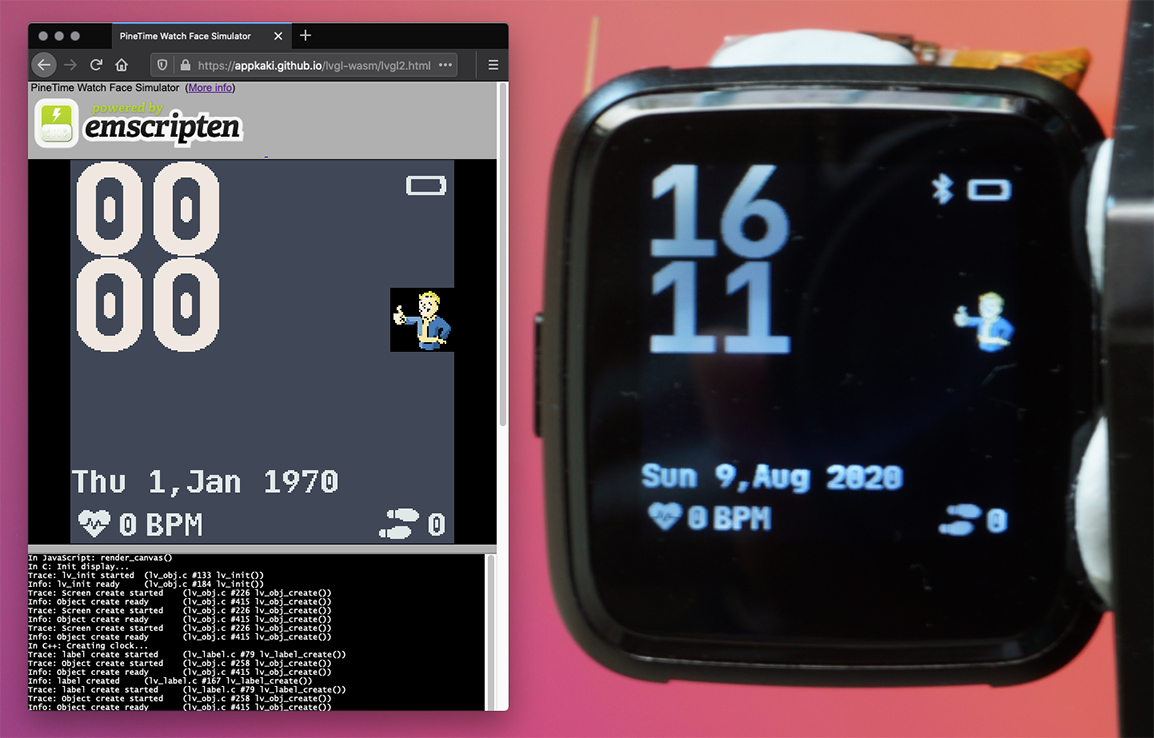
Custom PineTime Watch Face created in C++ by SravanSenthiln1: PineTime Watch Face Simulator vs Real PineTime
For Rust on Mynewt Watch Faces, see the mynewt branch
For Rust on RIOT Watch Faces, see the rust branch
Simulate PineTime Watch Face in Web Browser (with WebAssembly), for easier development of custom watch faces
Read the article...
-
Compiles actual PineTime Watch Face from C++ to WebAssembly:
Clock.cppwas converted to WebAssemblyclock -
Auto Convert any PineTime Watch Face from C++ to WebAssembly with
sedand GitHub Actions / GitLab CD. Custom Watch Face Demo / Source Code -
Uses GitHub Actions Workflow to build any fork of InfiniTime Watch Face into WebAssembly
-
Renders LVGL to HTML Canvas directly via WebAssembly, without using SDL2. See
lvgl.html -
Includes PineTime Fonts and Symbols from
LittleVgl.cpp -
Supports RGB565 Framebuffer Format used by PineTime Display Controller, so that bitmaps will be rendered correctly. Custom Bitmap Demo / Source Code
-
Shows current date and time
-
We fork the PineTime InfiniTime Firmware repo in GitHub (or GitLab):
github.com/JF002/Pinetime -
Enable GitHub Pages (or GitLab Pages) publishing for
masterbranch,docsfolder -
Add the GitHub Actions Workflow (or GitLab CD):
.github/workflows/simulate.yml -
Enable the workflow
-
We edit
DisplayApp/Screens/Clock.cppin the web browser via GitHub (or GitLab Web IDE) -
Which triggers a PineTime Firmware Build in GitHub Actions (or GitLab CD), assuming
.github/workflows/main.ymlhas been installed -
Which also builds the PineTime Watch Face Simulator in WebAssembly
-
And then pushes the generated WebAssembly files to GitHub Pages (or GitLab Pages)
-
We preview the PineTime Watch Face through the Simulator in a web browser:
https://YOUR_ACCOUNT.github.io/Pinetime(See Online Demo) -
If we are happy with the Watch Face, we flash the built firmware to PineTime over Bluetooth. See "Test Our PineTime Fimware"
-
Accept Touch Input for LVGL
-
Convert
Clock.cppfrom C++ to Rust withlvgl-rs -
Allow PineTime Watch Faces to be built online in Rust with online preview
To build PineTime Watch Face Simulator on Linux x64 or Arm64...
