmp)), "edge")
- # if multiple length-scales are given, calculate the anisotropies
- out_anis = np.zeros(dim - 1, dtype=np.double)
- for i in range(1, dim):
- out_anis[i - 1] = ls_tmp[i] / ls_tmp[0]
- # sanity check
- for ani in out_anis:
- if not ani > 0.0:
- raise ValueError(
- f"anisotropy-ratios needs to be > 0, got: {out_anis}"
- )
- # no spatial anisotropy for latlon
- if latlon:
- out_anis[:2] = 1.0
- return out_len_scale, out_anis
-
-
-def set_model_angles(dim, angles, latlon=False, temporal=False):
- """Set the model angles for the given dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the angles of the SRF
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the model is describing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude.
- Default: False
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether a time-dimension is appended.
- Default: False
-
- Returns
- -------
- angles : :class:`float`
- the angles fitting to the dimension
-
- Notes
- -----
- If too few angles are given, they are filled up with `0`.
- """
- if latlon:
- return np.array(no_of_angles(dim) * [0], dtype=np.double)
- out_angles = set_angles(dim, angles)
- if temporal:
- # no rotation between spatial dimensions and temporal dimension
- out_angles[no_of_angles(dim - 1) :] = 0.0
- return out_angles
-
-
-def check_bounds(bounds):
- """
- Check if given bounds are valid.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- bounds : list
- bound can contain 2 to 3 values:
- 1. lower bound
- float
- 2. upper bound
- float
- 3. Interval type (optional)
- * "oo" : open - open
- * "oc" : open - close
- * "co" : close - open
- * "cc" : close - close
- """
- if len(bounds) not in (2, 3):
- return False
- if bounds[1] <= bounds[0]:
- return False
- if len(bounds) == 3 and bounds[2] not in ("oo", "oc", "co", "cc"):
- return False
- return True
-
-
-def check_arg_in_bounds(model, arg, val=None):
- """Check if given argument value is in bounds of the given model."""
- if arg not in model.arg_bounds:
- raise ValueError(f"check bounds: unknown argument: {arg}")
- bnd = list(model.arg_bounds[arg])
- val = getattr(model, arg) if val is None else val
- val = np.asarray(val)
- error_case = 0
- if len(bnd) == 2:
- bnd.append("cc") # use closed intervals by default
- if bnd[2][0] == "c":
- if np.any(val < bnd[0]):
- error_case = 1
- else:
- if np.any(val <= bnd[0]):
- error_case = 2
- if bnd[2][1] == "c":
- if np.any(val > bnd[1]):
- error_case = 3
- else:
- if np.any(val >= bnd[1]):
- error_case = 4
- return error_case
-
-
-def default_arg_from_bounds(bounds):
- """
- Determine a default value from given bounds.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- bounds : list
- bounds for the value.
-
- Returns
- -------
- float
- Default value in the given bounds.
- """
- if bounds[0] > -np.inf and bounds[1] < np.inf:
- return (bounds[0] + bounds[1]) / 2.0
- if bounds[0] > -np.inf:
- return bounds[0] + 1.0
- if bounds[1] < np.inf:
- return bounds[1] - 1.0
- return 0.0 # pragma: no cover
-
-
-# outsourced routines
-
-
-def spectral_rad_pdf(model, r):
- """
- Spectral radians PDF of a model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- r : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Given radii.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- PDF values.
-
- """
- r = np.asarray(np.abs(r), dtype=np.double)
- if model.dim > 1:
- r_gz = np.logical_not(np.isclose(r, 0))
- # to prevent numerical errors, we just calculate where r>0
- res = np.zeros_like(r, dtype=np.double)
- res[r_gz] = rad_fac(model.dim, r[r_gz]) * np.abs(
- model.spectral_density(r[r_gz])
- )
- else:
- res = rad_fac(model.dim, r) * np.abs(model.spectral_density(r))
- # prevent numerical errors in hankel for small r values (set 0)
- res[np.logical_not(np.isfinite(res))] = 0.0
- # prevent numerical errors in hankel for big r (set non-negative)
- res = np.maximum(res, 0.0)
- return res
-
-
-def percentile_scale(model, per=0.9):
- """
- Calculate the percentile scale of the isotrope model.
-
- This is the distance, where the given percentile of the variance
- is reached by the variogram
-
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- per : float, optional
- Percentile to use. The default is 0.9.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When percentile is not in (0, 1).
-
- Returns
- -------
- float
- Percentile scale.
-
- """
- # check the given percentile
- if not 0.0 < per < 1.0:
- raise ValueError(f"percentile needs to be within (0, 1), got: {per}")
-
- # define a curve, that has its root at the wanted point
- def curve(x):
- return 1.0 - model.correlation(x) - per
-
- # take 'per * len_rescaled' as initial guess
- return root(curve, per * model.len_rescaled)["x"][0]
-
-
-def set_arg_bounds(model, check_args=True, **kwargs):
- r"""Set bounds for the parameters of the model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- check_args : bool, optional
- Whether to check if the arguments are in their valid bounds.
- In case not, a proper default value will be determined.
- Default: True
- **kwargs
- Parameter name as keyword ("var", "len_scale", "nugget", )
- and a list of 2 or 3 values as value:
-
- * ``[a, b]`` or
- * ``[a, b, ]``
-
- is one of ``"oo"``, ``"cc"``, ``"oc"`` or ``"co"``
- to define if the bounds are open ("o") or closed ("c").
- """
- # if variance needs to be resetted, do this at last
- var_bnds = []
- for arg, bounds in kwargs.items():
- if not check_bounds(bounds):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Given bounds for '{arg}' are not valid, got: {bounds}"
- )
- if arg in model.opt_arg:
- model._opt_arg_bounds[arg] = bounds
- elif arg == "var":
- var_bnds = bounds
- continue
- elif arg == "len_scale":
- model.len_scale_bounds = bounds
- elif arg == "nugget":
- model.nugget_bounds = bounds
- elif arg == "anis":
- model.anis_bounds = bounds
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"set_arg_bounds: unknown argument '{arg}'")
- if check_args and check_arg_in_bounds(model, arg) > 0:
- def_arg = default_arg_from_bounds(bounds)
- if arg == "anis":
- setattr(model, arg, [def_arg] * (model.dim - 1))
- else:
- setattr(model, arg, def_arg)
- # set var last like always
- if var_bnds:
- model.var_bounds = var_bnds
- if check_args and check_arg_in_bounds(model, "var") > 0:
- model.var = default_arg_from_bounds(var_bnds)
-
-
-def check_arg_bounds(model):
- """
- Check arguments to be within their given bounds.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When an argument is not in its valid bounds.
- """
- # check var, len_scale, nugget and optional-arguments
- for arg in model.arg_bounds:
- if not model.arg_bounds[arg]:
- continue # no bounds given during init (called from self.dim)
- bnd = list(model.arg_bounds[arg])
- val = getattr(model, arg)
- error_case = check_arg_in_bounds(model, arg)
- if error_case == 1:
- raise ValueError(f"{arg} needs to be >= {bnd[0]}, got: {val}")
- if error_case == 2:
- raise ValueError(f"{arg} needs to be > {bnd[0]}, got: {val}")
- if error_case == 3:
- raise ValueError(f"{arg} needs to be <= {bnd[1]}, got: {val}")
- if error_case == 4:
- raise ValueError(f"{arg} needs to be < {bnd[1]}, got: {val}")
-
-
-def set_dim(model, dim):
- """
- Set the dimension in the given model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- dim : :class:`int`
- dimension of the model.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When dimension is < 1.
- """
- # check if a fixed dimension should be used
- if model.fix_dim() is not None and model.fix_dim() != dim:
- warnings.warn(
- f"{model.name}: using fixed dimension {model.fix_dim()}",
- AttributeWarning,
- )
- dim = model.fix_dim()
- if model.latlon and dim != (3 + int(model.temporal)):
- raise ValueError(
- f"{model.name}: using fixed dimension {model.fix_dim()}, "
- f"which is not compatible with a latlon model (with temporal={model.temporal})."
- )
- # force dim=3 (or 4 when temporal=True) for latlon models
- dim = (3 + int(model.temporal)) if model.latlon else dim
- # set the dimension
- if dim < 1:
- raise ValueError("Only dimensions of d >= 1 are supported.")
- if not model.check_dim(dim):
- warnings.warn(
- f"Dimension {dim} is not appropriate for this model.",
- AttributeWarning,
- )
- model._dim = int(dim)
- # create fourier transform just once (recreate for dim change)
- model._sft = SFT(ndim=model.dim, **model.hankel_kw)
- # recalculate dimension related parameters
- if model._anis is not None:
- model._len_scale, model._anis = set_len_anis(
- model.dim, model._len_scale, model._anis
- )
- if model._angles is not None:
- model._angles = set_model_angles(
- model.dim, model._angles, model.latlon, model.temporal
- )
- model.check_arg_bounds()
-
-
-def compare(this, that):
- """
- Compare CovModels.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- this / that : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance models to compare.
- """
- # prevent attribute error in opt_arg if the are not equal
- if set(this.opt_arg) != set(that.opt_arg):
- return False
- # prevent dim error in anis and angles
- if this.dim != that.dim:
- return False
- equal = True
- equal &= this.name == that.name
- equal &= np.isclose(this.var, that.var)
- equal &= np.isclose(this.var_raw, that.var_raw) # ?! needless?
- equal &= np.isclose(this.nugget, that.nugget)
- equal &= np.isclose(this.len_scale, that.len_scale)
- equal &= np.all(np.isclose(this.anis, that.anis))
- equal &= np.all(np.isclose(this.angles, that.angles))
- equal &= np.isclose(this.rescale, that.rescale)
- equal &= this.latlon == that.latlon
- equal &= this.temporal == that.temporal
- for opt in this.opt_arg:
- equal &= np.isclose(getattr(this, opt), getattr(that, opt))
- return equal
-
-
-def model_repr(model): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Generate the model string representation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- The covariance model in use.
- """
- m = model
- p = model._prec
- opt_str = ""
- t_str = ", temporal=True" if m.temporal else ""
- if not np.isclose(m.rescale, m.default_rescale()):
- opt_str += f", rescale={m.rescale:.{p}}"
- for opt in m.opt_arg:
- opt_str += f", {opt}={getattr(m, opt):.{p}}"
- if m.latlon:
- ani_str = (
- ""
- if m.is_isotropic or not m.temporal
- else f", anis={m.anis[-1]:.{p}}"
- )
- r_str = (
- ""
- if np.isclose(m.geo_scale, 1)
- else f", geo_scale={m.geo_scale:.{p}}"
- )
- repr_str = (
- f"{m.name}(latlon={m.latlon}{t_str}, var={m.var:.{p}}, "
- f"len_scale={m.len_scale:.{p}}, nugget={m.nugget:.{p}}"
- f"{ani_str}{r_str}{opt_str})"
- )
- else:
- # only print anis and angles if model is anisotropic or rotated
- ani_str = "" if m.is_isotropic else f", anis={list_format(m.anis, p)}"
- ang_str = (
- f", angles={list_format(m.angles, p)}" if m.do_rotation else ""
- )
- repr_str = (
- f"{m.name}(dim={m.spatial_dim}{t_str}, var={m.var:.{p}}, "
- f"len_scale={m.len_scale:.{p}}, nugget={m.nugget:.{p}}"
- f"{ani_str}{ang_str}{opt_str})"
- )
- return repr_str
diff --git a/src/gstools/covmodel/tpl_models.py b/src/gstools/covmodel/tpl_models.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b728e7b98..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/covmodel/tpl_models.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,570 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing truncated power law covariance models.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.covmodel.tpl_models
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- TPLGaussian
- TPLExponential
- TPLStable
- TPLSimple
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, E1101
-import warnings
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.covmodel.base import CovModel
-from gstools.covmodel.tools import AttributeWarning
-from gstools.tools.special import (
- tpl_exp_spec_dens,
- tpl_gau_spec_dens,
- tplstable_cor,
-)
-
-__all__ = ["TPLGaussian", "TPLExponential", "TPLStable", "TPLSimple"]
-
-
-class TPLCovModel(CovModel):
- """Truncated-Power-Law Covariance Model base class for super-position."""
-
- @property
- def len_up(self):
- """:class:`float`: Upper length scale truncation of the model.
-
- * ``len_up = len_low + len_scale``
- """
- return self.len_low + self.len_scale
-
- @property
- def len_up_rescaled(self):
- """:class:`float`: Upper length scale truncation rescaled.
-
- * ``len_up_rescaled = (len_low + len_scale) / rescale``
- """
- return self.len_up / self.rescale
-
- @property
- def len_low_rescaled(self):
- """:class:`float`: Lower length scale truncation rescaled.
-
- * ``len_low_rescaled = len_low / rescale``
- """
- return self.len_low / self.rescale
-
- def var_factor(self):
- """Factor for C (intensity of variation) to result in variance."""
- return (
- self.len_up_rescaled ** (2 * self.hurst)
- - self.len_low_rescaled ** (2 * self.hurst)
- ) / (2 * self.hurst)
-
- def cor(self, h):
- """TPL - normalized correlation function."""
-
- def correlation(self, r):
- """TPL - correlation function."""
-
-
-# Truncated power law #########################################################
-
-
-class TPLGaussian(TPLCovModel):
- r"""Truncated-Power-Law with Gaussian modes.
-
- Notes
- -----
- The truncated power law is given by a superposition of scale-dependent
- variograms [Federico1997]_:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) =
- \intop_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}}}^{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}
- \gamma(r,\lambda) \frac{\rm d \lambda}{\lambda}
-
- with `Gaussian` modes on each scale:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r,\lambda) &=
- \sigma^2(\lambda)\cdot\left(1-
- \exp\left[- \left(\frac{r}{\lambda}\right)^{2}\right]
- \right)\\
- \sigma^2(\lambda) &= C\cdot\lambda^{2H}
-
- This results in:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}(r) &=
- \sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\cdot\left(1-
- H \cdot
- \frac{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}^{2H} \cdot
- E_{1+H}
- \left[\left(\frac{r}{\ell_{\mathrm{up}}}\right)^{2}\right]
- - \ell_{\mathrm{low}}^{2H} \cdot
- E_{1+H}
- \left[\left(\frac{r}{\ell_{\mathrm{low}}}\right)^{2}\right]}
- {\ell_{\mathrm{up}}^{2H}-\ell_{\mathrm{low}}^{2H}}
- \right) \\
- \sigma^2_{\ell_{\mathrm{low}},\ell_{\mathrm{up}}} &=
- \frac{C\cdot\left(\ell_{\mathrm{up}}^{2H}
- -\ell_{\mathrm{low}}^{2H}\right)}{2H}
-
- The "length scale" of this model is equivalent by the integration range:
-
- .. math::
- \ell = \ell_{\mathrm{up}} -\ell_{\mathrm{low}}
-
- If you want to define an upper scale truncation, you should set ``len_low``
- and ``len_scale`` accordingly.
-
- The following Parameters occur:
-
- * :math:`C>0` :
- scaling factor from the Power-Law (intensity of variation)
- This parameter will be calculated internally by the given variance.
- You can access C directly by ``model.var_raw``
- * :math:`00` :
- scaling factor from the Power-Law (intensity of variation)
- This parameter will be calculated internally by the given variance.
- You can access C directly by ``model.var_raw``
- * :math:`00` :
- scaling factor from the Power-Law (intensity of variation)
- This parameter will be calculated internally by the given variance.
- You can access C directly by ``model.var_raw``
- * :math:`0 1 and value.size != dim: # vector mean
- raise ValueError(f"Mean/Trend: Wrong size ({value})")
- return value if value.size > 1 else value.item()
-
-
-class Field:
- """A base class for random fields, kriging fields, etc.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`, optional
- Covariance Model related to the field.
- value_type : :class:`str`, optional
- Value type of the field. Either "scalar" or "vector".
- The default is "scalar".
- mean : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Mean of the field if wanted. Could also be a callable.
- The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the field.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Trend of the denormalized fields. If no normalizer is applied,
- this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- dim : :any:`None` or :class:`int`, optional
- Dimension of the field if no model is given.
- """
-
- valid_value_types = ["scalar", "vector"]
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: valid field value types."""
-
- default_field_names = ["field"]
- """:class:`list`: Default field names."""
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model=None,
- value_type="scalar",
- mean=None,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- dim=None,
- ):
- # initialize attributes
- self._mesh_type = "unstructured" # default
- self._pos = None
- self._field_shape = None
- self._field_names = []
- self._model = None
- self._value_type = None
- self._mean = None
- self._normalizer = None
- self._trend = None
- self._dim = dim if dim is None else int(dim)
- # set properties
- self.model = model
- self.value_type = value_type
- self.mean = mean
- self.normalizer = normalizer
- self.trend = trend
-
- def __len__(self):
- return len(self.field_names)
-
- def __contains__(self, item):
- return item in self.field_names
-
- def __getitem__(self, key):
- if key in self.field_names:
- return getattr(self, key)
- if isinstance(key, int):
- return self[self.field_names[key]]
- if isinstance(key, slice):
- return [self[f] for f in self.field_names[key]]
- if isinstance(key, Iterable) and not isinstance(key, str):
- return [self[f] for f in key]
- raise KeyError(f"{self.name}: requested field '{key}' not present")
-
- def __delitem__(self, key):
- names = []
- if key in self.field_names:
- names = [key]
- elif isinstance(key, int):
- names = [self.field_names[key]]
- elif isinstance(key, slice):
- names = self.field_names[key]
- elif isinstance(key, Iterable) and not isinstance(key, str):
- for k in key:
- k = self.field_names[k] if isinstance(key, int) else k
- names.append(k)
- else:
- raise KeyError(f"{self.name}: requested field '{key}' not present")
- for name in names:
- if name not in self.field_names:
- raise KeyError(
- f"{self.name}: requested field '{name}' not present"
- )
- delattr(self, name)
- del self._field_names[self._field_names.index(name)]
-
- def __call__(
- self,
- pos=None,
- field=None,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- post_process=True,
- store=True,
- ):
- """Generate the field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`, optional
- the field values. Will be all zeros if :any:`None` is given.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'. Default: 'unstructured'
- post_process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to apply mean, normalizer and trend to the field.
- Default: `True`
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field (True/False) with default name
- or with specified name.
- The default is :any:`True` for default name "field".
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the field values.
- """
- name, save = self.get_store_config(store)
- pos, shape = self.pre_pos(pos, mesh_type)
- if field is None:
- field = np.zeros(shape, dtype=np.double)
- else:
- field = np.asarray(field, dtype=np.double).reshape(shape)
- return self.post_field(field, name, post_process, save)
-
- def structured(self, *args, **kwargs):
- """Generate a field on a structured mesh.
-
- See :any:`__call__`
- """
- if self.pos is None:
- self.mesh_type = "structured"
- if not (args or "pos" in kwargs) and self.mesh_type == "unstructured":
- raise ValueError("Field.structured: can't reuse present 'pos'")
- call = partial(self.__call__, mesh_type="structured")
- return call(*args, **kwargs)
-
- def unstructured(self, *args, **kwargs):
- """Generate a field on an unstructured mesh.
-
- See :any:`__call__`
- """
- if self.pos is None:
- self.mesh_type = "unstructured"
- if not (args or "pos" in kwargs) and self.mesh_type != "unstructured":
- raise ValueError("Field.unstructured: can't reuse present 'pos'")
- call = partial(self.__call__, mesh_type="unstructured")
- return call(*args, **kwargs)
-
- def mesh(
- self, mesh, points="centroids", direction="all", name="field", **kwargs
- ):
- """Generate a field on a given meshio, ogs5py or PyVista mesh.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- mesh : meshio.Mesh or ogs5py.MSH or PyVista mesh
- The given mesh
- points : :class:`str`, optional
- The points to evaluate the field at.
- Either the "centroids" of the mesh cells
- (calculated as mean of the cell vertices) or the "points"
- of the given mesh.
- Default: "centroids"
- direction : :class:`str` or :class:`list`, optional
- Here you can state which direction should be chosen for
- lower dimension. For example, if you got a 2D mesh in xz direction,
- you have to pass "xz". By default, all directions are used.
- One can also pass a list of indices.
- Default: "all"
- name : :class:`str` or :class:`list` of :class:`str`, optional
- Name(s) to store the field(s) in the given mesh as point_data or
- cell_data. If to few names are given, digits will be appended.
- Default: "field"
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to :any:`__call__`.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This will store the field in the given mesh under the given name,
- if a meshio or PyVista mesh was given.
-
- See:
- - meshio: https://github.com/nschloe/meshio
- - ogs5py: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/ogs5py
- - PyVista: https://github.com/pyvista/pyvista
- """
- return generate_on_mesh(self, mesh, points, direction, name, **kwargs)
-
- def pre_pos(self, pos=None, mesh_type="unstructured", info=False):
- """
- Preprocessing positions and mesh_type.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: `"unstructured"`
- info : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return information
-
- Returns
- -------
- iso_pos : (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Isometrized position tuple.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the resulting field.
- info : :class:`dict`, optional
- Information about settings.
-
- Warnings
- --------
- When setting a new position tuple that differs from the present one,
- all stored fields will be deleted.
- """
- info_ret = {"deleted": False}
- if pos is None:
- if self.pos is None:
- raise ValueError("Field: no position tuple 'pos' present")
- else:
- info_ret = self.set_pos(pos, mesh_type, info=True)
- if self.mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos = generate_grid(self.pos)
- else:
- pos = self.pos
- # return isometrized pos tuple, field shape and possible info
- info_ret = (info_ret,)
- if self.model is None:
- return (pos, self.field_shape) + info * info_ret
- return (self.model.isometrize(pos), self.field_shape) + info * info_ret
-
- def post_field(self, field, name="field", process=True, save=True):
- """
- Postprocessing field values.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Field values.
- name : :class:`str`, optional
- Name. to store the field.
- The default is "field".
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process field to apply mean, normalizer and trend.
- The default is True.
- save : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store the field under the given name.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Processed field values.
- """
- if self.field_shape is None:
- raise ValueError("post_field: no 'field_shape' present.")
- field = np.asarray(field, dtype=np.double).reshape(self.field_shape)
- if process:
- field = apply_mean_norm_trend(
- pos=self.pos,
- field=field,
- mesh_type=self.mesh_type,
- value_type=self.value_type,
- mean=self.mean,
- normalizer=self.normalizer,
- trend=self.trend,
- check_shape=False,
- stacked=False,
- )
- if save:
- name = str(name)
- if not name.isidentifier() or (
- name not in self.field_names and name in dir(self)
- ):
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field: given field name '{name}' is not valid"
- )
- # allow resetting present fields
- if name not in self._field_names:
- self._field_names.append(name)
- setattr(self, name, field)
- return field
-
- def delete_fields(self, select=None):
- """Delete selected fields."""
- del self[self.field_names if select is None else select]
-
- def transform(
- self, method, field="field", store=True, process=False, **kwargs
- ):
- """
- Apply field transformation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- method : :class:`str`
- Method to use.
- See :py:mod:`gstools.transform` for available transformations.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to selected method.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When method is unknown.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- return apply(
- self, method, field=field, store=store, process=process, **kwargs
- )
-
- def to_pyvista(
- self, field_select="field", fieldname="field"
- ): # pragma: no cover
- """Create a VTK/PyVista grid of the stored field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field_select : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be stored. Can be:
- "field", "raw_field", "krige_field", "err_field" or "krige_var".
- Default: "field"
- fieldname : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of the field in the VTK file. Default: "field"
- """
- grid = to_vtk_helper(
- self, filename=None, field_select=field_select, fieldname=fieldname
- )
- return grid
-
- def vtk_export(
- self, filename, field_select="field", fieldname="field"
- ): # pragma: no cover
- """Export the stored field to vtk.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- filename : :class:`str`
- Filename of the file to be saved, including the path. Note that an
- ending (.vtr or .vtu) will be added to the name.
- field_select : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be stored. Can be:
- "field", "raw_field", "krige_field", "err_field" or "krige_var".
- Default: "field"
- fieldname : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of the field in the VTK file. Default: "field"
- """
- if not isinstance(filename, str):
- raise TypeError("Please use a string filename.")
- return to_vtk_helper(
- self,
- filename=filename,
- field_select=field_select,
- fieldname=fieldname,
- )
-
- def plot(
- self, field="field", fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
- ): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot the spatial random field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be plotted.
- Default: "field"
- fig : :class:`Figure` or :any:`None`
- Figure to plot the axes on. If `None`, a new one will be created.
- Default: `None`
- ax : :class:`Axes` or :any:`None`
- Axes to plot on. If `None`, a new one will be added to the figure.
- Default: `None`
- **kwargs
- Forwarded to the plotting routine.
- """
- # just import if needed; matplotlib is not required by setup
- from gstools.field.plot import plot_field, plot_vec_field
-
- if self.value_type is None:
- raise ValueError(
- "Field value type not set! "
- "Specify 'scalar' or 'vector' before plotting."
- )
-
- if self.value_type == "scalar":
- r = plot_field(self, field, fig, ax, **kwargs)
- elif self.value_type == "vector":
- if self.dim == 2:
- r = plot_vec_field(self, field, fig, ax, **kwargs)
- else:
- raise NotImplementedError(
- "Streamflow plotting only supported for 2d case."
- )
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"Unknown field value type: {self.value_type}")
-
- return r
-
- def set_pos(self, pos, mesh_type="unstructured", info=False):
- """
- Set positions and mesh_type.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: `"unstructured"`
- info : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return information
-
- Returns
- -------
- info : :class:`dict`, optional
- Information about settings.
-
- Warnings
- --------
- When setting a new position tuple that differs from the present one,
- all stored fields will be deleted.
- """
- info_ret = {"deleted": False}
- old_type = copy(self.mesh_type)
- old_pos = copy(self.pos)
- # save pos and mesh-type
- self.mesh_type = mesh_type
- self.pos = pos
- # remove present fields if new pos is different from current
- if old_type != self.mesh_type or not _pos_equal(old_pos, self.pos):
- self.delete_fields()
- info_ret["deleted"] = True
- del old_pos
- return info_ret if info else None
-
- def get_store_config(self, store, default=None, fld_cnt=None):
- """
- Get storage configuration from given selection.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool` or :class:`list`, optional
- Whether to store fields (True/False) with default names
- or with specified names.
- The default is :any:`True` for default names.
- default : :class:`str` or :class:`list`, optional
- Default field names. The default is "field".
- fld_cnt : :any:`None` or :class:`int`, optional
- Number of fields when using lists. The default is None.
-
- Returns
- -------
- name : :class:`str` or :class:`list`
- Name(s) of field.
- save : :class:`bool` or :class:`list`
- Whether to save field(s).
- """
- if default is None:
- if fld_cnt is None:
- default = self.default_field_names[0]
- else:
- default = self.default_field_names
- # single field
- if fld_cnt is None:
- save = isinstance(store, str) or bool(store)
- name = store if isinstance(store, str) else default
- return name, save
- # multiple fields
- default = _names(default, fld_cnt)
- save = [True] * fld_cnt
- if isinstance(store, str):
- store = [store]
- if isinstance(store, Iterable):
- store = list(store)[:fld_cnt]
- store += [True] * (fld_cnt - len(store))
- name = [None] * fld_cnt
- for i, val in enumerate(store):
- save[i] = isinstance(val, str) or bool(val)
- name[i] = val if isinstance(val, str) else default[i]
- else:
- save = [bool(store)] * fld_cnt
- name = copy(default)
- return name, save
-
- @property
- def pos(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: The position tuple of the field."""
- return self._pos
-
- @pos.setter
- def pos(self, pos):
- if self.mesh_type == "unstructured":
- self._pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape(self.dim, -1)
- self._field_shape = np.shape(self._pos[0])
- else:
- self._pos, self._field_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(pos, self.dim)
- # prepend dimension if we have a vector field
- if self.value_type == "vector":
- self._field_shape = (self.dim,) + self._field_shape
- if self.latlon:
- raise ValueError("Field: Vector fields not allowed for latlon")
-
- @property
- def all_fields(self):
- """:class:`list`: All fields as stacked list."""
- return self[self.field_names]
-
- @property
- def field_names(self):
- """:class:`list`: Names of present fields."""
- return self._field_names
-
- @field_names.deleter
- def field_names(self):
- self.delete_fields()
-
- @property
- def field_shape(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: The shape of the field."""
- return self._field_shape
-
- @property
- def mesh_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: The mesh type of the field."""
- return self._mesh_type
-
- @mesh_type.setter
- def mesh_type(self, mesh_type):
- self._mesh_type = str(mesh_type)
-
- @property
- def model(self):
- """:any:`CovModel`: The covariance model of the field."""
- return self._model
-
- @model.setter
- def model(self, model):
- if model is not None:
- if not isinstance(model, CovModel):
- raise ValueError(
- "Field: 'model' is not an instance of 'gstools.CovModel'"
- )
- self._model = model
- self._dim = None
- elif self._dim is None:
- raise ValueError("Field: either needs 'model' or 'dim'.")
- else:
- self._model = None
-
- @property
- def mean(self):
- """:class:`float` or :any:`callable`: The mean of the field."""
- return self._mean
-
- @mean.setter
- def mean(self, mean):
- self._mean = _set_mean_trend(mean, self.dim)
-
- @property
- def normalizer(self):
- """:any:`Normalizer`: Normalizer of the field."""
- return self._normalizer
-
- @normalizer.setter
- def normalizer(self, normalizer):
- self._normalizer = _check_normalizer(normalizer)
-
- @property
- def trend(self):
- """:class:`float` or :any:`callable`: The trend of the field."""
- return self._trend
-
- @trend.setter
- def trend(self, trend):
- self._trend = _set_mean_trend(trend, self.dim)
-
- @property
- def value_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: Type of the field values (scalar, vector)."""
- return self._value_type
-
- @value_type.setter
- def value_type(self, value_type):
- if value_type not in self.valid_value_types:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field: value type not in {self.valid_value_types}"
- )
- self._value_type = value_type
-
- @property
- def dim(self):
- """:class:`int`: Dimension of the field."""
- return self._dim if self.model is None else self.model.field_dim
-
- @property
- def latlon(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the field depends on geographical coords."""
- return False if self.model is None else self.model.latlon
-
- @property
- def temporal(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the field depends on time."""
- return False if self.model is None else self.model.temporal
-
- @property
- def name(self):
- """:class:`str`: The name of the class."""
- return self.__class__.__name__
-
- def _fmt_mean_norm_trend(self):
- # fmt_mean_norm_trend for all child classes
- return fmt_mean_norm_trend(self)
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- if self.model is None:
- dim_str = f"dim={self.dim}"
- else:
- dim_str = f"model={self.model.name}"
- return (
- f"{self.name}({dim_str}, "
- f"value_type='{self.value_type}'{self._fmt_mean_norm_trend()})"
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/cond_srf.py b/src/gstools/field/cond_srf.py
deleted file mode 100644
index c3e03fe29..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/cond_srf.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,313 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing a class for conditioned spatial random fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.cond_srf
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- CondSRF
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0231, W0221, W0222, E1102
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.field.base import Field
-from gstools.field.generator import Generator, RandMeth
-from gstools.krige import Krige
-
-__all__ = ["CondSRF"]
-
-GENERATOR = {
- "RandMeth": RandMeth,
-}
-"""dict: Standard generators for conditioned spatial random fields."""
-
-
-class CondSRF(Field):
- """A class to generate conditioned spatial random fields (SRF).
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- krige : :any:`Krige`
- Kriging setup to condition the spatial random field.
- generator : :class:`str` or :any:`Generator`, optional
- Name or class of the field generator to be used.
- At the moment, only the following generator is provided:
-
- * "RandMeth" : The Randomization Method.
- See: :any:`RandMeth`
-
- Default: "RandMeth"
- **generator_kwargs
- Keyword arguments that are forwarded to the generator in use.
- Have a look at the provided generators for further information.
- """
-
- valid_value_types = ["scalar"]
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: valid field value types."""
-
- default_field_names = ["field", "raw_field", "raw_krige"]
- """:class:`list`: Default field names."""
-
- def __init__(self, krige, generator="RandMeth", **generator_kwargs):
- if not isinstance(krige, Krige):
- raise ValueError("CondSRF: krige should be an instance of Krige.")
- self._krige = krige
- # initialize attributes
- self._field_names = []
- # initialize private attributes
- self._generator = None
- # initialize attributes
- self.set_generator(generator, **generator_kwargs)
-
- def __call__(
- self,
- pos=None,
- seed=np.nan,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- post_process=True,
- store=True,
- krige_store=True,
- **kwargs,
- ):
- """Generate the conditioned spatial random field.
-
- The field is saved as `self.field` and is also returned.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- seed : :class:`int`, optional
- seed for RNG for resetting. Default: keep seed from generator
- mesh_type : :class:`str`
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- post_process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to apply mean, normalizer and trend to the field.
- Default: `True`
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool` or :class:`list`, optional
- Whether to store fields (True/False) with default names
- or with specified names.
- The default is :any:`True` for default names
- ["field", "raw_field", "raw_krige"].
- krige_store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool` or :class:`list`, optional
- Whether to store kriging fields (True/False) with default name
- or with specified names.
- The default is :any:`True` for default names
- ["field", "krige_var"].
- **kwargs
- keyword arguments that are forwarded to the kriging routine in use.
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the conditioned SRF
- """
- name, save = self.get_store_config(store=store, fld_cnt=3)
- krige_name, krige_save = self.krige.get_store_config(
- store=krige_store, fld_cnt=2
- )
- kwargs["mesh_type"] = mesh_type
- kwargs["only_mean"] = False # overwrite if given
- kwargs["return_var"] = True # overwrite if given
- kwargs["post_process"] = False # overwrite if given
- kwargs["store"] = [False, krige_name[1] if krige_save[1] else False]
- # update the model/seed in the generator if any changes were made
- self.generator.update(self.model, seed)
- # get isometrized positions and the resulting field-shape
- iso_pos, shape, info = self.pre_pos(pos, mesh_type, info=True)
- # generate the field
- rawfield = np.reshape(self.generator(iso_pos, add_nugget=False), shape)
- # call krige on already set pos (reuse already calculated fields)
- if (
- not info["deleted"]
- and name[2] in self.field_names
- and krige_name[1] in self.krige.field_names
- ):
- reuse = True
- rawkrige, krige_var = self[name[2]], self.krige[krige_name[1]]
- else:
- reuse = False
- rawkrige, krige_var = self.krige(**kwargs)
- var_scale, nugget = self.get_scaling(krige_var, shape)
- # store krige field (need a copy to not alter field by reference)
- if not reuse or krige_name[0] not in self.krige.field_names:
- self.krige.post_field(
- rawkrige.copy(), krige_name[0], post_process, krige_save[0]
- )
- # store raw krige field
- if not reuse:
- self.post_field(rawkrige, name[2], False, save[2])
- # store raw random field
- self.post_field(rawfield, name[1], False, save[1])
- # store cond random field
- return self.post_field(
- field=rawkrige + var_scale * rawfield + nugget,
- name=name[0],
- process=post_process,
- save=save[0],
- )
-
- def get_scaling(self, krige_var, shape):
- """
- Get scaling coefficients for the random field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- krige_var : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Kriging variance.
- shape : :class:`tuple` of :class:`int`
- Field shape.
-
- Returns
- -------
- var_scale : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Variance scaling factor for the random field.
- nugget : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :class:`int`
- Nugget to be added to the field.
- """
- if self.model.nugget > 0:
- var_scale = np.maximum(krige_var - self.model.nugget, 0)
- nug_scale = np.sqrt((krige_var - var_scale) / self.model.nugget)
- var_scale = np.sqrt(var_scale / self.model.var)
- nugget = nug_scale * self.generator.get_nugget(shape)
- else:
- var_scale = np.sqrt(krige_var / self.model.var)
- nugget = 0
- return var_scale, nugget
-
- def set_generator(self, generator, **generator_kwargs):
- """Set the generator for the field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- generator : :class:`str` or :any:`Generator`, optional
- Name or class of the generator to use for field generation.
- Default: "RandMeth"
- **generator_kwargs
- keyword arguments that are forwarded to the generator in use.
- """
- gen = GENERATOR[generator] if generator in GENERATOR else generator
- if not (isinstance(gen, type) and issubclass(gen, Generator)):
- raise ValueError(
- f"gstools.CondSRF: Unknown or wrong generator: {generator}"
- )
- self._generator = gen(self.model, **generator_kwargs)
- self.value_type = self.generator.value_type
-
- def set_pos(self, pos, mesh_type="unstructured", info=False):
- """
- Set positions and mesh_type.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: `"unstructured"`
- info : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return information
-
- Returns
- -------
- info : :class:`dict`, optional
- Information about settings.
-
- Warnings
- --------
- When setting a new position tuple that differs from the present one,
- all stored fields will be deleted.
- """
- info_ret = super().set_pos(pos, mesh_type, info=True)
- if info_ret["deleted"]:
- self.krige.delete_fields()
- return info_ret if info else None
-
- @property
- def pos(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: The position tuple of the field."""
- return self.krige.pos
-
- @pos.setter
- def pos(self, pos):
- self.krige.pos = pos
-
- @property
- def field_shape(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: The shape of the field."""
- return self.krige.field_shape
-
- @property
- def mesh_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: The mesh type of the field."""
- return self.krige.mesh_type
-
- @mesh_type.setter
- def mesh_type(self, mesh_type):
- self.krige.mesh_type = mesh_type
-
- @property
- def krige(self):
- """:any:`Krige`: The underlying kriging class."""
- return self._krige
-
- @property
- def generator(self):
- """:any:`callable`: The generator of the field."""
- return self._generator
-
- @property
- def model(self):
- """:any:`CovModel`: The covariance model of the field."""
- return self.krige.model
-
- @model.setter
- def model(self, model):
- self.krige.model = model
-
- @property
- def mean(self):
- """:class:`float` or :any:`callable`: The mean of the field."""
- return self.krige.mean
-
- @mean.setter
- def mean(self, mean):
- self.krige.mean = mean
-
- @property
- def normalizer(self):
- """:any:`Normalizer`: Normalizer of the field."""
- return self.krige.normalizer
-
- @normalizer.setter
- def normalizer(self, normalizer):
- self.krige.normalizer = normalizer
-
- @property
- def trend(self):
- """:class:`float` or :any:`callable`: The trend of the field."""
- return self.krige.trend
-
- @trend.setter
- def trend(self, trend):
- self.krige.trend = trend
-
- @property
- def value_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: Type of the field values (scalar, vector)."""
- return self.krige.value_type
-
- @value_type.setter
- def value_type(self, value_type):
- self.krige.value_type = value_type
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return (
- f"{self.name}(krige={self.krige}, generator={self.generator.name})"
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/generator.py b/src/gstools/field/generator.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 5beab10db..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/generator.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,534 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing generators for spatial random fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.generator
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- Generator
- RandMeth
- IncomprRandMeth
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0222, C0412, W0231
-import warnings
-from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
-from copy import deepcopy as dcp
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import config
-from gstools.covmodel.base import CovModel
-from gstools.random.rng import RNG
-
-if config.USE_RUST: # pragma: no cover
- # pylint: disable=E0401
- from gstools_core import summate, summate_incompr
-else:
- from gstools.field.summator import summate, summate_incompr
-
-__all__ = ["Generator", "RandMeth", "IncomprRandMeth"]
-
-
-SAMPLING = ["auto", "inversion", "mcmc"]
-
-
-class Generator(ABC):
- """
- Abstract generator class.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance model
- **kwargs
- Placeholder for keyword-args
- """
-
- @abstractmethod
- def __init__(self, model, **kwargs):
- pass
-
- @abstractmethod
- def update(self, model=None, seed=np.nan):
- """Update the model and the seed.
-
- If model and seed are not different, nothing will be done.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel` or :any:`None`, optional
- covariance model. Default: :any:`None`
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None` or :any:`numpy.nan`, optional
- the seed of the random number generator.