-
Install emscripten and wabt. See instructions below.
-
Enter...
git clone https://github.com/AppKaki/lvgl-wasm cd lvgl-wasm -
For Arm64 Only (Raspberry Pi 64, Pinebook Pro):
We need to prevent
makefrom running parallel builds, because the machine will freeze due to high I/O.Edit
wasm/lvgl.sh(wasm/lvgl.sh) and change...make -j
To...
make
-
Copy
DisplayApp/Screens/Clock.cppfrom our fork of the InfiniTime repo toclock/Clock.cpp...# Assume that our fork of InfiniTime is at ~/Pinetime cp ~/Pinetime/src/DisplayApp/Screens/Clock.cpp clock/Clock.cpp
This is the Watch Face that will be built into the Simulator.
-
Build the LVGL WebAssembly app containing our Watch Face...
# Build LVGL app: wasm/lvgl.html, lvgl.js, lvgl.wasm wasm/lvgl.shWe should see...
... clock/ClockTmp.cpp:172:32: warning: format specifies type 'unsigned long' but the argument has type 'unsigned int' [-Wformat] sprintf(stepBuffer, "%lu", stepCount.Get()); ~~~ ^~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ %u 17 warnings generated. + wasm-objdump -x wasm/lvgl.wasm + mv wasm/lvgl.html wasm/lvgl.old.htmlThis produces
wasm/lvgl.html,wasm/lvgl.jsandwasm/lvgl.wasm -
Copy the generated WebAssembly files to the
docsfolder (used by GitHub Pages)...cp wasm/lvgl.js wasm/lvgl.wasm docs
We don't need
lvgl.htmlbecausedocsalready contains a version oflvgl.htmlwith custom JavaScript. -
Start a Web Server for the
docsfolder, because WebAssembly doesn't work when opened from the filesystem.For Arm64: Use
darkhttpd...darkhttpd docs
For x64: Use the Chrome Extension Web Server for Chrome and set the folder to
docs -
Launch a Web Browser and open the URL shown by
darkhttpdor Web Server for Chrome.Enter
lvgl.htmlin the URL bar to view the PineTime Watch Face Simulator.
In case of problems, compare with the GitHub Actions build log
PineTime Watch Face Simulator was compiled from C and C++ to WebAssembly with emscripten...
Let's study the Build Script: wasm/lvgl.sh
# Rewrite Clock.cpp to build with WebAssembly:
# Change <libs/date/includes/date/date.h>
# To "date.h"
# Change <Components/DateTime/DateTimeController.h>
# To "DateTimeController.h"
# Change <libs/lvgl/lvgl.h>
# To "../lvgl.h"
# Change "../DisplayApp.h"
# To "DisplayApp.h"
# Change obj->user_data
# To backgroundLabel_user_data
# Change backgroundLabel->user_data
# To backgroundLabel_user_data
# Remove Screen(app),
cat clock/Clock.cpp \
| sed 's/<libs\/date\/includes\/date\/date.h>/"date.h"/' \
| sed 's/<Components\/DateTime\/DateTimeController.h>/"DateTimeController.h"/' \
| sed 's/<libs\/lvgl\/lvgl.h>/"..\/lvgl.h"/' \
| sed 's/"..\/DisplayApp.h"/"DisplayApp.h"/' \
| sed 's/obj->user_data/backgroundLabel_user_data/' \
| sed 's/backgroundLabel->user_data/backgroundLabel_user_data/' \
| sed 's/Screen(app),//' \
>clock/ClockTmp.cppWe call sed to rewrite Clock.cpp so that it compiles with the InfiniTime Sandbox...
-
Include paths are flattened...
#include <Components/DateTime/DateTimeController.h>
Becomes...
#include "DateTimeController.h"
The InfiniTime Sandbox header and source files are located in the clock folder, the same folder as
Clock.cpp -
We simplify Base Classes...
Clock::Clock(...) : Screen(app), currentDateTime{{}}, ... {Becomes
Clock::Clock(...) : currentDateTime{{}}, ... {In the InfiniTime Sandbox, the
Screenclass has been replaced by a Mock Class that uses no constructor. -
We rewrite LVGL references like
user_data.TODO: This may be removed, we now support
user_datawith the updatedlv_config.h
This step creates the file ClockTmp.cpp, which is compiled instead of the original Clock.cpp.
We build the LVGL app in WebAssembly...
# Build LVGL app: wasm/lvgl.html, lvgl.js, lvgl.wasm
make -jThe make command triggers this command in the Makefile...
emcc -o wasm/lvgl.html \
-Wl,--start-group \
clock/ClockTmp.cpp \
(List of C and C++ object files from LVGL and InfiniTime Sandbox) \
-Wl,--end-group \
-g \
-I src/lv_core \
-D LV_USE_DEMO_WIDGETS \
-s WASM=1 \
-s "EXPORTED_FUNCTIONS=[ '_main', '_get_display_buffer', '_get_display_width', '_get_display_height', '_test_display', '_init_display', '_render_display', '_render_widgets', '_create_clock', '_refresh_clock', '_update_clock' ]"The emscripten compiler emcc generates three files in folder wasm...
-
lvgl.wasm: WebAssembly Executable Code, containing our Watch Face, LVGL and the InfiniTime Sandbox. Sample File -
lvgl.js: Provides the JavaScript glue that's needed to loadlvgl.wasmand run it in a Web Browser. Sample File -
lvgl.html: The HTML file that callslvgl.jsto render the user interface.We won't be using this file, because we have a custom version of
lvgl.html
EXPORTED_FUNCTIONS are the C functions that will be exposed from WebAssembly to JavaScript. See the section on "Exported Functions" below.
For troubleshooting, we dump the text version of the WebAssembly module to lvgl.txt...
# Dump the WebAssembly modules
wasm-objdump -x wasm/lvgl.wasm >wasm/lvgl.txtBecause we use a custom lvgl.html, we rename the generated lvgl.html to prevent overwriting...
# Rename the HTML files so we don't overwrite the updates
mv wasm/lvgl.html wasm/lvgl.old.htmlIn future we shall be mixing C WebAssembly with Rust WebAssembly, so that the Watch Face code in Clock.cpp may be programmed in Rust instead.
Check out the rust branch of lvgl-asm
Here's a test of C WebAssembly calling Rust WebAssembly...
-
Generated Files:
test_rust.html,test_rust.js,test_rust.wasm
Here's how we build Rust and C WebAssembly: wasm/lvgl.sh
# Install Rust Toolchain for emscripten
rustup default nightly
rustup target add wasm32-unknown-emscripten
# Build Rust modules with emscripten compatibility
cargo build --target=wasm32-unknown-emscripten
# Build sample Rust app: wasm/test_rust.html, test_rust.js, test_rust.wasm
emcc \
-g \
wasm/test_rust.c \
-s WASM=1 \
-s "EXPORTED_FUNCTIONS=[ '_main', '_get_display_buffer', '_get_display_width', '_get_display_height', '_test_display', '_test_c', '_test_c_set_buffer', '_test_c_get_buffer', '_test_c_buffer_address', '_test_rust', '_test_rust2', '_test_rust3', '_test_rust_set_buffer', '_test_rust_get_buffer' ]" \
-o wasm/test_rust.html \
-I src/lv_core \
target/wasm32-unknown-emscripten/debug/liblvgl_wasm_rust.a
# Dump the WebAssembly modules
wasm-objdump -x wasm/test_rust.wasm >wasm/test_rust.txt
# Rename the HTML files so we don't overwrite the updates
mv wasm/test_rust.html wasm/test_rust.old.htmlPineTime Web Simulator runs in a Web Browser based on WebAssembly (somewhat similar to Java Applets). More about WebAssembly
Clock.cpp is our C++ class that contains the Watch Face code. Clock.cpp calls functions from two providers...