- If :any:`None`, a random seed is used. If :any:`numpy.nan`,
- the actual seed will be kept. Default: :any:`numpy.nan`
- """
-
- @abstractmethod
- def get_nugget(self, shape):
- """
- Generate normal distributed values for the nugget simulation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- the shape of the summed modes
-
- Returns
- -------
- nugget : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the nugget in the same shape as the summed modes
- """
-
- @abstractmethod
- def __call__(self, pos, add_nugget=True):
- """
- Generate the field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the position tuple with d dimensions and n points.
- add_nugget : :class:`bool`
- Whether to add nugget noise to the field.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the random modes
- """
-
- @property
- @abstractmethod
- def value_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: Type of the field values (scalar, vector)."""
-
- @property
- def name(self):
- """:class:`str`: Name of the generator."""
- return self.__class__.__name__
-
-
-class RandMeth(Generator):
- r"""Randomization method for calculating isotropic random fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance model
- mode_no : :class:`int`, optional
- Number of Fourier modes. Default: ``1000``
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- The seed of the random number generator.
- If "None", a random seed is used. Default: :any:`None`
- sampling : :class:`str`, optional
- Sampling strategy. Either
-
- * "auto": select best strategy depending on given model
- * "inversion": use inversion method
- * "mcmc": use mcmc sampling
-
- **kwargs
- Placeholder for keyword-args
-
- Notes
- -----
- The Randomization method is used to generate isotropic
- spatial random fields characterized by a given covariance model.
- The calculation looks like [Hesse2014]_:
-
- .. math::
- u\left(x\right)=
- \sqrt{\frac{\sigma^{2}}{N}}\cdot
- \sum_{i=1}^{N}\left(
- Z_{1,i}\cdot\cos\left(\left\langle k_{i},x\right\rangle \right)+
- Z_{2,i}\cdot\sin\left(\left\langle k_{i},x\right\rangle \right)
- \right)
-
- where:
-
- * :math:`N` : fourier mode number
- * :math:`Z_{j,i}` : random samples from a normal distribution
- * :math:`k_i` : samples from the spectral density distribution of
- the covariance model
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Hesse2014] Heße, F., Prykhodko, V., Schlüter, S., and Attinger, S.,
- "Generating random fields with a truncated power-law variogram:
- A comparison of several numerical methods",
- Environmental Modelling & Software, 55, 32-48., (2014)
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- *,
- mode_no=1000,
- seed=None,
- sampling="auto",
- **kwargs,
- ):
- if kwargs:
- warnings.warn("gstools.RandMeth: **kwargs are ignored")
- # initialize attributes
- self._mode_no = int(mode_no)
- # initialize private attributes
- self._model = None
- self._seed = None
- self._rng = None
- self._z_1 = None
- self._z_2 = None
- self._cov_sample = None
- self._value_type = "scalar"
- # set sampling strategy
- self._sampling = None
- self.sampling = sampling
- # set model and seed
- self.update(model, seed)
-
- def __call__(self, pos, add_nugget=True):
- """Calculate the random modes for the randomization method.
-
- This method calls the `summate_*` Cython methods, which are the
- heart of the randomization method.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the position tuple with d dimensions and n points.
- add_nugget : :class:`bool`
- Whether to add nugget noise to the field.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the random modes
- """
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double)
- summed_modes = summate(
- self._cov_sample, self._z_1, self._z_2, pos, config.NUM_THREADS
- )
- nugget = self.get_nugget(summed_modes.shape) if add_nugget else 0.0
- return np.sqrt(self.model.var / self._mode_no) * summed_modes + nugget
-
- def get_nugget(self, shape):
- """
- Generate normal distributed values for the nugget simulation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- the shape of the summed modes
-
- Returns
- -------
- nugget : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the nugget in the same shape as the summed modes
- """
- if self.model.nugget > 0:
- nugget = np.sqrt(self.model.nugget) * self._rng.random.normal(
- size=shape
- )
- else:
- nugget = 0.0
- return nugget
-
- def update(self, model=None, seed=np.nan):
- """Update the model and the seed.
-
- If model and seed are not different, nothing will be done.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel` or :any:`None`, optional
- covariance model. Default: :any:`None`
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None` or :any:`numpy.nan`, optional
- the seed of the random number generator.
- If :any:`None`, a random seed is used. If :any:`numpy.nan`,
- the actual seed will be kept. Default: :any:`numpy.nan`
- """
- # check if a new model is given
- if isinstance(model, CovModel):
- if self.model != model:
- self._model = dcp(model)
- if seed is None or not np.isnan(seed):
- self.reset_seed(seed)
- else:
- self.reset_seed(self._seed)
- # just update the seed, if its a new one
- elif seed is None or not np.isnan(seed):
- self.seed = seed
- # or just update the seed, when no model is given
- elif model is None and (seed is None or not np.isnan(seed)):
- if isinstance(self._model, CovModel):
- self.seed = seed
- else:
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.field.generator.RandMeth: no 'model' given"
- )
- # if the user tries to trick us, we beat him!
- elif model is None and np.isnan(seed):
- if not (
- isinstance(self._model, CovModel)
- and self._z_1 is not None
- and self._z_2 is not None
- and self._cov_sample is not None
- ):
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.field.generator.RandMeth: "
- "neither 'model' nor 'seed' given!"
- )
- # wrong model type
- else:
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.field.generator.RandMeth: 'model' is not an "
- "instance of 'gstools.CovModel'"
- )
-
- def reset_seed(self, seed=np.nan):
- """
- Recalculate the random amplitudes and wave numbers with the given seed.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None` or :any:`numpy.nan`, optional
- the seed of the random number generator.
- If :any:`None`, a random seed is used. If :any:`numpy.nan`,
- the actual seed will be kept. Default: :any:`numpy.nan`
-
- Notes
- -----
- Even if the given seed is the present one, modes will be recalculated.
- """
- if seed is None or not np.isnan(seed):
- self._seed = seed
- self._rng = RNG(self._seed)
- # normal distributed samples for randmeth
- self._z_1 = self._rng.random.normal(size=self._mode_no)
- self._z_2 = self._rng.random.normal(size=self._mode_no)
- # sample uniform on a sphere
- sphere_coord = self._rng.sample_sphere(self.model.dim, self._mode_no)
- # sample radii according to radial spectral density of the model
- if self.sampling == "inversion" or (
- self.sampling == "auto" and self.model.has_ppf
- ):
- pdf, cdf, ppf = self.model.dist_func
- rad = self._rng.sample_dist(
- size=self._mode_no, pdf=pdf, cdf=cdf, ppf=ppf, a=0
- )
- else:
- rad = self._rng.sample_ln_pdf(
- ln_pdf=self.model.ln_spectral_rad_pdf,
- size=self._mode_no,
- sample_around=1.0 / self.model.len_rescaled,
- )
- # get fully spatial samples by multiplying sphere samples and radii
- self._cov_sample = rad * sphere_coord
-
- @property
- def sampling(self):
- """:class:`str`: Sampling strategy."""
- return self._sampling
-
- @sampling.setter
- def sampling(self, sampling):
- if sampling not in ["auto", "inversion", "mcmc"]:
- raise ValueError(f"RandMeth: sampling not in {SAMPLING}.")
- self._sampling = sampling
-
- @property
- def seed(self):
- """:class:`int`: Seed of the master RNG.
-
- Notes
- -----
- If a new seed is given, the setter property not only saves the
- new seed, but also creates new random modes with the new seed.
- """
- return self._seed
-
- @seed.setter
- def seed(self, new_seed):
- if new_seed is not self._seed:
- self.reset_seed(new_seed)
-
- @property
- def model(self):
- """:any:`CovModel`: Covariance model of the spatial random field."""
- return self._model
-
- @model.setter
- def model(self, model):
- self.update(model)
-
- @property
- def mode_no(self):
- """:class:`int`: Number of modes in the randomization method."""
- return self._mode_no
-
- @mode_no.setter
- def mode_no(self, mode_no):
- if int(mode_no) != self._mode_no:
- self._mode_no = int(mode_no)
- self.reset_seed(self._seed)
-
- @property
- def value_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: Type of the field values (scalar, vector)."""
- return self._value_type
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return (
- f"{self.name}(model={self.model}, "
- f"mode_no={self._mode_no}, seed={self.seed})"
- )
-
-
-class IncomprRandMeth(RandMeth):
- r"""RandMeth for incompressible random vector fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- covariance model
- mean_velocity : :class:`float`, optional
- the mean velocity in x-direction
- mode_no : :class:`int`, optional
- number of Fourier modes. Default: ``1000``
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- the seed of the random number generator.
- If "None", a random seed is used. Default: :any:`None`
- sampling : :class:`str`, optional
- Sampling strategy. Either
-
- * "auto": select best strategy depending on given model
- * "inversion": use inversion method
- * "mcmc": use mcmc sampling
-
- **kwargs
- Placeholder for keyword-args
-
- Notes
- -----
- The Randomization method is used to generate isotropic
- spatial incompressible random vector fields characterized
- by a given covariance model. The equation is [Kraichnan1970]_:
-
- .. math::
- u_i\left(x\right)= \bar{u_i} \delta_{i1} +
- \bar{u_i}\sqrt{\frac{\sigma^{2}}{N}}\cdot
- \sum_{j=1}^{N}p_i(k_{j})\left(
- Z_{1,j}\cdot\cos\left(\left\langle k_{j},x\right\rangle \right)+
- Z_{2,j}\cdot\sin\left(\left\langle k_{j},x\right\rangle \right)
- \right)
-
- where:
-
- * :math:`\bar u` : mean velocity in :math:`e_1` direction
- * :math:`N` : fourier mode number
- * :math:`Z_{k,j}` : random samples from a normal distribution
- * :math:`k_j` : samples from the spectral density distribution of
- the covariance model
- * :math:`p_i(k_j) = e_1 - \frac{k_i k_1}{k^2}` : the projector
- ensuring the incompressibility
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Kraichnan1970] Kraichnan, R. H.,
- "Diffusion by a random velocity field.",
- The physics of fluids, 13(1), 22-31., (1970)
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- *,
- mean_velocity=1.0,
- mode_no=1000,
- seed=None,
- sampling="auto",
- **kwargs,
- ):
- if model.dim < 2 or model.dim > 3:
- raise ValueError(
- "Only 2D and 3D incompressible fields can be generated."
- )
- super().__init__(
- model=model,
- mode_no=mode_no,
- seed=seed,
- sampling=sampling,
- **kwargs,
- )
-
- self.mean_u = mean_velocity
- self._value_type = "vector"
-
- def __call__(self, pos, add_nugget=True):
- """Calculate the random modes for the randomization method.
-
- This method calls the `summate_incompr_*` Cython methods,
- which are the heart of the randomization method.
- In this class the method contains a projector to
- ensure the incompressibility of the vector field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the position tuple with d dimensions and n points.
- add_nugget : :class:`bool`
- Whether to add nugget noise to the field.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the random modes
- """
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double)
- summed_modes = summate_incompr(
- self._cov_sample,
- self._z_1,
- self._z_2,
- pos,
- config.NUM_THREADS,
- )
- nugget = self.get_nugget(summed_modes.shape) if add_nugget else 0.0
- e1 = self._create_unit_vector(summed_modes.shape)
- return (
- self.mean_u * e1
- + self.mean_u
- * np.sqrt(self.model.var / self._mode_no)
- * summed_modes
- + nugget
- )
-
- def _create_unit_vector(self, broadcast_shape, axis=0):
- """Create a unit vector.
-
- Can be multiplied with a vector of shape broadcast_shape
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- broadcast_shape : :class:`tuple`
- the shape of the array with which
- the unit vector is to be multiplied
- axis : :class:`int`, optional
- the direction of the unit vector. Default: ``0``
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the unit vector
- """
- shape = np.ones(len(broadcast_shape), dtype=int)
- shape[0] = self.model.dim
-
- e1 = np.zeros(shape)
- e1[axis] = 1.0
- return e1
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/plot.py b/src/gstools/field/plot.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b17cfc715..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/plot.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,402 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing plotting routines for spatial fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.plot
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- plot_field
- plot_vec_field
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0613, E1101, E0606
-import numpy as np
-from scipy import interpolate as inter
-from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
-
-from gstools.tools.geometric import rotation_planes
-from gstools.tools.misc import get_fig_ax
-
-try:
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- from matplotlib.widgets import RadioButtons, Slider
-except ImportError as exc:
- raise ImportError("Plotting: Matplotlib not installed.") from exc
-
-
-__all__ = ["plot_field", "plot_vec_field"]
-
-
-# plotting routines #######################################################
-
-
-def plot_field(
- fld, field="field", fig=None, ax=None, **kwargs
-): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot a spatial field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :class:`Field`
- The given Field class instance.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be plotted. Default: "field"
- fig : :class:`Figure` or :any:`None`, optional
- Figure to plot the axes on. If `None`, a new one will be created.
- Default: `None`
- ax : :class:`Axes` or :any:`None`, optional
- Axes to plot on. If `None`, a new one will be added to the figure.
- Default: `None`
- **kwargs
- Forwarded to the plotting routine.
- """
- if fld.dim == 1:
- return plot_1d(fld.pos, fld[field], fig, ax, fld.temporal, **kwargs)
- return plot_nd(
- fld.pos,
- fld[field],
- fld.mesh_type,
- fig,
- ax,
- fld.latlon,
- fld.temporal,
- **kwargs,
- )
-
-
-def plot_1d(
- pos, field, fig=None, ax=None, temporal=False, ax_names=None
-): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot a 1D field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing either the point coordinates (x, y, ...)
- or the axes descriptions (for mesh_type='structured')
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Field values.
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Indicate a metric spatio-temporal covariance model.
- The time-dimension is assumed to be appended,
- meaning the pos tuple is (x,y,z,...,t) or (lat, lon, t).
- Default: False
- fig : :class:`Figure` or :any:`None`, optional
- Figure to plot the axes on. If `None`, a new one will be created.
- Default: `None`
- ax : :class:`Axes` or :any:`None`, optional
- Axes to plot on. If `None`, a new one will be added to the figure.
- Default: `None`
- ax_names : :class:`list` of :class:`str`, optional
- Axes names. The default is ["$x$", "field"].
-
- Returns
- -------
- ax : :class:`Axes`
- Axis containing the plot.
- """
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- title = f"Field 1D: {field.shape}"
- x = pos[0]
- x = x.flatten()
- arg = np.argsort(x)
- ax_names = _ax_names(1, temporal=temporal, ax_names=ax_names)
- ax.plot(x[arg], field.ravel()[arg])
- ax.set_xlabel(ax_names[0])
- ax.set_ylabel(ax_names[1])
- ax.set_title(title)
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_nd(
- pos,
- field,
- mesh_type,
- fig=None,
- ax=None,
- latlon=False,
- temporal=False,
- resolution=128,
- ax_names=None,
- aspect="quad",
- show_colorbar=True,
- convex_hull=False,
- contour_plot=True,
- **kwargs,
-): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot field in arbitrary dimensions.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing either the point coordinates (x, y, ...)
- or the axes descriptions (for mesh_type='structured')
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Field values.
- fig : :class:`Figure` or :any:`None`, optional
- Figure to plot the axes on. If `None`, a new one will be created.
- Default: `None`
- ax : :class:`Axes` or :any:`None`, optional
- Axes to plot on. If `None`, a new one will be added to the figure.
- Default: `None`
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the data is representing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude. When using this, the estimator will
- use great-circle distance for variogram estimation.
- Note, that only an isotropic variogram can be estimated and a
- ValueError will be raised, if a direction was specified.
- Bin edges need to be given in radians in this case.
- Default: False
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Indicate a metric spatio-temporal covariance model.
- The time-dimension is assumed to be appended,
- meaning the pos tuple is (x,y,z,...,t) or (lat, lon, t).
- Default: False
- resolution : :class:`int`, optional
- Resolution of the imshow plot. The default is 128.
- ax_names : :class:`list` of :class:`str`, optional
- Axes names. The default is ["$x$", "field"].
- aspect : :class:`str` or :any:`None` or :class:`float`, optional
- Aspect of the plot. Can be "auto", "equal", "quad", None or a number
- describing the aspect ratio.
- The default is "quad".
- show_colorbar : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to show the colorbar. The default is True.
- convex_hull : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to show the convex hull in 2D with unstructured data.
- The default is False.
- contour_plot : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to use a contour-plot in 2D. The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- ax : :class:`Axes`
- Axis containing the plot.
- """
- dim = len(pos)
- assert dim > 1
- assert not latlon or dim == 2 + int(bool(temporal))
- if dim == 2 and contour_plot:
- return _plot_2d(
- pos,
- field,
- mesh_type,
- fig,
- ax,
- latlon,
- temporal,
- ax_names,
- **kwargs,
- )
- if latlon:
- # swap lat-lon to lon-lat (x-y)
- if temporal:
- pos = (pos[1], pos[0], pos[2])
- else:
- pos = (pos[1], pos[0])
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- field = np.moveaxis(field, [0, 1], [1, 0])
- ax_names = _ax_names(dim, latlon, temporal, ax_names)
- # init planes
- planes = rotation_planes(dim)
- plane_names = [f" {ax_names[p[0]]} - {ax_names[p[1]]}" for p in planes]
- ax_ends = [[p.min(), p.max()] for p in pos]
- ax_rngs = [end[1] - end[0] for end in ax_ends]
- ax_steps = [rng / resolution for rng in ax_rngs]
- ax_extents = [ax_ends[p[0]] + ax_ends[p[1]] for p in planes]
- # create figure
- reformat = fig is None and ax is None
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- ax.set_title(f"Field {dim}D {mesh_type} {field.shape}")
- if reformat: # only format fig if it was created here
- fig.set_size_inches(8, 5.5 + 0.5 * (dim - 2))
- # init additional axis, radio-buttons and sliders
- s_frac = 0.5 * (dim - 2) / (6 + 0.5 * (dim - 2))
- s_size = s_frac / max(dim - 2, 1)
- left, bottom = (0.25, s_frac + 0.13) if dim > 2 else (None, None)
- fig.subplots_adjust(left=left, bottom=bottom)
- slider = []
- for i in range(dim - 2, 0, -1):
- slider_ax = fig.add_axes([0.3, i * s_size, 0.435, s_size * 0.6])
- slider.append(Slider(slider_ax, "", 0, 1, facecolor="grey"))
- slider[-1].vline.set_color("k")
- # create radio buttons
- if dim > 2:
- rax = fig.add_axes(
- [0.05, 0.85 - 2 * s_frac, 0.15, 2 * s_frac], frame_on=0, alpha=0
- )
- rax.set_title(" Plane", loc="left")
- radio = RadioButtons(rax, plane_names, activecolor="grey")
- elif mesh_type == "unstructured" and convex_hull:
- # show convex hull in 2D
- hull = ConvexHull(pos.T)
- for simplex in hull.simplices:
- ax.plot(pos[0, simplex], pos[1, simplex], "k")
- # init imshow and colorbar axis
- grid = np.mgrid[0 : 1 : resolution * 1j, 0 : 1 : resolution * 1j]
- f_ini, vmin, vmax = np.full_like(grid[0], np.nan), field.min(), field.max()
- im = ax.imshow(
- f_ini.T, interpolation="bicubic", origin="lower", vmin=vmin, vmax=vmax
- )
-
- # actions
- def inter_plane(cuts, axes):
- """Interpolate plane."""
- plane_ax = []
- for i, (rng, end, cut) in enumerate(zip(ax_rngs, ax_ends, cuts)):
- if i in axes:
- plane_ax.append(grid[axes.index(i)] * rng + end[0])
- else:
- plane_ax.append(np.full_like(grid[0], cut, dtype=float))
- # needs to be a tuple
- plane_ax = tuple(plane_ax)
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- return inter.interpn(pos, field, plane_ax, bounds_error=False)
- return inter.griddata(pos.T, field, plane_ax, method="nearest")
-
- def update_field(*args):
- """Sliders update."""
- p = plane_names.index(radio.value_selected) if dim > 2 else 0
- # dummy cut values for selected plane-axes (setting to 0)
- cuts = [s.val for s in slider]
- cuts.insert(planes[p][0], 0)
- cuts.insert(planes[p][1], 0)
- im.set_array(inter_plane(cuts, planes[p]).T)
- fig.canvas.draw_idle()
-
- def update_plane(label):
- """Radio button update."""
- p = plane_names.index(label)
- cut_select = [i for i in range(dim) if i not in planes[p]]
- # reset sliders
- for i, s in zip(cut_select, slider):
- s.label.set_text(ax_names[i])
- s.valmin, s.valmax = ax_ends[i]
- s.valinit = ax_ends[i][0] + ax_rngs[i] / 2.0
- s.valstep = ax_steps[i]
- s.ax.set_xlim(*ax_ends[i])
- # update representation
- s.vline.set_data(2 * [s.valinit], [-0.1, 1.1])
- s.reset()
- im.set_extent(ax_extents[p])
- asp = 1.0 # init value
- if aspect == "quad":
- asp = ax_rngs[planes[p][0]] / ax_rngs[planes[p][1]]
- if aspect is not None:
- ax.set_aspect(asp if aspect == "quad" else aspect)
- ax.set_xlabel(ax_names[planes[p][0]])
- ax.set_ylabel(ax_names[planes[p][1]])
- update_field()
-
- # initial plot on xy plane
- update_plane(plane_names[0])
- # bind actions
- if dim > 2:
- radio.on_clicked(update_plane)
- for s in slider:
- s.on_changed(update_field)
- if show_colorbar:
- fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax)
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def plot_vec_field(fld, field="field", fig=None, ax=None): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Plot a spatial random vector field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :class:`Field`
- The given field class instance.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be plotted. Default: "field"
- fig : :class:`Figure` or :any:`None`, optional
- Figure to plot the axes on. If `None`, a new one will be created.
- Default: `None`
- ax : :class:`Axes` or :any:`None`, optional
- Axes to plot on. If `None`, a new one will be added to the figure.
- Default: `None`
- """
- if fld.mesh_type == "unstructured":
- raise RuntimeError(
- "Only structured vector fields are supported "
- "for plotting. Please create one on a structured grid."
- )
- plt_fld = fld[field]
- norm = np.sqrt(plt_fld[0, :].T ** 2 + plt_fld[1, :].T ** 2)
-
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- title = f"Field 2D {fld.mesh_type}: {plt_fld.shape}"
- x = fld.pos[0]
- y = fld.pos[1]
-
- sp = plt.streamplot(
- x,
- y,
- plt_fld[0, :].T,
- plt_fld[1, :].T,
- color=norm,
- linewidth=norm / 2,
- )
- ax.set_xlabel("X")
- ax.set_ylabel("Y")
- ax.set_title(title)
- fig.colorbar(sp.lines)
- fig.show()
- return ax
-
-
-def _ax_names(dim, latlon=False, temporal=False, ax_names=None):
- t_fac = int(bool(temporal))
- if ax_names is not None:
- assert len(ax_names) >= dim
- return ax_names[:dim]
- if dim == 2 + t_fac and latlon:
- return ["lon", "lat"] + t_fac * ["time"]
- if dim - t_fac <= 3:
- return (
- ["$x$", "$y$", "$z$"][: dim - t_fac]
- + t_fac * ["time"]
- + (dim == 1) * ["field"]
- )
- return [f"$x_{{{i}}}$" for i in range(dim - t_fac)] + t_fac * ["time"]
-
-
-def _plot_2d(
- pos,
- field,
- mesh_type,
- fig=None,
- ax=None,
- latlon=False,
- temporal=False,
- ax_names=None,
- levels=64,
- antialias=True,
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Plot a 2d field with a contour plot."""
- fig, ax = get_fig_ax(fig, ax)
- title = f"Field 2D {mesh_type}: {field.shape}"
- ax_names = _ax_names(2, latlon, temporal, ax_names=ax_names)
- x, y = pos[::-1] if latlon else pos
- if mesh_type == "unstructured":
- cont = ax.tricontourf(x, y, field.ravel(), levels=levels)
- if antialias:
- ax.tricontour(x, y, field.ravel(), levels=levels, zorder=-10)
- else:
- plt_fld = field if latlon else field.T
- cont = ax.contourf(x, y, plt_fld, levels=levels)
- if antialias:
- ax.contour(x, y, plt_fld, levels=levels, zorder=-10)
- ax.set_xlabel(ax_names[0])
- ax.set_ylabel(ax_names[1])
- ax.set_title(title)
- fig.colorbar(cont)
- fig.show()
- return ax
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/srf.py b/src/gstools/field/srf.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d88e46c09..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/srf.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,218 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing a class for standard spatial random fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.srf
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- SRF
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0221, E1102
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.field.base import Field
-from gstools.field.generator import Generator, IncomprRandMeth, RandMeth
-from gstools.field.upscaling import var_coarse_graining, var_no_scaling
-
-__all__ = ["SRF"]
-
-GENERATOR = {
- "RandMeth": RandMeth,
- "IncomprRandMeth": IncomprRandMeth,
- "VectorField": IncomprRandMeth,
- "VelocityField": IncomprRandMeth,
-}
-"""dict: Standard generators for spatial random fields."""
-
-UPSCALING = {
- "coarse_graining": var_coarse_graining,
- "no_scaling": var_no_scaling,
-}
-"""dict: Upscaling routines for spatial random fields."""
-
-
-class SRF(Field):
- """A class to generate spatial random fields (SRF).
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model of the spatial random field.
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Mean of the SRF (in normal form). Could also be a callable.
- The default is 0.0.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the SRF to transform the field values.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Trend of the SRF (in transformed form).
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- upscaling : :class:`str`, optional
- Method to be used for upscaling the variance at each point
- depending on the related element volume.
- See the ``point_volumes`` keyword in the :any:`SRF.__call__` routine.
- At the moment, the following upscaling methods are provided:
-
- * "no_scaling" : No upscaling is applied to the variance.
- See: :any:`var_no_scaling`
- * "coarse_graining" : A volume depended variance is
- calculated by the upscaling technique coarse graining.
- See: :any:`var_coarse_graining`
-
- Default: "no_scaling"
- generator : :class:`str` or :any:`Generator`, optional
- Name or class of the field generator to be used.
- At the moment, the following generators are provided:
-
- * "RandMeth" : The Randomization Method.
- See: :any:`RandMeth`
- * "IncomprRandMeth" : The incompressible Randomization Method.
- This is the original algorithm proposed by Kraichnan 1970
- See: :any:`IncomprRandMeth`
- * "VectorField" : an alias for "IncomprRandMeth"
- * "VelocityField" : an alias for "IncomprRandMeth"
-
- Default: "RandMeth"
- **generator_kwargs
- Keyword arguments that are forwarded to the generator in use.
- Have a look at the provided generators for further information.
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- mean=0.0,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- upscaling="no_scaling",
- generator="RandMeth",
- **generator_kwargs,
- ):
- super().__init__(model, mean=mean, normalizer=normalizer, trend=trend)
- # initialize private attributes
- self._generator = None
- self._upscaling = None
- self._upscaling_func = None
- # initialize attributes
- self.upscaling = upscaling
- self.set_generator(generator, **generator_kwargs)
-
- def __call__(
- self,
- pos=None,
- seed=np.nan,
- point_volumes=0.0,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- post_process=True,
- store=True,
- ):
- """Generate the spatial random field.
-
- The field is saved as `self.field` and is also returned.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- seed : :class:`int`, optional
- seed for RNG for resetting. Default: keep seed from generator
- point_volumes : :class:`float` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- If your evaluation points for the field are coming from a mesh,
- they are probably representing a certain element volume.
- This volume can be passed by `point_volumes` to apply the
- given variance upscaling. If `point_volumes` is ``0`` nothing
- is changed. Default: ``0``
- mesh_type : :class:`str`
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- post_process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to apply mean, normalizer and trend to the field.
- Default: `True`
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field (True/False) with default name
- or with specified name.
- The default is :any:`True` for default name "field".
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the SRF
- """
- name, save = self.get_store_config(store)
- # update the model/seed in the generator if any changes were made
- self.generator.update(self.model, seed)
- # get isometrized positions and the resulting field-shape
- iso_pos, shape = self.pre_pos(pos, mesh_type)
- # generate the field
- field = np.reshape(self.generator(iso_pos), shape)
- # upscaled variance
- if not np.isscalar(point_volumes) or not np.isclose(point_volumes, 0):
- scaled_var = self.upscaling_func(self.model, point_volumes)
- if np.size(scaled_var) > 1:
- scaled_var = np.reshape(scaled_var, shape)
- field *= np.sqrt(scaled_var / self.model.sill)
- return self.post_field(field, name, post_process, save)
-
- def upscaling_func(self, *args, **kwargs):
- """Upscaling method applied to the field variance."""
- return self._upscaling_func(*args, **kwargs)
-
- def set_generator(self, generator, **generator_kwargs):
- """Set the generator for the field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- generator : :class:`str` or :any:`Generator`, optional
- Name or class of the field generator to be used.
- Default: "RandMeth"
- **generator_kwargs
- keyword arguments that are forwarded to the generator in use.
- """
- gen = GENERATOR[generator] if generator in GENERATOR else generator
- if not (isinstance(gen, type) and issubclass(gen, Generator)):
- raise ValueError(
- f"gstools.SRF: Unknown or wrong generator: {generator}"
- )
- self._generator = gen(self.model, **generator_kwargs)
- self.value_type = self.generator.value_type
-
- for val in [self.mean, self.trend]:
- if not callable(val) and val is not None:
- if np.size(val) > 1 and self.value_type == "scalar":
- raise ValueError(f"Mean/Trend: Wrong size ({val})")
-
- @property
- def generator(self):
- """:any:`callable`: The generator of the field.
-
- Default: :any:`RandMeth`
- """
- return self._generator
-
- @property
- def upscaling(self): # pragma: no cover
- """:class:`str`: Name of the upscaling method.
-
- See the ``point_volumes`` keyword in the :any:`SRF.__call__` routine.
- Default: "no_scaling"
- """
- return self._upscaling
-
- @upscaling.setter
- def upscaling(self, upscaling):
- if upscaling in UPSCALING:
- self._upscaling = upscaling
- self._upscaling_func = UPSCALING[upscaling]
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"SRF: Unknown upscaling method: {upscaling}")
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return (
- f"{self.name}(model={self.model.name}"
- f"{self._fmt_mean_norm_trend()}, generator={self.generator.name})"
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/tools.py b/src/gstools/field/tools.py
deleted file mode 100644
index dfa2e3c65..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/tools.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,257 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for Fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.tools
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- fmt_mean_norm_trend
- to_vtk_helper
- generate_on_mesh
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=W0212, C0415
-import meshio
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.normalizer import Normalizer
-from gstools.tools.export import to_vtk, vtk_export
-from gstools.tools.misc import list_format
-
-__all__ = ["fmt_mean_norm_trend", "to_vtk_helper", "generate_on_mesh"]
-
-
-def _fmt_func_val(f_cls, func_val): # pragma: no cover
- if func_val is None:
- return str(None)
- if callable(func_val):
- return "" # or format(func_val.__name__)
- if np.size(func_val) > 1:
- return list_format(func_val, prec=f_cls.model._prec)
- return f"{float(func_val):.{f_cls.model._prec}}"
-
-
-def _fmt_normalizer(f_cls): # pragma: no cover
- norm = f_cls.normalizer
- return str(None) if norm.__class__ is Normalizer else norm.name
-
-
-def fmt_mean_norm_trend(f_cls): # pragma: no cover
- """Format string repr. for mean, normalizer and trend of a field."""
- args = [
- "mean=" + _fmt_func_val(f_cls, f_cls.mean),
- "normalizer=" + _fmt_normalizer(f_cls),
- "trend=" + _fmt_func_val(f_cls, f_cls.trend),
- ]
- return "".join([", " + arg for arg in args if not arg.endswith("None")])
-
-
-def to_vtk_helper(
- f_cls, filename=None, field_select="field", fieldname="field"
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Create a VTK/PyVista grid of the field or save it as a VTK file.
-
- This is an internal helper that will handle saving or creating objects
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- f_cls : :any:`Field`
- Field class in use.
- filename : :class:`str`
- Filename of the file to be saved, including the path. Note that an
- ending (.vtr or .vtu) will be added to the name. If ``None`` is
- passed, a PyVista dataset of the appropriate type will be returned.
- field_select : :class:`str`, optional
- Field that should be stored. Can be:
- "field", "raw_field", "krige_field", "err_field" or "krige_var".
- Default: "field"
- fieldname : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of the field in the VTK file. Default: "field"
- """
- field = f_cls[field_select] if field_select in f_cls.field_names else None
- if f_cls.value_type == "vector":
- if not (f_cls.pos is None or field is None or f_cls.mesh_type is None):
- suf = ["_X", "_Y", "_Z"]
- fields = {}
- for i in range(f_cls.model.dim):
- fields[fieldname + suf[i]] = field[i]
- if filename is None:
- return to_vtk(f_cls.pos, fields, f_cls.mesh_type)
- return vtk_export(filename, f_cls.pos, fields, f_cls.mesh_type)
- raise ValueError(f"Field.to_vtk: '{field_select}' not available.")
- if f_cls.value_type == "scalar":
- if not (f_cls.pos is None or field is None or f_cls.mesh_type is None):
- if filename is None:
- return to_vtk(f_cls.pos, {fieldname: field}, f_cls.mesh_type)
- return vtk_export(
- filename, f_cls.pos, {fieldname: field}, f_cls.mesh_type
- )
- raise ValueError(f"Field.to_vtk: '{field_select}' not available.")
- raise ValueError(f"Unknown field value type: {f_cls.value_type}")
-
-
-def generate_on_mesh(
- f_cls, mesh, points="centroids", direction="all", name="field", **kwargs
-):
- """Generate a field on a given meshio, ogs5py or pyvista mesh.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- f_cls : :any:`Field`
- The field class in use.
- mesh : meshio.Mesh or ogs5py.MSH or PyVista mesh
- The given meshio, ogs5py, or PyVista mesh
- points : :class:`str`, optional
- The points to evaluate the field at.
- Either the "centroids" of the mesh cells
- (calculated as mean of the cell vertices) or the "points"
- of the given mesh.
- Default: "centroids"
- direction : :class:`str` or :class:`list`, optional
- Here you can state which direction should be chosen for
- lower dimension. For example, if you got a 2D mesh in xz direction,
- you have to pass "xz". By default, all directions are used.
- One can also pass a list of indices.
- Default: "all"
- name : :class:`str` or :class:`list` of :class:`str`, optional
- Name(s) to store the field(s) in the given mesh as point_data or
- cell_data. If to few names are given, digits will be appended.
- Default: "field"
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to `Field.__call__`.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This will store the field in the given mesh under the given name,
- if a meshio or PyVista mesh was given.
-
- See: https://github.com/nschloe/meshio
-
- See: https://github.com/GeoStat-Framework/ogs5py
-
- See: https://github.com/pyvista/pyvista
- """
- has_pyvista = False
- has_ogs5py = False
-
- try:
- import pyvista as pv
-
- has_pyvista = True
- except ImportError:
- pass
- try:
- import ogs5py as ogs
-
- has_ogs5py = True
- except ImportError:
- pass
-
- if isinstance(direction, str) and direction == "all":
- select = list(range(f_cls.dim))
- elif isinstance(direction, str):
- select = _get_select(direction)[: f_cls.dim]
- else:
- select = direction[: f_cls.dim]
- if len(select) < f_cls.dim:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field.mesh: need at least {f_cls.dim} direction(s), "
- f"got '{direction}'"
- )
- # convert pyvista mesh
- if has_pyvista and pv.is_pyvista_dataset(mesh):
- if points == "centroids":
- pnts = mesh.cell_centers().points.T[select]
- else:
- pnts = mesh.points.T[select]
- out = f_cls.unstructured(pos=pnts, **kwargs)
- # Deal with the output
- fields = [out] if isinstance(out, np.ndarray) else out
- if f_cls.value_type == "vector":
- fields = [f.T for f in fields]
- for f_name, field in zip(_names(name, len(fields)), fields):
- mesh[f_name] = field
- # convert ogs5py mesh
- elif has_ogs5py and isinstance(mesh, ogs.MSH):
- if points == "centroids":
- pnts = mesh.centroids_flat.T[select]
- else:
- pnts = mesh.NODES.T[select]
- out = f_cls.unstructured(pos=pnts, **kwargs)
- # convert meshio mesh
- elif isinstance(mesh, meshio.Mesh):
- if points == "centroids":
- # define unique order of cells
- offset = []
- length = []
- mesh_dim = mesh.points.shape[1]
- if mesh_dim < f_cls.dim:
- raise ValueError("Field.mesh: mesh dimension too low!")
- pnts = np.empty((0, mesh_dim), dtype=np.double)
- for cell in mesh.cells:
- pnt = np.mean(mesh.points[cell.data], axis=1)
- offset.append(pnts.shape[0])
- length.append(pnt.shape[0])
- pnts = np.vstack((pnts, pnt))
- # generate pos for __call__
- pnts = pnts.T[select]
- out = f_cls.unstructured(pos=pnts, **kwargs)
- fields = [out] if isinstance(out, np.ndarray) else out
- if f_cls.value_type == "vector":
- fields = [f.T for f in fields]
- f_lists = []
- for field in fields:
- f_list = []
- for off, leng in zip(offset, length):
- f_list.append(field[off : off + leng])
- f_lists.append(f_list)
- for f_name, f_list in zip(_names(name, len(f_lists)), f_lists):
- mesh.cell_data[f_name] = f_list
- else:
- out = f_cls.unstructured(pos=mesh.points.T[select], **kwargs)
- fields = [out] if isinstance(out, np.ndarray) else out
- if f_cls.value_type == "vector":
- fields = [f.T for f in fields]
- for f_name, field in zip(_names(name, len(fields)), fields):
- mesh.point_data[f_name] = field
- else:
- raise ValueError("Field.mesh: Unknown mesh format!")
- return out
-
-
-def _names(name, cnt):
- name = [name] if isinstance(name, str) else list(name)[:cnt]
- if len(name) < cnt:
- name += [f"{name[-1]}{i + 1}" for i in range(cnt - len(name))]
- return name
-
-
-def _get_select(direction):
- select = []
- if not 0 < len(direction) < 4:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field.mesh: need 1 to 3 direction(s), got '{direction}'"
- )
- for axis in direction:
- if axis == "x":
- if 0 in select:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field.mesh: got duplicate directions {direction}"
- )
- select.append(0)
- elif axis == "y":
- if 1 in select:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field.mesh: got duplicate directions {direction}"
- )
- select.append(1)
- elif axis == "z":
- if 2 in select:
- raise ValueError(
- f"Field.mesh: got duplicate directions {direction}"
- )
- select.append(2)
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"Field.mesh: got unknown direction {axis}")
- return select
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/upscaling.py b/src/gstools/field/upscaling.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 857bfc454..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/field/upscaling.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,98 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing upscaling routines for the spatial random field.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.field.upscaling
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- var_coarse_graining
- var_no_scaling
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=W0613
-import warnings
-
-import numpy as np
-
-__all__ = ["var_coarse_graining", "var_no_scaling"]
-
-
-# scaling routines ############################################################
-
-
-def var_coarse_graining(model, point_volumes=0.0):
- r"""Coarse Graning procedure to upscale the variance for uniform flow.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for the field.
- point_volumes : :class:`float` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Volumes of the elements at the given points. Default: ``0``
-
- Returns
- -------
- scaled_var : :class:`float` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The upscaled variance
-
- Notes
- -----
- This procedure was presented in [Attinger03]_. It applies the
- upscaling procedure 'Coarse Graining' to the Groundwater flow equation
- under uniform flow on a lognormal distributed conductivity field following
- a gaussian covariance function. A filter over a cube with a given
- edge-length :math:`\lambda` is applied and an upscaled conductivity field
- is obtained.
- The upscaled field is again following a gaussian covariance function with
- scale dependent variance and length-scale:
-
- .. math::
- \lambda &= V^{\frac{1}{d}} \\
- \sigma^2\left(\lambda\right) &=
- \sigma^2\cdot\left(
- \frac{\ell^2}{\ell^2+\left(\frac{\lambda}{2}\right)^2}
- \right)^{\frac{d}{2}} \\
- \ell\left(\lambda\right) &=
- \left(\ell^2+\left(\frac{\lambda}{2}\right)^2\right)^{\frac{1}{2}}
-
- Therby :math:`\lambda` will be calculated from the given
- ``point_volumes`` :math:`V` by assuming a cube with the given volume.
-
- The upscaled length scale will be ignored by this routine.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Attinger03] Attinger, S. 2003,
- ''Generalized coarse graining procedures for flow in porous media'',
- Computational Geosciences, 7(4), 253–273.
- """
- if not np.isclose(model.nugget, 0):
- warnings.warn(
- "var_coarse_graining: non-zero nugget will violate upscaling!"
- )
- # interpret volume as a hypercube and calculate the edge length
- edge = point_volumes ** (1.0 / model.dim)
- var_factor = (
- model.len_scale**2 / (model.len_scale**2 + edge**2 / 4)
- ) ** (model.dim / 2.0)
-
- return model.sill * var_factor
-
-
-def var_no_scaling(model, *args, **kwargs):
- r"""Dummy function to bypass scaling.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for the field.
-
- Returns
- -------
- var : :class:`float`
- The model variance.
- """
- return model.sill
diff --git a/src/gstools/krige/__init__.py b/src/gstools/krige/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 66d032464..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/krige/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,29 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing kriging.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige
-
-Kriging Classes
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- Krige
- Simple
- Ordinary
- Universal
- ExtDrift
- Detrended
-"""
-
-from gstools.krige.base import Krige
-from gstools.krige.methods import (
- Detrended,
- ExtDrift,
- Ordinary,
- Simple,
- Universal,
-)
-
-__all__ = ["Krige", "Simple", "Ordinary", "Universal", "ExtDrift", "Detrended"]
diff --git a/src/gstools/krige/base.py b/src/gstools/krige/base.py
deleted file mode 100755
index 78aa2a9f7..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/krige/base.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,729 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing a base class for kriging.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige.base
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- Krige
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, W0221, E1102, R0201, C0412
-import collections
-
-import numpy as np
-import scipy.linalg as spl
-from scipy.spatial.distance import cdist
-
-from gstools import config
-from gstools.field.base import Field
-from gstools.krige.tools import get_drift_functions, set_condition
-from gstools.tools.geometric import rotated_main_axes
-from gstools.tools.misc import eval_func
-from gstools.variogram import vario_estimate
-
-if config.USE_RUST: # pragma: no cover
- # pylint: disable=E0401
- from gstools_core import calc_field_krige, calc_field_krige_and_variance
-else:
- from gstools.krige.krigesum import (
- calc_field_krige,
- calc_field_krige_and_variance,
- )
-
-__all__ = ["Krige"]
-
-
-P_INV = {"pinv": spl.pinv, "pinvh": spl.pinvh}
-"""dict: Standard pseudo-inverse routines"""
-
-
-class Krige(Field):
- """
- A Swiss Army knife for kriging.
-
- A Kriging class enabling the basic kriging routines:
- Simple-, Ordinary-, Universal-, External Drift-
- and detrended/regression-Kriging as well as
- Kriging the Mean [Wackernagel2003]_.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- drift_functions : :class:`list` of :any:`callable`, :class:`str` or :class:`int`
- Either a list of callable functions, an integer representing
- the polynomial order of the drift or one of the following strings:
-
- * "linear" : regional linear drift (equals order=1)
- * "quadratic" : regional quadratic drift (equals order=2)
-
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`, optional
- the external drift values at the given cond. positions.
- mean : :class:`float`, optional
- mean value used to shift normalized conditioning data.
- Could also be a callable. The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- This is used for detrended kriging, where the trended is subtracted
- from the conditions before kriging is applied.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- unbiased : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging weights should sum up to 1, so the estimator
- is unbiased. If unbiased is `False` and no drifts are given,
- this results in simple kriging.
- Default: True
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
-
- Notes
- -----
- If you have changed any properties in the class, you can update the kriging
- setup by calling :any:`Krige.set_condition` without any arguments.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Wackernagel2003] Wackernagel, H.,
- "Multivariate geostatistics",
- Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg (2003)
- """
-
- valid_value_types = ["scalar"]
- """:class:`list` of :class:`str`: valid field value types."""
-
- default_field_names = ["field", "krige_var", "mean_field"]
- """:class:`list`: Default field names."""
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- drift_functions=None,
- ext_drift=None,
- mean=None,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- unbiased=True,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(model, mean=mean, normalizer=normalizer, trend=trend)
- self._unbiased = bool(unbiased)
- self._exact = bool(exact)
- self._pseudo_inv = bool(pseudo_inv)
- self._pseudo_inv_type = None
- self.pseudo_inv_type = pseudo_inv_type
- # initialize private attributes
- self._cond_pos = None
- self._cond_val = None
- self._cond_err = None
- self._krige_mat = None
- self._krige_pos = None
- self._cond_trend = None
- self._cond_ext_drift = np.array([])
- self._drift_functions = None
- self.set_drift_functions(drift_functions)
- self.set_condition(
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- ext_drift,
- cond_err,
- fit_normalizer,
- fit_variogram,
- )
-
- def __call__(
- self,
- pos=None,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- ext_drift=None,
- chunk_size=None,
- only_mean=False,
- return_var=True,
- post_process=True,
- store=True,
- ):
- """
- Generate the kriging field.
-
- The field is saved as `self.field` and is also returned.
- The error variance is saved as `self.krige_var` and is also returned.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions (x, [y, z])
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`, optional
- the external drift values at the given positions (only for EDK)
- chunk_size : :class:`int`, optional
- Chunk size to cut down the size of the kriging system to prevent
- memory errors.
- Default: None
- only_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to only calculate the mean of the kriging field.
- Default: `False`
- return_var : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return the variance along with the field.
- Default: `True`
- post_process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to apply mean, normalizer and trend to the field.
- Default: `True`
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool` or :class:`list`, optional
- Whether to store kriging fields (True/False) with default name
- or with specified names.
- The default is :any:`True` for default names
- ["field", "krige_var"] or "mean_field" if `only_mean=True`.
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the kriged field or mean_field
- krige_var : :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the kriging error variance
- (if return_var is True and only_mean is False)
- """
- return_var &= not only_mean # don't return variance when calc. mean
- fld_cnt = 2 if return_var else 1
- default = self.default_field_names[2] if only_mean else None
- name, save = self.get_store_config(store, default, fld_cnt)
-
- iso_pos, shape = self.pre_pos(pos, mesh_type)
- pnt_cnt = len(iso_pos[0])
-
- field = np.empty(pnt_cnt, dtype=np.double)
- krige_var = np.empty(pnt_cnt, dtype=np.double) if return_var else None
- # set constant mean if present and wanted
- if only_mean and self.drift_no == 0:
- field[...] = self.get_mean(post_process=False)
- # execute the kriging routine
- else:
- # set chunk size
- chunk_size = pnt_cnt if chunk_size is None else int(chunk_size)
- chunk_no = int(np.ceil(pnt_cnt / chunk_size))
- ext_drift = self._pre_ext_drift(pnt_cnt, ext_drift)
- # iterate chunks
- for i in range(chunk_no):
- # get chunk slice for actual chunk
- chunk_slice = (
- i * chunk_size,
- min(pnt_cnt, (i + 1) * chunk_size),
- )
- c_slice = slice(*chunk_slice)
- # get RHS of the kriging system
- k_vec = self._get_krige_vecs(
- iso_pos, chunk_slice, ext_drift, only_mean
- )
- # generate the raw kriging field and error variance
- self._summate(field, krige_var, c_slice, k_vec, return_var)
- # reshape field if we got a structured mesh
- field = np.reshape(field, shape)
- # save field to class
- field = self.post_field(field, name[0], post_process, save[0])
- if return_var: # care about the estimated error variance
- krige_var = np.reshape(
- np.maximum(self.model.sill - krige_var, 0), shape
- )
- krige_var = self.post_field(krige_var, name[1], False, save[1])
- return field, krige_var
- return field
-
- def _summate(self, field, krige_var, c_slice, k_vec, return_var):
- if return_var: # estimate error variance
- field[c_slice], krige_var[c_slice] = calc_field_krige_and_variance(
- self._krige_mat, k_vec, self._krige_cond
- )
- else: # solely calculate the interpolated field
- field[c_slice] = calc_field_krige(
- self._krige_mat, k_vec, self._krige_cond
- )
-
- def _inv(self, mat):
- # return pseudo-inverted matrix if wanted (numerically more stable)
- if self.pseudo_inv:
- # if the given type is a callable, call it
- if callable(self.pseudo_inv_type):
- return self.pseudo_inv_type(mat)
- # use the selected method to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix
- return P_INV[self.pseudo_inv_type](mat)
- # if no pseudo-inverse is wanted, calculate the real inverse
- return spl.inv(mat)
-
- def _get_krige_mat(self):
- """Calculate the inverse matrix of the kriging equation."""
- res = np.empty((self.krige_size, self.krige_size), dtype=np.double)
- # fill the kriging matrix with the covariance
- res[: self.cond_no, : self.cond_no] = self.model.covariance(
- self._get_dists(self._krige_pos)
- )
- # apply the measurement error (nugget by default)
- res[np.diag_indices(self.cond_no)] += self.cond_err
- # set unbias condition (weights have to sum up to 1)
- if self.unbiased:
- res[self.cond_no, : self.cond_no] = 1
- res[: self.cond_no, self.cond_no] = 1
- # set functional drift terms
- for i, f in enumerate(self.drift_functions):
- drift_tmp = f(*self.cond_pos)
- res[-self.drift_no + i, : self.cond_no] = drift_tmp
- res[: self.cond_no, -self.drift_no + i] = drift_tmp
- # set external drift terms
- if self.ext_drift_no > 0:
- ext_size = self.krige_size - self.ext_drift_no
- res[ext_size:, : self.cond_no] = self.cond_ext_drift
- res[: self.cond_no, ext_size:] = self.cond_ext_drift.T
- # set lower right part of the matrix to 0
- res[self.cond_no :, self.cond_no :] = 0
- return self._inv(res)
-
- def _get_krige_vecs(
- self, pos, chunk_slice=(0, None), ext_drift=None, only_mean=False
- ):
- """Calculate the RHS of the kriging equation."""
- # determine the chunk size
- chunk_size = len(pos[0]) if chunk_slice[1] is None else chunk_slice[1]
- chunk_size -= chunk_slice[0]
- chunk_pos = None # init value
- res = np.empty((self.krige_size, chunk_size), dtype=np.double)
- if only_mean:
- # set points to limit of the covariance to only get the mean
- res[: self.cond_no, :] = 0
- else:
- # get correct covariance functions (depending on exact values)
- cf = self.model.cov_nugget if self.exact else self.model.covariance
- res[: self.cond_no, :] = cf(
- self._get_dists(self._krige_pos, pos, chunk_slice)
- )
- # apply the unbiased condition
- if self.unbiased:
- res[self.cond_no, :] = 1
- # drift function need the anisotropic and rotated positions
- if self.int_drift_no > 0:
- chunk_pos = self.model.anisometrize(pos)[:, slice(*chunk_slice)]
- # apply functional drift
- for i, f in enumerate(self.drift_functions):
- res[-self.drift_no + i, :] = f(*chunk_pos)
- # apply external drift
- if self.ext_drift_no > 0:
- ext_size = self.krige_size - self.ext_drift_no
- res[ext_size:, :] = ext_drift[:, slice(*chunk_slice)]
- return res
-
- def _pre_ext_drift(self, pnt_cnt, ext_drift=None, set_cond=False):
- """
- Preprocessor for external drifts.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pnt_cnt : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Number of points of the mesh.
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`, optional
- the external drift values at the given positions (only for EDK)
- For multiple external drifts, the first dimension
- should be the index of the drift term.
- set_cond : :class:`bool`, optional
- State if the given external drift is set for the conditioning
- points. Default: False
-
- Returns
- -------
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`
- the drift values at the given positions
- """
- if ext_drift is not None:
- ext_drift = np.atleast_2d(np.asarray(ext_drift, dtype=np.double))
- if ext_drift.size == 0: # treat empty array as no ext_drift
- return np.array([])
- if set_cond:
- if len(ext_drift.shape) > 2 or ext_drift.shape[1] != pnt_cnt:
- raise ValueError("Krige: wrong number of ext. drifts.")
- return ext_drift
- ext_shape = np.shape(ext_drift)
- shape = (self.ext_drift_no, pnt_cnt)
- if self.drift_no > 1 and ext_shape[0] != self.ext_drift_no:
- raise ValueError("Krige: wrong number of external drifts.")
- if np.prod(ext_shape) != np.prod(shape):
- raise ValueError("Krige: wrong number of ext. drift values.")
- return np.asarray(ext_drift, dtype=np.double).reshape(shape)
- if not set_cond and self._cond_ext_drift.size > 0:
- raise ValueError("Krige: wrong number of ext. drift values.")
- return np.array([])
-
- def _get_dists(self, pos1, pos2=None, pos2_slice=(0, None)):
- """
- Calculate pairwise distances.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos1 : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the first position tuple
- pos2 : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the second position tuple. If none, the first one is taken.
- pos2_slice : :class:`tuple` of :class:`int`, optional
- Start and stop of slice for the pos2 array. Default: all values.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Matrix containing the pairwise distances.
- """
- if pos2 is None:
- return cdist(pos1.T, pos1.T)
- return cdist(pos1.T, pos2.T[slice(*pos2_slice), ...])
-
- def get_mean(self, post_process=True):
- """Calculate the estimated mean of the detrended field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- post_process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to apply field-mean and normalizer.
- Default: `True`
-
- Returns
- -------
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`None`
- Mean of the Kriging System.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Only not ``None`` if the Kriging System has a constant mean.
- This means, no drift is given and the given field-mean is constant.
- The result is neglecting a potential given trend.
- """
- # if there are drift-terms, no constant mean can be calculated -> None
- # if mean should not be post-processed, it exists when no drift given
- if not self.has_const_mean and (post_process or self.drift_no > 0):
- return None
- res = 0.0 # for simple kriging return the given mean
- # correctly setting given mean
- mean = 0.0 if self.mean is None else self.mean
- # for ordinary kriging return the estimated mean
- if self.unbiased:
- # set the right side of the kriging system to the limit of cov.
- mean_est = np.concatenate((np.full_like(self.cond_val, 0.0), [1]))
- # execute the kriging routine with einsum
- res = np.einsum(
- "i,ij,j", self._krige_cond, self._krige_mat, mean_est
- )
- return self.normalizer.denormalize(res + mean) if post_process else res
-
- def set_condition(
- self,
- cond_pos=None,
- cond_val=None,
- ext_drift=None,
- cond_err=None,
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- """Set the conditions for kriging.
-
- This method could also be used to update the kriging setup, when
- properties were changed. Then you can call it without arguments.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- cond_pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple of the conditions (x, [y, z]). Default: current.
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored).
- Default: current.
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :any:`None`, optional
- the external drift values at the given conditions (only for EDK)
- For multiple external drifts, the first dimension
- should be the index of the drift term. When passing `None`, the
- extisting external drift will be used.
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float`, :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied
- to all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
- # only use existing external drift, if no new positions are given
- ext_drift = (
- self._cond_ext_drift
- if (ext_drift is None and cond_pos is None)
- else ext_drift
- )
- # use existing values or set default
- cond_pos = self._cond_pos if cond_pos is None else cond_pos
- cond_val = self._cond_val if cond_val is None else cond_val
- cond_err = self._cond_err if cond_err is None else cond_err
- cond_err = "nugget" if cond_err is None else cond_err # default
- if cond_pos is None or cond_val is None:
- raise ValueError("Krige.set_condition: missing cond_pos/cond_val.")
- # correctly format cond_pos and cond_val
- self._cond_pos, self._cond_val = set_condition(
- cond_pos, cond_val, self.dim
- )
- if fit_normalizer: # fit normalizer to detrended data
- self.normalizer.fit(self.cond_val - self.cond_trend)
- if fit_variogram: # fitting model to empirical variogram of data
- # normalize field
- if self.model.latlon and self.model.temporal:
- msg = "Krige: can't fit variogram for spatio-temporal latlon data."
- raise ValueError(msg)
- field = self.normalizer.normalize(self.cond_val - self.cond_trend)
- field -= self.cond_mean
- sill = np.var(field)
- if self.model.is_isotropic:
- emp_vario = vario_estimate(
- self.cond_pos,
- field,
- latlon=self.model.latlon,
- geo_scale=self.model.geo_scale,
- )
- else:
- axes = rotated_main_axes(self.model.dim, self.model.angles)
- emp_vario = vario_estimate(
- self.cond_pos, field, direction=axes
- )
- # set the sill to the field variance
- self.model.fit_variogram(*emp_vario, sill=sill)
- # set the measurement errors
- self.cond_err = cond_err
- # set the external drift values and the conditioning points
- self._cond_ext_drift = self._pre_ext_drift(
- self.cond_no, ext_drift, set_cond=True
- )
- # upate the internal kriging settings
- self._krige_pos = self.model.isometrize(self.cond_pos)
- # krige pos are the unrotated and isotropic condition positions
- self._krige_mat = self._get_krige_mat()
-
- def set_drift_functions(self, drift_functions=None):
- """
- Set the drift functions for universal kriging.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- drift_functions : :class:`list` of :any:`callable`, :class:`str` or :class:`int`
- Either a list of callable functions, an integer representing
- the polynomial order of the drift or one of the following strings:
-
- * "linear" : regional linear drift (equals order=1)
- * "quadratic" : regional quadratic drift (equals order=2)
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- If the given drift functions are not callable.
- """
- if drift_functions is None:
- self._drift_functions = []
- elif isinstance(drift_functions, (str, int)):
- self._drift_functions = get_drift_functions(
- self.dim, drift_functions
- )
- else:
- if isinstance(drift_functions, collections.abc.Iterator):
- drift_functions = list(drift_functions)
- # check for a single content thats not a string
- try:
- iter(drift_functions)
- except TypeError:
- drift_functions = [drift_functions]
- for f in drift_functions:
- if not callable(f):
- raise ValueError("Krige: Drift functions not callable")
- self._drift_functions = drift_functions
-
- @property
- def _krige_cond(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: The prepared kriging conditions."""
- pad_size = self.drift_no + int(self.unbiased)
- # detrend data and normalize
- val = self.normalizer.normalize(self.cond_val - self.cond_trend)
- # set to zero mean
- val -= self.cond_mean
- return np.pad(val, (0, pad_size), mode="constant", constant_values=0)
-
- @property
- def cond_pos(self):
- """:class:`list`: The position tuple of the conditions."""
- return self._cond_pos
-
- @property
- def cond_val(self):
- """:class:`list`: The values of the conditions."""
- return self._cond_val
-
- @property
- def cond_err(self):
- """:class:`list`: The measurement errors at the condition points."""
- if isinstance(self._cond_err, str) and self._cond_err == "nugget":
- return self.model.nugget
- return self._cond_err
-
- @cond_err.setter
- def cond_err(self, value):
- if isinstance(value, str) and value == "nugget":
- self._cond_err = value
- else:
- if self.exact:
- raise ValueError(
- "krige.cond_err: measurement errors can't be given, "
- "when interpolator should be exact."
- )
- value = np.asarray(value, dtype=np.double).reshape(-1)
- if value.size == 1:
- self._cond_err = value.item()
- else:
- if value.size != self.cond_no:
- raise ValueError(
- "krige.cond_err: wrong number of measurement errors."
- )
- self._cond_err = value
-
- @property
- def cond_no(self):
- """:class:`int`: The number of the conditions."""
- return len(self._cond_val)
-
- @property
- def cond_ext_drift(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: The ext. drift at the conditions."""
- return self._cond_ext_drift
-
- @property
- def cond_mean(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: Trend at the conditions."""
- return eval_func(self.mean, self.cond_pos, self.dim, broadcast=True)
-
- @property
- def cond_trend(self):
- """:class:`numpy.ndarray`: Trend at the conditions."""
- return eval_func(self.trend, self.cond_pos, self.dim, broadcast=True)
-
- @property
- def unbiased(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the kriging is unbiased or not."""
- return self._unbiased
-
- @property
- def exact(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the interpolator is exact."""
- return self._exact
-
- @property
- def pseudo_inv(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether pseudo inverse matrix is used."""
- return self._pseudo_inv
-
- @property
- def pseudo_inv_type(self):
- """:class:`str`: Method selector for pseudo inverse calculation."""
- return self._pseudo_inv_type
-
- @pseudo_inv_type.setter
- def pseudo_inv_type(self, val):
- if val not in P_INV and not callable(val):
- raise ValueError(f"Krige: pseudo_inv_type not in {sorted(P_INV)}")
- self._pseudo_inv_type = val
-
- @property
- def drift_functions(self):
- """:class:`list` of :any:`callable`: The drift functions."""
- return self._drift_functions
-
- @property
- def has_const_mean(self):
- """:class:`bool`: Whether the field has a constant mean or not."""
- return self.drift_no == 0 and not callable(self.mean)
-
- @property
- def krige_size(self):
- """:class:`int`: Size of the kriging system."""
- return self.cond_no + self.drift_no + int(self.unbiased)
-
- @property
- def drift_no(self):
- """:class:`int`: Number of drift values per point."""
- return self.int_drift_no + self.ext_drift_no
-
- @property
- def int_drift_no(self):
- """:class:`int`: Number of internal drift values per point."""
- return len(self.drift_functions)
-
- @property
- def ext_drift_no(self):
- """:class:`int`: Number of external drift values per point."""
- return self.cond_ext_drift.shape[0]
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return (
- f"{self.name}(model={self.model.name}, "
- f"cond_no={self.cond_no}{self._fmt_mean_norm_trend()})"
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/krige/methods.py b/src/gstools/krige/methods.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 19ffed56d..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/krige/methods.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,520 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing a class for simple kriging.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige.methods
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- Simple
- Ordinary
- Universal
- ExtDrift
- Detrended
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103
-from gstools.krige.base import Krige
-
-__all__ = ["Simple", "Ordinary", "Universal", "ExtDrift", "Detrended"]
-
-
-class Simple(Krige):
- """
- Simple kriging.
-
- Simple kriging is used to interpolate data with a given mean.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- mean : :class:`float`, optional
- mean value used to shift normalized conditioning data.
- Could also be a callable. The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- This is used for detrended kriging, where the trended is subtracted
- from the conditions before kriging is applied.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- mean=0.0,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- mean=mean,
- normalizer=normalizer,
- trend=trend,
- unbiased=False,
- exact=exact,
- cond_err=cond_err,
- pseudo_inv=pseudo_inv,
- pseudo_inv_type=pseudo_inv_type,
- fit_normalizer=fit_normalizer,
- fit_variogram=fit_variogram,
- )
-
-
-class Ordinary(Krige):
- """
- Ordinary kriging.
-
- Ordinary kriging is used to interpolate data and estimate a proper mean.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- This is used for detrended kriging, where the trended is subtracted
- from the conditions before kriging is applied.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- trend=trend,
- normalizer=normalizer,
- exact=exact,
- cond_err=cond_err,
- pseudo_inv=pseudo_inv,
- pseudo_inv_type=pseudo_inv_type,
- fit_normalizer=fit_normalizer,
- fit_variogram=fit_variogram,
- )
-
-
-class Universal(Krige):
- """
- Universal kriging.
-
- Universal kriging is used to interpolate given data with a variable mean,
- that is determined by a functional drift.
-
- This estimator is set to be unbiased by default.
- This means, that the weights in the kriging equation sum up to 1.
- Consequently no constant function needs to be given for a constant drift,
- since the unbiased condition is applied to all given drift functions.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- drift_functions : :class:`list` of :any:`callable`, :class:`str` or :class:`int`
- Either a list of callable functions, an integer representing
- the polynomial order of the drift or one of the following strings:
-
- * "linear" : regional linear drift (equals order=1)
- * "quadratic" : regional quadratic drift (equals order=2)
-
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- This is used for detrended kriging, where the trended is subtracted
- from the conditions before kriging is applied.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- drift_functions,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- drift_functions=drift_functions,
- normalizer=normalizer,
- trend=trend,
- exact=exact,
- cond_err=cond_err,
- pseudo_inv=pseudo_inv,
- pseudo_inv_type=pseudo_inv_type,
- fit_normalizer=fit_normalizer,
- fit_variogram=fit_variogram,
- )
-
-
-class ExtDrift(Krige):
- """
- External drift kriging (EDK).
-
- External drift kriging is used to interpolate given data
- with a variable mean, that is determined by an external drift.
-
- This estimator is set to be unbiased by default.
- This means, that the weights in the kriging equation sum up to 1.
- Consequently no constant external drift needs to be given to estimate
- a proper mean.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- ext_drift : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the external drift values at the given condition positions.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- This is used for detrended kriging, where the trended is subtracted
- from the conditions before kriging is applied.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given conditioning data.
- Default: False
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- ext_drift,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_normalizer=False,
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- ext_drift=ext_drift,
- normalizer=normalizer,
- trend=trend,
- exact=exact,
- cond_err=cond_err,
- pseudo_inv=pseudo_inv,
- pseudo_inv_type=pseudo_inv_type,
- fit_normalizer=fit_normalizer,
- fit_variogram=fit_variogram,
- )
-
-
-class Detrended(Krige):
- """
- Detrended simple kriging.
-
- In detrended kriging, the data is detrended before interpolation by
- simple kriging with zero mean.
-
- The trend needs to be a callable function the user has to provide.
- This can be used for regression kriging, where the trend function
- is determined by an external regression algorithm.
-
- This is just a shortcut for simple kriging with a given trend function,
- zero mean and no normalizer.
-
- A trend can be given with EVERY provided kriging routine.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- model : :any:`CovModel`
- Covariance Model used for kriging.
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- tuple, containing the given condition positions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- trend_function : :any:`callable`
- The callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z])
- exact : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the interpolator should reproduce the exact input values.
- If `False`, `cond_err` is interpreted as measurement error
- at the conditioning points and the result will be more smooth.
- Default: False
- cond_err : :class:`str`, :class :class:`float` or :class:`list`, optional
- The measurement error at the conditioning points.
- Either "nugget" to apply the model-nugget, a single value applied to
- all points or an array with individual values for each point.
- The measurement error has to be <= nugget.
- The "exact=True" variant only works with "cond_err='nugget'".
- Default: "nugget"
- pseudo_inv : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the kriging system is solved with the pseudo inverted
- kriging matrix. If `True`, this leads to more numerical stability
- and redundant points are averaged. But it can take more time.
- Default: True
- pseudo_inv_type : :class:`str` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Here you can select the algorithm to compute the pseudo-inverse matrix:
-
- * `"pinv"`: use `pinv` from `scipy` which uses `SVD`
- * `"pinvh"`: use `pinvh` from `scipy` which uses eigen-values
-
- If you want to use another routine to invert the kriging matrix,
- you can pass a callable which takes a matrix and returns the inverse.
- Default: `"pinv"`
- fit_variogram : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the given variogram model to the data.
- Directional variogram fitting is triggered by setting
- any anisotropy factor of the model to anything unequal 1
- but the main axes of correlation are taken from the model
- rotation angles. If the model is a spatio-temporal latlon
- model, this will raise an error.
- This assumes the sill to be the data variance and with
- standard bins provided by the :any:`standard_bins` routine.
- Default: False
- """
-
- def __init__(
- self,
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- trend,
- exact=False,
- cond_err="nugget",
- pseudo_inv=True,
- pseudo_inv_type="pinv",
- fit_variogram=False,
- ):
- super().__init__(
- model,
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- trend=trend,
- unbiased=False,
- exact=exact,
- cond_err=cond_err,
- pseudo_inv=pseudo_inv,
- pseudo_inv_type=pseudo_inv_type,
- fit_variogram=fit_variogram,
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/krige/tools.py b/src/gstools/krige/tools.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 629265957..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/krige/tools.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,96 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for Kriging.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.krige.tools
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- set_condition
- get_drift_functions
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103
-from itertools import combinations_with_replacement
-
-import numpy as np
-
-__all__ = ["set_condition", "get_drift_functions"]
-
-
-def set_condition(cond_pos, cond_val, dim):
- """
- Set the conditions for kriging.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple of the conditions (x, [y, z])
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the values of the conditions (nan values will be ignored)
- dim : :class:`int`, optional
- Spatial dimension
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- If the given data does not match the given dimension.
-
- Returns
- -------
- cond_pos : :class:`list`
- the error checked cond_pos with all finite values
- cond_val : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the error checked cond_val for all finite cond_pos values
- """
- # convert the input for right shapes and dimension checks
- cond_val = np.asarray(cond_val, dtype=np.double).reshape(-1)
- cond_pos = np.asarray(cond_pos, dtype=np.double).reshape(dim, -1)
- if len(cond_pos[0]) != len(cond_val):
- raise ValueError(
- "Please check your 'cond_pos' and 'cond_val' parameters. "
- "The shapes do not match."
- )
- mask = np.isfinite(cond_val)
- return cond_pos[:, mask], cond_val[mask]
-
-
-def get_drift_functions(dim, drift_type):
- """
- Get functions for a given drift type in universal kriging.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- Given dimension.
- drift_type : :class:`str` or :class:`int`
- Drift type: 'linear' or 'quadratic' or an integer for the polynomial
- order of the drift type. (linear equals 1, quadratic equals 2 ...)
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`list` of :any:`callable`
- List of drift functions.
- """
- if drift_type in ["lin", "linear"]:
- drift_type = 1
- elif drift_type in ["quad", "quadratic"]:
- drift_type = 2
- else:
- drift_type = int(drift_type)
- drift_functions = []
- for d in range(drift_type):
- selects = combinations_with_replacement(range(dim), d + 1)
- for select in selects:
- drift_functions.append(_f_factory(select))
- return drift_functions
-
-
-def _f_factory(select):
- def f(*pos):
- res = 1.0
- for i in select:
- res *= np.asarray(pos[i])
- return res
-
- return f
diff --git a/src/gstools/normalizer/__init__.py b/src/gstools/normalizer/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 505a6d67f..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/normalizer/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,61 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing normalization routines.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.normalizer
-
-Base-Normalizer
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- Normalizer
-
-Field-Normalizer
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- LogNormal
- BoxCox
- BoxCoxShift
- YeoJohnson
- Modulus
- Manly
-
-Convenience Routines
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- apply_mean_norm_trend
- remove_trend_norm_mean
-"""
-
-from gstools.normalizer.base import Normalizer
-from gstools.normalizer.methods import (
- BoxCox,
- BoxCoxShift,
- LogNormal,
- Manly,
- Modulus,
- YeoJohnson,
-)
-from gstools.normalizer.tools import (
- apply_mean_norm_trend,
- remove_trend_norm_mean,
-)
-
-__all__ = [
- "Normalizer",
- "LogNormal",
- "BoxCox",
- "BoxCoxShift",
- "YeoJohnson",
- "Modulus",
- "Manly",
- "apply_mean_norm_trend",
- "remove_trend_norm_mean",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/normalizer/base.py b/src/gstools/normalizer/base.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 4a8477c60..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/normalizer/base.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,260 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing the base class for normalizers.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.normalizer.base
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- Normalizer
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=R0201
-import warnings
-
-import numpy as np
-import scipy.misc as spm
-import scipy.optimize as spo
-
-
-class Normalizer:
- """Normalizer class.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- **parameter
- Specified parameters given by name. If not given, default parameters
- will be used.
- """
-
- default_parameter = {}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameters of the Normalizer."""
- normalize_range = (-np.inf, np.inf)
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for input data."""
- denormalize_range = (-np.inf, np.inf)
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for output/normal data."""
- _dx = 1e-6 # dx for numerical derivative
-
- def __init__(self, data=None, **parameter):
- # only use parameter, that have a provided default value
- for key, value in self.default_parameter.items():
- setattr(self, key, parameter.get(key, value))
- # fit parameters if data is given
- if data is not None:
- self.fit(data)
- # optimization results
- self._opti = None
- # precision for printing
- self._prec = 3
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- return data
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- return data
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return spm.derivative(self._normalize, data, dx=self._dx)
-
- def _loglikelihood(self, data):
- add = -0.5 * np.size(data) * (np.log(2 * np.pi) + 1)
- return self._kernel_loglikelihood(data) + add
-
- def _kernel_loglikelihood(self, data):
- res = -0.5 * np.size(data) * np.log(np.var(self._normalize(data)))
- return res + np.sum(np.log(np.maximum(1e-16, self._derivative(data))))
-
- def _check_input(self, data, data_range=None, return_output_template=True):
- is_data = np.logical_not(np.isnan(data))
- if return_output_template:
- out = np.full_like(data, np.nan, dtype=np.double)
- data = np.asarray(data, dtype=np.double)[is_data]
- if data_range is not None and np.min(np.abs(data_range)) < np.inf:
- dat_in = np.logical_and(data > data_range[0], data < data_range[1])
- if not np.all(dat_in):
- warnings.warn(
- f"{self.name}: "
- f"data (min: {np.min(data)}, max: {np.max(data)}) "
- f"out of range: {data_range}. "
- "Affected values will be treated as NaN."
- )
- is_data[is_data] &= dat_in
- data = data[dat_in]
- if return_output_template:
- return data, is_data, out
- return data
-
- def denormalize(self, data):
- """Transform to input distribution.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data (normal distributed).
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Denormalized data.
- """
- data, is_data, out = self._check_input(data, self.denormalize_range)
- out[is_data] = self._denormalize(data)
- return out
-
- def normalize(self, data):
- """Transform to normal distribution.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data (not normal distributed).
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normalized data.
- """
- data, is_data, out = self._check_input(data, self.normalize_range)
- out[is_data] = self._normalize(data)
- return out
-
- def derivative(self, data):
- """Factor for normal PDF to gain target PDF.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data (not normal distributed).
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Derivative of the normalization transformation function.
- """
- data, is_data, out = self._check_input(data, self.normalize_range)
- out[is_data] = self._derivative(data)
- return out
-
- def likelihood(self, data):
- """Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- Likelihood of the given data.
- """
- return np.exp(self.loglikelihood(data))
-
- def loglikelihood(self, data):
- """Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- Log-Likelihood of the given data.
- """
- data = self._check_input(data, self.normalize_range, False)
- return self._loglikelihood(data)
-
- def kernel_loglikelihood(self, data):
- """Kernel Log-Likelihood for given data with current parameters.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- Kernel Log-Likelihood of the given data.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This loglikelihood function is neglecting additive constants,
- that are not needed for optimization.
- """
- data = self._check_input(data, self.normalize_range, False)
- return self._kernel_loglikelihood(data)
-
- def fit(self, data, skip=None, **kwargs):
- """Fitting the transformation to data by maximizing Log-Likelihood.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like
- Input data to fit the transformation to in order to gain normality.
- skip : :class:`list` of :class:`str` or :any:`None`, optional
- Names of parameters to be skipped in fitting.
- The default is None.
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments passed to :any:`scipy.optimize.minimize_scalar`
- when only one parameter present or :any:`scipy.optimize.minimize`.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`dict`
- Optimal parameters given by names.
- """
- skip = [] if skip is None else skip
- all_names = sorted(self.default_parameter)
- para_names = [name for name in all_names if name not in skip]
-
- def _neg_kllf(par, dat):
- for name, val in zip(para_names, np.atleast_1d(par)):
- setattr(self, name, val)
- return -self.kernel_loglikelihood(dat)
-
- if len(para_names) == 0: # transformations without para. (no opti.)
- warnings.warn(f"{self.name}.fit: no parameters!")
- return {}
- if len(para_names) == 1: # one-para. transformations (simple opti.)
- # default bracket like in scipy's boxcox (if not given)
- kwargs.setdefault("bracket", (-2, 2))
- out = spo.minimize_scalar(_neg_kllf, args=(data,), **kwargs)
- else: # general case
- # init guess from current parameters (if x0 not given)
- kwargs.setdefault("x0", [getattr(self, p) for p in para_names])
- out = spo.minimize(_neg_kllf, args=(data,), **kwargs)
- # save optimization results
- self._opti = out
- for name, val in zip(para_names, np.atleast_1d(out.x)):
- setattr(self, name, val)
- return {name: getattr(self, name) for name in all_names}
-
- def __eq__(self, other):
- """Compare Normalizers."""
- # check for correct base class
- if type(self) is not type(other):
- return False
- # if base class is same, this is safe
- for val in self.default_parameter:
- if not np.isclose(getattr(self, val), getattr(other, val)):
- return False
- return True
-
- @property
- def name(self):
- """:class:`str`: The name of the normalizer class."""
- return self.__class__.__name__
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- para_strs = [
- f"{p}={float(getattr(self, p)):.{self._prec}}"
- for p in sorted(self.default_parameter)
- ]
- return f"{self.name}({', '.join(para_strs)})"
diff --git a/src/gstools/normalizer/methods.py b/src/gstools/normalizer/methods.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a46dc2306..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/normalizer/methods.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,363 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing different normalizer transformations.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.normalizer.methods
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- LogNormal
- BoxCox
- BoxCoxShift
- YeoJohnson
- Modulus
- Manly
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=E1101
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.normalizer.base import Normalizer
-
-
-class LogNormal(Normalizer):
- r"""Log-normal fields.
-
- Notes
- -----
- This parameter-free transformation is given by:
-
- .. math::
- y=\log(x)
- """
-
- normalize_range = (0.0, np.inf)
- """Valid range for input data."""
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- return np.exp(data)
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- return np.log(data)
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return np.power(data, -1)
-
-
-class BoxCox(Normalizer):
- r"""Box-Cox (1964) transformed fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Default: 1
-
- Notes
- -----
- This transformation is given by [Box1964]_:
-
- .. math::
- y=\begin{cases}
- \frac{x^{\lambda} - 1}{\lambda} & \lambda\neq 0 \\
- \log(x) & \lambda = 0
- \end{cases}
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Box1964] G.E.P. Box and D.R. Cox,
- "An Analysis of Transformations",
- Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 26, 211-252, (1964)
- """
-
- default_parameter = {"lmbda": 1}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameter of the BoxCox-Normalizer."""
- normalize_range = (0.0, np.inf)
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for input data."""
-
- @property
- def denormalize_range(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for output data depending on lmbda.
-
- `(-1/lmbda, inf)` or `(-inf, -1/lmbda)`
- """
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return (-np.inf, np.inf)
- if self.lmbda < 0:
- return (-np.inf, -np.divide(1, self.lmbda))
- return (-np.divide(1, self.lmbda), np.inf)
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.exp(data)
- return (1 + np.multiply(data, self.lmbda)) ** (1 / self.lmbda)
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.log(data)
- return (np.power(data, self.lmbda) - 1) / self.lmbda
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return np.power(data, self.lmbda - 1)
-
-
-class BoxCoxShift(Normalizer):
- r"""Box-Cox (1964) transformed fields including shifting.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Default: 1
- shift : :class:`float`, optional
- Shift parameter. Default: 0
-
- Notes
- -----
- This transformation is given by [Box1964]_:
-
- .. math::
- y=\begin{cases}
- \frac{(x+s)^{\lambda} - 1}{\lambda} & \lambda\neq 0 \\
- \log(x+s) & \lambda = 0
- \end{cases}
-
- Fitting the shift parameter is rather hard. You should consider skipping
- "shift" during fitting:
-
- >>> data = range(5)
- >>> norm = BoxCoxShift(shift=0.5)
- >>> norm.fit(data, skip=["shift"])
- {'shift': 0.5, 'lmbda': 0.6747515267420799}
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Box1964] G.E.P. Box and D.R. Cox,
- "An Analysis of Transformations",
- Journal of the Royal Statistical Society B, 26, 211-252, (1964)
- """
-
- default_parameter = {"shift": 0, "lmbda": 1}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameters of the BoxCoxShift-Normalizer."""
-
- @property
- def normalize_range(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for input data depending on shift.
-
- `(-shift, inf)`
- """
- return (-self.shift, np.inf)
-
- @property
- def denormalize_range(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for output data depending on lmbda.