-
InfiniTime Operating System based on FreeRTOS
lvgl-wasm simulates the minimal set of InfiniTime functions needed for rendering Watch Faces. (FreeRTOS is not supported by the Simulator)
Hence lvgl-wasm works like a Sandbox. Here's how the InfiniTime Sandbox works...
The Sandbox exports the following WebAssembly functions from C to JavaScript...
These functions create the Clock class from Clock.cpp, render the LVGL widgets on the Watch Face, and update the time...
-
create_clock()Create an instance of the clock.
-
refresh_clock()Redraw the clock.
-
update_clock(year, month, day, hour, minute, second)Set the current date and time in
DateTimeController. The time needs to be adjusted for the current timezone, see the JavaScript call toupdate_clock()below.
These functions initialise the LVGL library and render the LVGL Widgets to the WebAssembly Display Buffer...
-
init_display()Init the LVGL display.
From
wasm/lvgl.c -
render_display()Render the LVGL display in 16-bit RGB565 format. From
wasm/lvgl.cCalls the WebAssembly Display Driver defined in
wasm/lv_port_disp.cWhich calls
put_display_px()to draw individual pixels to the the WebAssembly Display Buffer:wasm/lvgl.c
The WebAssembly Display Driver maintains a Display Buffer: 240 x 240 array of pixels, 4 bytes per pixel, in RGBA colour format: wasm/lvgl.c
/// RGBA WebAssembly Display Buffer that will be rendered to HTML Canvas
#define LV_HOR_RES_MAX 240
#define LV_VER_RES_MAX 240
#define DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL 4
uint8_t display_buffer[LV_HOR_RES_MAX * LV_VER_RES_MAX * DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL];Our JavaScript code copies the Display Buffer from WebAssembly Memory and renders to HTML Canvas by calling the following functions...
-
get_display_width()Returns 240, the width of the WebAssembly Display Buffer.
From
wasm/lvgl.c -
get_display_height()Returns 240, the height of the WebAssembly Display Buffer.
From
wasm/lvgl.c -
get_display_buffer()Return the WebAssembly Address of the WebAssembly Display Buffer.
From
wasm/lvgl.c
Note that JavaScript is allowed to read and write to WebAssembly Memory (treating it like a JavaScript array of bytes). But WebAssembly can't access any JavaScript Memory.
That's why we designed the Display Buffer Functions to manipulate WebAssembly Memory.
For testing only...
-
test_display()(For Testing) Render a colour box to the WebAssembly Display Buffer.
From
wasm/lvgl.c -
render_widgets()(For Testing) Render a Button Widget and a Label Widget.
From
wasm/lvgl.c
-
main(): Does nothing.From
wasm/lvgl.c
The Sandbox simulates InfiniTime OS by exposing the following API Classes to Clock.cpp...
The following classes were created for the Simulator...
-
Exposes the Clock Functions for creating and rendering the Watch Face:
create_clock(),refresh_clock()andupdate_clock()
The following classes from InfiniTime were mocked up (i.e. made non-functional) to run in the Simulator...
-
Mocked-up
DisplayAppclass.Based on
DisplayApp/DisplayApp.h -
Mocked-up
Screenclass.Based on
DisplayApp/Screens/Screen.h
The following classes were reused from InfiniTime with minor changes (e.g. include paths changed, functions stubbed out)...
-
Simulated battery functions.
-
Battery icons.
Based on
DisplayApp/Screens/BatteryIcon.h,.cpp -
Simulated BLE controller.
Based on
Components/Ble/BleController.h,.cpp -
BLE icons.
Based on
DisplayApp/Screens/BleIcon.h,.cpp -
Watch Face code.
Clock.cppcontains the Custom Watch Face code.Clock.his fixed for all Watch Faces.Clock.cppis transformed bysedtoClockTmp.cpp. (See "How It Works" above)ClockTmp.cppis the actual file that's compiled by the emscripten compiler.Based on
DisplayApp/Screens/Clock.h,.cpp -
Date and time functions.
Based on
Components/DateTime/DateTimeController.h,.cpp -
LVGL Style functions.
The changes here are quite massive and incomplete because InfiniTime uses LVGL Version 6 Styles whereas the Simulator uses LVGL Version 7 Styles. See the section below on "Migrating LVGL Version 6 to 7"
Based on
DisplayApp/LittleVgl.h,.cpp -
Watch Face symbols.
Based on
DisplayApp/Screens/Symbols.h -
Date functions.