-
- `(-1/lmbda, inf)` or `(-inf, -1/lmbda)`
- """
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return (-np.inf, np.inf)
- if self.lmbda < 0:
- return (-np.inf, -np.divide(1, self.lmbda))
- return (-np.divide(1, self.lmbda), np.inf)
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.exp(data) - self.shift
- return (1 + np.multiply(data, self.lmbda)) ** (
- 1 / self.lmbda
- ) - self.shift
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.log(np.add(data, self.shift))
- return (np.add(data, self.shift) ** self.lmbda - 1) / self.lmbda
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return np.power(np.add(data, self.shift), self.lmbda - 1)
-
-
-class YeoJohnson(Normalizer):
- r"""Yeo-Johnson (2000) transformed fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Default: 1
-
- Notes
- -----
- This transformation is given by [Yeo2000]_:
-
- .. math::
- y=\begin{cases}
- \frac{(x+1)^{\lambda} - 1}{\lambda}
- & x\geq 0,\, \lambda\neq 0 \\
- \log(x+1)
- & x\geq 0,\, \lambda = 0 \\
- -\frac{(|x|+1)^{2-\lambda} - 1}{2-\lambda}
- & x<0,\, \lambda\neq 2 \\
- -\log(|x|+1)
- & x<0,\, \lambda = 2
- \end{cases}
-
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Yeo2000] I.K. Yeo and R.A. Johnson,
- "A new family of power transformations to improve normality or
- symmetry." Biometrika, 87(4), pp.954-959, (2000).
- """
-
- default_parameter = {"lmbda": 1}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameter of the YeoJohnson-Normalizer."""
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- data = np.asanyarray(data)
- res = np.zeros_like(data, dtype=np.double)
- pos = data >= 0
- # when data >= 0
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- res[pos] = np.expm1(data[pos])
- else: # self.lmbda != 0
- res[pos] = np.power(data[pos] * self.lmbda + 1, 1 / self.lmbda) - 1
- # when data < 0
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 2):
- res[~pos] = -np.expm1(-data[~pos])
- else: # self.lmbda != 2
- res[~pos] = 1 - np.power(
- -(2 - self.lmbda) * data[~pos] + 1, 1 / (2 - self.lmbda)
- )
- return res
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- data = np.asanyarray(data)
- res = np.zeros_like(data, dtype=np.double)
- pos = data >= 0
- # when data >= 0
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- res[pos] = np.log1p(data[pos])
- else: # self.lmbda != 0
- res[pos] = (np.power(data[pos] + 1, self.lmbda) - 1) / self.lmbda
- # when data < 0
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 2):
- res[~pos] = -np.log1p(-data[~pos])
- else: # self.lmbda != 2
- res[~pos] = -(np.power(-data[~pos] + 1, 2 - self.lmbda) - 1) / (
- 2 - self.lmbda
- )
- return res
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return (np.abs(data) + 1) ** (np.sign(data) * (self.lmbda - 1))
-
-
-class Modulus(Normalizer):
- r"""Modulus or John-Draper (1980) transformed fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Default: 1
-
- Notes
- -----
- This transformation is given by [John1980]_:
-
- .. math::
- y=\begin{cases}
- \mathrm{sgn}(x)\frac{(|x|+1)^{\lambda} - 1}{\lambda} & \lambda\neq 0 \\
- \mathrm{sgn}(x)\log(|x|+1) & \lambda = 0
- \end{cases}
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [John1980] J. A. John, and N. R. Draper,
- "An Alternative Family of Transformations." Journal
- of the Royal Statistical Society C, 29.2, 190-197, (1980)
- """
-
- default_parameter = {"lmbda": 1}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameter of the Modulus-Normalizer."""
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.sign(data) * np.expm1(np.abs(data))
- return np.sign(data) * (
- (1 + self.lmbda * np.abs(data)) ** (1 / self.lmbda) - 1
- )
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return np.sign(data) * np.log1p(np.abs(data))
- return (
- np.sign(data) * ((np.abs(data) + 1) ** self.lmbda - 1) / self.lmbda
- )
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return np.power(np.abs(data) + 1, self.lmbda - 1)
-
-
-class Manly(Normalizer):
- r"""Manly (1971) transformed fields.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- data : array_like, optional
- Input data to fit the transformation in order to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter. Default: 1
-
- Notes
- -----
- This transformation is given by [Manly1976]_:
-
- .. math::
- y=\begin{cases}
- \frac{\exp(\lambda x) - 1}{\lambda} & \lambda\neq 0 \\
- x & \lambda = 0
- \end{cases}
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Manly1976] B. F. J. Manly, "Exponential data transformations.",
- Journal of the Royal Statistical Society D, 25.1, 37-42 (1976).
- """
-
- default_parameter = {"lmbda": 1}
- """:class:`dict`: Default parameter of the Manly-Normalizer."""
-
- @property
- def denormalize_range(self):
- """:class:`tuple`: Valid range for output data depending on lmbda.
-
- `(-1/lmbda, inf)` or `(-inf, -1/lmbda)`
- """
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return (-np.inf, np.inf)
- if self.lmbda < 0:
- return (-np.inf, np.divide(1, self.lmbda))
- return (-np.divide(1, self.lmbda), np.inf)
-
- def _denormalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return data
- return np.log1p(np.multiply(data, self.lmbda)) / self.lmbda
-
- def _normalize(self, data):
- if np.isclose(self.lmbda, 0):
- return data
- return np.expm1(np.multiply(data, self.lmbda)) / self.lmbda
-
- def _derivative(self, data):
- return np.exp(np.multiply(data, self.lmbda))
diff --git a/src/gstools/normalizer/tools.py b/src/gstools/normalizer/tools.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 3e395d290..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/normalizer/tools.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,186 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for Normalizers.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.normalizer.tools
-
-The following classes and functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- apply_mean_norm_trend
- remove_trend_norm_mean
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.normalizer.base import Normalizer
-from gstools.tools.geometric import (
- format_struct_pos_shape,
- format_unstruct_pos_shape,
-)
-from gstools.tools.misc import eval_func
-
-__all__ = ["apply_mean_norm_trend", "remove_trend_norm_mean"]
-
-
-def _check_normalizer(normalizer):
- if isinstance(normalizer, type) and issubclass(normalizer, Normalizer):
- normalizer = normalizer()
- elif normalizer is None:
- normalizer = Normalizer()
- elif not isinstance(normalizer, Normalizer):
- raise ValueError("Check: 'normalizer' not of type 'Normalizer'.")
- return normalizer
-
-
-def apply_mean_norm_trend(
- pos,
- field,
- mean=None,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- value_type="scalar",
- check_shape=True,
- stacked=False,
-):
- """
- Apply mean, de-normalization and trend to given field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- Position tuple, containing main direction and transversal directions.
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The spatially distributed data.
- You can pass a list of fields, that will be used simultaneously.
- Then you need to set ``stacked=True``.
- mean : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Mean of the field if wanted. Could also be a callable.
- The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the field.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Trend of the denormalized fields. If no normalizer is applied,
- this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: 'unstructured'
- value_type : :class:`str`, optional
- Value type of the field. Either "scalar" or "vector".
- The default is "scalar".
- check_shape : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to check pos and field shapes. The default is True.
- stacked : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the field is stacked or not. The default is False.
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The transformed field.
- """
- normalizer = _check_normalizer(normalizer)
- if check_shape:
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos, shape, dim = format_struct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=stacked
- )
- else:
- pos, shape, dim = format_unstruct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=stacked
- )
- field = np.asarray(field, dtype=np.double).reshape(shape)
- else:
- dim = len(pos)
- if not stacked:
- field = [field]
- field_cnt = len(field)
- for i in range(field_cnt):
- field[i] += eval_func(mean, pos, dim, mesh_type, value_type, True)
- field = normalizer.denormalize(field)
- for i in range(field_cnt):
- field[i] += eval_func(trend, pos, dim, mesh_type, value_type, True)
- return field if stacked else field[0]
-
-
-def remove_trend_norm_mean(
- pos,
- field,
- mean=None,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- value_type="scalar",
- check_shape=True,
- stacked=False,
- fit_normalizer=False,
-):
- """
- Remove trend, de-normalization and mean from given field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- Position tuple, containing main direction and transversal directions.
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The spatially distributed data.
- You can pass a list of fields, that will be used simultaneously.
- Then you need to set ``stacked=True``.
- mean : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Mean of the field if wanted. Could also be a callable.
- The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the field.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- Trend of the denormalized fields. If no normalizer is applied,
- this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: 'unstructured'
- value_type : :class:`str`, optional
- Value type of the field. Either "scalar" or "vector".
- The default is "scalar".
- check_shape : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to check pos and field shapes. The default is True.
- stacked : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the field is stacked or not. The default is False.
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given (detrended) field.
- Default: False
-
- Returns
- -------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The cleaned field.
- normalizer : :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- The fitted normalizer for the given data.
- Only provided if `fit_normalizer` is True.
- """
- normalizer = _check_normalizer(normalizer)
- if check_shape:
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos, shape, dim = format_struct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=stacked
- )
- else:
- pos, shape, dim = format_unstruct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=stacked
- )
- field = np.asarray(field, dtype=np.double).reshape(shape)
- else:
- dim = len(pos)
- if not stacked:
- field = [field]
- field_cnt = len(field)
- for i in range(field_cnt):
- field[i] -= eval_func(trend, pos, dim, mesh_type, value_type, True)
- if fit_normalizer:
- normalizer.fit(field)
- field = normalizer.normalize(field)
- for i in range(field_cnt):
- field[i] -= eval_func(mean, pos, dim, mesh_type, value_type, True)
- out = field if stacked else field[0]
- return (out, normalizer) if fit_normalizer else out
diff --git a/src/gstools/random/__init__.py b/src/gstools/random/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index af8f73786..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/random/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,36 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage for random number generation.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.random
-
-Random Number Generator
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- RNG
-
-Seed Generator
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- MasterRNG
-
-Distribution factory
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- dist_gen
-
-----
-"""
-
-from gstools.random.rng import RNG
-from gstools.random.tools import MasterRNG, dist_gen
-
-__all__ = ["RNG", "MasterRNG", "dist_gen"]
diff --git a/src/gstools/random/rng.py b/src/gstools/random/rng.py
deleted file mode 100644
index ad07c6aab..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/random/rng.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,221 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing the core of the spatial random field generation.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.random.rng
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- RNG
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=E1101
-import emcee as mc
-import numpy as np
-import numpy.random as rand
-from emcee.state import State
-
-from gstools.random.tools import MasterRNG, dist_gen
-
-__all__ = ["RNG"]
-
-
-class RNG:
- """
- A random number generator for different distributions and multiple streams.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- The seed of the master RNG, if ``None``,
- a random seed is used. Default: ``None``
- """
-
- def __init__(self, seed=None):
- # set seed
- self._master_rng = None
- self.seed = seed
-
- def sample_ln_pdf(
- self,
- ln_pdf,
- size=None,
- sample_around=1.0,
- nwalkers=50,
- burn_in=20,
- oversampling_factor=10,
- ):
- """Sample from a distribution given by ln(pdf).
-
- This algorithm uses the :class:`emcee.EnsembleSampler`
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- ln_pdf : :any:`callable`
- The logarithm of the Probability density function
- of the given distribution, that takes a single argument
- size : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- sample size. Default: None
- sample_around : :class:`float`, optional
- Starting point for initial guess Default: 1.
- nwalkers : :class:`int`, optional
- The number of walkers in the mcmc sampler. Used for the
- emcee.EnsembleSampler class.
- Default: 50
- burn_in : :class:`int`, optional
- Number of burn-in runs in the mcmc algorithm.
- Default: 20
- oversampling_factor : :class:`int`, optional
- To guess the sample number needed for proper results, we use a
- factor for oversampling. The intern used sample-size is
- calculated by
-
- ``sample_size = max(burn_in, (size/nwalkers)*oversampling_factor)``
-
- So at least, as much as the burn-in runs.
- Default: 10
- """
- if size is None: # pragma: no cover
- sample_size = burn_in
- else:
- sample_size = max(burn_in, (size / nwalkers) * oversampling_factor)
- # sample_size needs to be integer for emcee >= 3.1
- sample_size = int(sample_size)
- # initial guess
- init_guess = (
- self.random.rand(nwalkers).reshape((nwalkers, 1)) * sample_around
- )
- # initialize the sampler
- sampler = mc.EnsembleSampler(nwalkers, 1, ln_pdf, vectorize=True)
- # burn in phase with saving of last position
- initial_state = State(init_guess, copy=True)
- initial_state.random_state = self.random.get_state()
- burn_in_state = sampler.run_mcmc(
- initial_state=initial_state, nsteps=burn_in
- )
- # reset after burn_in
- sampler.reset()
- # actual sampling
- initial_state = State(burn_in_state, copy=True)
- initial_state.random_state = self.random.get_state()
- sampler.run_mcmc(initial_state=initial_state, nsteps=sample_size)
- samples = sampler.get_chain(flat=True)[:, 0]
-
- # choose samples according to size
- return self.random.choice(samples, size)
-
- def sample_dist(self, pdf=None, cdf=None, ppf=None, size=None, **kwargs):
- """Sample from a distribution given by pdf, cdf and/or ppf.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pdf : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Probability density function of the given distribution,
- that takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- cdf : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Cumulative distribution function of the given distribution, that
- takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- ppf : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Percent point function of the given distribution, that
- takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- size : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- sample size. Default: None
- **kwargs
- Keyword-arguments that are forwarded to
- :any:`scipy.stats.rv_continuous`.
-
- Returns
- -------
- samples : :class:`float` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the samples from the given distribution
-
- Notes
- -----
- At least pdf or cdf needs to be given.
- """
- kwargs["seed"] = self.random
- dist = dist_gen(pdf_in=pdf, cdf_in=cdf, ppf_in=ppf, **kwargs)
- return dist.rvs(size=size)
-
- def sample_sphere(self, dim, size=None):
- """Uniform sampling on a d-dimensional sphere.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- Dimension of the sphere. Just 1, 2, and 3 supported.
- size : :class:`int`, optional
- sample size
-
- Returns
- -------
- coord : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- x[, y[, z]] coordinates on the sphere with shape (dim, size)
- """
- if size is None: # pragma: no cover
- coord = np.empty((dim, 1), dtype=np.double)
- else:
- coord = np.empty( # saver conversion of size to resulting shape
- (dim,) + tuple(np.atleast_1d(size)), dtype=np.double
- )
- if dim == 1:
- coord[0] = self.random.choice([-1, 1], size=size)
- elif dim == 2:
- ang1 = self.random.uniform(0.0, 2 * np.pi, size)
- coord[0] = np.cos(ang1)
- coord[1] = np.sin(ang1)
- elif dim == 3:
- ang1 = self.random.uniform(0.0, 2 * np.pi, size)
- ang2 = self.random.uniform(-1.0, 1.0, size)
- coord[0] = np.sqrt(1.0 - ang2**2) * np.cos(ang1)
- coord[1] = np.sqrt(1.0 - ang2**2) * np.sin(ang1)
- coord[2] = ang2
- else: # pragma: no cover
- # http://corysimon.github.io/articles/uniformdistn-on-sphere/
- coord = self.random.normal(size=coord.shape)
- while True: # loop until all norms are non-zero
- norm = np.linalg.norm(coord, axis=0)
- # check for zero norms
- zero_norms = np.isclose(norm, 0)
- # exit the loop if all norms are non-zero
- if not np.any(zero_norms):
- break
- # transpose, since the next transpose reverses axis order
- zero_samples = zero_norms.T.nonzero()
- # need to transpose to have dim-axis last
- new_shape = coord.T[zero_samples].shape
- # resample the zero norm samples
- coord.T[zero_samples] = self.random.normal(size=new_shape)
- # project onto sphere
- coord = coord / norm
- return np.reshape(coord, dim) if size is None else coord
-
- @property
- def random(self):
- """:any:`numpy.random.RandomState`: Randomstate.
-
- Get a stream to the numpy Random number generator.
- You can use this, to call any provided distribution
- from :any:`numpy.random.RandomState`.
- """
- return rand.RandomState(self._master_rng())
-
- @property # pragma: no cover
- def seed(self):
- """:class:`int`: Seed of the master RNG.
-
- The setter property not only saves the new seed, but also creates
- a new master RNG function with the new seed.
- """
- return self._master_rng.seed
-
- @seed.setter
- def seed(self, new_seed=None):
- self._master_rng = MasterRNG(new_seed)
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return f"RNG(seed={self.seed})"
diff --git a/src/gstools/random/tools.py b/src/gstools/random/tools.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d61327ea7..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/random/tools.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,183 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for random sampling.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.random.tools
-
-The following classes are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- MasterRNG
- dist_gen
-"""
-
-import numpy.random as rand
-from scipy.stats import rv_continuous
-
-__all__ = ["MasterRNG", "dist_gen"]
-
-
-class MasterRNG:
- """Master random number generator for generating seeds.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- The seed of the master RNG, if ``None``,
- a random seed is used. Default: ``None``
-
- """
-
- def __init__(self, seed):
- self._seed = seed
- self._master_rng_fct = rand.RandomState(seed)
- self._master_rng = lambda: self._master_rng_fct.randint(1, 2**16)
-
- def __call__(self):
- """Return a random seed."""
- return self._master_rng()
-
- @property # pragma: no cover
- def seed(self):
- """:class:`int`: Seed of the master RNG.
-
- The setter property not only saves the new seed, but also creates
- a new master RNG function with the new seed.
- """
- return self._seed
-
- def __repr__(self):
- """Return String representation."""
- return f"MasterRNG(seed={self.seed})"
-
-
-def dist_gen(pdf_in=None, cdf_in=None, ppf_in=None, **kwargs):
- """Distribution Factory.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pdf_in : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Probability distribution function of the given distribution, that
- takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- cdf_in : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Cumulative distribution function of the given distribution, that
- takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- ppf_in : :any:`callable` or :any:`None`, optional
- Percent point function of the given distribution, that
- takes a single argument
- Default: ``None``
- **kwargs
- Keyword-arguments forwarded to :any:`scipy.stats.rv_continuous`.
-
- Returns
- -------
- dist : :class:`scipy.stats.rv_continuous`
- The constructed distribution.
-
- Notes
- -----
- At least pdf or cdf needs to be given.
- """
- if ppf_in is None:
- if pdf_in is not None and cdf_in is None:
- return DistPdf(pdf_in, **kwargs)
- if pdf_in is None and cdf_in is not None:
- return DistCdf(cdf_in, **kwargs)
- if pdf_in is not None and cdf_in is not None:
- return DistPdfCdf(pdf_in, cdf_in, **kwargs)
- raise ValueError("Either pdf or cdf must be given")
-
- if pdf_in is not None and cdf_in is None:
- return DistPdfPpf(pdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs)
- if pdf_in is None and cdf_in is not None:
- return DistCdfPpf(cdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs)
- if pdf_in is not None and cdf_in is not None:
- return DistPdfCdfPpf(pdf_in, cdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs)
- raise ValueError("pdf or cdf must be given along with the ppf")
-
-
-class DistPdf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from pdf."""
-
- def __init__(self, pdf_in, **kwargs):
- self.pdf_in = pdf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _pdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.pdf_in(x)
-
-
-class DistCdf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from cdf."""
-
- def __init__(self, cdf_in, **kwargs):
- self.cdf_in = cdf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _cdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.cdf_in(x)
-
-
-class DistPdfCdf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from pdf and cdf."""
-
- def __init__(self, pdf_in, cdf_in, **kwargs):
- self.pdf_in = pdf_in
- self.cdf_in = cdf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _pdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.pdf_in(x)
-
- def _cdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.cdf_in(x)
-
-
-class DistPdfPpf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from pdf and ppf."""
-
- def __init__(self, pdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs):
- self.pdf_in = pdf_in
- self.ppf_in = ppf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _pdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.pdf_in(x)
-
- def _ppf(self, q, *args):
- return self.ppf_in(q)
-
-
-class DistCdfPpf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from cdf and ppf."""
-
- def __init__(self, cdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs):
- self.cdf_in = cdf_in
- self.ppf_in = ppf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _cdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.cdf_in(x)
-
- def _ppf(self, q, *args):
- return self.ppf_in(q)
-
-
-class DistPdfCdfPpf(rv_continuous):
- """Generate distribution from pdf, cdf and ppf."""
-
- def __init__(self, pdf_in, cdf_in, ppf_in, **kwargs):
- self.pdf_in = pdf_in
- self.cdf_in = cdf_in
- self.ppf_in = ppf_in
- super().__init__(**kwargs)
-
- def _pdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.pdf_in(x)
-
- def _cdf(self, x, *args):
- return self.cdf_in(x)
-
- def _ppf(self, q, *args):
- return self.ppf_in(q)
diff --git a/src/gstools/tools/__init__.py b/src/gstools/tools/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 1f68dbaf1..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/tools/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing miscellaneous tools.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools
-
-Export
-^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- vtk_export
- vtk_export_structured
- vtk_export_unstructured
- to_vtk
- to_vtk_structured
- to_vtk_unstructured
-
-Special functions
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- confidence_scaling
- inc_gamma
- inc_gamma_low
- exp_int
- inc_beta
- tplstable_cor
- tpl_exp_spec_dens
- tpl_gau_spec_dens
-
-Geometric
-^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- rotated_main_axes
- set_angles
- set_anis
- no_of_angles
- rotation_planes
- givens_rotation
- matrix_rotate
- matrix_derotate
- matrix_isotropify
- matrix_anisotropify
- matrix_isometrize
- matrix_anisometrize
- ang2dir
- generate_grid
- generate_st_grid
-
-Misc
-^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- EARTH_RADIUS
- KM_SCALE
- DEGREE_SCALE
- RADIAN_SCALE
-
-----
-
-.. autodata:: EARTH_RADIUS
-
-.. autodata:: KM_SCALE
-
-.. autodata:: DEGREE_SCALE
-
-.. autodata:: RADIAN_SCALE
-"""
-
-from gstools.tools.export import (
- to_vtk,
- to_vtk_structured,
- to_vtk_unstructured,
- vtk_export,
- vtk_export_structured,
- vtk_export_unstructured,
-)
-from gstools.tools.geometric import (
- ang2dir,
- generate_grid,
- generate_st_grid,
- givens_rotation,
- matrix_anisometrize,
- matrix_anisotropify,
- matrix_derotate,
- matrix_isometrize,
- matrix_isotropify,
- matrix_rotate,
- no_of_angles,
- rotated_main_axes,
- rotation_planes,
- set_angles,
- set_anis,
-)
-from gstools.tools.special import (
- confidence_scaling,
- exp_int,
- inc_beta,
- inc_gamma,
- inc_gamma_low,
- tpl_exp_spec_dens,
- tpl_gau_spec_dens,
- tplstable_cor,
-)
-
-EARTH_RADIUS = 6371.0
-"""float: earth radius for WGS84 ellipsoid in km"""
-
-KM_SCALE = 6371.0
-"""float: earth radius for WGS84 ellipsoid in km"""
-
-DEGREE_SCALE = 57.29577951308232
-"""float: radius for unit sphere in degree"""
-
-RADIAN_SCALE = 1.0
-"""float: radius for unit sphere"""
-
-
-__all__ = [
- "vtk_export",
- "vtk_export_structured",
- "vtk_export_unstructured",
- "to_vtk",
- "to_vtk_structured",
- "to_vtk_unstructured",
- "confidence_scaling",
- "inc_gamma",
- "inc_gamma_low",
- "exp_int",
- "inc_beta",
- "tplstable_cor",
- "tpl_exp_spec_dens",
- "tpl_gau_spec_dens",
- "set_angles",
- "set_anis",
- "no_of_angles",
- "rotation_planes",
- "givens_rotation",
- "matrix_rotate",
- "matrix_derotate",
- "matrix_isotropify",
- "matrix_anisotropify",
- "matrix_isometrize",
- "matrix_anisometrize",
- "rotated_main_axes",
- "ang2dir",
- "generate_grid",
- "generate_st_grid",
- "EARTH_RADIUS",
- "KM_SCALE",
- "DEGREE_SCALE",
- "RADIAN_SCALE",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/tools/export.py b/src/gstools/tools/export.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 38254cebe..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/tools/export.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,236 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing export routines.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools.export
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- vtk_export
- vtk_export_structured
- vtk_export_unstructured
- to_vtk
- to_vtk_structured
- to_vtk_unstructured
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, E1101
-import numpy as np
-from pyevtk.hl import gridToVTK, pointsToVTK
-
-try:
- import pyvista as pv
-except ImportError:
- pv = None
-
-__all__ = [
- "to_vtk_structured",
- "vtk_export_structured",
- "to_vtk_unstructured",
- "vtk_export_unstructured",
- "to_vtk",
- "vtk_export",
-]
-
-
-# export routines #############################################################
-
-
-def _vtk_structured_helper(pos, fields):
- """Extract field info for vtk rectilinear grid."""
- if not isinstance(fields, dict):
- fields = {"field": fields}
- if len(pos) > 3:
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.vtk_export_structured: "
- "vtk export only possible for dim=1,2,3"
- )
- x = pos[0]
- y = pos[1] if len(pos) > 1 else np.array([0])
- z = pos[2] if len(pos) > 2 else np.array([0])
- # need fortran order in VTK
- for field in fields:
- fields[field] = fields[field].reshape(-1, order="F")
- if len(fields[field]) != len(x) * len(y) * len(z):
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.vtk_export_structured: "
- "field shape doesn't match the given mesh"
- )
- return x, y, z, fields
-
-
-def to_vtk_structured(pos, fields): # pragma: no cover
- """Create a vtk structured rectilinear grid from a field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Structured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`pyvista.RectilinearGrid`
- A PyVista rectilinear grid of the structured field data. Data arrays
- live on the point data of this PyVista dataset.
- """
- x, y, z, fields = _vtk_structured_helper(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- if pv is not None:
- grid = pv.RectilinearGrid(x, y, z)
- grid.point_data.update(fields)
- else:
- raise ImportError("Please install PyVista to create VTK datasets.")
- return grid
-
-
-def vtk_export_structured(filename, pos, fields): # pragma: no cover
- """Export a field to vtk structured rectilinear grid file.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- filename : :class:`str`
- Filename of the file to be saved, including the path. Note that an
- ending (.vtr) will be added to the name.
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Structured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
- """
- x, y, z, fields = _vtk_structured_helper(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- return gridToVTK(filename, x, y, z, pointData=fields)
-
-
-def _vtk_unstructured_helper(pos, fields):
- if not isinstance(fields, dict):
- fields = {"field": fields}
- if len(pos) > 3:
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.vtk_export_structured: "
- "vtk export only possible for dim=1,2,3"
- )
- x = pos[0]
- y = pos[1] if len(pos) > 1 else np.zeros_like(x)
- z = pos[2] if len(pos) > 2 else np.zeros_like(x)
- for field in fields:
- fields[field] = fields[field].reshape(-1)
- if (
- len(fields[field]) != len(x)
- or len(fields[field]) != len(y)
- or len(fields[field]) != len(z)
- ):
- raise ValueError(
- "gstools.vtk_export_unstructured: "
- "field shape doesn't match the given mesh"
- )
- return x, y, z, fields
-
-
-def to_vtk_unstructured(pos, fields): # pragma: no cover
- """Export a field to vtk structured rectilinear grid file.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Unstructured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`pyvista.UnstructuredGrid`
- A PyVista unstructured grid of the unstructured field data. Data arrays
- live on the point data of this PyVista dataset. This is essentially
- a point cloud with no topology.
- """
- x, y, z, fields = _vtk_unstructured_helper(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- if pv is not None:
- grid = pv.PolyData(np.c_[x, y, z]).cast_to_unstructured_grid()
- grid.point_data.update(fields)
- else:
- raise ImportError("Please install PyVista to create VTK datasets.")
- return grid
-
-
-def vtk_export_unstructured(filename, pos, fields): # pragma: no cover
- """Export a field to vtk unstructured grid file.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- filename : :class:`str`
- Filename of the file to be saved, including the path. Note that an
- ending (.vtu) will be added to the name.
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Unstructured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
- """
- x, y, z, fields = _vtk_unstructured_helper(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- return pointsToVTK(filename, x, y, z, data=fields)
-
-
-def to_vtk(pos, fields, mesh_type="unstructured"): # pragma: no cover
- """Create a VTK/PyVista grid.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- [Un]structured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'. Default: structured
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`pyvista.RectilinearGrid` or :class:`pyvista.UnstructuredGrid`
- This will return a PyVista object for the given field data in its
- appropriate type. Structured meshes will return a
- :class:`pyvista.RectilinearGrid` and unstructured meshes will return
- an :class:`pyvista.UnstructuredGrid` object.
- """
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- grid = to_vtk_structured(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- else:
- grid = to_vtk_unstructured(pos=pos, fields=fields)
- return grid
-
-
-def vtk_export(
- filename, pos, fields, mesh_type="unstructured"
-): # pragma: no cover
- """Export a field to vtk.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- filename : :class:`str`
- Filename of the file to be saved, including the path. Note that an
- ending (.vtr or .vtu) will be added to the name.
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions
- fields : :class:`dict` or :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- [Un]structured fields to be saved.
- Either a single numpy array as returned by SRF,
- or a dictionary of fields with theirs names as keys.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'. Default: structured
- """
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- return vtk_export_structured(filename=filename, pos=pos, fields=fields)
- return vtk_export_unstructured(filename=filename, pos=pos, fields=fields)
diff --git a/src/gstools/tools/geometric.py b/src/gstools/tools/geometric.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 55408965e..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/tools/geometric.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,754 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing geometric tools.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools.geometric
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- set_angles
- set_anis
- no_of_angles
- rotation_planes
- givens_rotation
- matrix_rotate
- matrix_derotate
- matrix_isotropify
- matrix_anisotropify
- matrix_isometrize
- matrix_anisometrize
- rotated_main_axes
- generate_grid
- generate_st_grid
- format_struct_pos_dim
- format_struct_pos_shape
- format_unstruct_pos_shape
- ang2dir
- latlon2pos
- pos2latlon
- chordal_to_great_circle
- great_circle_to_chordal
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103
-import numpy as np
-
-__all__ = [
- "set_angles",
- "set_anis",
- "no_of_angles",
- "rotation_planes",
- "givens_rotation",
- "matrix_rotate",
- "matrix_derotate",
- "matrix_isotropify",
- "matrix_anisotropify",
- "matrix_isometrize",
- "matrix_anisometrize",
- "rotated_main_axes",
- "generate_grid",
- "generate_st_grid",
- "format_struct_pos_dim",
- "format_struct_pos_shape",
- "format_unstruct_pos_shape",
- "ang2dir",
- "latlon2pos",
- "pos2latlon",
- "chordal_to_great_circle",
-]
-
-
-# Geometric functions #########################################################
-
-
-def set_angles(dim, angles):
- """Set the angles for the given dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the angles of the SRF
-
- Returns
- -------
- angles : :class:`float`
- the angles fitting to the dimension
-
- Notes
- -----
- If too few angles are given, they are filled up with `0`.
- """
- out_angles = np.asarray(angles, dtype=np.double)
- out_angles = np.atleast_1d(out_angles)[: no_of_angles(dim)]
- # fill up the rotation angle array with zeros
- out_angles = np.pad(
- out_angles,
- (0, no_of_angles(dim) - len(out_angles)),
- "constant",
- constant_values=0.0,
- )
- return out_angles
-
-
-def set_anis(dim, anis):
- """Set the anisotropy ratios for the given dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal directions
-
- Returns
- -------
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales fitting the dimensions
-
- Notes
- -----
- If too few anisotropy ratios are given, they are filled up with `1`.
- """
- out_anis = np.asarray(anis, dtype=np.double)
- out_anis = np.atleast_1d(out_anis)[: dim - 1]
- if len(out_anis) < dim - 1:
- # fill up the anisotropies with ones, such that len()==dim-1
- out_anis = np.pad(
- out_anis,
- (dim - len(out_anis) - 1, 0),
- "constant",
- constant_values=1.0,
- )
- return out_anis
-
-
-def no_of_angles(dim):
- """Calculate number of rotation angles depending on the dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`int`
- Number of angles.
- """
- return (dim * (dim - 1)) // 2
-
-
-def rotation_planes(dim):
- """Get all 2D sub-planes for rotation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`list` of :class:`tuple` of :class:`int`
- All 2D sub-planes for rotation.
- """
- return [(i, j) for j in range(1, dim) for i in range(j)]
-
-
-def givens_rotation(dim, plane, angle):
- """Givens rotation matrix in arbitrary dimensions.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- plane : :class:`list` of :class:`int`
- the plane to rotate in, given by the indices of the two defining axes.
- For example the xy plane is defined by `(0,1)`
- angle : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angle in the given plane
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Rotation matrix.
- """
- result = np.eye(dim, dtype=np.double)
- result[plane[0], plane[0]] = np.cos(angle)
- result[plane[1], plane[1]] = np.cos(angle)
- result[plane[0], plane[1]] = -np.sin(angle)
- result[plane[1], plane[0]] = np.sin(angle)
- return result
-
-
-def matrix_rotate(dim, angles):
- """Create a matrix to rotate points to the target coordinate-system.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angles of the target coordinate-system
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Rotation matrix.
- """
- angles = set_angles(dim, angles)
- planes = rotation_planes(dim)
- result = np.eye(dim, dtype=np.double)
- for i, (angle, plane) in enumerate(zip(angles, planes)):
- # angles have alternating signs to match tait-bryan
- result = np.matmul(
- givens_rotation(dim, plane, (-1) ** i * angle), result
- )
- return result
-
-
-def matrix_derotate(dim, angles):
- """Create a matrix to derotate points to the initial coordinate-system.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angles of the target coordinate-system
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Rotation matrix.
- """
- # derotating by taking negative angles
- angles = -set_angles(dim, angles)
- planes = rotation_planes(dim)
- result = np.eye(dim, dtype=np.double)
- for i, (angle, plane) in enumerate(zip(angles, planes)):
- # angles have alternating signs to match tait bryan
- result = np.matmul(
- result, givens_rotation(dim, plane, (-1) ** i * angle)
- )
- return result
-
-
-def matrix_isotropify(dim, anis):
- """Create a stretching matrix to make things isotrope.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal directions
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Stretching matrix.
- """
- anis = set_anis(dim, anis)
- return np.diag(np.concatenate(([1.0], 1.0 / anis)))
-
-
-def matrix_anisotropify(dim, anis):
- """Create a stretching matrix to make things anisotrope.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal directions
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Stretching matrix.
- """
- anis = set_anis(dim, anis)
- return np.diag(np.concatenate(([1.0], anis)))
-
-
-def matrix_isometrize(dim, angles, anis):
- """Create a matrix to derotate points and make them isotrope.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angles of the target coordinate-system
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal directions
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformation matrix.
- """
- return np.matmul(
- matrix_isotropify(dim, anis), matrix_derotate(dim, angles)
- )
-
-
-def matrix_anisometrize(dim, angles, anis):
- """Create a matrix to rotate points and make them anisotrope.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angles of the target coordinate-system
- anis : :class:`list` of :class:`float`
- the anisotropy of length scales along the transversal directions
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformation matrix.
- """
- return np.matmul(
- matrix_rotate(dim, angles), matrix_anisotropify(dim, anis)
- )
-
-
-def rotated_main_axes(dim, angles):
- """Create list of the main axis defined by the given system rotations.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dim : :class:`int`
- spatial dimension
- angles : :class:`float` or :class:`list`
- the rotation angles of the target coordinate-system
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Main axes of the target coordinate-system.
- """
- return matrix_rotate(dim, angles).T
-
-
-# grid routines ###############################################################
-
-
-def generate_grid(pos):
- """
- Generate grid from a structured position tuple.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The structured position tuple.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Unstructured position tuple.
- """
- return np.asarray(
- np.meshgrid(*pos, indexing="ij"), dtype=np.double
- ).reshape((len(pos), -1))
-
-
-def generate_st_grid(pos, time, mesh_type="unstructured"):
- """
- Generate spatio-temporal grid from a position tuple and time array.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The (un-)structured position tuple.
- time : :any:`iterable`
- The time array.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: `"unstructured"`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Unstructured spatio-temporal point tuple.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Time dimension will be the last one.
- """
- time = np.asarray(time, dtype=np.double).reshape(-1)
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos = generate_grid(pos)
- else:
- pos = np.atleast_2d(np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double))
- out = [np.repeat(p.reshape(-1), np.size(time)) for p in pos]
- out.append(np.tile(time, np.size(pos[0])))
- return np.asarray(out, dtype=np.double)
-
-
-# conversion ##################################################################
-
-
-def format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim):
- """
- Format a structured position tuple with given dimension.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- Position tuple, containing main direction and transversal directions.
- dim : :class:`int`
- Spatial dimension.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When position tuple doesn't match the given dimension.
-
- Returns
- -------
- pos : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The formatted structured position tuple.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the resulting field.
- """
- if dim == 1:
- pos = (np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape(-1),)
- elif len(pos) != dim:
- raise ValueError("Formatting: position tuple doesn't match dimension.")
- else:
- pos = tuple(np.asarray(p, dtype=np.double).reshape(-1) for p in pos)
- shape = tuple(len(p) for p in pos)
- return pos, shape
-
-
-def format_struct_pos_shape(pos, shape, check_stacked_shape=False):
- """
- Format a structured position tuple with given shape.
-
- Shape could be stacked, when multiple fields are given.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- Position tuple, containing main direction and transversal directions.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the input field.
- check_stacked_shape : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to check if given shape comes from stacked fields.
- Default: False.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When position tuple doesn't match the given dimension.
-
- Returns
- -------
- pos : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The formatted structured position tuple.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the resulting field.
- dim : :class:`int`
- Spatial dimension.
- """
- # some help from the given shape
- shape_size = np.prod(shape)
- stacked_shape_size = np.prod(shape[1:])
- wrong_shape = False
- # now we try to be smart
- try:
- # if this works we have either:
- # - a 1D array
- # - nD array where all axes have same length (corner case)
- check_pos = np.array(pos, dtype=np.double, ndmin=2)
- except ValueError:
- # if it doesn't work, we have a tuple of differently sized axes (easy)
- dim = len(pos)
- pos, pos_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim)
- # determine if we have a stacked field if wanted
- if check_stacked_shape and stacked_shape_size == np.prod(pos_shape):
- shape = (shape[0],) + pos_shape
- # check if we have a single field with matching size
- elif shape_size == np.prod(pos_shape):
- shape = (1,) + pos_shape if check_stacked_shape else pos_shape
- # if nothing works, we raise an error
- else:
- wrong_shape = True
- else:
- struct_size = np.prod([p.size for p in check_pos])
- # case: 1D unstacked
- if check_pos.size == shape_size:
- dim = 1
- pos, pos_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(check_pos, dim)
- shape = (1,) + pos_shape if check_stacked_shape else pos_shape
- # case: 1D and stacked
- elif check_pos.size == stacked_shape_size:
- dim = 1
- pos, pos_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(check_pos, dim)
- cnt = shape[0]
- shape = (cnt,) + pos_shape
- wrong_shape = not check_stacked_shape
- # case: nD unstacked
- elif struct_size == shape_size:
- dim = len(check_pos)
- pos, pos_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim)
- shape = (1,) + pos_shape if check_stacked_shape else pos_shape
- # case: nD and stacked
- elif struct_size == stacked_shape_size:
- dim = len(check_pos)
- pos, pos_shape = format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim)
- cnt = shape[0]
- shape = (cnt,) + pos_shape
- wrong_shape = not check_stacked_shape
- # if nothing works, we raise an error
- else:
- wrong_shape = True
-
- # if shape was wrong at one point we raise an error
- if wrong_shape:
- raise ValueError("Formatting: position tuple doesn't match dimension.")
-
- return pos, shape, dim
-
-
-def format_unstruct_pos_shape(pos, shape, check_stacked_shape=False):
- """
- Format an unstructured position tuple with given shape.
-
- Shape could be stacked, when multiple fields were given.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :any:`iterable`
- Position tuple, containing point coordinates.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the input field.
- check_stacked_shape : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to check if given shape comes from stacked fields.
- Default: False.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When position tuple doesn't match the given dimension.
-
- Returns
- -------
- pos : :class:`tuple` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The formatted structured position tuple.
- shape : :class:`tuple`
- Shape of the resulting field.
- dim : :class:`int`
- Spatial dimension.
- """
- # some help from the given shape
- shape_size = np.prod(shape)
- stacked_shape_size = np.prod(shape[1:])
- wrong_shape = False
- # now we try to be smart
- pre_len = len(np.atleast_1d(pos))
- # care about 1D: pos can be given as 1D array here -> convert to 2D array
- pos = np.atleast_2d(np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double))
- post_len = len(pos)
- # first array dimension should be spatial dimension (1D is special case)
- dim = post_len if pre_len == post_len else 1
- pnt_cnt = pos[0].size
- # case: 1D unstacked
- if dim == 1 and pos.size == shape_size:
- shape = (1, pos.size) if check_stacked_shape else (pos.size,)
- # case: 1D and stacked
- elif dim == 1 and pos.size == stacked_shape_size:
- shape = (shape[0], pos.size)
- wrong_shape = not check_stacked_shape
- # case: nD unstacked
- elif pnt_cnt == shape_size:
- shape = (1, pnt_cnt) if check_stacked_shape else pnt_cnt
- # case: nD and stacked
- elif pnt_cnt == stacked_shape_size:
- shape = (shape[0], pnt_cnt)
- wrong_shape = not check_stacked_shape
- # if nothing works, we raise an error
- else:
- wrong_shape = True
-
- # if shape was wrong at one point we raise an error
- if wrong_shape:
- raise ValueError("Formatting: position tuple doesn't match dimension.")
-
- pos = pos.reshape((dim, -1))
-
- return pos, shape, dim
-
-
-def ang2dir(angles, dtype=np.double, dim=None):
- """Convert n-D spherical coordinates to Euclidean direction vectors.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- angles : :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- spherical coordinates given as angles.
- dtype : data-type, optional
- The desired data-type for the array.
- If not given, then the type will be determined as the minimum type
- required to hold the objects in the sequence. Default: None
- dim : :class:`int`, optional
- Cut of information above the given dimension.
- Otherwise, dimension is determined by number of angles
- Default: None
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the array of direction vectors
- """
- pre_dim = np.asanyarray(angles).ndim
- angles = np.atleast_2d(np.asarray(angles, dtype=dtype))
- if len(angles.shape) > 2:
- raise ValueError(f"Can't interpret angles array {angles}")
- dim = angles.shape[1] + 1 if dim is None else dim
- if dim == 2 and angles.shape[0] == 1 and pre_dim < 2:
- # fix for 2D where only one angle per direction is given
- angles = angles.T # can't be interpreted if dim=None is given
- if dim != angles.shape[1] + 1 or dim == 1:
- raise ValueError(f"Wrong dim. ({dim}) for angles {angles}")
- vec = np.empty((angles.shape[0], dim), dtype=dtype)
- vec[:, 0] = np.prod(np.sin(angles), axis=1)
- for i in range(1, dim):
- vec[:, i] = np.prod(np.sin(angles[:, i:]), axis=1) # empty prod = 1
- vec[:, i] *= np.cos(angles[:, (i - 1)])
- if dim in [2, 3]:
- vec[:, [0, 1]] = vec[:, [1, 0]] # to match convention in 2D and 3D
- return vec
-
-
-def latlon2pos(
- latlon, radius=1.0, dtype=np.double, temporal=False, time_scale=1.0
-):
- """Convert lat-lon geo coordinates to 3D position tuple.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- latlon : :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- latitude and longitude given in degrees.
- May includes an appended time axis if `time=True`.
- radius : :class:`float`, optional
- Sphere radius. Default: `1.0`
- dtype : data-type, optional
- The desired data-type for the array.
- If not given, then the type will be determined as the minimum type
- required to hold the objects in the sequence. Default: None
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether latlon includes an appended time axis.
- Default: False
- time_scale : :class:`float`, optional
- Scaling factor (e.g. anisotropy) for the time axis.
- Default: `1.0`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the 3D position array
- """
- latlon = np.asarray(latlon, dtype=dtype).reshape(
- (3 if temporal else 2, -1)
- )
- lat, lon = np.deg2rad(latlon[:2])
- pos_tuple = (
- radius * np.cos(lat) * np.cos(lon),
- radius * np.cos(lat) * np.sin(lon),
- radius * np.sin(lat) * np.ones_like(lon),
- )
- if temporal:
- return np.array(pos_tuple + (latlon[2] / time_scale,), dtype=dtype)
- return np.array(pos_tuple, dtype=dtype)
-
-
-def pos2latlon(
- pos, radius=1.0, dtype=np.double, temporal=False, time_scale=1.0
-):
- """Convert 3D position tuple from sphere to lat-lon geo coordinates.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The position tuple containing points on a unit-sphere.
- May includes an appended time axis if `time=True`.
- radius : :class:`float`, optional
- Sphere radius. Default: `1.0`
- dtype : data-type, optional
- The desired data-type for the array.
- If not given, then the type will be determined as the minimum type
- required to hold the objects in the sequence. Default: None
- temporal : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether latlon includes an appended time axis.
- Default: False
- time_scale : :class:`float`, optional
- Scaling factor (e.g. anisotropy) for the time axis.
- Default: `1.0`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the 3D position array
- """
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=dtype).reshape((4 if temporal else 3, -1))
- # prevent numerical errors in arcsin
- lat = np.arcsin(np.maximum(np.minimum(pos[2] / radius, 1.0), -1.0))
- lon = np.arctan2(pos[1], pos[0])
- latlon = np.rad2deg((lat, lon), dtype=dtype)
- if temporal:
- return np.array(
- (latlon[0], latlon[1], pos[3] * time_scale), dtype=dtype
- )
- return latlon
-
-
-def chordal_to_great_circle(dist, radius=1.0):
- """
- Calculate great circle distance corresponding to given chordal distance.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dist : array_like
- Chordal distance of two points on the sphere.
- radius : :class:`float`, optional
- Sphere radius. Default: `1.0`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Great circle distance corresponding to given chordal distance.
-
- Notes
- -----
- If given values are not in [0, 2 * radius], they will be truncated.
- """
- diameter = 2 * radius
- return diameter * np.arcsin(
- np.maximum(np.minimum(np.divide(dist, diameter), 1), 0)
- )
-
-
-def great_circle_to_chordal(dist, radius=1.0):
- """
- Calculate chordal distance corresponding to given great circle distance.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- dist : array_like
- Great circle distance of two points on the sphere.
- radius : :class:`float`, optional
- Sphere radius. Default: `1.0`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Chordal distance corresponding to given great circle distance.
- """
- diameter = 2 * radius
- return diameter * np.sin(np.divide(dist, diameter))
diff --git a/src/gstools/tools/misc.py b/src/gstools/tools/misc.py
deleted file mode 100755
index aaba1501e..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/tools/misc.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,143 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing miscellaneous tools.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools.misc
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- get_fig_ax
- list_format
- eval_func
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, C0415
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.tools.geometric import format_struct_pos_dim, generate_grid
-
-__all__ = ["get_fig_ax", "list_format", "eval_func"]
-
-
-def get_fig_ax(fig=None, ax=None, ax_name="rectilinear"): # pragma: no cover
- """
- Get correct matplotlib figure and axes.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fig : figure or :any:`None`
- desired figure.
- ax : axis or :any:`None`
- desired axis.
- ax_name : :class:`str`, optional
- Axis type name. The default is "rectilinear".
-
- Returns
- -------
- fig : figure
- desired figure.
- ax : axis
- desired axis.
- """
- try:
- from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
- except ImportError as exc:
- raise ImportError("Plotting: Matplotlib not installed.") from exc
-
- if fig is None and ax is None:
- fig = plt.figure()
- ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=ax_name)
- elif ax is None:
- ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=ax_name)
- elif fig is None:
- fig = ax.get_figure()
- assert ax.name == ax_name
- else:
- assert ax.name == ax_name
- assert ax.get_figure() == fig
- return fig, ax
-
-
-def list_format(lst, prec): # pragma: no cover
- """Format a list of floats."""
- return f"[{', '.join(f'{float(x):.{prec}}' for x in lst)}]"
-
-
-def eval_func(
- func_val,
- pos,
- dim,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- value_type="scalar",
- broadcast=False,
-):
- """
- Evaluate a function on a mesh.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- func_val : :any:`callable` or :class:`float` or :any:`None`
- Function to be called or single value to be filled.
- Should have the signature f(x, [y, z, ...]) in case of callable.
- In case of a float, the field will be filled with a single value and
- in case of None, this value will be set to 0.
- pos : :class:`list`
- The position tuple, containing main direction and transversal
- directions (x, [y, z, ...]).
- dim : :class:`int`
- The spatial dimension.
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured'
- Default: 'unstructured'
- value_type : :class:`str`, optional
- Value type of the field. Either "scalar" or "vector".
- The default is "scalar".
- broadcast : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to return a single value, if a single value was given.
- Default: False
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Function values at the given points.
- """
- # care about scalar inputs
- func_val = 0 if func_val is None else func_val
- if broadcast and not callable(func_val) and np.size(func_val) == 1:
- return np.asarray(func_val, dtype=np.double).item()
- if not callable(func_val):
- func_val = _func_from_single_val(func_val, dim, value_type=value_type)
- # care about mesh and function call
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos, shape = format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim)
- pos = generate_grid(pos)
- else:
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape(dim, -1)
- shape = np.shape(pos[0])
- # prepend dimension if we have a vector field
- if value_type == "vector":
- shape = (dim,) + shape
- return np.reshape(func_val(*pos), shape)
-
-
-def _func_from_single_val(value, dim=None, value_type="scalar"):
- # care about broadcasting vector values for each dim
- v_d = dim if value_type == "vector" else 1 # value dim
- if v_d is None: # pragma: no cover
- raise ValueError("_func_from_single_val: dim needed for vector value.")
- value = np.asarray(value, dtype=np.double).ravel()[:v_d]
- # fill up vector valued output to dimension with last value
- value = np.pad(
- value, (0, v_d - len(value)), "constant", constant_values=value[-1]
- )
-
- def _f(*pos):
- # zip uses shortest len of iterables given (correct for scalar value)
- return np.concatenate(
- [
- np.full_like(p, val, dtype=np.double)
- for p, val in zip(pos, value)
- ]
- )
-
- return _f
diff --git a/src/gstools/tools/special.py b/src/gstools/tools/special.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 1457b736e..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/tools/special.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,257 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing special functions.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.tools.special
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- inc_gamma
- inc_gamma_low
- exp_int
- inc_beta
- tplstable_cor
- tpl_exp_spec_dens
- tpl_gau_spec_dens
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, E1101
-import numpy as np
-from scipy import special as sps
-
-__all__ = [
- "confidence_scaling",
- "inc_gamma",
- "inc_gamma_low",
- "exp_int",
- "inc_beta",
- "tplstable_cor",
- "tpl_exp_spec_dens",
- "tpl_gau_spec_dens",
-]
-
-
-# special functions ###########################################################
-
-
-def confidence_scaling(per=0.95):
- """
- Scaling of standard deviation to get the desired confidence interval.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- per : :class:`float`, optional
- Confidence level. The default is 0.95.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- Scale to multiply the standard deviation with.
- """
- return np.sqrt(2) * sps.erfinv(per)
-
-
-def inc_gamma(s, x):
- r"""Calculate the (upper) incomplete gamma function.
-
- Given by: :math:`\Gamma(s,x) = \int_x^{\infty} t^{s-1}\,e^{-t}\,{\rm d}t`
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- s : :class:`float`
- exponent in the integral
- x : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- input values
- """
- if np.isclose(s, 0):
- return sps.exp1(x)
- if np.isclose(s, np.around(s)) and s < -0.5:
- return x**s * sps.expn(int(1 - np.around(s)), x)
- if s < 0:
- return (inc_gamma(s + 1, x) - x**s * np.exp(-x)) / s
- return sps.gamma(s) * sps.gammaincc(s, x)
-
-
-def inc_gamma_low(s, x):
- r"""Calculate the lower incomplete gamma function.
-
- Given by: :math:`\gamma(s,x) = \int_0^x t^{s-1}\,e^{-t}\,{\rm d}t`
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- s : :class:`float`
- exponent in the integral
- x : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- input values
- """
- if np.isclose(s, np.around(s)) and s < 0.5:
- return np.full_like(x, np.inf, dtype=np.double)
- if s < 0:
- return (inc_gamma_low(s + 1, x) + x**s * np.exp(-x)) / s
- return sps.gamma(s) * sps.gammainc(s, x)
-
-
-def exp_int(s, x):
- r"""Calculate the exponential integral :math:`E_s(x)`.
-
- Given by: :math:`E_s(x) = \int_1^\infty \frac{e^{-xt}}{t^s}\,\mathrm dt`
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- s : :class:`float`
- exponent in the integral (should be > -100)
- x : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- input values
- """
- if np.isclose(s, 1):
- return sps.exp1(x)
- if np.isclose(s, np.around(s)) and s > -0.5:
- return sps.expn(int(np.around(s)), x)
- x = np.asarray(x, dtype=np.double)
- x_neg = x < 0
- x = np.abs(x)
- x_compare = x ** min((10, max(((1 - s), 1))))
- res = np.empty_like(x)
- # use asymptotic behavior for zeros
- x_zero = np.isclose(x_compare, 0, atol=1e-20)
- x_inf = x > max(30, -s / 2) # function is like exp(-x)*(1/x + s/x^2)
- x_fin = np.logical_not(np.logical_or(x_zero, x_inf))
- x_fin_pos = np.logical_and(x_fin, np.logical_not(x_neg))
- if s > 1.0: # limit at x=+0
- res[x_zero] = 1.0 / (s - 1.0)
- else:
- res[x_zero] = np.inf
- res[x_inf] = np.exp(-x[x_inf]) * (x[x_inf] ** -1 - s * x[x_inf] ** -2)
- res[x_fin_pos] = inc_gamma(1 - s, x[x_fin_pos]) * x[x_fin_pos] ** (s - 1)
- res[x_neg] = np.nan # nan for x < 0
- return res
-
-
-def inc_beta(a, b, x):
- r"""Calculate the incomplete Beta function.
-
- Given by: :math:`B(a,b;\,x) = \int_0^x t^{a-1}\,(1-t)^{b-1}\,dt`
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- a : :class:`float`
- first exponent in the integral
- b : :class:`float`
- second exponent in the integral
- x : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- input values
- """
- return sps.betainc(a, b, x) * sps.beta(a, b)
-
-
-def tplstable_cor(r, len_scale, hurst, alpha):
- r"""Calculate the correlation function of the TPLStable model.
-
- Given by the following correlation function:
-
- .. math::
- \rho(r) =
- \frac{2H}{\alpha} \cdot
- E_{1+\frac{2H}{\alpha}}
- \left(\left(\frac{r}{\ell}\right)^{\alpha} \right)
-
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- r : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- input values
- len_scale : :class:`float`
- length-scale of the model.
- hurst : :class:`float`
- Hurst coefficient of the power law.
- alpha : :class:`float`, optional
- Shape parameter of the stable model.
- """
- r = np.asarray(np.abs(r / len_scale), dtype=np.double)
- r[np.isclose(r, 0)] = 0 # hack to prevent numerical errors
- res = np.ones_like(r)
- res[r > 0] = (2 * hurst / alpha) * exp_int(
- 1 + 2 * hurst / alpha, (r[r > 0]) ** alpha
- )
- return res
-
-
-def tpl_exp_spec_dens(k, dim, len_scale, hurst, len_low=0.0):
- r"""
- Spectral density of the TPLExponential covariance model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- k : :class:`float`
- Radius of the phase: :math:`k=\left\Vert\mathbf{k}\right\Vert`
- dim : :class:`int`
- Dimension of the model.
- len_scale : :class:`float`
- Length scale of the model.
- hurst : :class:`float`
- Hurst coefficient of the power law.
- len_low : :class:`float`, optional
- The lower length scale truncation of the model.
- Default: 0.0
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- spectral density of the TPLExponential model
- """
- if np.isclose(len_low, 0.0):
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- z = (k * len_scale) ** 2
- a = hurst + dim / 2.0
- b = hurst + 0.5
- c = hurst + dim / 2.0 + 1.0
- d = dim / 2.0 + 0.5
- fac = len_scale**dim * hurst * sps.gamma(d) / (np.pi**d * a)
- return fac / (1.0 + z) ** a * sps.hyp2f1(a, b, c, z / (1.0 + z))
- fac_up = (len_scale + len_low) ** (2 * hurst)
- spec_up = tpl_exp_spec_dens(k, dim, len_scale + len_low, hurst)
- fac_low = len_low ** (2 * hurst)
- spec_low = tpl_exp_spec_dens(k, dim, len_low, hurst)
- return (fac_up * spec_up - fac_low * spec_low) / (fac_up - fac_low)
-
-
-def tpl_gau_spec_dens(k, dim, len_scale, hurst, len_low=0.0):
- r"""
- Spectral density of the TPLGaussian covariance model.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- k : :class:`float`
- Radius of the phase: :math:`k=\left\Vert\mathbf{k}\right\Vert`
- dim : :class:`int`
- Dimension of the model.
- len_scale : :class:`float`
- Length scale of the model.
- hurst : :class:`float`
- Hurst coefficient of the power law.
- len_low : :class:`float`, optional
- The lower length scale truncation of the model.
- Default: 0.0
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`float`
- spectral density of the TPLExponential model
- """
- if np.isclose(len_low, 0.0):
- k = np.asarray(k, dtype=np.double)
- z = np.array((k * len_scale / 2.0) ** 2)
- res = np.empty_like(z)
- z_gz = z > 0.1 # greater zero
- z_nz = np.logical_not(z_gz) # near zero
- a = hurst + dim / 2.0
- fac = (len_scale / 2.0) ** dim * hurst / np.pi ** (dim / 2.0)
- res[z_gz] = fac * inc_gamma_low(a, z[z_gz]) / z[z_gz] ** a
- # first order approximation for z near zero
- res[z_nz] = fac * (1.0 / a - z[z_nz] / (a + 1.0))
- return res
- fac_up = (len_scale + len_low) ** (2 * hurst)
- spec_up = tpl_gau_spec_dens(k, dim, len_scale + len_low, hurst)
- fac_low = len_low ** (2 * hurst)
- spec_low = tpl_gau_spec_dens(k, dim, len_low, hurst)
- return (fac_up * spec_up - fac_low * spec_low) / (fac_up - fac_low)
diff --git a/src/gstools/transform/__init__.py b/src/gstools/transform/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b2e6ce4f2..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/transform/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,93 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing transformations to post-process normal fields.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.transform
-
-Wrapper
-^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- apply
-
-Field Transformations
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- binary
- discrete
- boxcox
- zinnharvey
- normal_force_moments
- normal_to_lognormal
- normal_to_uniform
- normal_to_arcsin
- normal_to_uquad
- apply_function
-
-Array Transformations
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- array_discrete
- array_boxcox
- array_zinnharvey
- array_force_moments
- array_to_lognormal
- array_to_uniform
- array_to_arcsin
- array_to_uquad
-
-----
-"""
-
-from gstools.transform.array import (
- array_boxcox,
- array_discrete,
- array_force_moments,
- array_to_arcsin,
- array_to_lognormal,
- array_to_uniform,
- array_to_uquad,
- array_zinnharvey,
-)
-from gstools.transform.field import (
- apply,
- apply_function,
- binary,
- boxcox,
- discrete,
- normal_force_moments,
- normal_to_arcsin,
- normal_to_lognormal,
- normal_to_uniform,
- normal_to_uquad,
- zinnharvey,
-)
-
-__all__ = [
- "apply",
- "apply_function",
- "binary",
- "discrete",
- "boxcox",
- "zinnharvey",
- "normal_force_moments",
- "normal_to_lognormal",
- "normal_to_uniform",
- "normal_to_arcsin",
- "normal_to_uquad",
- "array_discrete",
- "array_boxcox",
- "array_zinnharvey",
- "array_force_moments",
- "array_to_lognormal",
- "array_to_uniform",
- "array_to_arcsin",
- "array_to_uquad",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/transform/array.py b/src/gstools/transform/array.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 87564edf0..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/transform/array.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,360 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing array transformations.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.transform.array
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-Transformations
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- array_discrete
- array_boxcox
- array_zinnharvey
- array_force_moments
- array_to_lognormal
- array_to_uniform
- array_to_arcsin
- array_to_uquad
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, C0123, R0911
-from warnings import warn
-
-import numpy as np
-from scipy.special import erf, erfinv
-
-__all__ = [
- "array_discrete",
- "array_boxcox",
- "array_zinnharvey",
- "array_force_moments",
- "array_to_lognormal",
- "array_to_uniform",
- "array_to_arcsin",
- "array_to_uquad",
-]
-
-
-def array_discrete(
- field, values, thresholds="arithmetic", mean=None, var=None
-):
- """
- Discrete transformation.
-
- After this transformation, the field has only `len(values)` discrete
- values.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- values : :any:`numpy.ndarray`
- The discrete values the field will take
- thresholds : :class:`str` or :any:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the thresholds, where the value classes are separated
- possible values are:
- * "arithmetic": the mean of the 2 neighbouring values
- * "equal": divide the field into equal parts
- * an array of explicitly given thresholds
- Default: "arithmetic"
- mean : :class:`float`or :any:`None`
- Mean of the field for "equal" thresholds. Default: np.mean(field)
- var : :class:`float`or :any:`None`
- Variance of the field for "equal" thresholds. Default: np.var(field)
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- if thresholds == "arithmetic":
- # just in case, sort the values
- values = np.sort(values)
- thresholds = (values[1:] + values[:-1]) / 2
- elif thresholds == "equal":
- mean = np.mean(field) if mean is None else float(mean)
- var = np.var(field) if var is None else float(var)
- values = np.asarray(values)
- n = len(values)
- p = np.arange(1, n) / n # n-1 equal subdivisions of [0, 1]
- rescale = np.sqrt(var * 2)
- # use quantile of the normal distribution to get equal ratios
- thresholds = mean + rescale * erfinv(2 * p - 1)
- else:
- if len(values) != len(thresholds) + 1:
- raise ValueError(
- "discrete transformation: len(values) != len(thresholds) + 1"
- )
- values = np.asarray(values)
- thresholds = np.asarray(thresholds)
- # check thresholds
- if not np.all(thresholds[:-1] < thresholds[1:]):
- raise ValueError(
- "discrete transformation: thresholds need to be ascending"
- )
- # use a separate result so the intermediate results are not affected
- result = np.empty_like(field)
- # handle edge cases
- result[field <= thresholds[0]] = values[0]
- result[field > thresholds[-1]] = values[-1]
- for i, value in enumerate(values[1:-1]):
- result[
- np.logical_and(thresholds[i] < field, field <= thresholds[i + 1])
- ] = value
- return result
-
-
-def array_boxcox(field, lmbda=1, shift=0):
- """
- (Inverse) Box-Cox transformation to denormalize data.
-
- After this transformation, the again Box-Cox transformed field is normal
- distributed.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_transform#Box%E2%80%93Cox_transformation
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- The lambda parameter of the Box-Cox transformation.
- For ``lmbda=0`` one obtains the log-normal transformation.
- Default: ``1``
- shift : :class:`float`, optional
- The shift parameter from the two-parametric Box-Cox transformation.
- The field will be shifted by that value before transformation.
- Default: ``0``
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- result = field + shift
- if np.isclose(lmbda, 0):
- return array_to_lognormal(result)
- if np.min(result) < -1 / lmbda:
- warn("Box-Cox: Some values will be cut off!")
- return (np.maximum(lmbda * result + 1, 0)) ** (1 / lmbda)
-
-
-def array_zinnharvey(field, conn="high", mean=None, var=None):
- """
- Zinn and Harvey transformation to connect low or high values.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- conn : :class:`str`, optional
- Desired connectivity. Either "low" or "high".
- Default: "high"
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Mean of the given field. If None is given, the mean will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- var : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Variance of the given field.
- If None is given, the variance will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- mean = np.mean(field) if mean is None else float(mean)
- var = np.var(field) if var is None else float(var)
- result = np.abs((field - mean) / np.sqrt(var))
- result = np.sqrt(2) * erfinv(2 * erf(result / np.sqrt(2)) - 1)
- if conn == "high":
- result = -result
- return result * np.sqrt(var) + mean
-
-
-def array_force_moments(field, mean=0, var=1):
- """
- Force moments of a normal distributed field.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- mean : :class:`float`, optional
- Desired mean of the field.
- Default: 0
- var : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Desired variance of the field.
- Default: 1
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- var_in = np.var(field)
- mean_in = np.mean(field)
- rescale = np.sqrt(var / var_in)
- return rescale * (field - mean_in) + mean
-
-
-def array_to_lognormal(field):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to log-normal distribution.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- return np.exp(field)
-
-
-def array_to_uniform(field, mean=None, var=None, low=0.0, high=1.0):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to uniform distribution on [low, high].
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Mean of the given field. If None is given, the mean will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- var : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Variance of the given field.
- If None is given, the variance will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- low : :class:`float`, optional
- Lower bound for the uniform distribution.
- Default: 0.0
- high : :class:`float`, optional
- Upper bound for the uniform distribution.
- Default: 1.0
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- mean = np.mean(field) if mean is None else float(mean)
- var = np.var(field) if var is None else float(var)
- return (
- 0.5 * (1 + erf((field - mean) / np.sqrt(2 * var))) * (high - low) + low
- )
-
-
-def array_to_arcsin(field, mean=None, var=None, a=None, b=None):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to arcsin distribution.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcsine_distribution
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Mean of the given field. If None is given, the mean will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- var : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Variance of the given field.
- If None is given, the mean will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- a : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter a of the arcsin distribution (lower bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- b : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter b of the arcsin distribution (upper bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- mean = np.mean(field) if mean is None else float(mean)
- var = np.var(field) if var is None else float(var)
- a = mean - np.sqrt(2.0 * var) if a is None else float(a)
- b = mean + np.sqrt(2.0 * var) if b is None else float(b)
- return _uniform_to_arcsin(array_to_uniform(field, mean, var), a, b)
-
-
-def array_to_uquad(field, mean=None, var=None, a=None, b=None):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to U-quadratic distribution.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U-quadratic_distribution
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Normal distributed values.
- mean : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Mean of the given field. If None is given, the mean will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- var : :class:`float` or :any:`None`, optional
- Variance of the given field.
- If None is given, the variance will be calculated.
- Default: :any:`None`
- a : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter a of the U-quadratic distribution (lower bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- b : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter b of the U-quadratic distribution (upper bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- mean = np.mean(field) if mean is None else float(mean)
- var = np.var(field) if var is None else float(var)
- a = mean - np.sqrt(5.0 / 3.0 * var) if a is None else float(a)
- b = mean + np.sqrt(5.0 / 3.0 * var) if b is None else float(b)
- return _uniform_to_uquad(array_to_uniform(field, mean, var), a, b)
-
-
-def _uniform_to_arcsin(field, a=0, b=1):
- """
- PPF of your desired distribution.
-
- The PPF is the inverse of the CDF and is used to sample a distribution
- from uniform distributed values on [0, 1]
-
- in this case: the arcsin distribution
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcsine_distribution
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- return (b - a) * np.sin(np.pi * 0.5 * field) ** 2 + a
-
-
-def _uniform_to_uquad(field, a=0, b=1):
- """
- PPF of your desired distribution.
-
- The PPF is the inverse of the CDF and is used to sample a distribution
- from uniform distributed values on [0, 1]
-
- in this case: the U-quadratic distribution
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U-quadratic_distribution
- """
- field = np.asarray(field)
- al = 12 / (b - a) ** 3
- be = (a + b) / 2
- ga = (a - b) ** 3 / 8
- y_raw = 3 * field / al + ga
- result = np.zeros_like(y_raw)
- result[y_raw > 0] = y_raw[y_raw > 0] ** (1 / 3)
- result[y_raw < 0] = -((-y_raw[y_raw < 0]) ** (1 / 3))
- return result + be
diff --git a/src/gstools/transform/field.py b/src/gstools/transform/field.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a123e7987..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/transform/field.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,725 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing field transformations.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.transform.field
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-Wrapper
-^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- apply
-
-Transformations
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- apply_function
- binary
- discrete
- boxcox
- zinnharvey
- normal_force_moments
- normal_to_lognormal
- normal_to_uniform
- normal_to_arcsin
- normal_to_uquad
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0103, C0123, R0911, R1735
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.normalizer import (
- Normalizer,
- apply_mean_norm_trend,
- remove_trend_norm_mean,
-)
-from gstools.transform.array import (
- array_boxcox,
- array_discrete,
- array_force_moments,
- array_to_arcsin,
- array_to_lognormal,
- array_to_uniform,
- array_to_uquad,
- array_zinnharvey,
-)
-
-__all__ = [
- "apply",
- "apply_function",
- "binary",
- "discrete",
- "boxcox",
- "zinnharvey",
- "normal_force_moments",
- "normal_to_lognormal",
- "normal_to_uniform",
- "normal_to_arcsin",
- "normal_to_uquad",
-]
-
-
-def _pre_process(fld, data, keep_mean):
- return remove_trend_norm_mean(
- pos=fld.pos,
- field=data,
- mean=None if keep_mean else fld.mean,
- normalizer=fld.normalizer,
- trend=fld.trend,
- mesh_type=fld.mesh_type,
- value_type=fld.value_type,
- check_shape=False,
- )
-
-
-def _post_process(fld, data, keep_mean):
- return apply_mean_norm_trend(
- pos=fld.pos,
- field=data,
- mean=None if keep_mean else fld.mean,
- normalizer=fld.normalizer,
- trend=fld.trend,
- mesh_type=fld.mesh_type,
- value_type=fld.value_type,
- check_shape=False,
- )
-
-
-def _check_for_default_normal(fld):
- if not type(fld.normalizer) == Normalizer:
- raise ValueError(
- "transform: need a normal field but there is a normalizer defined"
- )
- if fld.trend is not None:
- raise ValueError(
- "transform: need a normal field but there is a trend defined"
- )
- if callable(fld.mean) or fld.mean is None:
- raise ValueError(
- "transform: need a normal field but mean is not constant"
- )
-
-
-def apply(fld, method, field="field", store=True, process=False, **kwargs):
- """
- Apply field transformation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- method : :class:`str`
- Method to use.
- See :py:mod:`gstools.transform` for available transformations.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or with a specified name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to selected method.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When method is unknown.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- kwargs["field"] = field
- kwargs["store"] = store
- kwargs["process"] = process
- method = str(method) # ensure method is a string
- if method == "binary":
- return binary(fld, **kwargs)
- if method == "discrete":
- return discrete(fld, **kwargs)
- if method == "boxcox":
- return boxcox(fld, **kwargs)
- if method == "zinnharvey":
- return zinnharvey(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("force_moments"):
- return normal_force_moments(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("lognormal"):
- return normal_to_lognormal(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("uniform"):
- return normal_to_uniform(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("arcsin"):
- return normal_to_arcsin(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("uquad"):
- return normal_to_uquad(fld, **kwargs)
- if method.endswith("function"):
- return apply_function(fld, **kwargs)
- raise ValueError(f"transform.apply: unknown method '{method}'")
-
-
-def apply_function(
- fld,
- function,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
- **kwargs,
-):
- """
- Apply function as field transformation.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- function : :any:`callable`
- Function to use.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
- **kwargs
- Keyword arguments forwarded to given function.
-
- Raises
- ------
- ValueError
- When function is not callable.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not callable(function):
- raise ValueError("transform.apply_function: function not a 'callable'")
- data = fld[field]
- name, save = fld.get_store_config(store, default=field)
- if process:
- data = _pre_process(fld, data, keep_mean=keep_mean)
- data = function(data, **kwargs)
- if process:
- data = _post_process(fld, data, keep_mean=keep_mean)
- return fld.post_field(data, name=name, process=False, save=save)
-
-
-def binary(
- fld,
- divide=None,
- upper=None,
- lower=None,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Binary transformation.
-
- After this transformation, the field only has two values.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- divide : :class:`float`, optional
- The dividing value.
- Default: ``fld.mean``
- upper : :class:`float`, optional
- The resulting upper value of the field.
- Default: ``mean + sqrt(fld.model.sill)``
- lower : :class:`float`, optional
- The resulting lower value of the field.
- Default: ``mean - sqrt(fld.model.sill)``
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process and divide is None:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- mean = 0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean
- divide = mean if divide is None else divide
- upper = mean + np.sqrt(fld.model.sill) if upper is None else upper
- lower = mean - np.sqrt(fld.model.sill) if lower is None else lower
- kw = dict(
- values=[lower, upper],
- thresholds=[divide],
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_discrete,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def discrete(
- fld,
- values,
- thresholds="arithmetic",
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Discrete transformation.
-
- After this transformation, the field has only `len(values)` discrete
- values.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- values : :any:`numpy.ndarray`
- The discrete values the field will take
- thresholds : :class:`str` or :any:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the thresholds, where the value classes are separated
- possible values are:
- * "arithmetic": the mean of the 2 neighbouring values
- * "equal": divide the field into equal parts
- * an array of explicitly given thresholds
- Default: "arithmetic"
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process and thresholds == "equal":
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- values=values,
- thresholds=thresholds,
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean,
- var=fld.model.sill,
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_discrete,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def boxcox(
- fld,
- lmbda=1,
- shift=0,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- (Inverse) Box-Cox transformation to denormalize data.
-
- After this transformation, the again Box-Cox transformed field is normal
- distributed.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Power_transform#Box%E2%80%93Cox_transformation
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- lmbda : :class:`float`, optional
- The lambda parameter of the Box-Cox transformation.
- For ``lmbda=0`` one obtains the log-normal transformation.
- Default: ``1``
- shift : :class:`float`, optional
- The shift parameter from the two-parametric Box-Cox transformation.
- The field will be shifted by that value before transformation.
- Default: ``0``
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- kw = dict(lmbda=lmbda, shift=shift)
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_boxcox,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def zinnharvey(
- fld,
- conn="high",
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Zinn and Harvey transformation to connect low or high values.
-
- After this transformation, the field is still normal distributed.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- conn : :class:`str`, optional
- Desired connectivity. Either "low" or "high".
- Default: "high"
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- conn=conn,
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean,
- var=fld.model.sill,
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_zinnharvey,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def normal_force_moments(
- fld,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Force moments of a normal distributed field.
-
- After this transformation, the field is still normal distributed.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean, var=fld.model.sill
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_force_moments,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def normal_to_lognormal(
- fld, field="field", store=True, process=False, keep_mean=True
-):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to log-normal distribution.
-
- After this transformation, the field is log-normal distributed.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_to_lognormal,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- )
-
-
-def normal_to_uniform(
- fld,
- low=0.0,
- high=1.0,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to uniform distribution on [0, 1].
-
- After this transformation, the field is uniformly distributed on [0, 1].
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- low : :class:`float`, optional
- Lower bound for the uniform distribution.
- Default: 0.0
- high : :class:`float`, optional
- Upper bound for the uniform distribution.
- Default: 1.0
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
- """
- if not process:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean,
- var=fld.model.sill,
- low=low,
- high=high,
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_to_uniform,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def normal_to_arcsin(
- fld,
- a=None,
- b=None,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to the bimodal arcsin distribution.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Arcsine_distribution
-
- After this transformation, the field is arcsin-distributed on [a, b].
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- a : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter a of the arcsin distribution (lower bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- b : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter b of the arcsin distribution (upper bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean,
- var=fld.model.sill,
- a=a,
- b=b,
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_to_arcsin,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
-
-
-def normal_to_uquad(
- fld,
- a=None,
- b=None,
- field="field",
- store=True,
- process=False,
- keep_mean=True,
-):
- """
- Transform normal distribution to U-quadratic distribution.
-
- See: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/U-quadratic_distribution
-
- After this transformation, the field is U-quadratic-distributed on [a, b].
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- fld : :any:`Field`
- Field class containing a generated field.
- a : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter a of the U-quadratic distribution (lower bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- b : :class:`float`, optional
- Parameter b of the U-quadratic distribution (upper bound).
- Default: keep mean and variance
- field : :class:`str`, optional
- Name of field to be transformed. The default is "field".
- store : :class:`str` or :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to store field inplace (True/False) or under a given name.
- The default is True.
- process : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to process in/out fields with trend, normalizer and mean
- of given Field instance. The default is False.
- keep_mean : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to keep the mean of the field if process=True.
- The default is True.
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- Transformed field.
- """
- if not process:
- _check_for_default_normal(fld)
- kw = dict(
- mean=0.0 if process and not keep_mean else fld.mean,
- var=fld.model.sill,
- a=a,
- b=b,
- )
- return apply_function(
- fld=fld,
- function=array_to_uquad,
- field=field,
- store=store,
- process=process,
- keep_mean=keep_mean,
- **kw,
- )
diff --git a/src/gstools/variogram/__init__.py b/src/gstools/variogram/__init__.py
deleted file mode 100644
index d8a5b238d..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/variogram/__init__.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,40 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for estimating and fitting variograms.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.variogram
-
-Variogram estimation
-^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- vario_estimate
- vario_estimate_axis
-
-Binning
-^^^^^^^
-
-.. autosummary::
- :toctree:
-
- standard_bins
-
-----
-"""
-
-from gstools.variogram.binning import standard_bins
-from gstools.variogram.variogram import (
- vario_estimate,
- vario_estimate_axis,
- vario_estimate_structured,
- vario_estimate_unstructured,
-)
-
-__all__ = [
- "vario_estimate",
- "vario_estimate_axis",
- "vario_estimate_unstructured",
- "vario_estimate_structured",
- "standard_bins",
-]
diff --git a/src/gstools/variogram/binning.py b/src/gstools/variogram/binning.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 86d4fdc27..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/variogram/binning.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,104 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing binning routines.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.variogram.binning
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- standard_bins
-"""
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools.tools import RADIAN_SCALE
-from gstools.tools.geometric import (
- chordal_to_great_circle,
- format_struct_pos_dim,
- generate_grid,
- latlon2pos,
-)
-
-__all__ = ["standard_bins"]
-
-
-def _sturges(pnt_cnt):
- return int(np.ceil(2 * np.log2(pnt_cnt) + 1))
-
-
-def standard_bins(
- pos=None,
- dim=2,
- latlon=False,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- bin_no=None,
- max_dist=None,
- geo_scale=RADIAN_SCALE,
-):
- r"""
- Get standard binning.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`, optional
- the position tuple, containing either the point coordinates (x, y, ...)
- or the axes descriptions (for mesh_type='structured')
- dim : :class:`int`, optional
- Field dimension.
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the data is representing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude. When using this, the estimator will
- use great-circle distance for variogram estimation.
- Note, that only an isotropic variogram can be estimated and a
- ValueError will be raised, if a direction was specified.
- Bin edges need to be given in radians in this case.
- Default: False
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured', indicates whether the pos tuple
- describes the axis or the point coordinates.
- Default: `'unstructured'`
- bin_no: :class:`int`, optional
- number of bins to create. If None is given, will be determined by
- Sturges' rule from the number of points.
- Default: None
- max_dist: :class:`float`, optional
- Cut of length for the bins. If None is given, it will be set to one
- third of the box-diameter from the given points.
- Default: None
- geo_scale : :class:`float`, optional
- Geographic unit scaling in case of latlon coordinates to get a
- meaningful bins unit.
- By default, bins are assumed to be in radians with latlon=True.
- Can be set to :any:`KM_SCALE` to have bins in km or
- :any:`DEGREE_SCALE` to have bins in degrees.
- Default: :any:`RADIAN_SCALE`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The generated bin edges.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Internally uses double precision and also returns doubles.
- """
- dim = 2 if latlon else int(dim)
- if bin_no is None or max_dist is None:
- if pos is None:
- raise ValueError("standard_bins: no pos tuple given.")