Based on
libs/date/includes/date/date.h
InfiniTime Sandbox exposes two LVGL Styles...
-
Default Style defined in
lv_conf.hwith fontjetbrains_mono_bold_20TODO: Use the Base Theme defined in
LittleVgl.cpp. It doesn't work with LVGL Version 7 because the LVGL 7 needs Style Callback Functions. -
LabelBigStyledefined inLittleVgl.cppwith fontjetbrains_mono_extrabold_compressed
The JavaScript functions here call the Exported WebAssembly Functions to render the Watch Face. From docs/lvgl.html
We register a callback in the emscripten API, to be notified when the WebAssembly Module lvgl.wasm has been loaded...
// In JavaScript: Wait for emscripten to be initialised
Module.onRuntimeInitialized = function() {
// Render LVGL to HTML Canvas
render_canvas();
};When the WebAssembly Module lvgl.wasm has been loaded, we call the WebAssembly Function init_display() to initialise the LVGL display...
/// In JavaScript: Create the Watch Face in WebAssembly
function render_canvas() {
// Init LVGL Display
Module._init_display();Then we create the LVGL Watch Face Class from Clock.cpp...
// Create the Watch Face in WebAssembly
Module._create_clock();Every minute we update the Watch Face time in DateTimeController...
/// In JavaScript: Update the Watch Face time in WebAssembly and render the WebAssembly Display Buffer to the HTML Canvas
function updateCanvas() {
// Update the WebAssembly Date and Time: year, month, day, hour, minute, second
const localTime = new Date();
const timezoneOffset = localTime.getTimezoneOffset(); // In mins
// Compensate for the time zone
const now = new Date(
localTime.valueOf() // Convert time to millisec
- (timezoneOffset * 60 * 1000) // Convert mins to millisec
);
Module._update_clock(
now.getFullYear(),
now.getMonth() - 1, // getMonth() returns 1 to 12
now.getDay(),
now.getHours(),
now.getMinutes(),
now.getSeconds()
);Note that we need to compensate for the timezone.
And redraw the Watch Face in Clock.cpp...
// Update the Watch Face time in WebAssembly
Module._refresh_clock();We call LVGL to render the Widgets into the WebAssembly Display Buffer...
// Render LVGL Widgets to the WebAssembly Display Buffer
Module._render_display();We resize the HTML Canvas to PineTime's 240 x 240 resolution, scaled by 2 times...
const DISPLAY_SCALE = 2; // Scale the canvas width and height
// Fetch the PineTime dimensions from WebAssembly Display Buffer
var width = Module._get_display_width();
var height = Module._get_display_height();
// Resize the canvas to PineTime dimensions (240 x 240)
if (
Module.canvas.width != width * DISPLAY_SCALE ||
Module.canvas.height != height * DISPLAY_SCALE
) {
Module.canvas.width = width * DISPLAY_SCALE;
Module.canvas.height = height * DISPLAY_SCALE;
}We fetch the HTML Canvas...
// Fetch the canvas pixels
var ctx = Module.canvas.getContext('2d');
var imageData = ctx.getImageData(0, 0, width * DISPLAY_SCALE, height * DISPLAY_SCALE);
var data = imageData.data;We copy the pixels from the WebAssembly Display Buffer to the HTML Canvas (which uses 24-bit RGBA format)...
const DISPLAY_SCALE = 2; // Scale the canvas width and height
const DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL = 4; // 4 bytes per pixel: RGBA
// Copy the pixels from the WebAssembly Display Buffer to the canvas
var addr = Module._get_display_buffer();
Module.print(`In JavaScript: get_display_buffer() returned ${toHex(addr)}`);
for (var y = 0; y < height; y++) {
// Scale the pixels vertically to fill the canvas
for (var ys = 0; ys < DISPLAY_SCALE; ys++) {
for (var x = 0; x < width; x++) {
// Copy from src to dest with scaling
const src = ((y * width) + x) * DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL;
const dest = ((((y * DISPLAY_SCALE + ys) * width) + x) * DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL)
* DISPLAY_SCALE;
// Scale the pixels horizontally to fill the canvas
for (var xs = 0; xs < DISPLAY_SCALE; xs++) {
const dest2 = dest + xs * DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL;
// Copy 4 bytes: RGBA
for (var b = 0; b < DISPLAY_BYTES_PER_PIXEL; b++) {
data[dest2 + b] = Module.HEAPU8[addr + src + b];
}
}
}
}
}Note that JavaScript is allowed to read and write to WebAssembly Memory (treating it like a JavaScript array of bytes in Module.HEAPU8[]). But WebAssembly can't access any JavaScript Memory.