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos = generate_grid(format_struct_pos_dim(pos, dim)[0])
- else:
- pos = np.asarray(pos, dtype=np.double).reshape(dim, -1)
- pos = latlon2pos(pos, radius=geo_scale) if latlon else pos
- pnt_cnt = len(pos[0])
- box = []
- for axis in pos:
- box.append([np.min(axis), np.max(axis)])
- box = np.asarray(box)
- diam = np.linalg.norm(box[:, 0] - box[:, 1])
- # convert diameter to great-circle distance if using latlon
- diam = chordal_to_great_circle(diam, geo_scale) if latlon else diam
- bin_no = _sturges(pnt_cnt) if bin_no is None else int(bin_no)
- max_dist = diam / 3 if max_dist is None else float(max_dist)
- return np.linspace(0, max_dist, num=bin_no + 1, dtype=np.double)
diff --git a/src/gstools/variogram/variogram.py b/src/gstools/variogram/variogram.py
deleted file mode 100644
index afcf336f4..000000000
--- a/src/gstools/variogram/variogram.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,499 +0,0 @@
-"""
-GStools subpackage providing tools for estimating and fitting variograms.
-
-.. currentmodule:: gstools.variogram.variogram
-
-The following functions are provided
-
-.. autosummary::
- vario_estimate
- vario_estimate_axis
-"""
-
-# pylint: disable=C0412
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import config
-from gstools.normalizer.tools import remove_trend_norm_mean
-from gstools.tools import RADIAN_SCALE
-from gstools.tools.geometric import (
- ang2dir,
- format_struct_pos_shape,
- format_unstruct_pos_shape,
- generate_grid,
-)
-from gstools.variogram.binning import standard_bins
-
-if config.USE_RUST: # pragma: no cover
- # pylint: disable=E0401
- from gstools_core import variogram_directional as directional
- from gstools_core import variogram_ma_structured as ma_structured
- from gstools_core import variogram_structured as structured
- from gstools_core import variogram_unstructured as unstructured
-else:
- from gstools.variogram.estimator import (
- directional,
- ma_structured,
- structured,
- unstructured,
- )
-
-__all__ = [
- "vario_estimate",
- "vario_estimate_axis",
- "vario_estimate_unstructured",
- "vario_estimate_structured",
-]
-
-
-AXIS = ["x", "y", "z"]
-AXIS_DIR = {"x": 0, "y": 1, "z": 2}
-
-
-def _set_estimator(estimator):
- """Translate the verbose Python estimator identifier to single char."""
- if estimator.lower() == "matheron":
- cython_estimator = "m"
- elif estimator.lower() == "cressie":
- cython_estimator = "c"
- else:
- raise ValueError(f"Unknown variogram estimator function: {estimator}")
- return cython_estimator
-
-
-def _separate_dirs_test(direction, angles_tol):
- """Check if given directions are separated."""
- if direction is None or direction.shape[0] < 2:
- return True
- separate_dirs = True
- for i in range(direction.shape[0] - 1):
- for j in range(i + 1, direction.shape[0]):
- s_prod = np.minimum(np.abs(np.dot(direction[i], direction[j])), 1)
- separate_dirs &= np.arccos(s_prod) >= 2 * angles_tol
- # gstools-core doesn't like the type `numpy.bool_`
- return bool(separate_dirs)
-
-
-def vario_estimate(
- pos,
- field,
- bin_edges=None,
- sampling_size=None,
- sampling_seed=None,
- estimator="matheron",
- latlon=False,
- direction=None,
- angles=None,
- angles_tol=np.pi / 8,
- bandwidth=None,
- no_data=np.nan,
- mask=np.ma.nomask,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- return_counts=False,
- mean=None,
- normalizer=None,
- trend=None,
- fit_normalizer=False,
- geo_scale=RADIAN_SCALE,
- **std_bins,
-):
- r"""
- Estimates the empirical variogram.
-
- The algorithm calculates following equation:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r_k) = \frac{1}{2 N(r_k)} \sum_{i=1}^{N(r_k)} (z(\mathbf x_i) -
- z(\mathbf x_i'))^2 \; ,
-
- with :math:`r_k \leq \| \mathbf x_i - \mathbf x_i' \| < r_{k+1}`
- being the bins.
-
- Or if the estimator "cressie" was chosen:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r_k) = \frac{\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{N(r_k)}\sum_{i=1}^{N(r_k)}
- \left|z(\mathbf x_i) - z(\mathbf x_i')\right|^{0.5}\right)^4}
- {0.457 + 0.494 / N(r_k) + 0.045 / N^2(r_k)} \; ,
-
- with :math:`r_k \leq \| \mathbf x_i - \mathbf x_i' \| < r_{k+1}`
- being the bins.
- The Cressie estimator is more robust to outliers [Webster2007]_.
-
- By providing `direction` vector[s] or angles, a directional variogram
- can be calculated. If multiple directions are given, a set of variograms
- will be returned.
- Directional bining is controlled by a given angle tolerance (`angles_tol`)
- and an optional `bandwidth`, that truncates the width of the search band
- around the given direction[s].
-
- To reduce the calculation time, `sampling_size` could be passed to sample
- down the number of field points.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- pos : :class:`list`
- the position tuple, containing either the point coordinates (x, y, ...)
- or the axes descriptions (for mesh_type='structured')
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The spatially distributed data.
- Can also be of type :class:`numpy.ma.MaskedArray` to use masked values.
- You can pass a list of fields, that will be used simultaneously.
- This could be helpful, when there are multiple realizations at the
- same points, with the same statistical properties.
- bin_edges : :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the bins on which the variogram will be calculated.
- If :any:`None` are given, standard bins provided by the
- :any:`standard_bins` routine will be used. Default: :any:`None`
- sampling_size : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- for large input data, this method can take a long
- time to compute the variogram, therefore this argument specifies
- the number of data points to sample randomly
- Default: :any:`None`
- sampling_seed : :class:`int` or :any:`None`, optional
- seed for samples if sampling_size is given.
- Default: :any:`None`
- estimator : :class:`str`, optional
- the estimator function, possible choices:
-
- * "matheron": the standard method of moments of Matheron
- * "cressie": an estimator more robust to outliers
-
- Default: "matheron"
- latlon : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether the data is representing 2D fields on earths surface described
- by latitude and longitude. When using this, the estimator will
- use great-circle distance for variogram estimation.
- Note, that only an isotropic variogram can be estimated and a
- ValueError will be raised, if a direction was specified.
- Bin edges need to be given in radians in this case.
- Default: False
- direction : :class:`list` of :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- directions to evaluate a directional variogram.
- Angular tolerance is given by `angles_tol`.
- bandwidth to cut off how wide the search for point pairs should be
- is given by `bandwidth`.
- You can provide multiple directions at once to get one variogram
- for each direction.
- For a single direction you can also use the `angles` parameter,
- to provide the direction by its spherical coordinates.
- Default: :any:`None`
- angles : :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- the angles of the main axis to calculate the variogram for in radians
- angle definitions from ISO standard 80000-2:2009
- for 1d this parameter will have no effect at all
- for 2d supply one angle which is
- azimuth :math:`\varphi` (ccw from +x in xy plane)
- for 3d supply two angles which are
- azimuth :math:`\varphi` (ccw from +x in xy plane)
- and inclination :math:`\theta` (cw from +z).
- Can be used instead of direction.
- Default: :any:`None`
- angles_tol : class:`float`, optional
- the tolerance around the variogram angle to count a point as being
- within this direction from another point (the angular tolerance around
- the directional vector given by angles)
- Default: `np.pi/8` = 22.5°
- bandwidth : class:`float`, optional
- bandwidth to cut off the angular tolerance for directional variograms.
- If None is given, only the `angles_tol` parameter will control the
- point selection.
- Default: :any:`None`
- no_data : :class:`float`, optional
- Value to identify missing data in the given field.
- Default: `numpy.nan`
- mask : :class:`numpy.ndarray` of :class:`bool`, optional
- Mask to deselect data in the given field.
- Default: :any:`numpy.ma.nomask`
- mesh_type : :class:`str`, optional
- 'structured' / 'unstructured', indicates whether the pos tuple
- describes the axis or the point coordinates.
- Default: `'unstructured'`
- return_counts: :class:`bool`, optional
- if set to true, this function will also return the number of data
- points found at each lag distance as a third return value
- Default: False
- mean : :class:`float`, optional
- mean value used to shift normalized input data.
- Can also be a callable. The default is None.
- normalizer : :any:`None` or :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- Normalizer to be applied to the input data to gain normality.
- The default is None.
- trend : :any:`None` or :class:`float` or :any:`callable`, optional
- A callable trend function. Should have the signature: f(x, [y, z, ...])
- If no normalizer is applied, this behaves equal to 'mean'.
- The default is None.
- fit_normalizer : :class:`bool`, optional
- Whether to fit the data-normalizer to the given (detrended) field.
- Default: False
- geo_scale : :class:`float`, optional
- Geographic unit scaling in case of latlon coordinates to get a
- meaningful bins unit.
- By default, bins are assumed to be in radians with latlon=True.
- Can be set to :any:`KM_SCALE` to have bins in km or
- :any:`DEGREE_SCALE` to have bins in degrees.
- Default: :any:`RADIAN_SCALE`
- **std_bins
- Optional arguments that are forwarded to the :any:`standard_bins` routine
- if no bins are given (bin_no, max_dist).
-
- Returns
- -------
- bin_centers : (n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The bin centers.
- gamma : (n) or (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- The estimated variogram values at bin centers.
- Is stacked if multiple `directions` (d>1) are given.
- counts : (n) or (d, n), :class:`numpy.ndarray`, optional
- The number of point pairs found for each bin.
- Is stacked if multiple `directions` (d>1) are given.
- Only provided if `return_counts` is True.
- normalizer : :any:`Normalizer`, optional
- The fitted normalizer for the given data.
- Only provided if `fit_normalizer` is True.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Internally uses double precision and also returns doubles.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
- if bin_edges is not None:
- bin_edges = np.atleast_1d(np.asarray(bin_edges, dtype=np.double))
- bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2.0
- # allow multiple fields at same positions (ndmin=2: first axis -> field ID)
- # need to convert to ma.array, since list of ma.array is not recognised
- field = np.ma.array(field, ndmin=2, dtype=np.double, copy=True)
- masked = np.ma.is_masked(field) or np.any(mask)
- # catch special case if everything is masked
- if masked and np.all(mask):
- bin_centers = np.empty(0) if bin_edges is None else bin_centers
- estimates = np.zeros_like(bin_centers)
- if return_counts:
- return bin_centers, estimates, np.zeros_like(estimates, dtype=int)
- return bin_centers, estimates
- if not masked:
- field = field.filled()
- # check mesh shape
- if mesh_type != "unstructured":
- pos, __, dim = format_struct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=True
- )
- pos = generate_grid(pos)
- else:
- pos, __, dim = format_unstruct_pos_shape(
- pos, field.shape, check_stacked_shape=True
- )
- if latlon and dim != 2:
- raise ValueError("Variogram: given field needs to be 2D for lat-lon.")
- # prepare the field
- pnt_cnt = len(pos[0])
- field = field.reshape((-1, pnt_cnt))
- # apply mask if wanted
- if masked:
- # if fields have different masks, take the minimal common mask
- # given mask will be applied in addition
- # selected region is the inverted masked (unmasked values)
- if np.size(mask) > 1: # not only np.ma.nomask
- select = np.invert(
- np.logical_or(
- np.reshape(mask, pnt_cnt), np.all(field.mask, axis=0)
- )
- )
- else:
- select = np.invert(np.all(field.mask, axis=0))
- pos = pos[:, select]
- field.fill_value = np.nan # use no-data val. for remaining masked vals
- field = field[:, select].filled() # convert to ndarray
- select = mask = None # free space
- # set no_data values
- if not np.isnan(no_data):
- field[np.isclose(field, float(no_data))] = np.nan
- # set directions
- dir_no = 0
- if direction is not None and dim > 1:
- direction = np.atleast_2d(np.asarray(direction, dtype=np.double))
- if len(direction.shape) > 2:
- raise ValueError(f"Can't interpret directions: {direction}")
- if direction.shape[1] != dim:
- raise ValueError(f"Can't interpret directions: {direction}")
- dir_no = direction.shape[0]
- # convert given angles to direction vector
- if angles is not None and direction is None and dim > 1:
- direction = ang2dir(angles=angles, dtype=np.double, dim=dim)
- dir_no = direction.shape[0]
- # prepare directional variogram
- if dir_no > 0:
- if latlon:
- raise ValueError("Directional variogram not allowed for lat-lon.")
- norms = np.linalg.norm(direction, axis=1)
- if np.any(np.isclose(norms, 0)):
- raise ValueError(f"Zero length directions: {direction}")
- # only unit-vectors for directions
- direction = np.divide(direction, norms[:, np.newaxis])
- # negative bandwidth to turn it off
- bandwidth = float(bandwidth) if bandwidth is not None else -1.0
- angles_tol = float(angles_tol)
- # prepare sampled variogram
- if sampling_size is not None and sampling_size < pnt_cnt:
- sampled_idx = np.random.RandomState(sampling_seed).choice(
- np.arange(pnt_cnt), sampling_size, replace=False
- )
- field = field[:, sampled_idx]
- pos = pos[:, sampled_idx]
- # create bins
- if bin_edges is None:
- bin_edges = standard_bins(
- pos, dim, latlon, geo_scale=geo_scale, **std_bins
- )
- bin_centers = (bin_edges[:-1] + bin_edges[1:]) / 2.0
- if latlon:
- # internally we always use radians
- bin_edges /= geo_scale
- # normalize field
- norm_field_out = remove_trend_norm_mean(
- *(pos, field, mean, normalizer, trend),
- check_shape=False,
- stacked=True,
- fit_normalizer=fit_normalizer,
- )
- field = norm_field_out[0] if fit_normalizer else norm_field_out
- norm_out = (norm_field_out[1],) if fit_normalizer else ()
- # select variogram estimator
- cython_estimator = _set_estimator(estimator)
- # run
- if dir_no == 0:
- # "h"aversine or "e"uclidean distance type
- distance_type = "h" if latlon else "e"
- estimates, counts = unstructured(
- field,
- bin_edges,
- pos,
- estimator_type=cython_estimator,
- distance_type=distance_type,
- num_threads=config.NUM_THREADS,
- )
- else:
- estimates, counts = directional(
- field,
- bin_edges,
- pos,
- direction,
- angles_tol,
- bandwidth,
- separate_dirs=_separate_dirs_test(direction, angles_tol),
- estimator_type=cython_estimator,
- num_threads=config.NUM_THREADS,
- )
- if dir_no == 1:
- estimates, counts = estimates[0], counts[0]
- est_out = (estimates, counts)
- return (bin_centers,) + est_out[: 2 if return_counts else 1] + norm_out
-
-
-def vario_estimate_axis(
- field, direction="x", estimator="matheron", no_data=np.nan
-):
- r"""Estimates the variogram along array axis.
-
- The indices of the given direction are used for the bins.
- Uniform spacings along the given axis are assumed.
-
- The algorithm calculates following equation:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r_k) = \frac{1}{2 N(r_k)} \sum_{i=1}^{N(r_k)} (z(\mathbf x_i) -
- z(\mathbf x_i'))^2 \; ,
-
- with :math:`r_k \leq \| \mathbf x_i - \mathbf x_i' \| < r_{k+1}`
- being the bins.
-
- Or if the estimator "cressie" was chosen:
-
- .. math::
- \gamma(r_k) = \frac{\frac{1}{2}\left(\frac{1}{N(r_k)}\sum_{i=1}^{N(r_k)}
- \left|z(\mathbf x_i) - z(\mathbf x_i')\right|^{0.5}\right)^4}
- {0.457 + 0.494 / N(r_k) + 0.045 / N^2(r_k)} \; ,
-
- with :math:`r_k \leq \| \mathbf x_i - \mathbf x_i' \| < r_{k+1}`
- being the bins.
- The Cressie estimator is more robust to outliers [Webster2007]_.
-
- Parameters
- ----------
- field : :class:`numpy.ndarray` or :class:`numpy.ma.MaskedArray`
- the spatially distributed data (can be masked)
- direction : :class:`str` or :class:`int`
- the axis over which the variogram will be estimated (x, y, z)
- or (0, 1, 2, ...)
- estimator : :class:`str`, optional
- the estimator function, possible choices:
-
- * "matheron": the standard method of moments of Matheron
- * "cressie": an estimator more robust to outliers
-
- Default: "matheron"
-
- no_data : :class:`float`, optional
- Value to identify missing data in the given field.
- Default: `numpy.nan`
-
- Returns
- -------
- :class:`numpy.ndarray`
- the estimated variogram along the given direction.
-
- Warnings
- --------
- It is assumed that the field is defined on an equidistant Cartesian grid.
-
- Notes
- -----
- Internally uses double precision and also returns doubles.
-
- References
- ----------
- .. [Webster2007] Webster, R. and Oliver, M. A.
- "Geostatistics for environmental scientists.",
- John Wiley & Sons. (2007)
- """
- missing_mask = (
- np.isnan(field) if np.isnan(no_data) else np.isclose(field, no_data)
- )
- missing = np.any(missing_mask)
- masked = np.ma.is_masked(field) or missing
- if masked:
- field = np.ma.array(field, ndmin=1, dtype=np.double)
- if missing:
- field.mask = np.logical_or(field.mask, missing_mask)
- mask = np.ma.getmaskarray(field)
- if not config.USE_RUST:
- mask = np.asarray(mask, dtype=np.int32)
- else:
- field = np.atleast_1d(np.asarray(field, dtype=np.double))
- missing_mask = None # free space
-
- axis_to_swap = AXIS_DIR[direction] if direction in AXIS else int(direction)
- # desired axis first, convert to 2D array afterwards
- field = field.swapaxes(0, axis_to_swap)
- field = field.reshape((field.shape[0], -1))
- if masked:
- mask = mask.swapaxes(0, axis_to_swap)
- mask = mask.reshape((mask.shape[0], -1))
-
- cython_estimator = _set_estimator(estimator)
-
- if masked:
- return ma_structured(
- field, mask, cython_estimator, num_threads=config.NUM_THREADS
- )
- return structured(field, cython_estimator, num_threads=config.NUM_THREADS)
-
-
-# for backward compatibility
-vario_estimate_unstructured = vario_estimate
-vario_estimate_structured = vario_estimate_axis
diff --git a/src/gstools_cython/__init__.py b/src/gstools_cython/__init__.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..e4adec986
--- /dev/null
+++ b/src/gstools_cython/__init__.py
@@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
+"""
+Purpose
+=======
+
+GeoStatTools is a library providing geostatistical tools
+for random field generation, conditioned field generation,
+kriging and variogram estimation
+based on a list of provided or even user-defined covariance models.
+
+This package provides the Cython backend implementations for GSTools.
+
+Subpackages
+===========
+
+.. autosummary::
+ :toctree: api
+
+ field
+ krige
+ variogram
+"""
+
+# Hooray!
+from . import field, krige, variogram
+
+try:
+ from ._version import __version__
+except ModuleNotFoundError: # pragma: no cover
+ # package is not installed
+ __version__ = "unknown"
+
+__all__ = ["__version__"]
+__all__ += ["field", "krige", "variogram"]
diff --git a/src/gstools/field/summator.pyx b/src/gstools_cython/field.pyx
similarity index 64%
rename from src/gstools/field/summator.pyx
rename to src/gstools_cython/field.pyx
index 8f6c6f7f8..489a211b0 100644
--- a/src/gstools/field/summator.pyx
+++ b/src/gstools_cython/field.pyx
@@ -1,6 +1,17 @@
# cython: language_level=3, boundscheck=False, wraparound=False, cdivision=True
"""
This is the randomization method summator, implemented in cython.
+
+.. currentmodule:: gstools_cython.field
+
+Functions
+^^^^^^^^^
+
+.. autosummary::
+ :toctree:
+
+ summate
+ summate_incompr
"""
import numpy as np
@@ -33,6 +44,27 @@ def summate(
const double[:, :] pos,
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Fourier summator for random field generation using the randomization method.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ cov_samples : double[:, :]
+ samples from the spectral density distribution of the covariance model
+ z_1 : double[:]
+ random samples from a normal distribution
+ z_2 : double[:]
+ random samples from a normal distribution
+ pos : double[:, :]
+ the position (d,n) tuple with d dimensions and n points.
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ summed_modes : double[:]
+ summed random modes
+ """
cdef int i, j, d
cdef double phase
cdef int dim = pos.shape[0]
@@ -71,6 +103,27 @@ def summate_incompr(
const double[:, :] pos,
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Fourier summator for random vector field generation using the randomization method.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ cov_samples : double[:, :]
+ samples from the spectral density distribution of the covariance model
+ z_1 : double[:]
+ random samples from a normal distribution
+ z_2 : double[:]
+ random samples from a normal distribution
+ pos : double[:, :]
+ the position (d,n) tuple with d dimensions and n points.
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ summed_modes : double[:, :]
+ summed random modes
+ """
cdef int i, j, d
cdef double phase
cdef double k_2
diff --git a/src/gstools/krige/krigesum.pyx b/src/gstools_cython/krige.pyx
similarity index 66%
rename from src/gstools/krige/krigesum.pyx
rename to src/gstools_cython/krige.pyx
index 7611f4a0a..5d943e2c6 100644
--- a/src/gstools/krige/krigesum.pyx
+++ b/src/gstools_cython/krige.pyx
@@ -1,6 +1,17 @@
# cython: language_level=3, boundscheck=False, wraparound=False, cdivision=True
"""
This is a summator for the kriging routines
+
+.. currentmodule:: gstools_cython.krige
+
+Functions
+^^^^^^^^^
+
+.. autosummary::
+ :toctree:
+
+ calc_field_krige_and_variance
+ calc_field_krige
"""
import numpy as np
@@ -31,7 +42,27 @@ def calc_field_krige_and_variance(
const double[:] cond,
num_threads=None,
):
-
+ """
+ Calculate kriging field and error variance.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ krig_mat : double[:, :]
+ kriging matrix
+ krig_vecs : double[:, :]
+ RHS of the kriging equation
+ cond : double[:]
+ values at the conditioning points
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ field : double[:]
+ kriging field
+ error : double[:]
+ kriging error variance
+ """
cdef int mat_i = krig_mat.shape[0]
cdef int res_i = krig_vecs.shape[1]
@@ -60,9 +91,27 @@ def calc_field_krige(
const double[:, :] krig_mat,
const double[:, :] krig_vecs,
const double[:] cond,
- const int num_threads=1,
+ num_threads=None,
):
-
+ """
+ Calculate kriging field without error variance.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ krig_mat : double[:, :]
+ kriging matrix
+ krig_vecs : double[:, :]
+ RHS of the kriging equation
+ cond : double[:]
+ values at the conditioning points
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ field : double[:]
+ kriging field
+ """
cdef int mat_i = krig_mat.shape[0]
cdef int res_i = krig_vecs.shape[1]
diff --git a/src/gstools/variogram/estimator.pyx b/src/gstools_cython/variogram.pyx
similarity index 76%
rename from src/gstools/variogram/estimator.pyx
rename to src/gstools_cython/variogram.pyx
index e00824be7..ff4c41d4a 100644
--- a/src/gstools/variogram/estimator.pyx
+++ b/src/gstools_cython/variogram.pyx
@@ -2,6 +2,19 @@
# distutils: language = c++
"""
This is the variogram estimater, implemented in cython.
+
+.. currentmodule:: gstools_cython.variogram
+
+Functions
+^^^^^^^^^
+
+.. autosummary::
+ :toctree:
+
+ directional
+ unstructured
+ structured
+ ma_structured
"""
import numpy as np
@@ -199,6 +212,43 @@ def directional(
str estimator_type='m',
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Directional variogram estimator.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ f : double[:, :]
+ unstructured random field
+ bin_edges : double[:]
+ edges for the variogram bins
+ pos : double[:, :]
+ the position (d,n) tuple with d dimensions and n points.
+ directions : double[:, :]
+ vectors specifying the directions
+ angles_tol : double, optional
+ angle tolerance around direction vectors in radians, default: PI/8.0
+ bandwidth : double, optional
+ maximal distance to direction vector.
+ negative values used to turn of bandwidth search. Default: -1.0
+ separate_dirs : bint, optional
+ whether the direction bands shouldn't overlap, default: False
+ estimator_type : str, optional
+ the estimator function, possible choices:
+
+ * "m": the standard method of moments of Matheron
+ * "c": an estimator more robust to outliers by Cressie
+
+ Default: "m"
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ variogram : double[:, :]
+ estimated variogram per direction
+ counts : np.int64_t[:, :]
+ counts of samples per bin and direciton
+ """
if pos.shape[1] != f.shape[1]:
raise ValueError(f'len(pos) = {pos.shape[1]} != len(f) = {f.shape[1])}')
@@ -260,6 +310,41 @@ def unstructured(
str distance_type='e',
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Omnidirectional variogram estimator.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ f : double[:, :]
+ unstructured random field
+ bin_edges : double[:]
+ edges for the variogram bins
+ pos : double[:, :]
+ the position (d,n) tuple with d dimensions and n points.
+ estimator_type : str, optional
+ the estimator function, possible choices:
+
+ * "m": the standard method of moments of Matheron
+ * "c": an estimator more robust to outliers by Cressie
+
+ Default: "m"
+ distance_type : str, optional
+ dinstance function type, possible choices:
+
+ * "e": euclidean distance
+ * "h": haversine distance for lat-lon coordinates
+
+ Default: "e"
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ variogram : double[:]
+ estimated variogram
+ counts : np.int64_t[:]
+ counts of samples per bin
+ """
cdef int dim = pos.shape[0]
cdef _dist_func distance
@@ -314,6 +399,28 @@ def structured(
str estimator_type='m',
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Variogram estimator for structured fields.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ f : double[:, :]
+ structured random field
+ estimator_type : str, optional
+ the estimator function, possible choices:
+
+ * "m": the standard method of moments of Matheron
+ * "c": an estimator more robust to outliers by Cressie
+
+ Default: "m"
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ variogram : double[:]
+ estimated variogram
+ """
cdef _estimator_func estimator_func = choose_estimator_func(estimator_type)
cdef _normalization_func normalization_func = (
choose_estimator_normalization(estimator_type)
@@ -346,6 +453,30 @@ def ma_structured(
str estimator_type='m',
num_threads=None,
):
+ """
+ Variogram estimator for masked structured fields.
+
+ Parameters
+ ----------
+ f : double[:, :]
+ structured random field
+ mask : bint[:, :]
+ mask for the structured random field
+ estimator_type : str, optional
+ the estimator function, possible choices:
+
+ * "m": the standard method of moments of Matheron
+ * "c": an estimator more robust to outliers by Cressie
+
+ Default: "m"
+ num_threads : None or int, optional
+ number of OpenMP threads, default: None
+
+ Returns
+ -------
+ variogram : double[:]
+ estimated variogram
+ """
cdef _estimator_func estimator_func = choose_estimator_func(estimator_type)
cdef _normalization_func normalization_func = (
choose_estimator_normalization(estimator_type)
diff --git a/tests/test_condition.py b/tests/test_condition.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 8d5d0535e..000000000
--- a/tests/test_condition.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,159 +0,0 @@
-"""This is the unittest of CondSRF class."""
-
-import unittest
-from copy import copy
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class TestCondition(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_models = [
- gs.Gaussian,
- gs.Exponential,
- ]
- self.dims = range(1, 4)
- self.data = np.array(
- [
- [0.3, 1.2, 0.5, 0.47],
- [1.9, 0.6, 1.0, 0.56],
- [1.1, 3.2, 1.5, 0.74],
- [3.3, 4.4, 2.0, 1.47],
- [4.7, 3.8, 2.5, 1.74],
- ]
- )
- self.cond_pos = (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1], self.data[:, 2])
- self.cond_val = self.data[:, 3]
- self.mean = np.mean(self.cond_val)
- grid = np.linspace(5, 20, 10)
- self.grid_x = np.concatenate((self.cond_pos[0], grid))
- self.grid_y = np.concatenate((self.cond_pos[1], grid))
- self.grid_z = np.concatenate((self.cond_pos[2], grid))
- self.pos = (self.grid_x, self.grid_y, self.grid_z)
-
- def test_simple(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- model = Model(
- dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2, anis=[0.1, 1], angles=[0.5, 0, 0]
- )
- krige = gs.krige.Simple(
- model, self.cond_pos[0], self.cond_val, self.mean
- )
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige, seed=19970221)
- field_1 = crf.unstructured(self.pos[0])
- field_2 = crf.structured(self.pos[0])
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_1[i], places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_2[(i,)], places=2)
-
- for dim in self.dims[1:]:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=0.5,
- len_scale=2,
- anis=[0.1, 1],
- angles=[0.5, 0, 0],
- )
- krige = gs.krige.Simple(
- model, self.cond_pos[:dim], self.cond_val, self.mean
- )
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige, seed=19970221)
- field_1 = crf.unstructured(self.pos[:dim])
- field_2 = crf.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- # check reuse
- raw_kr2 = copy(crf["raw_krige"])
- crf(seed=19970222)
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(raw_kr2, crf["raw_krige"]))
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_1[i], places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_2[dim * (i,)], places=2)
-
- def test_ordinary(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- model = Model(
- dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2, anis=[0.1, 1], angles=[0.5, 0, 0]
- )
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(model, self.cond_pos[0], self.cond_val)
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige, seed=19970221)
- field_1 = crf.unstructured(self.pos[0])
- field_2 = crf.structured(self.pos[0])
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_1[i], places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_2[(i,)], places=2)
-
- for dim in self.dims[1:]:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=0.5,
- len_scale=2,
- anis=[0.1, 1],
- angles=[0.5, 0, 0],
- )
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model, self.cond_pos[:dim], self.cond_val
- )
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige, seed=19970221)
- field_1 = crf.unstructured(self.pos[:dim])
- field_2 = crf.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_1[i], places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_2[dim * (i,)], places=2)
-
- def test_raise_error(self):
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.CondSRF, gs.Gaussian())
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(gs.Stable(), self.cond_pos, self.cond_val)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.CondSRF, krige, generator="unknown")
-
- def test_nugget(self):
- model = gs.Gaussian(
- nugget=0.01,
- var=0.5,
- len_scale=2,
- anis=[0.1, 1],
- angles=[0.5, 0, 0],
- )
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model, self.cond_pos, self.cond_val, exact=True
- )
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige, seed=19970221)
- field_1 = crf.unstructured(self.pos)
- field_2 = crf.structured(self.pos)
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_1[i], places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(val, field_2[3 * (i,)], places=2)
-
- def test_setter(self):
- krige1 = gs.krige.Krige(gs.Exponential(), self.cond_pos, self.cond_val)
- krige2 = gs.krige.Krige(
- gs.Gaussian(var=2),
- self.cond_pos,
- self.cond_val,
- mean=-1,
- trend=-2,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson(),
- )
- crf1 = gs.CondSRF(krige1)
- crf2 = gs.CondSRF(krige2, seed=19970221)
- # update settings
- crf1.model = gs.Gaussian(var=2)
- crf1.mean = -1
- crf1.trend = -2
- # also checking correctly setting uninitialized normalizer
- crf1.normalizer = gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson
- # check if setting went right
- self.assertTrue(crf1.model == crf2.model)
- self.assertTrue(crf1.normalizer == crf2.normalizer)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(crf1.mean, crf2.mean)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(crf1.trend, crf2.trend)
- # reset kriging
- crf1.krige.set_condition()
- # compare fields
- field1 = crf1(self.pos, seed=19970221)
- field2 = crf2(self.pos)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(field1, field2)))
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_covmodel.py b/tests/test_covmodel.py
deleted file mode 100644
index a2729dd68..000000000
--- a/tests/test_covmodel.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,424 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest of CovModel class.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import (
- Circular,
- CovModel,
- Cubic,
- Exponential,
- Gaussian,
- HyperSpherical,
- Integral,
- JBessel,
- Linear,
- Matern,
- Rational,
- Spherical,
- Stable,
- SuperSpherical,
- TPLExponential,
- TPLGaussian,
- TPLSimple,
- TPLStable,
-)
-from gstools.covmodel.tools import (
- AttributeWarning,
- check_arg_in_bounds,
- check_bounds,
-)
-
-
-class Gau_var(CovModel):
- def variogram(self, r):
- h = np.abs(r) / self.len_rescaled
- return self.var * (1.0 - np.exp(-(h**2))) + self.nugget
-
-
-class Gau_cov(CovModel):
- def covariance(self, r):
- h = np.abs(r) / self.len_rescaled
- return self.var * np.exp(-(h**2))
-
-
-class Gau_cor(CovModel):
- def correlation(self, r):
- h = np.abs(r) / self.len_rescaled
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
-
-class Gau_fix(CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
- def fix_dim(self):
- return 2
-
-
-class Mod_add(CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return 1.0
-
- def default_opt_arg(self):
- return {"alpha": 1}
-
-
-class TestCovModel(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.std_cov_models = [
- Gaussian,
- Exponential,
- Stable,
- Rational,
- Cubic,
- Matern,
- Linear,
- Circular,
- Spherical,
- HyperSpherical,
- SuperSpherical,
- JBessel,
- TPLSimple,
- Integral,
- ]
- self.tpl_cov_models = [
- TPLGaussian,
- TPLExponential,
- TPLStable,
- ]
- self.cov_models = self.std_cov_models + self.tpl_cov_models
- self.dims = range(1, 4)
- self.lens = [[10, 5, 2]]
- self.anis = [[0.5, 0.2]]
- self.nuggets = [0, 1]
- self.vars = [1, 2]
- self.angles = [[1, 2, 3]]
-
- self.gamma_x = [1.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 9.0, 11.0]
- self.gamma_y = [0.2, 0.5, 0.6, 0.8, 0.8, 0.9]
-
- def test_creation(self):
- with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
- CovModel()
-
- class User(CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
- user = User(len_scale=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(user.correlation(1), np.exp(-0.25))
-
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- for angles in self.angles:
- for nugget in self.nuggets:
- for len_scale, anis in zip(self.lens, self.anis):
- model = Model(
- dim=dim, len_scale=len_scale, angles=angles
- )
- model1 = Model(
- dim=dim, len_scale=10, anis=anis, angles=angles
- )
- self.assertTrue(model == model1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.variogram(1),
- model.var + model.nugget - model.covariance(1),
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.covariance(1),
- model.var * model.correlation(1),
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.covariance(1),
- model.var * model.correlation(1),
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.vario_spatial(([1], [2], [3])[:dim])[0],
- model.var
- + model.nugget
- - model.cov_spatial(([1], [2], [3])[:dim])[0],
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.cor_spatial(([1], [2], [3])[:dim])[0],
- model.cov_spatial(([1], [2], [3])[:dim])[0]
- / model.var,
- )
- for d in range(dim):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.vario_axis(1, axis=d),
- model.var
- + model.nugget
- - model.cov_axis(1, axis=d),
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.cor_axis(1, axis=d),
- model.cov_axis(1, axis=d) / model.var,
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.cov_nugget(0), model.sill
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.vario_nugget(0), 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.cov_nugget(1), model.covariance(1)
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.vario_nugget(0), 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model.vario_nugget(1), model.variogram(1)
- )
- # check if callable
- model.vario_spatial((1, 2, 3)[:dim])
- model.spectral_density([0, 1])
- model.spectrum([0, 1])
- model.spectral_rad_pdf([0, 1])
- model.ln_spectral_rad_pdf([0, 1])
- model.integral_scale_vec
- model.percentile_scale(0.9)
- if model.has_cdf:
- model.spectral_rad_cdf([0, 1])
- if model.has_ppf:
- model.spectral_rad_ppf([0.0, 0.99])
- model.pykrige_kwargs
- # check arg bound setting
- model.set_arg_bounds(
- var=[2, np.inf], nugget=[1, 2]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 3)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 1.5)
-
- def test_tpl_models(self):
- for Model in self.tpl_cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(dim=dim, len_scale=9, len_low=1, rescale=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.len_up_rescaled, 5)
- model.len_low = 0.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.cor(2), model.correlation(9))
- # also check resetting of var when sill is given lower
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=1.1, nugget=False
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 1.1, delta=1e-5)
- # check var_raw handling
- model = Model(var_raw=1, len_low=0, integral_scale=10)
- var_save = model.var
- model.var_raw = 1.1
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, var_save * 1.1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.integral_scale, 10)
- # integral scale is not setable when len_low is not 0
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- Model(var_raw=1, len_low=5, integral_scale=10)
-
- def test_fitting(self):
- for Model in self.std_cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(dim=dim)
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, nugget=False)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 0.0)
- model = Model(dim=dim)
- # also check resetting of var when sill is given lower
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=0.9)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget + model.var, 0.9)
- model = Model(dim=dim)
- # more detailed checks
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=2, nugget=False
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 2.0)
- model = Model(dim=dim)
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=2, nugget=1
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 1)
- model = Model(dim=dim)
- ret = model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x,
- self.gamma_y,
- loss="linear",
- return_r2=True,
- weights="inv",
- init_guess="current",
- )
- self.assertEqual(len(ret), 3)
-
- # treatment of sill/var/nugget by fitting
- model = Stable()
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, nugget=False, var=False, sill=2
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 1)
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, var=2, sill=3)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 1)
- model.var = 3
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, nugget=False, var=False, sill=2
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 0)
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, weights="inv")
- len_save = model.len_scale
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, weights=lambda x: 1 / (1 + x)
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.len_scale, len_save, places=6)
- # check ValueErrors
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=2, var=3)
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=2, nugget=3)
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, method="wrong")
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, wrong=False)
- model.var_bounds = [0, 1]
- model.nugget_bounds = [0, 1]
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, sill=3)
- # init guess
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, init_guess="wrong")
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, self.gamma_y, init_guess={"wrong": 1}
- )
- # sill fixing
- model.var_bounds = [0, np.inf]
- model.fit_variogram(
- self.gamma_x, np.array(self.gamma_y) + 1, sill=2, alpha=False
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var + model.nugget, 2)
- # check isotropicity for latlon models
- model = Stable(latlon=True)
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(self.gamma_x, 3 * [self.gamma_y])
-
- def test_covmodel_class(self):
- model_std = Gaussian(rescale=3, var=1.1, nugget=1.2, len_scale=1.3)
- model_var = Gau_var(rescale=3, var=1.1, nugget=1.2, len_scale=1.3)
- model_cov = Gau_cov(rescale=3, var=1.1, nugget=1.2, len_scale=1.3)
- model_cor = Gau_cor(rescale=3, var=1.1, nugget=1.2, len_scale=1.3)
- var = model_std.variogram(2.5)
- cov = model_std.covariance(2.5)
- corr = model_std.correlation(2.5)
- cor = model_std.cor(2.5)
-
- self.assertFalse(check_bounds(bounds=[0]))
- self.assertFalse(check_bounds(bounds=[1, -1]))
- self.assertFalse(check_bounds(bounds=[0, 1, 2, 3]))
- self.assertFalse(check_bounds(bounds=[0, 1, "kk"]))
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, model_std.set_arg_bounds, wrong_arg=[1])
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, model_std.set_arg_bounds, wrong_arg=[-1, 1]
- )
-
- # checking some properties
- model_par = Stable()
- self.assertFalse(model_par.do_rotation)
- self.assertEqual(len(model_par.arg), len(model_par.arg_list))
- self.assertEqual(len(model_par.iso_arg), len(model_par.iso_arg_list))
- self.assertEqual(len(model_par.arg), len(model_par.iso_arg) + 2)
- self.assertEqual(len(model_par.len_scale_vec), model_par.dim)
- self.assertFalse(Gaussian() == Stable())
- model_par.hankel_kw = {"N": 300}
- self.assertEqual(model_par.hankel_kw["N"], 300)
-
- # arg in bounds check
- model_std.set_arg_bounds(var=[0.5, 1.5])
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.var = 0.4
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.var = 1.6
- model_std.set_arg_bounds(var=[0.5, 1.5, "oo"])
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.var = 0.5
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.var = 1.5
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.var_bounds = [1, -1]
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.len_scale_bounds = [1, -1]
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.nugget_bounds = [1, -1]
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model_std.anis_bounds = [1, -1]
- # reset the standard model
- model_std = Gaussian(rescale=3, var=1.1, nugget=1.2, len_scale=1.3)
- # std value from bounds with neg. inf and finit bound
- model_add = Mod_add()
- model_add.set_arg_bounds(alpha=[-np.inf, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model_add.alpha, -1)
- # special treatment of anis check
- model_std.set_arg_bounds(anis=[2, 4, "oo"])
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(model_std.anis, 3)))
- # dim specific checks
- with self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning):
- Gau_fix(dim=1)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, Gaussian, dim=0)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, Gau_fix, latlon=True)
- # check inputs
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, model_std.percentile_scale, per=-1.0)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, Gaussian, anis=-1.0)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, Gaussian, len_scale=[1, -1])
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, check_arg_in_bounds, model_std, "wrong")
- self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning, Gaussian, wrong_arg=1.0)
- with self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning):
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, Gaussian, len_rescaled=1.0)
-
- # check correct subclassing
- with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
-
- class Gau_err(CovModel):
- pass
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(var, model_var.variogram(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(var, model_cov.variogram(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(var, model_cor.variogram(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cov, model_var.covariance(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cov, model_cov.covariance(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cov, model_cor.covariance(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(corr, model_var.correlation(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(corr, model_cov.correlation(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(corr, model_cor.correlation(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cor, model_var.cor(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cor, model_cov.cor(2.5))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(cor, model_cor.cor(2.5))
-
- def test_rescale(self):
- model1 = Exponential()
- model2 = Exponential(rescale=2.1)
- model3 = Exponential(rescale=2.1, len_scale=2.1)
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- model1.integral_scale, 2.1 * model2.integral_scale
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model1.integral_scale, model3.integral_scale)
-
- def test_special_models(self):
- # Matern and Integral converge to gaussian
- model0 = Integral(rescale=0.5)
- model0.set_arg_bounds(nu=[0, 1001])
- model0.nu = 1000
- model1 = Matern()
- model1.set_arg_bounds(nu=[0, 101])
- model1.nu = 100
- model2 = Gaussian(rescale=0.5)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model0.variogram(1), model2.variogram(1), 2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model0.spectrum(1), model2.spectrum(1), 2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model1.variogram(1), model2.variogram(1))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model1.spectrum(1), model2.spectrum(1), 2)
- # stable model gets unstable for alpha < 0.3
- with self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning):
- Stable(alpha=0.2)
- with self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning):
- TPLStable(alpha=0.2)
- # corner case for JBessel model
- with self.assertWarns(AttributeWarning):
- JBessel(dim=3, nu=0.5)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_export.py b/tests/test_export.py
deleted file mode 100644
index b32898f45..000000000
--- a/tests/test_export.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,64 +0,0 @@
-"""Test the PyVista/VTK export methods"""
-
-import os
-import shutil
-import tempfile
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import SRF, Exponential, Gaussian
-from gstools.random import MasterRNG
-
-HAS_PYVISTA = False
-try:
- import pyvista as pv
-
- HAS_PYVISTA = True
-except ImportError:
- pass
-
-
-class TestExport(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.test_dir = tempfile.mkdtemp()
- # structured field with a size 100x100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1x1
- x = y = z = range(50)
- model = Gaussian(dim=3, var=0.6, len_scale=20)
- self.srf_structured = SRF(model)
- self.srf_structured((x, y, z), mesh_type="structured")
- # unstrucutred field
- seed = MasterRNG(19970221)
- rng = np.random.RandomState(seed())
- x = rng.randint(0, 100, size=1000)
- y = rng.randint(0, 100, size=1000)
- model = Exponential(
- dim=2, var=1, len_scale=[12.0, 3.0], angles=np.pi / 8.0
- )
- self.srf_unstructured = SRF(model, seed=20170519)
- self.srf_unstructured([x, y])
-
- def tearDown(self):
- # Remove the test data directory after the test
- shutil.rmtree(self.test_dir)
-
- @unittest.skipIf(not HAS_PYVISTA, "PyVista is not installed.")
- def test_pyvista(self):
- mesh = self.srf_structured.to_pyvista()
- self.assertIsInstance(mesh, pv.RectilinearGrid)
- mesh = self.srf_unstructured.to_pyvista()
- self.assertIsInstance(mesh, pv.UnstructuredGrid)
-
- def test_pyevtk_export(self):
- # Structured
- sfilename = os.path.join(self.test_dir, "structured")
- self.srf_structured.vtk_export(sfilename)
- self.assertTrue(os.path.isfile(sfilename + ".vtr"))
- # Unstructured
- ufilename = os.path.join(self.test_dir, "unstructured")
- self.srf_unstructured.vtk_export(ufilename)
- self.assertTrue(os.path.isfile(ufilename + ".vtu"))
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_field.py b/tests/test_field.py
index cdb0365d6..bf18db113 100644
--- a/tests/test_field.py
+++ b/tests/test_field.py
@@ -7,114 +7,169 @@
import numpy as np
-import gstools as gs
+import gstools_cython as gs_cy
class TestField(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1.5, len_scale=4.0)
- rng = np.random.RandomState(123018)
- x = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
- y = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
- self.field = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
- self.pos = np.array([x, y])
+ def test_summate(self):
+ # x = np.linspace(0,1,5)
+ # mod = gs.Gaussian(dim=1)
+ # srf = gs.SRF(mod, mode_no=10, seed=1234)
+ # srf(x)
+ cov_samples = np.array(
+ [
+ [
+ -0.49995807783373075,
+ -0.7820163721559825,
+ 1.690118803237597,
+ 1.9756208177659687,
+ 0.03945771863093044,
+ 2.127277879098216,
+ -1.4576342168089562,
+ 0.5947643837384975,
+ 0.09811641644885175,
+ -0.003565139481429214,
+ ]
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ z_1 = np.array(
+ [
+ 0.9946988048718556,
+ 1.814210031079757,
+ 1.1686180785678166,
+ -0.374250826058506,
+ 1.208282071166948,
+ 1.044190549877576,
+ -1.7850832797400267,
+ 1.1341225325719555,
+ 0.005871108068883179,
+ 0.4918288313002647,
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ z_2 = np.array(
+ [
+ 0.38320431788616655,
+ -0.6158908046660203,
+ -1.5221152986631148,
+ 0.4213284409858781,
+ -1.2858750366939806,
+ -0.1286138436420879,
+ -0.031244435678407644,
+ 0.16914501403169677,
+ -0.04578215996092473,
+ -0.48668407941054204,
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ pos = np.array([[0.0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1.0]], dtype=np.double)
+ summed_modes = np.array(
+ [5.7024879, 5.16758284, 4.46056939, 3.73413573, 3.14911511], dtype=np.double
+ )
+ summed = gs_cy.field.summate(cov_samples, z_1, z_2, pos)
+ np.testing.assert_allclose(summed_modes, summed)
- def test_standalone(self):
- fld = gs.field.Field(dim=2)
- fld_cov = gs.field.Field(model=self.cov_model)
- field1 = fld(self.pos, self.field)
- field2 = fld_cov(self.pos, self.field)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(field1, field2)))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(field1, self.field)))
-
- def test_raise(self):
- # vector field on latlon
- fld = gs.field.Field(gs.Gaussian(latlon=True), value_type="vector")
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, fld, [1, 2], [1, 2])
- # no pos tuple present
- fld = gs.field.Field(dim=2)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, fld.post_field, [1, 2])
- # wrong model type
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.field.Field(model=3.1415)
- # no model and no dim given
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.field.Field()
- # wrong value type
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.field.Field(dim=2, value_type="complex")
- # wrong mean shape
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.field.Field(dim=3, mean=[1, 2])
-
- def test_pos_compare(self):
- fld = gs.field.Field(dim=1)
- fld.set_pos([1, 2])
- fld._dim = 2
- info = fld.set_pos([[1], [2]], info=True)
- self.assertTrue(info["deleted"])
- info = fld.set_pos([[2], [3]], info=True)
- self.assertTrue(info["deleted"])
-
- def test_magic(self):
- fld = gs.field.Field(dim=1)
- f1 = np.array([0, 0], dtype=np.double)
- f2 = np.array([2, 3], dtype=np.double)
- fld([1, 2], store="f1") # default field with zeros
- fld([1, 2], f2, store="f2")
- fields1 = fld[:]
- fields2 = fld[[0, 1]]
- fields3 = fld[["f1", "f2"]]
- fields4 = fld.all_fields
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose([f1, f2], fields1))
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose([f1, f2], fields2))
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose([f1, f2], fields3))
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose([f1, f2], fields4))
- self.assertEqual(len(fld), 2)
- self.assertTrue("f1" in fld)
- self.assertTrue("f2" in fld)
- self.assertFalse("f3" in fld)
- # subscription
- with self.assertRaises(KeyError):
- fld["f3"]
- with self.assertRaises(KeyError):
- del fld["f3"]
- with self.assertRaises(KeyError):
- del fld[["f3"]]
- del fld["f1"]
- self.assertFalse("f1" in fld)
- fld([1, 2], f1, store="f1")
- del fld[-1]
- self.assertFalse("f1" in fld)
- fld([1, 2], f1, store="f1")
- del fld[:]
- self.assertEqual(len(fld), 0)
- fld([1, 2], f1, store="f1")
- del fld.field_names
- self.assertEqual(len(fld), 0)
- # store config (missing check)
- name, save = fld.get_store_config(store="fld", fld_cnt=1)
- self.assertEqual(name, ["fld"])
- self.assertTrue(save[0])
-
- def test_reuse(self):
- fld = gs.field.Field(dim=1)
- # no pos tuple
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- fld()
- # no field shape
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- fld.post_field([1, 2])
- # bad name
- fld.set_pos([1, 2])
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- fld.post_field([1, 2], process=False, name=0)
- # incompatible reuse
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- fld.structured()
- fld.set_pos([1, 2], "structured")
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- fld.unstructured()
+ def test_summate_incompr(self):
+ # x = y = np.linspace(0,1,3)
+ # mod = gs.Gaussian(dim=2)
+ # srf = gs.SRF(mod, generator="VectorField", mode_no=10, seed=1234)
+ # srf.structured((x, y))
+ cov_samples = np.array(
+ [
+ [
+ -1.024970238789004,
+ -0.8240580540129643,
+ 2.2180425521549676,
+ -0.3936617167321944,
+ 0.27486363934743613,
+ 2.0706439558766294,
+ 0.14405381961860603,
+ -0.13186433446921356,
+ -0.39813741816987425,
+ -0.009242543307168134,
+ ],
+ [
+ -0.3396282286113363,
+ -1.1400706088519987,
+ -0.7152472598352912,
+ -2.5770200983873353,
+ 0.06603124248012006,
+ 1.8138240750039616,
+ -2.097665482523384,
+ -1.1869215683139556,
+ -0.2095286706436547,
+ 0.08398183470003417,
+ ],
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ z_1 = np.array(
+ [
+ 0.9946988048718556,
+ 1.814210031079757,
+ 1.1686180785678166,
+ -0.374250826058506,
+ 1.208282071166948,
+ 1.044190549877576,
+ -1.7850832797400267,
+ 1.1341225325719555,
+ 0.005871108068883179,
+ 0.4918288313002647,
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ z_2 = np.array(
+ [
+ 0.38320431788616655,
+ -0.6158908046660203,
+ -1.5221152986631148,
+ 0.4213284409858781,
+ -1.2858750366939806,
+ -0.1286138436420879,
+ -0.031244435678407644,
+ 0.16914501403169677,
+ -0.04578215996092473,
+ -0.48668407941054204,
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ pos = np.array(
+ [
+ [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0],
+ [0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0],
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ summed_modes = np.array(
+ [
+ [
+ 1.38449093,
+ 1.71111119,
+ 2.74104654,
+ 0.86548576,
+ 0.71454466,
+ 1.75446747,
+ 0.04791079,
+ -0.21360334,
+ 1.06275366,
+ ],
+ [
+ -1.74849962,
+ -1.24325646,
+ -0.32330441,
+ -1.9262243,
+ -0.95014749,
+ 0.07508429,
+ -1.41925949,
+ -0.67520382,
+ -0.10531391,
+ ],
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ summed = gs_cy.field.summate_incompr(cov_samples, z_1, z_2, pos)
+ np.testing.assert_allclose(summed_modes, summed)
if __name__ == "__main__":
diff --git a/tests/test_incomprrandmeth.py b/tests/test_incomprrandmeth.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 9156b1b17..000000000
--- a/tests/test_incomprrandmeth.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,63 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest of the RandMeth class.
-"""
-
-import copy
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-from gstools.field.generator import IncomprRandMeth
-
-
-class TestIncomprRandMeth(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_model_2d = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1.5, len_scale=2.5)
- self.cov_model_3d = copy.deepcopy(self.cov_model_2d)
- self.cov_model_3d.dim = 3
- self.seed = 19031977
- self.x_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 9)
- self.y_grid = np.linspace(-5.0, 5.0, 16)
- self.z_grid = np.linspace(-6.0, 7.0, 8)
- self.x_tuple = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 10)
- self.y_tuple = np.linspace(-5.0, 5.0, 10)
- self.z_tuple = np.linspace(-6.0, 8.0, 10)
-
- self.rm_2d = IncomprRandMeth(
- self.cov_model_2d, mode_no=100, seed=self.seed
- )
- self.rm_3d = IncomprRandMeth(
- self.cov_model_3d, mode_no=100, seed=self.seed
- )
-
- def test_unstruct_2d(self):
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0, 0], 0.50751115)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0, 1], 1.03291018)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1, 1], -0.22003005)
-
- def test_unstruct_3d(self):
- modes = self.rm_3d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0, 0], 0.7924546333550331)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0, 1], 1.660747056686244)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1, 0], -0.28049855754819514)
-
- def test_assertions(self):
- cov_model_1d = gs.Gaussian(dim=1, var=1.5, len_scale=2.5)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, IncomprRandMeth, cov_model_1d)
-
- def test_vector_mean(self):
- srf = gs.SRF(
- self.cov_model_2d,
- mean=(0.5, 0),
- generator="VectorField",
- seed=198412031,
- )
- srf.structured((self.x_grid, self.y_grid))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(srf.field[0]), 1.3025621393180298)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(srf.field[1]), -0.04729596839446052)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_krige.py b/tests/test_krige.py
index d702b0eef..e07fde3ad 100644
--- a/tests/test_krige.py
+++ b/tests/test_krige.py
@@ -6,285 +6,48 @@
import numpy as np
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def trend(*xyz):
- return xyz[0]
-
-
-def mean_func(*xyz):
- return 2 * xyz[0]
+import gstools_cython as gs_cy
class TestKrige(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self):
- self.cov_models = [gs.Gaussian, gs.Exponential, gs.Spherical]
- self.dims = range(1, 4)
- self.data = np.array(
+ # cond_pos = [0.3, 1.9, 1.1]
+ # cond_val = [0.47, 0.56, 0.74]
+ # x = [0.5, 1.5]
+ # model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=0.5, len_scale=2)
+ # krig = krige.Simple(model, mean=1, cond_pos=cond_pos, cond_val=cond_val)
+ # field, error = krig(x)
+ self.krig_mat = np.array(
[
- [0.3, 1.2, 0.5, 0.47],
- [1.9, 0.6, 1.0, 0.56],
- [1.1, 3.2, 1.5, 0.74],
- [3.3, 4.4, 2.0, 1.47],
- [4.7, 3.8, 2.5, 1.74],
- ]
+ [22.779309008408386, 17.71701030060681, -35.714164777816634],
+ [17.717010300606795, 22.779309008408426, -35.714164777816656],
+ [-35.71416477781662, -35.71416477781667, 64.9934565679449],
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
)
- # redundant data for pseudo-inverse
- self.p_data = np.zeros((3, 3))
- self.p_vals = np.array([1.0, 2.0, 6.0])
- self.p_meth = [1, 2, 3] # method selector
- # indices for the date in the grid
- self.data_idx = tuple(np.array(self.data[:, :3] * 10, dtype=int).T)
- # x, y, z componentes for the conditon position
- self.cond_pos = (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1], self.data[:, 2])
- # condition values
- self.cond_val = self.data[:, 3]
- self.cond_err = np.array([0.01, 0.0, 0.1, 0.05, 0])
- # the arithmetic mean of the conditions
- self.mean = np.mean(self.cond_val)
- # the grid
- self.x = np.linspace(0, 5, 51)
- self.y = np.linspace(0, 6, 61)
- self.z = np.linspace(0, 7, 71)
- self.pos = (self.x, self.y, self.z)
- self.grids = [self.x]
- self.grids.append(np.meshgrid(self.x, self.y, indexing="ij"))
- self.grids.append(np.meshgrid(self.x, self.y, self.z, indexing="ij"))
- self.grid_shape = [51, 61, 71]
-
- def test_simple(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=2,
- anis=[0.9, 0.8],
- angles=[2, 1, 0.5],
- )
- simple = gs.krige.Simple(
- model, self.cond_pos[:dim], self.cond_val, self.mean
- )
- field_1, __ = simple.unstructured(self.grids[dim - 1])
- field_1 = field_1.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- field_2, __ = simple.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.max(np.abs(field_1 - field_2)), 0.0, places=2
- )
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field_1[self.data_idx[:dim]][i], val, places=2
- )
-
- def test_ordinary(self):
- for trend_func in [None, trend]:
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=5,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.9, 0.8],
- angles=[2, 1, 0.5],
- )
- ordinary = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model,
- self.cond_pos[:dim],
- self.cond_val,
- trend=trend_func,
- )
- field_1, __ = ordinary.unstructured(self.grids[dim - 1])
- field_1 = field_1.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- field_2, __ = ordinary.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.max(np.abs(field_1 - field_2)), 0.0, places=2
- )
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field_1[self.data_idx[:dim]][i], val, places=2
- )
-
- def test_universal(self):
- # "quad" -> to few conditional points
- for drift in ["linear", 0, 1, trend]:
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.9, 0.8],
- angles=[2, 1, 0.5],
- )
- universal = gs.krige.Universal(
- model, self.cond_pos[:dim], self.cond_val, drift
- )
- field_1, __ = universal.unstructured(self.grids[dim - 1])
- field_1 = field_1.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- field_2, __ = universal.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.max(np.abs(field_1 - field_2)), 0.0, places=2
- )
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field_2[self.data_idx[:dim]][i], val, places=2
- )
-
- def test_detrended(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.5, 0.2],
- angles=[0.4, 0.2, 0.1],
- )
- detrended = gs.krige.Detrended(
- model, self.cond_pos[:dim], self.cond_val, trend
- )
- field_1, __ = detrended.unstructured(self.grids[dim - 1])
- field_1 = field_1.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- field_2, __ = detrended.structured(self.pos[:dim])
- # detrended.plot()
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.max(np.abs(field_1 - field_2)), 0.0, places=2
- )
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field_2[self.data_idx[:dim]][i], val, places=2
- )
-
- def test_extdrift(self):
- ext_drift = []
- cond_drift = []
- for i, grid in enumerate(self.grids):
- dim = i + 1
- model = gs.Exponential(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.9, 0.8],
- angles=[2, 1, 0.5],
- )
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- field = srf(grid)
- ext_drift.append(field)
- field = field.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- cond_drift.append(field[self.data_idx[:dim]])
-
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.5, 0.2],
- angles=[0.4, 0.2, 0.1],
- )
- extdrift = gs.krige.ExtDrift(
- model,
- self.cond_pos[:dim],
- self.cond_val,
- cond_drift[dim - 1],
- )
- field_1, __ = extdrift.unstructured(
- self.grids[dim - 1], ext_drift=ext_drift[dim - 1]
- )
- field_1 = field_1.reshape(self.grid_shape[:dim])
- field_2, __ = extdrift.structured(
- self.pos[:dim], ext_drift=ext_drift[dim - 1]
- )
- # extdrift.plot()
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.max(np.abs(field_1 - field_2)), 0.0, places=2
- )
- for i, val in enumerate(self.cond_val):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field_2[self.data_idx[:dim]][i], val, places=2
- )
-
- def test_pseudo(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=2,
- len_scale=10,
- anis=[0.5, 0.2],
- angles=[0.4, 0.2, 0.1],
- )
- for meth in self.p_meth:
- krig = gs.krige.Krige(
- model, self.p_data[:dim], self.p_vals, unbiased=False
- )
- field, __ = krig([0, 0, 0][:dim])
- # with the pseudo-inverse, the estimated value
- # should be the mean of the 3 redundant input values
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- field[0], np.mean(self.p_vals), places=2
- )
-
- def test_error(self):
- for Model in self.cov_models:
- for dim in self.dims:
- model = Model(
- dim=dim,
- var=5,
- len_scale=10,
- nugget=0.1,
- anis=[0.9, 0.8],
- angles=[2, 1, 0.5],
- )
- ordinary = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model,
- self.cond_pos[:dim],
- self.cond_val,
- exact=False,
- cond_err=self.cond_err,
- )
- field, err = ordinary(self.cond_pos[:dim])
- # when the given measurement error is 0, the kriging-var
- # should equal the nugget of the model
- self.assertAlmostEqual(err[1], model.nugget, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(err[4], model.nugget, places=2)
+ self.krig_vecs = np.array(
+ [
+ [0.49608839014628076, 0.37685660597823356],
+ [0.34027802306393057, 0.4845362131524053],
+ [0.4658772855496882, 0.4845362131524053],
+ ],
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ self.cond = np.array([-0.53, -0.43999999999999995, -0.26], dtype=np.double)
- def test_raise(self):
- # no cond_pos/cond_val given
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.krige.Krige, gs.Stable(), None, None)
+ self.field_ref = np.array([-0.42936306, -0.29739613], dtype=np.double)
+ self.error_ref = np.array([0.49987232, 0.49982352], dtype=np.double)
- def test_krige_mean(self):
- # check for constant mean (simple kriging)
- krige = gs.krige.Simple(gs.Gaussian(), self.cond_pos, self.cond_val)
- mean_f = krige.structured(self.pos, only_mean=True)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(mean_f, 0)))
- krige = gs.krige.Simple(
- gs.Gaussian(),
- self.cond_pos,
- self.cond_val,
- mean=mean_func,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson,
- trend=trend,
+ def test_calc_field_krige_and_variance(self):
+ field, error = gs_cy.krige.calc_field_krige_and_variance(
+ self.krig_mat, self.krig_vecs, self.cond
)
- # check applying mean, norm, trend
- mean_f1 = krige.structured(self.pos, only_mean=True)
- mean_f2 = gs.normalizer.tools.apply_mean_norm_trend(
- self.pos,
- np.zeros(tuple(map(len, self.pos))),
- mean=mean_func,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson,
- trend=trend,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(mean_f1, mean_f2)))
- krige = gs.krige.Simple(gs.Gaussian(), self.cond_pos, self.cond_val)
- mean_f = krige.structured(self.pos, only_mean=True)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(mean_f, 0)))
- # check for constant mean (ordinary kriging)
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(gs.Gaussian(), self.cond_pos, self.cond_val)
- mean_f = krige.structured(self.pos, only_mean=True)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(mean_f, krige.get_mean())))
+ np.testing.assert_allclose(field, self.field_ref)
+ np.testing.assert_allclose(error, self.error_ref)
+
+ def test_calc_field_krige(self):
+ field = gs_cy.krige.calc_field_krige(self.krig_mat, self.krig_vecs, self.cond)
+ np.testing.assert_allclose(field, self.field_ref)
if __name__ == "__main__":
diff --git a/tests/test_latlon.py b/tests/test_latlon.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 98088db85..000000000
--- a/tests/test_latlon.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,172 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest for latlon related routines.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def _rel_err(a, b):
- return np.abs(a / ((a + b) / 2) - 1)
-
-
-class ErrMod(gs.CovModel):
- def cor(self, h):
- return np.exp(-(h**2))
-
- def fix_dim(self):
- return 2
-
-
-class TestLatLon(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cmod = gs.Gaussian(
- latlon=True, var=2, len_scale=777, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE
- )
- self.lat = self.lon = range(-80, 81)
-
- self.data = np.array(
- [
- [52.9336, 8.237, 15.7],
- [48.6159, 13.0506, 13.9],
- [52.4853, 7.9126, 15.1],
- [50.7446, 9.345, 17.0],
- [52.9437, 12.8518, 21.9],
- [53.8633, 8.1275, 11.9],
- [47.8342, 10.8667, 11.4],
- [51.0881, 12.9326, 17.2],
- [48.406, 11.3117, 12.9],
- [49.7273, 8.1164, 17.2],
- [49.4691, 11.8546, 13.4],
- [48.0197, 12.2925, 13.9],
- [50.4237, 7.4202, 18.1],
- [53.0316, 13.9908, 21.3],
- [53.8412, 13.6846, 21.3],
- [54.6792, 13.4343, 17.4],
- [49.9694, 9.9114, 18.6],
- [51.3745, 11.292, 20.2],
- [47.8774, 11.3643, 12.7],
- [50.5908, 12.7139, 15.8],
- ]
- )
-
- def test_conv(self):
- p_ll = gs.tools.geometric.latlon2pos((self.lat, self.lon), 2.56)
- ll_p = gs.tools.geometric.pos2latlon(p_ll, 2.56)
- for i, v in enumerate(self.lat):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v, ll_p[0, i])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v, ll_p[1, i])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 8, self.cmod.anisometrize(self.cmod.isometrize((8, 6)))[0, 0]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 6, self.cmod.anisometrize(self.cmod.isometrize((8, 6)))[1, 0]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- gs.EARTH_RADIUS,
- self.cmod.isometrize(
- self.cmod.anisometrize((gs.EARTH_RADIUS, 0, 0))
- )[0, 0],
- )
-
- def test_cov_model(self):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- self.cmod.vario_yadrenko(1.234),
- self.cmod.sill - self.cmod.cov_yadrenko(1.234),
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- self.cmod.cov_yadrenko(1.234),
- self.cmod.var * self.cmod.cor_yadrenko(1.234),
- )
- # test if correctly handling tries to set anisotropy
- self.cmod.anis = [1, 2]
- self.cmod.angles = [1, 2, 3]
- self.assertAlmostEqual(self.cmod.anis[0], 1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(self.cmod.anis[1], 1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(self.cmod.angles[0], 0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(self.cmod.angles[1], 0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(self.cmod.angles[2], 0)
-
- def test_vario_est(self):
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cmod, seed=12345)
- field = srf.structured((self.lat, self.lon))
-
- bin_edges = np.linspace(0, 3 * 777, 30)
- bin_center, emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- *((self.lat, self.lon), field, bin_edges),
- latlon=True,
- mesh_type="structured",
- sampling_size=2000,
- sampling_seed=12345,
- geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE,
- )
- mod = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
- mod.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, nugget=False)
- # allow 10 percent relative error
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(mod.var, self.cmod.var), 0.1)
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(mod.len_scale, self.cmod.len_scale), 0.1)
-
- def test_krige(self):
- bin_max = np.deg2rad(8)
- bin_edges = np.linspace(0, bin_max, 5)
- emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]),
- self.data[:, 2],
- bin_edges,
- latlon=True,
- )
- mod = gs.Spherical(latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
- mod.fit_variogram(*emp_vario, nugget=False)
- kri = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- mod,
- (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]),
- self.data[:, 2],
- )
- field, var = kri((self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]))
- for i, dat in enumerate(self.data[:, 2]):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[i], dat)
-
- def test_cond_srf(self):
- bin_max = np.deg2rad(8)
- bin_edges = np.linspace(0, bin_max, 5)
- emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]),
- self.data[:, 2],
- bin_edges,
- latlon=True,
- )
- mod = gs.Spherical(latlon=True, geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE)
- mod.fit_variogram(*emp_vario, nugget=False)
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- mod, (self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]), self.data[:, 2]
- )
- crf = gs.CondSRF(krige)
- field = crf((self.data[:, 0], self.data[:, 1]))
- for i, dat in enumerate(self.data[:, 2]):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[i], dat, 3)
-
- def test_error(self):
- # try fitting directional variogram
- mod = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True)
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- mod.fit_variogram([0, 1], [[0, 1], [0, 1], [0, 1]])
- # try to use fixed dim=2 with latlon
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- ErrMod(latlon=True)
- # try to estimate latlon vario on wrong dim
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.vario_estimate([[1], [1], [1]], [1], [0, 1], latlon=True)
- # try to estimate directional vario with latlon
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- gs.vario_estimate([[1], [1]], [1], [0, 1], latlon=True, angles=1)
- # try to create a vector field with latlon
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf = gs.SRF(mod, generator="VectorField", mode_no=2)
- srf([1, 2])
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_normalizer.py b/tests/test_normalizer.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 9ab0f45e0..000000000
--- a/tests/test_normalizer.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,223 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest of the Normalizer class.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-def _rel_err(a, b):
- return np.abs(a / ((a + b) / 2) - 1)
-
-
-class TestNormalizer(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.seed = 20210111
- self.rng = gs.random.RNG(self.seed)
- self.mean = 11.1
- self.std = 2.25
- self.smp = self.rng.random.normal(self.mean, self.std, 1000)
- self.lmb = 1.5
-
- def test_fitting(self):
- # boxcox with given data to init
- bc_samples = gs.normalizer.BoxCox(lmbda=self.lmb).denormalize(self.smp)
- bc_norm = gs.normalizer.BoxCox(data=bc_samples)
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(self.lmb, bc_norm.lmbda), 1e-2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- bc_norm.likelihood(bc_samples),
- np.exp(bc_norm.loglikelihood(bc_samples)),
- )
- # yeo-johnson with calling fit
- yj_norm = gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson(lmbda=self.lmb)
- yj_samples = yj_norm.denormalize(self.smp)
- yj_norm.fit(yj_samples)
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(self.lmb, yj_norm.lmbda), 1e-2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- yj_norm.likelihood(yj_samples),
- np.exp(yj_norm.loglikelihood(yj_samples)),
- )
- # modulus with calling fit
- mo_norm = gs.normalizer.Modulus(lmbda=self.lmb)
- mo_samples = mo_norm.denormalize(self.smp)
- mo_norm.fit(mo_samples)
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(self.lmb, mo_norm.lmbda), 1e-2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- mo_norm.likelihood(mo_samples),
- np.exp(mo_norm.loglikelihood(mo_samples)),
- )
- # manly with calling fit
- ma_norm = gs.normalizer.Manly(lmbda=self.lmb)
- ma_samples = ma_norm.denormalize(self.smp)
- ma_norm.fit(ma_samples)
- self.assertLess(_rel_err(self.lmb, ma_norm.lmbda), 1e-2)
- # self.assertAlmostEqual(
- # ma_norm.likelihood(ma_samples),
- # np.exp(ma_norm.loglikelihood(ma_samples)),
- # ) # this is comparing infs
-
- def test_boxcox(self):
- # without shift
- bc = gs.normalizer.BoxCox(lmbda=0)
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, bc.normalize(bc.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- bc.lmbda = self.lmb
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, bc.normalize(bc.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- # with shift
- bc = gs.normalizer.BoxCoxShift(lmbda=0, shift=1.1)
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, bc.normalize(bc.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- bc.lmbda = self.lmb
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, bc.normalize(bc.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
-
- def test_yeojohnson(self):
- yj = gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson(lmbda=0)
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(
- self.smp - self.mean,
- yj.normalize(yj.denormalize(self.smp - self.mean)),
- )
- )
- )
- yj.lmbda = 2
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(
- self.smp - self.mean,
- yj.normalize(yj.denormalize(self.smp - self.mean)),
- )
- )
- )
- # with shift
- yj.lmbda = self.lmb
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(
- self.smp - self.mean,
- yj.normalize(yj.denormalize(self.smp - self.mean)),
- )
- )
- )
-
- def test_modulus(self):
- mo = gs.normalizer.Modulus(lmbda=0)
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, mo.normalize(mo.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- mo.lmbda = self.lmb
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, mo.normalize(mo.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
-
- def test_manly(self):
- ma = gs.normalizer.Manly(lmbda=0)
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, ma.normalize(ma.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- ma.lmbda = self.lmb
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, ma.normalize(ma.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
-
- def test_parameterless(self):
- no = gs.normalizer.LogNormal()
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, no.normalize(no.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
- no = gs.normalizer.Normalizer()
- self.assertTrue(
- np.all(
- np.isclose(self.smp, no.normalize(no.denormalize(self.smp)))
- )
- )
-
- def test_compare(self):
- norm1 = gs.normalizer.BoxCox()
- norm2 = gs.normalizer.BoxCox(lmbda=0.5)
- norm3 = gs.normalizer.YeoJohnson()
- norm4 = "this is not a normalizer"
- # check campare
- self.assertTrue(norm1 == norm1)
- self.assertTrue(norm1 != norm2)
- self.assertTrue(norm1 != norm3)
- self.assertTrue(norm1 != norm4)
-
- def test_check(self):
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.field.Field, gs.Cubic(), normalizer=5)
-
- def test_auto_fit(self):
- x = y = range(60)
- pos = gs.generate_grid([x, y])
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
- srf = gs.SRF(
- model, seed=20170519, normalizer=gs.normalizer.LogNormal()
- )
- srf(pos)
- ids = np.arange(srf.field.size)
- samples = np.random.RandomState(20210201).choice(
- ids, size=60, replace=False
- )
- # sample conditioning points from generated field
- cond_pos = pos[:, samples]
- cond_val = srf.field[samples]
- krige = gs.krige.Ordinary(
- model=gs.Stable(dim=2),
- cond_pos=cond_pos,
- cond_val=cond_val,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.BoxCox(),
- fit_normalizer=True,
- fit_variogram=True,
- )
- # test fitting during kriging
- self.assertTrue(np.abs(krige.normalizer.lmbda - 0.0) < 1e-1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(krige.model.len_scale, 10.2677, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- krige.model.sill,
- krige.normalizer.normalize(cond_val).var(),
- places=4,
- )
- # test fitting during vario estimate
- bin_center, gamma, normalizer = gs.vario_estimate(
- cond_pos,
- cond_val,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.BoxCox,
- fit_normalizer=True,
- )
- model = gs.Stable(dim=2)
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, gamma)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.var, 0.6426670183, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.len_scale, 9.635193952, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.nugget, 0.001617908408, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(model.alpha, 2.0, places=4)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_randmeth.py b/tests/test_randmeth.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 7cbb962fb..000000000
--- a/tests/test_randmeth.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,75 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest of the RandMeth class.
-"""
-
-import copy
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-from gstools import Gaussian
-from gstools.field.generator import RandMeth
-
-
-class TestRandMeth(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_model_1d = Gaussian(dim=1, var=1.5, len_scale=3.5)
- self.cov_model_2d = copy.deepcopy(self.cov_model_1d)
- self.cov_model_2d.dim = 2
- self.cov_model_3d = copy.deepcopy(self.cov_model_1d)
- self.cov_model_3d.dim = 3
- self.seed = 19031977
- self.x_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 9)
- self.y_grid = np.linspace(-5.0, 5.0, 16)
- self.z_grid = np.linspace(-6.0, 7.0, 8)
- self.x_tuple = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 10)
- self.y_tuple = np.linspace(-5.0, 5.0, 10)
- self.z_tuple = np.linspace(-6.0, 8.0, 10)
-
- self.rm_1d = RandMeth(self.cov_model_1d, mode_no=100, seed=self.seed)
- self.rm_2d = RandMeth(self.cov_model_2d, mode_no=100, seed=self.seed)
- self.rm_3d = RandMeth(self.cov_model_3d, mode_no=100, seed=self.seed)
-
- def test_unstruct_1d(self):
- modes = self.rm_1d((self.x_tuple,))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 3.19799030)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 2.44848295)
-
- def test_unstruct_2d(self):
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 1.67318010)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 2.12310269)
-
- def test_unstruct_3d(self):
- modes = self.rm_3d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 1.3240234883187239)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 1.6367244277732766)
-
- def test_reset(self):
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 1.67318010)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 2.12310269)
-
- self.rm_2d.seed = self.rm_2d.seed
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 1.67318010)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 2.12310269)
-
- self.rm_2d.seed = 74893621
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], -1.94278053)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], -1.12401651)
-
- self.rm_1d.model = self.cov_model_3d
- modes = self.rm_1d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], 1.3240234883187239)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], 1.6367244277732766)
-
- self.rm_2d.mode_no = 800
- modes = self.rm_2d((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[0], -3.20809251)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(modes[1], -2.62032778)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_rng.py b/tests/test_rng.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 8fe167281..000000000
--- a/tests/test_rng.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,116 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest of the RNG class.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-from scipy.stats import kurtosis, normaltest, skew
-
-from gstools import Gaussian, TPLStable
-from gstools.random.rng import RNG
-
-
-class TestRNG(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.seed = 19031977
- self.rng = RNG(self.seed)
- self.many_modes = 1000000
- self.few_modes = 100
-
- def test_rng_normal_consistency(self):
- rng = RNG(21021997)
- z1_refs = [-1.93013270, 0.46330478]
- z2_refs = [-0.25536086, 0.98298696]
-
- z1 = self.rng.random.normal(size=self.few_modes)
- z2 = self.rng.random.normal(size=self.few_modes)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z1[0], z1_refs[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z1[1], z1_refs[1])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z2[0], z2_refs[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z2[1], z2_refs[1])
- self.rng.seed = self.seed
- z1 = self.rng.random.normal(size=self.few_modes)
- z2 = self.rng.random.normal(size=self.few_modes)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z1[0], z1_refs[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z1[1], z1_refs[1])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z2[0], z2_refs[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(z2[1], z2_refs[1])
-
- def test_sample_sphere_1d(self):
- dim = 1
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.few_modes)
- self.assertEqual(sphere_coord.shape, (dim, self.few_modes))
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.many_modes)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(sphere_coord), 0.0, places=3)
-
- def test_sample_sphere_2d(self):
- dim = 2
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.few_modes)
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- np.ones(self.few_modes),
- sphere_coord[0, :] ** 2 + sphere_coord[1, :] ** 2,
- )
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.many_modes)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(sphere_coord), 0.0, places=3)
-
- def test_sample_sphere_3d(self):
- dim = 3
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.few_modes)
- self.assertEqual(sphere_coord.shape, (dim, self.few_modes))
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- np.ones(self.few_modes),
- sphere_coord[0, :] ** 2
- + sphere_coord[1, :] ** 2
- + sphere_coord[2, :] ** 2,
- )
- sphere_coord = self.rng.sample_sphere(dim, self.many_modes)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(sphere_coord), 0.0, places=3)
-
- def test_sample_dist(self):
- model = Gaussian(dim=1, var=3.5, len_scale=8.0)
- pdf, cdf, ppf = model.dist_func
- rad = self.rng.sample_dist(
- size=self.few_modes, pdf=pdf, cdf=cdf, ppf=ppf, a=0
- )
- self.assertEqual(rad.shape[0], self.few_modes)
-
- model = Gaussian(dim=2, var=3.5, len_scale=8.0)
- pdf, cdf, ppf = model.dist_func
- rad = self.rng.sample_dist(
- size=self.few_modes, pdf=pdf, cdf=cdf, ppf=ppf, a=0
- )
- self.assertEqual(rad.shape[0], self.few_modes)
-
- model = Gaussian(dim=3, var=3.5, len_scale=8.0)
- pdf, cdf, ppf = model.dist_func
- rad = self.rng.sample_dist(
- size=self.few_modes, pdf=pdf, cdf=cdf, ppf=ppf, a=0
- )
- self.assertEqual(rad.shape[0], self.few_modes)
-
- # model = Gaussian(dim=2, var=3.5, len_scale=8.)