That's why we designed the Display Buffer Functions to manipulate WebAssembly Memory.
Finally we update the HTML Canvas...
// Paint the canvas
ctx.putImageData(imageData, 0, 0);
}See the GitHub Actions Workflow...
Look for the steps...
-
"Install emscripten"
-
"Install wabt"
Change /tmp to a permanent path like ~
Then add emscripten and wabt to the PATH...
# Add emscripten and wabt to the PATH
source ~/emsdk/emsdk_env.sh
export PATH=$PATH:~/wabt/buildWorks on Pinebook Pro with Manjaro...
sudo pacman -S emscripten
sudo pacman -S wabt
source /etc/profile.d/emscripten.sh
emcc --version
# Shows emscripten version 1.39.20
wasm-as --version
# Shows binaryen version 95emscripten and binaryen will probably work, skip the rest of this section.
This will fail during the build, because emscripten 1.39 needs binaryen version 93, not 95.
We could install binaryen version 93... But emcc will fail with an error "stackSave already exists". That's because binaryen 93 generates the "stackSave" that conflicts with emscripten 1.39.20. More details here
To fix this, we install binaryen version 94, but rename it as version 93...
# Download binaryen 94
git clone --branch version_94 https://github.com/WebAssembly/binaryen
cd binaryen
nano CMakeLists.txt Change
project(binaryen LANGUAGES C CXX VERSION 94)
To
project(binaryen LANGUAGES C CXX VERSION 93)
Then build and install binaryen...
cmake .
make -j 5
sudo cp bin/* /usr/bin
sudo cp lib/* /usr/lib
wasm-as --version
# Shows binaryen "version 93 (version_94)"binaryen is now version 93, which is correct. Proceed to build the app...
cd lvgl-wasm
rm -rf ~/.emscripten_cache
make clean
make -j 5The app build should complete successfully.
If we see this error...
emcc: error: unexpected binaryen version: 95 (expected 93) [-Wversion-check] [-Werror]
FAIL: Compilation failed!: ['/usr/lib/emscripten/emcc', '-D_GNU_SOURCE', '-o', '/tmp/tmpbe4ik5na.js', '/tmp/tmpzu5jusdg.c', '-O0', '--js-opts', '0', '--memory-init-file', '0', '-Werror', '-Wno-format', '-s', 'BOOTSTRAPPING_STRUCT_INFO=1', '-s', 'WARN_ON_UNDEFINED_SYMBOLS=0', '-s', 'STRICT=1', '-s', 'SINGLE_FILE=1']
Then we need to install the right version of binaryen (see above)
If we see this error...
Fatal: Module::addExport: stackSave already exists
emcc: error: '/usr/bin/wasm-emscripten-finalize --detect-features --global-base=1024 --check-stack-overflow /tmp/emscripten_temp_84xtyzya/tmpzet09r88.wasm -o /tmp/emscripten_temp_84xtyzya/tmpzet09r88.wasm.o.wasm' failed (1)
FAIL: Compilation failed!: ['/usr/lib/emscripten/emcc', '-D_GNU_SOURCE', '-o', '/tmp/tmpzet09r88.js', '/tmp/tmpxk8zxvza.c', '-O0', '--js-opts', '0', '--memory-init-file', '0', '-Werror', '-Wno-format', '-s', 'BOOTSTRAPPING_STRUCT_INFO=1', '-s', 'WARN_ON_UNDEFINED_SYMBOLS=0', '-s', 'STRICT=1', '-s', 'SINGLE_FILE=1']
That means binaryen 93 generates the "stackSave" that conflicts with emscripten 1.39.20. More details here
We need to install branch version_94 of binaryen, change version in CMakeLists.txt to version 93 (see above)
Enter these commands...