- # pdf, cdf, ppf = model.dist_func
- # rad = self.rng.sample_dist(
- # size=self.many_modes, pdf=pdf, cdf=cdf, ppf=ppf, a=0)
- # import matplotlib.pyplot as pt
- # pt.hist(rad, bins=30)
- # print(rad)
- # pt.show()
-
- # TODO test with different models
-
- # TODO rework this
- # def test_gau(self):
- # for d in range(len(self.rngs)):
- # Z, k = self.rngs[d]('gau', self.len_scale, self.many_modes)
- # self.assertEqual(k.shape, (d+1, self.many_modes))
- # self.assertAlmostEqual(np.mean(k), 0., places=2)
- # self.assertAlmostEqual(np.std(k), 1/self.len_scale, places=2)
- # self.assertAlmostEqual(skew(k[0, :]), 0., places=2)
- # self.assertAlmostEqual(kurtosis(k[0, :]), 0., places=1)
- # self.assertLess(normaltest(k[0, :])[1], 0.05)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_srf.py b/tests/test_srf.py
deleted file mode 100644
index eb9468ca4..000000000
--- a/tests/test_srf.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,334 +0,0 @@
-#!/usr/bin/env python
-"""
-This is the unittest of SRF class.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import meshio
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-from gstools import transform as tf
-
-HAS_PYVISTA = False
-try:
- import pyvista as pv
-
- HAS_PYVISTA = True
-except ImportError:
- pass
-
-
-class TestSRF(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1.5, len_scale=4.0)
- self.mean = 0.3
- self.mode_no = 100
-
- self.seed = 825718662
- self.x_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 12.0, 48)
- self.y_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 46)
- self.z_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 40)
-
- self.x_grid_c = np.linspace(-6.0, 6.0, 8)
- self.y_grid_c = np.linspace(-6.0, 6.0, 8)
- self.z_grid_c = np.linspace(-6.0, 6.0, 8)
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(123018)
- self.x_tuple = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
- self.y_tuple = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
- self.z_tuple = rng.uniform(0.0, 10, 100)
-
- def test_shape_1d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 1
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_str = srf([self.x_grid], seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured")
- field_unstr = srf(
- [self.x_tuple], seed=self.seed, mesh_type="unstructured"
- )
- self.assertEqual(field_str.shape, (len(self.x_grid),))
- self.assertEqual(field_unstr.shape, (len(self.x_tuple),))
-
- def test_shape_2d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 2
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_str = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured"
- )
- field_unstr = srf(
- (self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- )
- self.assertEqual(field_str.shape, (len(self.x_grid), len(self.y_grid)))
- self.assertEqual(field_unstr.shape, (len(self.x_tuple),))
-
- def test_shape_3d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 3
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_str = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid, self.z_grid),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- field_unstr = srf(
- (self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple),
- seed=987654,
- mesh_type="unstructured",
- )
- self.assertEqual(
- field_str.shape,
- (len(self.x_grid), len(self.y_grid), len(self.z_grid)),
- )
- self.assertEqual(field_unstr.shape, (len(self.x_tuple),))
-
- def test_anisotropy_2d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 2
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_iso = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured"
- )
- self.cov_model.anis = 0.5
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_aniso = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured"
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 0], field_aniso[0, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 4], field_aniso[0, 2])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 10], field_aniso[0, 5])
-
- def test_anisotropy_3d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 3
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_iso = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid, self.z_grid),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- self.cov_model.anis = (0.5, 4.0)
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_aniso = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid, self.z_grid),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 0, 0], field_aniso[0, 0, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 4, 0], field_aniso[0, 2, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 10, 0], field_aniso[0, 5, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 0, 0], field_aniso[0, 0, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 0, 1], field_aniso[0, 0, 4])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_iso[0, 0, 3], field_aniso[0, 0, 12])
-
- def test_rotation_unstruct_2d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 2
- x_len = len(self.x_grid_c)
- y_len = len(self.y_grid_c)
- x_u, y_u = np.meshgrid(self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c)
- x_u = np.reshape(x_u, x_len * y_len)
- y_u = np.reshape(y_u, x_len * y_len)
-
- self.cov_model.anis = 0.25
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
-
- field = srf((x_u, y_u), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="unstructured")
- field_str = np.reshape(field, (y_len, x_len))
-
- self.cov_model.angles = -np.pi / 2.0
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_rot = srf((x_u, y_u), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="unstructured")
- field_rot_str = np.reshape(field_rot, (y_len, x_len))
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_str[0, 0], field_rot_str[-1, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_str[1, 2], field_rot_str[-3, 1])
-
- def test_rotation_struct_2d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 2
- self.cov_model.anis = 0.25
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field = srf(
- (self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
-
- self.cov_model.angles = -np.pi / 2.0
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_rot = srf(
- (self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0], field_rot[0, -1])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[1, 2], field_rot[2, 6])
-
- def test_rotation_unstruct_3d(self):
- self.cov_model = gs.Gaussian(
- dim=3, var=1.5, len_scale=4.0, anis=(0.25, 0.5)
- )
- x_len = len(self.x_grid_c)
- y_len = len(self.y_grid_c)
- z_len = len(self.z_grid_c)
- x_u, y_u, z_u = np.meshgrid(
- self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c, self.z_grid_c
- )
- x_u = np.reshape(x_u, x_len * y_len * z_len)
- y_u = np.reshape(y_u, x_len * y_len * z_len)
- z_u = np.reshape(z_u, x_len * y_len * z_len)
-
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field = srf((x_u, y_u, z_u), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="unstructured")
- field_str = np.reshape(field, (y_len, x_len, z_len))
-
- self.cov_model.angles = (-np.pi / 2.0, -np.pi / 2.0)
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_rot = srf(
- (x_u, y_u, z_u), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="unstructured"
- )
- field_rot_str = np.reshape(field_rot, (y_len, x_len, z_len))
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_str[0, 0, 0], field_rot_str[-1, -1, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_str[1, 2, 0], field_rot_str[-3, -1, 1])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field_str[0, 0, 1], field_rot_str[-1, -2, 0])
-
- def test_rotation_struct_3d(self):
- self.cov_model.dim = 3
- self.cov_model.anis = 0.25
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field = srf(
- (self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c, self.z_grid_c),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
-
- self.cov_model.angles = -np.pi / 2.0
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_rot = srf(
- (self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c, self.z_grid_c),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0, 0], field_rot[0, 7, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0, 1], field_rot[0, 7, 1])
-
- self.cov_model.angles = (0, -np.pi / 2.0)
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field_rot = srf(
- (self.x_grid_c, self.y_grid_c, self.z_grid_c),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0, 0], field_rot[7, 0, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 1, 0], field_rot[7, 1, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[1, 1, 0], field_rot[7, 1, 1])
-
- def test_calls(self):
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- field = srf((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple), seed=self.seed)
- field2 = srf.unstructured((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple), seed=self.seed)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0], srf.field[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0], field2[0])
- field = srf(
- (self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple),
- seed=self.seed,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- field2 = srf.structured((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple), seed=self.seed)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0], srf.field[0, 0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0], field2[0, 0])
-
- @unittest.skipIf(not HAS_PYVISTA, "PyVista is not installed")
- def test_mesh_pyvista(self):
- """Test the `.mesh` call with various PyVista meshes."""
- # Create model
- self.cov_model.dim = 3
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- # Get the field the normal way for comparison
- field = srf((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple), seed=self.seed)
- # Create mesh space with PyVista
- pv_mesh = pv.PolyData(np.c_[self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple])
- # Run the helper
- _ = srf.mesh(pv_mesh, seed=self.seed, points="centroids")
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(field, pv_mesh["field"]))
- # points="centroids"
- _ = srf.mesh(pv_mesh, seed=self.seed, points="points")
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(field, pv_mesh["field"]))
-
- def test_incomprrandmeth(self):
- self.cov_model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=0.5, len_scale=1.0)
- srf = gs.SRF(
- self.cov_model,
- mean=self.mean,
- mode_no=self.mode_no,
- generator="IncomprRandMeth",
- mean_velocity=0.5,
- )
- field = srf((self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple), seed=476356)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0], 1.23693272)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 1], 0.89242284)
- field = srf(
- (self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=4734654, mesh_type="structured"
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 0, 0], 1.07812013)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(field[0, 1, 0], 1.06180674)
-
- # TODO put these checks into test_cov_model
- def test_assertions(self):
- # self.cov_model.dim = 0
- # self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.SRF, self.cov_model, self.mean, self.mode_no)
- # self.cov_model.dim = 4
- # self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.SRF, self.cov_model, self.mean, self.mode_no)
- self.cov_model.dim = 3
- self.cov_model.anis = (0.25, 0.5)
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, srf, [self.x_tuple])
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, srf, [self.x_grid, self.y_grid])
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, srf, [self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple])
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, srf, [self.x_grid, self.y_grid, self.z_grid]
- )
- # everything not "unstructured" is treated as "structured"
- # self.assertRaises(
- # ValueError,
- # srf,
- # [self.x_tuple, self.y_tuple, self.z_tuple],
- # self.seed,
- # mesh_type="hyper_mesh",
- # )
-
- def test_meshio(self):
- points = np.array(
- [
- [0.0, 0.0, 0.0],
- [0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
- [0.0, 0.0, 1.0],
- [1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
- ]
- )
- cells = [("tetra", np.array([[0, 1, 2, 3]]))]
- mesh = meshio.Mesh(points, cells)
- model = gs.Gaussian(dim=3, len_scale=0.1)
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- srf.mesh(mesh, points="points")
- self.assertEqual(len(srf.field), 4)
- srf.mesh(mesh, points="centroids")
- self.assertEqual(len(srf.field), 1)
-
- def test_grid_generation(self):
- pos1 = [self.x_grid, self.y_grid, self.z_grid]
- pos2 = gs.generate_grid(pos1)
- time = np.arange(10)
- grid1 = gs.generate_grid(pos1 + [time])
- grid2 = gs.generate_st_grid(pos1, time, mesh_type="structured")
- grid3 = gs.generate_st_grid(pos2, time, mesh_type="unstructured")
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(grid1, grid2)))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(grid1, grid3)))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.isclose(grid2, grid3)))
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_temporal.py b/tests/test_temporal.py
deleted file mode 100644
index c179db1c2..000000000
--- a/tests/test_temporal.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,78 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is the unittest for temporal related routines.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class TestTemporal(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.mod = gs.Gaussian(
- latlon=True,
- temporal=True,
- len_scale=1000,
- anis=0.5,
- geo_scale=gs.KM_SCALE,
- )
-
- def test_latlon(self):
- mod = gs.Gaussian(
- latlon=True, temporal=True, angles=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
- )
- self.assertEqual(mod.dim, 4)
- self.assertEqual(mod.field_dim, 3)
- self.assertEqual(mod.spatial_dim, 2)
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(mod.angles, 0))
-
- mod1 = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, temporal=True, len_scale=[10, 5])
- mod2 = gs.Gaussian(latlon=True, temporal=True, len_scale=10, anis=0.5)
-
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(mod1.anis, mod2.anis))
- self.assertAlmostEqual(mod1.len_scale, mod2.len_scale)
-
- def test_latlon2pos(self):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 8, self.mod.anisometrize(self.mod.isometrize((8, 6, 9)))[0, 0]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 6, self.mod.anisometrize(self.mod.isometrize((8, 6, 9)))[1, 0]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 9, self.mod.anisometrize(self.mod.isometrize((8, 6, 9)))[2, 0]
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- gs.EARTH_RADIUS,
- self.mod.isometrize(
- self.mod.anisometrize((gs.EARTH_RADIUS, 0, 0, 10))
- )[0, 0],
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- 10,
- self.mod.isometrize(
- self.mod.anisometrize((gs.EARTH_RADIUS, 0, 0, 10))
- )[3, 0],
- )
-
- def test_rotation(self):
- mod = gs.Gaussian(
- spatial_dim=3, temporal=True, angles=[1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
- )
- self.assertTrue(np.allclose(mod.angles, [1, 2, 3, 0, 0, 0]))
- self.assertEqual(mod.dim, 4)
-
- def test_krige(self):
- # auto-fitting latlon-temporal model in kriging not possible
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- kri = gs.Krige(self.mod, 3 * [[1, 2]], [1, 2], fit_variogram=True)
-
- def test_field(self):
- srf = gs.SRF(self.mod)
- self.assertTrue(srf.temporal)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_transform.py b/tests/test_transform.py
deleted file mode 100644
index abc5505b0..000000000
--- a/tests/test_transform.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,189 +0,0 @@
-"""This is the unittest of the transform submodule."""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class TestTransform(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- self.cov_model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1.5, len_scale=4.0)
- self.mean = 0.3
- self.mode_no = 100
-
- self.seed = 825718662
- self.x_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 12.0, 48)
- self.y_grid = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 46)
-
- self.methods = [
- "binary",
- "boxcox",
- "zinnharvey",
- "normal_force_moments",
- "normal_to_lognormal",
- "normal_to_uniform",
- "normal_to_arcsin",
- "normal_to_uquad",
- ]
-
- def test_transform_normal(self):
- srf = gs.SRF(self.cov_model, mean=self.mean, mode_no=self.mode_no)
- srf((self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured")
- for method in self.methods:
- srf.transform(method, store=method)
- std = np.sqrt(srf.model.var)
- self.assertTrue(set(self.methods) == set(srf.field_names[1:]))
- # force moments
- self.assertAlmostEqual(srf["normal_force_moments"].mean(), srf.mean)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(srf["normal_force_moments"].var(), std**2)
- # binary
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- np.unique(srf.binary), srf.mean + np.array([-std, std])
- )
- # boxcox
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- srf.field, gs.normalizer.BoxCox().normalize(srf.boxcox)
- )
- with self.assertWarns(Warning):
- srf.transform("boxcox", store="boxcox_warn", lmbda=2)
- # lognormal
- np.testing.assert_allclose(srf.field, np.log(srf.normal_to_lognormal))
- srf.transform("boxcox", store="boxcox2", lmbda=0)
- np.testing.assert_allclose(srf.boxcox2, srf.normal_to_lognormal)
- # unifrom
- self.assertTrue(np.all(srf.normal_to_uniform < 1))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(srf.normal_to_uniform > 0))
- # how to test arcsin and uquad?!
-
- # discrete
- values = [-1, 0, 1]
- thresholds = [-0.9, 0.1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete", values=values, thresholds=thresholds, store="f1"
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(srf.f1), [-1, 0, 1])
-
- values = [-1, 0, 1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete", values=values, thresholds="arithmetic", store="f2"
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(srf.f2), [-1.0, 0.0, 1.0])
-
- values = [-1, 0, 0.5, 1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete", values=values, thresholds="equal", store="f3"
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(srf.f3), values)
- # checks
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf.transform("discrete", values=values, thresholds=[1])
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf.transform("discrete", values=values, thresholds=[1, 3, 2])
-
- # function
- srf.transform("function", function=lambda x: 2 * x, store="f4")
- np.testing.assert_allclose(2 * srf.field, srf.f4)
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf.transform("function", function=None)
-
- # unknown method
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf.transform("foobar")
-
- def test_transform_denormal(self):
- srf_fail = gs.SRF(
- model=self.cov_model,
- mean=self.mean,
- mode_no=self.mode_no,
- trend=lambda x, y: x,
- )
- srf_fail((self.x_grid, self.y_grid), mesh_type="structured")
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf_fail.transform("zinnharvey")
-
- srf_fail = gs.SRF(
- model=self.cov_model,
- mean=lambda x, y: x,
- mode_no=self.mode_no,
- )
- srf_fail((self.x_grid, self.y_grid), mesh_type="structured")
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf_fail.transform("zinnharvey")
-
- srf = gs.SRF(
- model=self.cov_model,
- mean=self.mean,
- mode_no=self.mode_no,
- normalizer=gs.normalizer.LogNormal,
- )
- srf((self.x_grid, self.y_grid), seed=self.seed, mesh_type="structured")
-
- for method in self.methods:
- if method in ("normal_to_lognormal", "boxcox"):
- continue
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- srf.transform(method, store=method)
-
- for method in self.methods:
- srf.transform(method, store=method, process=True)
- std = np.sqrt(srf.model.var)
- self.assertTrue(set(self.methods) == set(srf.field_names[1:]))
- # force moments
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.log(srf["normal_force_moments"]).mean(), srf.mean
- )
- self.assertAlmostEqual(
- np.log(srf["normal_force_moments"]).var(), std**2
- )
- # binary
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- np.unique(np.log(srf.binary)), srf.mean + np.array([-std, std])
- )
- # boxcox
- np.testing.assert_allclose(
- np.log(srf.field),
- gs.normalizer.BoxCox().normalize(np.log(srf.boxcox)),
- )
- # lognormal
- np.testing.assert_allclose(srf.field, np.log(srf.normal_to_lognormal))
- # unifrom
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.log(srf.normal_to_uniform) < 1))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(np.log(srf.normal_to_uniform) > 0))
-
- # discrete
- values = [-1, 0, 1]
- thresholds = [-0.9, 0.1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete",
- values=values,
- thresholds=thresholds,
- store="f1",
- process=True,
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(np.log(srf.f1)), [-1, 0, 1])
-
- values = [-1, 0, 1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete",
- values=values,
- thresholds="arithmetic",
- store="f2",
- process=True,
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(np.log(srf.f2)), [-1.0, 0.0, 1.0])
-
- values = [-1, 0, 0.5, 1]
- srf.transform(
- "discrete",
- values=values,
- thresholds="equal",
- store="f3",
- process=True,
- )
- np.testing.assert_allclose(np.unique(np.log(srf.f3)), values)
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_variogram.py b/tests/test_variogram.py
new file mode 100644
index 000000000..4580b231e
--- /dev/null
+++ b/tests/test_variogram.py
@@ -0,0 +1,144 @@
+"""
+This is a unittest of the variogram module.
+"""
+
+import unittest
+
+import numpy as np
+
+import gstools_cython as gs_cy
+
+
+class TestVariogram(unittest.TestCase):
+ def test_directional(self):
+ x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
+ y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
+ x, y = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c)
+ x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
+ y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
+ pos = np.array((x, y), dtype=np.double)
+ dirs = np.array(((1, 0), (0, 1)), dtype=np.double)
+
+ rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
+ field = np.asarray([rng.rand(len(x))], dtype=np.double)
+ bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10, dtype=np.double)
+
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+
+ gamma, counts = gs_cy.variogram.directional(field, bins, pos, dirs)
+ print(counts)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0, 0], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0, len(gamma[0]) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0, -1], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1, 0], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1, len(gamma[0]) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1, -1], var, places=2)
+
+ def test_unstructured(self):
+ x = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
+ z = np.array(
+ (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
+ x = np.atleast_2d(x)
+ z = np.atleast_2d(z)
+
+ gamma, counts = gs_cy.variogram.unstructured(z, bins, x)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.4917, places=4)
+ self.assertEqual(counts[0], 9)
+
+ x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
+ y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
+ x, y = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c)
+ x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
+ y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
+ pos = np.array((x, y), dtype=np.double)
+
+ rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
+ field = np.asarray([rng.rand(len(x))], dtype=np.double)
+ bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10, dtype=np.double)
+
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+
+ gamma, counts = gs_cy.variogram.unstructured(field, bins, pos)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
+
+ gamma, counts = gs_cy.variogram.unstructured(
+ field, bins, pos, estimator_type="c"
+ )
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
+
+ def test_structured(self):
+ z = np.array(
+ (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ # need 2d arrays
+ z = z.reshape((z.shape[0], -1))
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.structured(z)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.structured(z, estimator_type="c")
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 1.546 / 2.0, places=3)
+
+ rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
+ field = np.asarray(rng.rand(80, 60), dtype=np.double)
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.structured(field)
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.structured(field, estimator_type="c")
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=1)
+
+ def test_ma_structured(self):
+ z = np.array(
+ (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
+ dtype=np.double,
+ )
+ mask = np.array((1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0), dtype=np.int32)
+ # need 2d arrays
+ z = z.reshape((z.shape[0], -1))
+ mask = mask.reshape((mask.shape[0], -1))
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.ma_structured(z, mask)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0000, places=4)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4906, places=4)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[2], 0.7107, places=4)
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.ma_structured(z, mask, estimator_type="c")
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0000, places=4)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.7399, places=4)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[2], 0.8660, places=4)
+
+ rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
+ field = np.asarray(rng.rand(80, 60), dtype=np.double)
+ mask = np.zeros_like(field, dtype=np.int32)
+ mask[0, 0] = 1
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.ma_structured(field, mask)
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
+
+ gamma = gs_cy.variogram.ma_structured(field, mask, estimator_type="c")
+ var = 1.0 / 12.0
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
+ self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
+
+
+if __name__ == "__main__":
+ unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_variogram_structured.py b/tests/test_variogram_structured.py
deleted file mode 100644
index e0a3525aa..000000000
--- a/tests/test_variogram_structured.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,278 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is a unittest of the variogram module.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class TestVariogramStructured(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- pass
-
- def test_doubles(self):
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
-
- def test_ints(self):
- z = np.array((10, 20, 30, 40), dtype=int)
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 50.0, places=4)
-
- def test_mixed(self):
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
-
- z = np.array((10, 20, 30, 40), dtype=int)
-
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 50.0, places=4)
-
- def test_list(self):
- z = [41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3]
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
-
- def test_cressie_1d(self):
- z = [41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3]
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z, estimator="cressie")
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 1.546 / 2.0, places=3)
-
- def test_1d(self):
- # literature values
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0000, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[2], 0.7625, places=4)
-
- def test_masked_1d(self):
- # literature values
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- z_ma = np.ma.masked_array(z, mask=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z_ma)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0000, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4917, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[2], 0.7625, places=4)
- z_ma = np.ma.masked_array(z, mask=[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(z_ma)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0000, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.4906, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[2], 0.7107, places=4)
-
- def test_masked_2d(self):
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(80, 60)
- mask = np.zeros_like(field)
- field_ma = np.ma.masked_array(field, mask=mask)
-
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="x")
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="y")
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[len(gamma_x) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[-1], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[len(gamma_y) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[-1], var, places=2)
-
- mask = np.zeros_like(field)
- mask[0, 0] = 1
- field = np.ma.masked_array(field, mask=mask)
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="x")
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="y")
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=2)
-
- def test_masked_3d(self):
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(30, 30, 30)
- mask = np.zeros_like(field)
- field_ma = np.ma.masked_array(field, mask=mask)
-
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="x")
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="y")
- gamma_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="z")
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[len(gamma_x) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[-1], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[len(gamma_y) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[-1], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z[len(gamma_y) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z[-1], var, places=2)
-
- mask = np.zeros_like(field)
- mask[0, 0, 0] = 1
- field = np.ma.masked_array(field, mask=mask)
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="x")
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="y")
- gamma_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_ma, direction="z")
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z[0], 0.0, places=2)
-
- def test_uncorrelated_2d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 80)
- y = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 60)
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x), len(y))
-
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, direction="x")
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, direction="y")
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[len(gamma_x) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[-1], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[len(gamma_y) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_uncorrelated_cressie_2d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 80)
- y = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 60)
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x), len(y))
-
- gamma_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(
- field, direction="x", estimator="cressie"
- )
- gamma_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(
- field, direction="y", estimator="cressie"
- )
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[0], 0.0, places=1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x[len(gamma_x) // 2], var, places=1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[0], 0.0, places=1)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y[len(gamma_y) // 2], var, places=1)
-
- def test_uncorrelated_3d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
- y = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
- z = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 30)
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x), len(y), len(z))
-
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "x")
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "y")
- gamma = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "z")
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.0, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_directions_2d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 20.0, 100)
- y = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 80)
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- x_rand = rng.rand(len(x))
- y_rand = rng.rand(len(y))
- # random values repeated along y-axis
- field_x = np.tile(x_rand, (len(y), 1)).T
- # random values repeated along x-axis
- field_y = np.tile(y_rand, (len(x), 1))
-
- # gamma_x_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_x, direction="x")
- gamma_x_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_x, direction="y")
-
- gamma_y_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_y, direction="x")
- # gamma_y_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_y, direction="y")
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[-1], 0.0)
-
- def test_directions_3d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 20)
- y = np.linspace(0.0, 15.0, 25)
- z = np.linspace(0.0, 20.0, 30)
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- x_rand = rng.rand(len(x))
- y_rand = rng.rand(len(y))
- z_rand = rng.rand(len(z))
-
- field_x = np.tile(x_rand.reshape((len(x), 1, 1)), (1, len(y), len(z)))
- field_y = np.tile(y_rand.reshape((1, len(y), 1)), (len(x), 1, len(z)))
- field_z = np.tile(z_rand.reshape((1, 1, len(z))), (len(x), len(y), 1))
-
- # gamma_x_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_x, direction="x")
- gamma_x_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_x, direction="y")
- gamma_x_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_x, direction="z")
-
- gamma_y_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_y, direction="x")
- # gamma_y_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_y, direction="y")
- gamma_y_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_y, direction="z")
-
- gamma_z_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_z, direction="x")
- gamma_z_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_z, direction="y")
- # gamma_z_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field_z, direction="z")
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_y[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_z[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_z[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_x_z[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_x[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_z[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_z[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_y_z[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_x[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_x[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_x[-1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_y[1], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_y[len(gamma_x_y) // 2], 0.0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma_z_y[-1], 0.0)
-
- def test_exceptions(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 20)
- # rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- # x_rand = rng.rand(len(x))
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.vario_estimate_axis, x, "a")
-
- def test_missing(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 10.0, 10)
- x_nan = x.copy()
- x_nan[0] = np.nan
- x_mask = np.isnan(x_nan)
- x = np.ma.array(x, mask=x_mask)
- v1 = gs.vario_estimate_axis(x_nan)
- v2 = gs.vario_estimate_axis(x)
- for i in range(len(v1)):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v1[i], v2[i])
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
diff --git a/tests/test_variogram_unstructured.py b/tests/test_variogram_unstructured.py
deleted file mode 100644
index 10b085bf0..000000000
--- a/tests/test_variogram_unstructured.py
+++ /dev/null
@@ -1,409 +0,0 @@
-"""
-This is a unittest of the variogram module.
-"""
-
-import unittest
-
-import numpy as np
-
-import gstools as gs
-
-
-class TestVariogramUnstructured(unittest.TestCase):
- def setUp(self):
- model = gs.Exponential(dim=3, len_scale=[12, 6, 3])
- x = y = z = range(10)
- self.pos = (x, y, z)
- srf = gs.SRF(model, seed=123456)
- self.field = srf((x, y, z), mesh_type="structured")
-
- def test_doubles(self):
- x = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.4917, places=4)
-
- def test_ints(self):
- x = np.arange(1, 5, 1, dtype=int)
- z = np.array((10, 20, 30, 40), dtype=int)
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=int)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 50.0, places=4)
-
- def test_mixed(self):
- x = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=int)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.4917, places=4)
-
- x = np.arange(1, 5, 1, dtype=np.double)
- z = np.array((10, 20, 30, 40), dtype=int)
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=int)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 50.0, places=4)
-
- x = np.arange(1, 5, 1, dtype=np.double)
- z = np.array((10, 20, 30, 40), dtype=int)
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 50.0, places=4)
-
- def test_list(self):
- x = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- z = [41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3]
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.7625, places=4)
-
- def test_1d(self):
- x = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- # literature values
- z = np.array(
- (41.2, 40.2, 39.7, 39.2, 40.1, 38.3, 39.1, 40.0, 41.1, 40.3),
- dtype=np.double,
- )
- bins = np.arange(1, 11, 1, dtype=np.double)
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate([x], z, bins)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], 0.4917, places=4)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[1], 0.7625, places=4)
-
- def test_uncorrelated_2d(self):
- x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 60)
- y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 60)
- x, y = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c)
- x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
- y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x))
-
- bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
-
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y), field, bins)
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_uncorrelated_3d(self):
- x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 15)
- y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 15)
- z_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 15)
- x, y, z = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c, z_c)
- x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
- y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
- z = np.reshape(z, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x))
-
- bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
-
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate((x, y, z), field, bins)
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_sampling_1d(self):
- x = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 21000)
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x))
-
- bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
-
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate(
- [x], field, bins, sampling_size=5000, sampling_seed=1479373475
- )
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_sampling_2d(self):
- x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 600)
- y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 600)
- x, y = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c)
- x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
- y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c))
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x))
-
- bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
-
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate(
- (x, y), field, bins, sampling_size=2000, sampling_seed=1479373475
- )
-
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_sampling_3d(self):
- x_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 100)
- y_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 100)
- z_c = np.linspace(0.0, 100.0, 100)
- x, y, z = np.meshgrid(x_c, y_c, z_c)
- x = np.reshape(x, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
- y = np.reshape(y, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
- z = np.reshape(z, len(x_c) * len(y_c) * len(z_c))
-
- rng = np.random.RandomState(1479373475)
- field = rng.rand(len(x))
-
- bins = np.arange(0, 100, 10)
-
- bin_centres, gamma = gs.vario_estimate(
- (x, y, z),
- field,
- bins,
- sampling_size=2000,
- sampling_seed=1479373475,
- )
- var = 1.0 / 12.0
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[0], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[len(gamma) // 2], var, places=2)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[-1], var, places=2)
-
- def test_assertions(self):
- x = np.arange(0, 10)
- x_e = np.arange(0, 11)
- y = np.arange(0, 11)
- y_e = np.arange(0, 12)
- z = np.arange(0, 12)
- z_e = np.arange(0, 15)
- bins = np.arange(0, 3)
- # bins_e = np.arange(0, 1)
- field = np.arange(0, 10)
- field_e = np.arange(0, 9)
-
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, [x_e], field, bins)
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, (x, y_e), field, bins)
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, (x, y_e, z), field, bins
- )
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, (x, y, z_e), field, bins
- )
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, (x_e, y, z), field, bins
- )
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, (x, y, z), field_e, bins
- )
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, [x], field_e, bins)
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, [x], field, bins, estimator="bla"
- )
-
- def test_multi_field(self):
- x = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(100) * 100.0
- model = gs.Exponential(dim=1, var=2, len_scale=10)
- srf = gs.SRF(model)
- field1 = srf(x, seed=19970221)
- field2 = srf(x, seed=20011012)
- bins = np.arange(20) * 2
- bin_center, gamma1 = gs.vario_estimate(x, field1, bins)
- bin_center, gamma2 = gs.vario_estimate(x, field2, bins)
- bin_center, gamma = gs.vario_estimate(x, [field1, field2], bins)
- gamma_mean = 0.5 * (gamma1 + gamma2)
- for i in range(len(gamma)):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma[i], gamma_mean[i], places=2)
-
- def test_no_data(self):
- x1 = np.random.RandomState(19970221).rand(100) * 100.0
- field1 = np.random.RandomState(20011012).rand(100) * 100.0
- field1[:10] = np.nan
- x2 = x1[10:]
- field2 = field1[10:]
- bins = np.arange(20) * 2
- bin_center, gamma1 = gs.vario_estimate(x1, field1, bins)
- bin_center, gamma2 = gs.vario_estimate(x2, field2, bins)
- for i in range(len(gamma1)):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(gamma1[i], gamma2[i], places=2)
-
- def test_direction_axis(self):
- field = np.ma.array(self.field)
- field.mask = np.abs(field) < 0.1
- bins = range(10)
- __, vario_u = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(self.pos, field, bins),
- direction=((1, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 1)), # x-, y- and z-axis
- bandwidth=0.25, # bandwith small enough to only match lines
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- vario_s_x = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "x")
- vario_s_y = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "y")
- vario_s_z = gs.vario_estimate_axis(field, "z")
- for i in range(len(bins) - 1):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(vario_u[0][i], vario_s_x[i])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(vario_u[1][i], vario_s_y[i])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(vario_u[2][i], vario_s_z[i])
-
- def test_direction_angle(self):
- bins = range(0, 10, 2)
- __, v2, c2 = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(self.pos[:2], self.field[0], bins),
- angles=np.pi / 4, # 45 deg
- mesh_type="structured",
- return_counts=True,
- )
- __, v1, c1 = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(self.pos[:2], self.field[0], bins),
- direction=(1, 1), # 45 deg
- mesh_type="structured",
- return_counts=True,
- )
- for i in range(len(bins) - 1):
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v1[i], v2[i])
- self.assertEqual(c1[i], c2[i])
-
- def test_direction_assertion(self):
- pos = [[1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3]]
- bns = [1, 2]
- fld = np.ma.array([1, 2, 3])
- self.assertRaises( # degenerated direction
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, pos, fld, bns, direction=[0, 0]
- )
- self.assertRaises( # wrong shape of direction
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, pos, fld, bns, direction=[[[3, 1]]]
- )
- self.assertRaises( # wrong dimension of direction
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, pos, fld, bns, direction=[[3, 1, 2]]
- )
- self.assertRaises( # wrong shape of angles
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, pos, fld, bns, angles=[[[1]]]
- )
- self.assertRaises( # wrong dimension of angles
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, pos, fld, bns, angles=[[1, 1]]
- )
- self.assertRaises( # direction on latlon
- ValueError,
- gs.vario_estimate,
- pos,
- fld,
- bns,
- direction=[1, 0],
- latlon=True,
- )
-
- def test_mask_no_data(self):
- pos = [[1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]]
- bns = [0, 4]
- fld1 = np.ma.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
- fld2 = np.ma.array([np.nan, 2, 3, 4, 5])
- fld3 = np.ma.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
- mask = [False, False, True, False, False]
- fld1.mask = [True, False, False, False, False]
- fld2.mask = mask
- __, v1, c1 = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(pos, fld1, bns),
- mask=mask,
- return_counts=True,
- )
- __, v2, c2 = gs.vario_estimate(*(pos, fld2, bns), return_counts=True)
- __, v3, c3 = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(pos, fld3, bns),
- no_data=1,
- mask=mask,
- return_counts=True,
- )
- __, v4, c4 = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(pos, fld3, bns),
- mask=True,
- return_counts=True,
- )
- __, v5 = gs.vario_estimate(*(pos, fld3, bns), mask=True)
-
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v1[0], v2[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v1[0], v3[0])
- self.assertEqual(c1[0], c2[0])
- self.assertEqual(c1[0], c3[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v4[0], 0.0)
- self.assertEqual(c4[0], 0)
- self.assertAlmostEqual(v5[0], 0.0)
-
- def test_fit_directional(self):
- model = gs.Stable(dim=3)
- bins = [0, 3, 6, 9, 12]
- model.len_scale_bounds = [0, 20]
- bin_center, emp_vario, counts = gs.vario_estimate(
- *(self.pos, self.field, bins),
- direction=model.main_axes(),
- mesh_type="structured",
- return_counts=True,
- )
- # check if this succeeds
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, sill=1, return_r2=True)
- self.assertTrue(1 > model.anis[0] > model.anis[1])
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, sill=1, anis=[0.5, 0.25])
- self.assertTrue(15 > model.len_scale)
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, sill=1, weights=counts)
- len_save = model.len_scale
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario, sill=1, weights=counts[0])
- self.assertAlmostEqual(len_save, model.len_scale)
- # catch wrong dim for dir.-vario
- with self.assertRaises(ValueError):
- model.fit_variogram(bin_center, emp_vario[:2])
-
- def test_auto_binning(self):
- # structured mesh
- bin_center, emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- self.pos,
- self.field,
- mesh_type="structured",
- )
- self.assertEqual(len(bin_center), 21)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center[1:] > bin_center[:-1]))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center > 0))
- # unstructured mesh
- bin_center, emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- self.pos,
- self.field[:, 0, 0],
- )
- self.assertEqual(len(bin_center), 8)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center[1:] > bin_center[:-1]))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center > 0))
- # latlon coords
- bin_center, emp_vario = gs.vario_estimate(
- self.pos[:2],
- self.field[..., 0],
- mesh_type="structured",
- latlon=True,
- )
- self.assertEqual(len(bin_center), 15)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center[1:] > bin_center[:-1]))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bin_center > 0))
-
- def test_standard_bins(self):
- # structured mesh
- bins = gs.standard_bins(self.pos, dim=3, mesh_type="structured")
- self.assertEqual(len(bins), 22)
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bins[1:] > bins[:-1]))
- self.assertTrue(np.all(bins[1:] > 0))
- # no pos given
- self.assertRaises(ValueError, gs.standard_bins)
-
- def test_raise(self):
- # 1d field given for latlon estimation -> needs 2d
- self.assertRaises(
- ValueError, gs.vario_estimate, [[1, 2]], [1, 2], latlon=True
- )
-
-
-if __name__ == "__main__":
- unittest.main()
 -
- -
-


 -
-
-
- -
-GeoStatTools provides geostatistical tools for various purposes:
-- random field generation
-- simple, ordinary, universal and external drift kriging
-- conditioned field generation
-- incompressible random vector field generation
-- (automated) variogram estimation and fitting
-- directional variogram estimation and modelling
-- data normalization and transformation
-- many readily provided and even user-defined covariance models
-- metric spatio-temporal modelling
-- plotting and exporting routines
-
## Installation
@@ -88,275 +59,19 @@ You can cite the Zenodo code publication of GSTools by:
If you want to cite a specific version, have a look at the [Zenodo site](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628).
-## Documentation for GSTools
-
-You can find the documentation under [geostat-framework.readthedocs.io][doc_link].
-
-
-### Tutorials and Examples
-
-The documentation also includes some [tutorials][tut_link], showing the most important use cases of GSTools, which are
-
-- [Random Field Generation][tut1_link]
-- [The Covariance Model][tut2_link]
-- [Variogram Estimation][tut3_link]
-- [Random Vector Field Generation][tut4_link]
-- [Kriging][tut5_link]
-- [Conditioned random field generation][tut6_link]
-- [Field transformations][tut7_link]
-- [Geographic Coordinates][tut8_link]
-- [Spatio-Temporal Modelling][tut9_link]
-- [Normalizing Data][tut10_link]
-- [Miscellaneous examples][tut0_link]
-
-The associated python scripts are provided in the `examples` folder.
-
-
-## Spatial Random Field Generation
-
-The core of this library is the generation of spatial random fields. These fields are generated using the randomisation method, described by [Heße et al. 2014][rand_link].
-
-[rand_link]: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.01.013
-
-
-### Examples
-
-#### Gaussian Covariance Model
-
-This is an example of how to generate a 2 dimensional spatial random field with a gaussian covariance model.
+## Documentation
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-# structured field with a size 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.plot()
-```
-
-
-GeoStatTools provides geostatistical tools for various purposes:
-- random field generation
-- simple, ordinary, universal and external drift kriging
-- conditioned field generation
-- incompressible random vector field generation
-- (automated) variogram estimation and fitting
-- directional variogram estimation and modelling
-- data normalization and transformation
-- many readily provided and even user-defined covariance models
-- metric spatio-temporal modelling
-- plotting and exporting routines
-
## Installation
@@ -88,275 +59,19 @@ You can cite the Zenodo code publication of GSTools by:
If you want to cite a specific version, have a look at the [Zenodo site](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1313628).
-## Documentation for GSTools
-
-You can find the documentation under [geostat-framework.readthedocs.io][doc_link].
-
-
-### Tutorials and Examples
-
-The documentation also includes some [tutorials][tut_link], showing the most important use cases of GSTools, which are
-
-- [Random Field Generation][tut1_link]
-- [The Covariance Model][tut2_link]
-- [Variogram Estimation][tut3_link]
-- [Random Vector Field Generation][tut4_link]
-- [Kriging][tut5_link]
-- [Conditioned random field generation][tut6_link]
-- [Field transformations][tut7_link]
-- [Geographic Coordinates][tut8_link]
-- [Spatio-Temporal Modelling][tut9_link]
-- [Normalizing Data][tut10_link]
-- [Miscellaneous examples][tut0_link]
-
-The associated python scripts are provided in the `examples` folder.
-
-
-## Spatial Random Field Generation
-
-The core of this library is the generation of spatial random fields. These fields are generated using the randomisation method, described by [Heße et al. 2014][rand_link].
-
-[rand_link]: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2014.01.013
-
-
-### Examples
-
-#### Gaussian Covariance Model
-
-This is an example of how to generate a 2 dimensional spatial random field with a gaussian covariance model.
+## Documentation
-```python
-import gstools as gs
-# structured field with a size 100x100 and a grid-size of 1x1
-x = y = range(100)
-model = gs.Gaussian(dim=2, var=1, len_scale=10)
-srf = gs.SRF(model)
-srf((x, y), mesh_type='structured')
-srf.plot()
-```
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
- -
-