brew install emscripten
brew install binaryen
# Upgrade llvm to 10.0.0
brew install llvm
brew upgrade llvm
nano /usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/.emscriptenChange BINARYEN_ROOT and LLVM_ROOT to
BINARYEN_ROOT = os.path.expanduser(os.getenv('BINARYEN', '/usr/local')) # directory
LLVM_ROOT = os.path.expanduser(os.getenv('LLVM', '/usr/local/opt/llvm/bin')) # directoryFails with error:
emcc: warning: LLVM version appears incorrect (seeing "10.0", expected "12.0") [-Wversion-check]
shared:INFO: (Emscripten: Running sanity checks)
clang-10: error: unknown argument: '-fignore-exceptions'
emcc: error: '/usr/local/opt/llvm/bin/clang -target wasm32-unknown-emscripten -D__EMSCRIPTEN_major__=1 -D__EMSCRIPTEN_minor__=40 -D__EMSCRIPTEN_tiny__=1 -D_LIBCPP_ABI_VERSION=2 -Dunix -D__unix -D__unix__ -Werror=implicit-function-declaration -Xclang -nostdsysteminc -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/include/compat -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/include -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/include/libc -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/lib/libc/musl/arch/emscripten -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/local/include -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/include/SSE -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/lib/compiler-rt/include -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/lib/libunwind/include -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/cache/wasm/include -DEMSCRIPTEN -fignore-exceptions -Isrc/lv_core -D LV_USE_DEMO_WIDGETS ././src/lv_core/lv_group.c -Xclang -isystem/usr/local/Cellar/emscripten/1.40.1/libexec/system/include/SDL -c -o /var/folders/gp/jb0b68fn3b187mgyyrjml3km0000gn/T/emscripten_temp_caxv1fls/lv_group_0.o -mllvm -combiner-global-alias-analysis=false -mllvm -enable-emscripten-sjlj -mllvm -disable-lsr' failed (1)
Here is a sample WebAssembly Stack Trace that appears in the web browser. It happens when we don't initialise the LVGL Style LabelBigStyle used by Clock.cpp
lvgl.js:1839 Fetch finished loading: GET "http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm".
instantiateAsync @ lvgl.js:1839
createWasm @ lvgl.js:1866
(anonymous) @ lvgl.js:2113
lvgl2.html:1237 In JavaScript: render_canvas()
lvgl2.html:1237 In C: Init display...
lvgl2.html:1237 Init display...
Uncaught RuntimeError: memory access out of bounds
at _lv_style_get_int (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[229]:0x21bfb)
at _lv_style_list_get_int (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[234]:0x22bf7)
at _lv_obj_get_style_int (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[87]:0xe524)
at lv_obj_get_style_shadow_width (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[162]:0x17d1b)
at lv_obj_get_draw_rect_ext_pad_size (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[43]:0x70ae)
at lv_obj_signal (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[33]:0x55e6)
at lv_label_signal (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[261]:0x27804)
at lv_obj_refresh_ext_draw_pad (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[45]:0x886f)
at lv_obj_signal (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[33]:0x5793)
at lv_label_signal (http://127.0.0.1:8887/lvgl.wasm:wasm-function[261]:0x27804)
_lv_style_get_int @
_lv_style_list_get_int @
_lv_obj_get_style_int @
lv_obj_get_style_shadow_width @
lv_obj_get_draw_rect_ext_pad_size @
lv_obj_signal @
lv_label_signal @
lv_obj_refresh_ext_draw_pad @
lv_obj_signal @
lv_label_signal @
lv_obj_refresh_style @
lv_obj_add_style @
Pinetime::Applications::Screens::Clock::Clock(DisplayApp*, Pinetime::Controllers::DateTime&, Pinetime::Controllers::Battery&, Pinetime::Controllers::Ble&) @
create_clock @
(anonymous) @ lvgl.js:1734
render_canvas @ lvgl2.html:1311
Module.onRuntimeInitialized @ lvgl2.html:1354
doRun @ lvgl.js:2496
(anonymous) @ lvgl.js:2509
setTimeout (async)
run @ lvgl.js:2505
runCaller @ lvgl.js:2411
removeRunDependency @ lvgl.js:1632
receiveInstance @ lvgl.js:1799
receiveInstantiatedSource @ lvgl.js:1816
Promise.then (async)
(anonymous) @ lvgl.js:1841
Promise.then (async)
instantiateAsync @ lvgl.js:1839
createWasm @ lvgl.js:1866
(anonymous) @ lvgl.js:2113
PineTime runs on LVGL version 6 while our WebAssembly port runs on LVGL version 7. And programs built for LVGL version 6 will not compile with LVGL version 7.
Here's how we migrated our code from LVGL Version 6...
To LVGL Version 7...
Compare the original and converted files...
-
Clock.cpp: LVGL Version 6 vs Version 7
Click
Files Changed, thenChanged Filesand look forClock/Clock.cpp -
LittleVgl.cpp: LVGL Version 6 vs Version 7
Click
Files Changed, thenChanged Filesand look forClock/LittleVgl.cpp
Code that uses lv_label_set_style...
lv_label_set_style(label_time, LV_LABEL_STYLE_MAIN, LabelBigStyle);Should be changed to lv_obj_reset_style_list and lv_obj_add_style...
// Remove the styles coming from the theme
lv_obj_reset_style_list(label_time, LV_LABEL_PART_MAIN);
// Then add style
lv_obj_add_style(label_time, LV_LABEL_PART_MAIN, LabelBigStyle);Or define a macro like so...
/// Change LVGL v6 lv_label_set_style() to LVGL v7 lv_obj_reset_style_list() and lv_obj_add_style()
#define lv_label_set_style(label, style_type, style) \
{ \
lv_obj_reset_style_list(label, LV_LABEL_PART_MAIN); \
lv_obj_add_style(label, LV_LABEL_PART_MAIN, style); \
}
lv_label_set_style(label_time, LV_LABEL_STYLE_MAIN, LabelBigStyle);lv_style_plain has been removed in LVGL 7. Code like this...
lv_style_copy(&def, &lv_style_plain);Should be changed to...
lv_style_init(&def);In LVL 6, setting the default font for a Theme used to be easy...
lv_style_init(&def);
lv_style_set_text_font(&def, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, &jetbrains_mono_bold_20);
...
lv_theme_set_current(&theme);But in LVL 7, we need to use Theme Callback Functions to apply the style.
A simpler solution is to set the default font in lv_conf.h...
#define LV_FONT_CUSTOM_DECLARE LV_FONT_DECLARE(jetbrains_mono_bold_20)
#define LV_THEME_DEFAULT_FONT_SMALL &jetbrains_mono_bold_20
#define LV_THEME_DEFAULT_FONT_NORMAL &jetbrains_mono_bold_20
#define LV_THEME_DEFAULT_FONT_SUBTITLE &jetbrains_mono_bold_20
#define LV_THEME_DEFAULT_FONT_TITLE &jetbrains_mono_bold_20Change LVL 6 Style...
lv_style_copy(&bg, &lv_style_plain);
bg.body.main_color = LV_COLOR_BLACK;
bg.body.grad_color = LV_COLOR_BLACK;
bg.text.color = LV_COLOR_WHITE;
bg.text.font = font;
bg.image.color = LV_COLOR_WHITE;To LVL 7 Style...
lv_style_init(&bg);
lv_style_set_bg_color(&bg, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_COLOR_BLACK);
lv_style_set_bg_grad_color(&bg, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_COLOR_BLACK);
lv_style_set_text_color(&bg, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_COLOR_WHITE);
lv_style_set_text_font(&bg, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, font);
lv_style_set_image_recolor(&bg, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_COLOR_WHITE);Change LVL 6 Style...
lv_style_copy(&panel, &bg);
panel.body.main_color = lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 11, 18);
panel.body.grad_color = lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 11, 18);
panel.body.radius = LV_DPI / 20;
panel.body.border.color = lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 10, 25);
panel.body.border.width = 1;
panel.body.border.opa = LV_OPA_COVER;
panel.body.padding.left = LV_DPI / 10;
panel.body.padding.right = LV_DPI / 10;
panel.body.padding.top = LV_DPI / 10;
panel.body.padding.bottom = LV_DPI / 10;
panel.line.color = lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 20, 40);
panel.line.width = 1;To LVL 7 Style...
lv_style_copy(&panel, &bg);
lv_style_set_bg_color(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 11, 18));
lv_style_set_bg_grad_color(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 11, 18));
lv_style_set_radius(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_DPI / 20);
lv_style_set_border_color(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 10, 25));
lv_style_set_border_width(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, 1);
lv_style_set_border_opa(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_OPA_COVER);
lv_style_set_pad_left(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_DPI / 10);
lv_style_set_pad_right(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_DPI / 10);
lv_style_set_pad_top(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_DPI / 10);
lv_style_set_pad_bottom(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, LV_DPI / 10);
lv_style_set_line_color(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, lv_color_hsv_to_rgb(hue, 20, 40));
lv_style_set_line_width(&panel, LV_STATE_DEFAULT, 1); For more examples of LVL Style migration, see...
LittleVgl.cpp: LVGL Version 6 vs Version 7
Click Files Changed, then Changed Files and look for Clock/LittleVgl.cpp